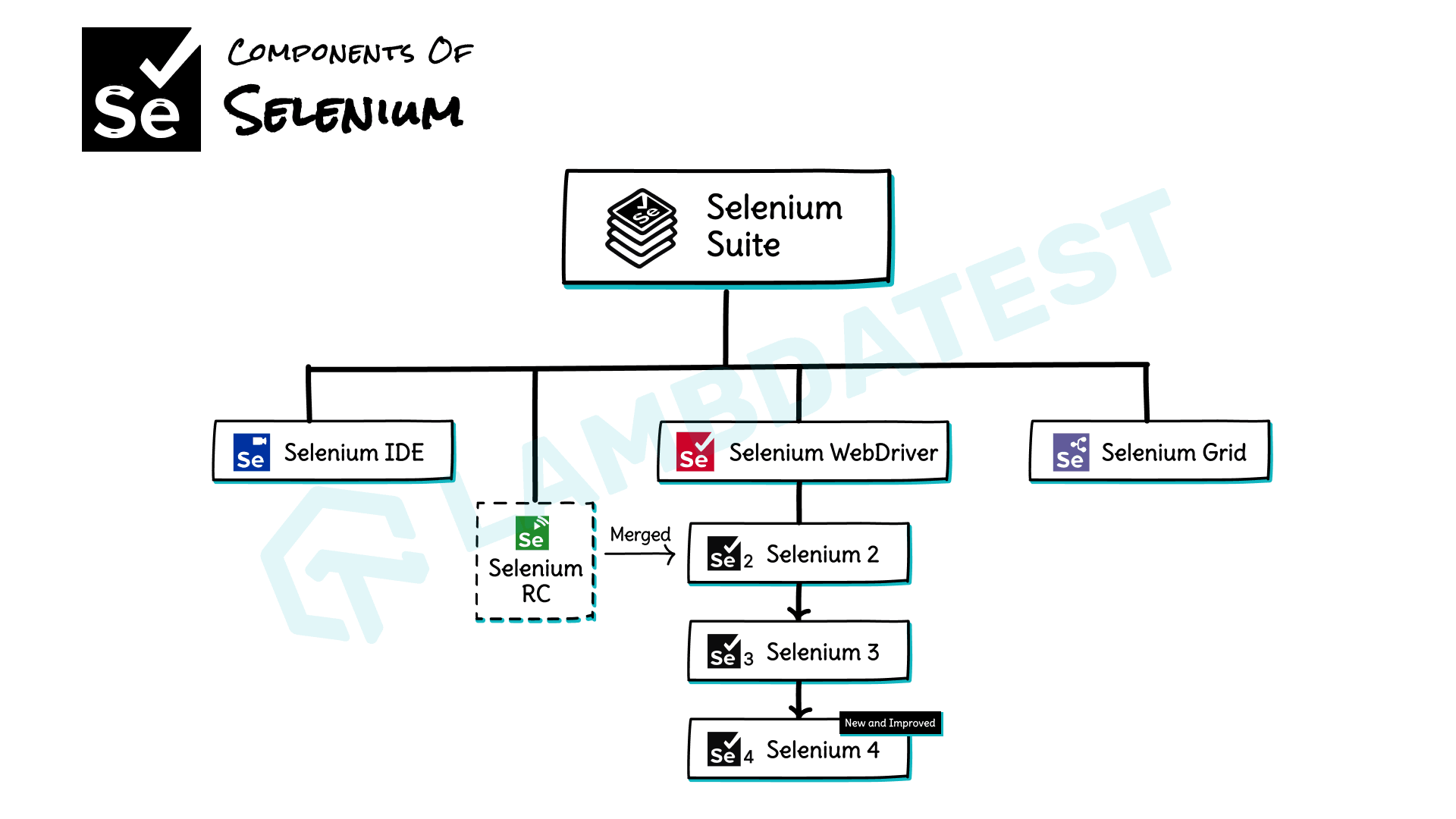
This article is a part of our Learning Hub. For more in-depth resources, check out our hub on Selenium Tutorial.
Selenium WebDriver provides features to interact with different types of web elements, such as text fields, drop-down lists, radio buttons, and checkboxes. It also supports various advanced interactions like drag and drop, mouse movements, and keyboard actions.
Enhance your Selenium interview proficiency with our meticulously curated compilation of questions and answers. Explore the comprehensive list of Selenium Interview Questions and Answers for valuable insights.
Different Types of Selenium Framework
In this section of the tutorial, we will look at three different frameworks for Selenium – Data Driven Framework, Keyword Driven Framework, and Hybrid framework.
Data Driven Framework
A Data Driven Framework in Selenium is a method that empowers testers to organize their test scripts and test data more effectively. It involves storing test data separately from the test scripts, enabling the execution of test cases with different data inputs in a more efficient manner.
We will look at the Data Driven Framework in the light of the following parameters:
- Concepts and Benefits
- Designing
- Implementing
- Advanced features
Concept and Benefits of a Data Driven Framework
A Data Driven Framework can be defined as a type of Selenium framework that separates test data from the test script.
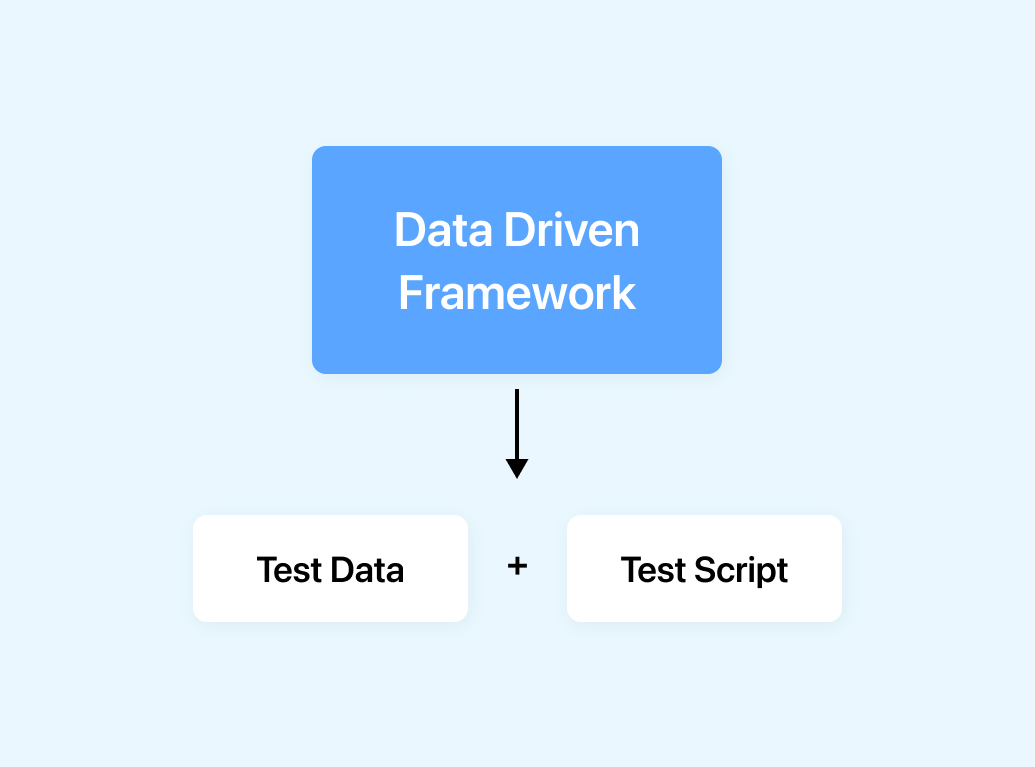
In this approach, the test data is stored in an external file or, a database. The test script reads the test data during runtime. The test script then uses the test data to execute the test cases. This approach is mainly preferred for testing applications with large data sets or multiple test scenarios.
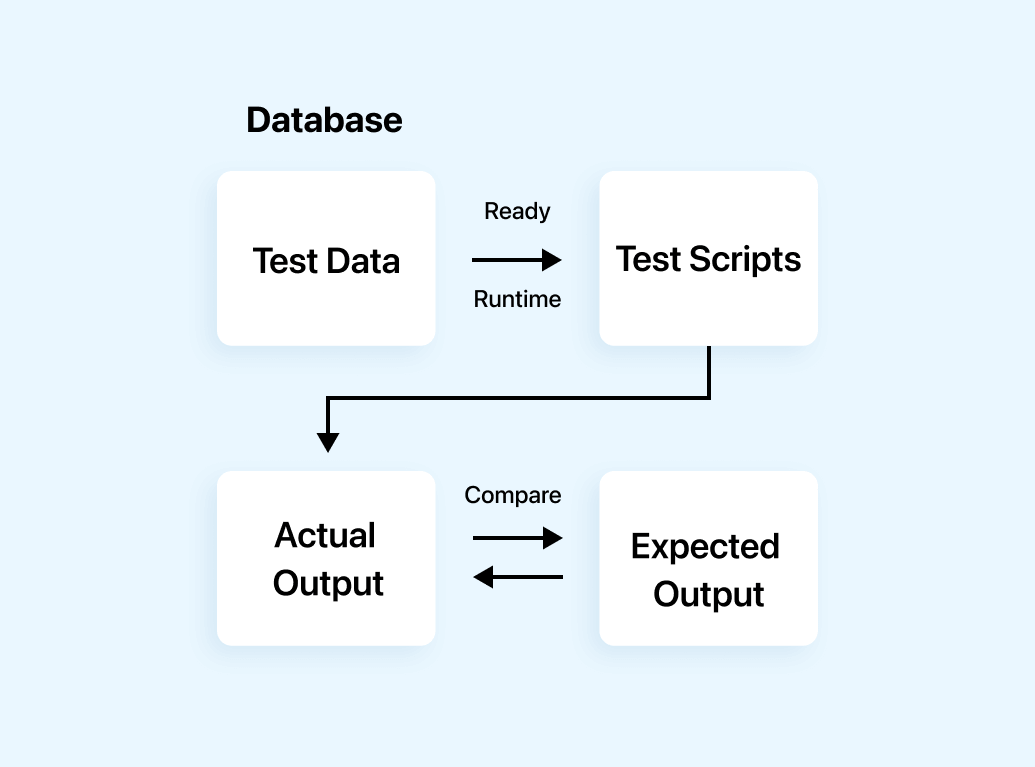
The benefits of using a Data Driven Framework include:
- Scalability: A Data Driven Framework handles a large number of test cases with minimal or no changes to the test script. This makes it easier to scale test automation efforts and handle different testing scenarios.
- Reusability: By separating the test data from the test script, testers can create reusable test scripts which can be used for multiple test scenarios. This effectively saves time and effort in creating and maintaining test cases every time.
- Maintainability: Data Driven Frameworks are easier to maintain as changes to the test data can be made easily without the necessity of modifying the test script. This makes it easier to update the test cases when changes are made to the application or the entire test data.
- Flexibility: A Data Driven Framework provides testers the flexibility to use different data formats, including Excel, CSV, or XML, depending on the preferences and requirements. This makes it easier to integrate with existing systems and tools.
- Better reporting: A Data Driven Framework provides better reporting and analysis as the test data can be used to generate detailed reports and metrics. This helps to identify areas of the application that require improvement and track the progress of testing efforts.

Designing a Data Driven Framework
- Identify test scenarios: First, identify the test scenarios that will be automated. This generally includes the different types of test data that will be used, for example, positive and negative scenarios.
- Define data sources: Determine the data sources to be used for the test data, for example, Excel spreadsheets, CSV files, or databases.
- Create test data: Create test data for each scenario identified in step 1, using the data sources identified in step 2.
- Create test scripts: Create the test scripts that will be used to execute the test cases.
- Modularize the test scripts: Modularize the test scripts by separating the test data from the test scripts. This helps maintain the test scripts and update the test data without modifying the test scripts.
- Create test reports: Create test reports that provide information on the test execution results, including pass/fail status, error messages, screenshots, etc.
- Integrate with other frameworks: Integrate the Data Driven Framework with other frameworks, for example, Page Object Model (POM) or Behavior Driven Development (BDD) to create a custom test automation solution that meets the specific needs of the organization.
Implementing a Data Driven Framework
To convert the blueprint into practice, carrying out a Data Driven Framework is essential. When it comes to implementing a Data Driven Framework, these pointers can come in handy:
- Collect and organize the data: The initial step is to gather the essential data required to feed into the said framework. This necessary data can arise from different sources such as APIs, user-generated content, or databases. After collecting the requested information, it’s crucial to organize and store it in a precise way that’ll enhance accessibility and searchability.
- Clean and preprocess the data: When analyzing data, one of the most vital steps you can take is cleaning and preprocessing it. This step includes taking out any redundancies or data that is not pertinent while also standardizing and normalizing the information to ensure that the analysis is effective.
- Develop the analytical models: After cleansing and preprocessing the data, it’s time to craft analytical models. This step means choosing the right statistical methods and machine learning procedures that’ll accurately extract insights and make predictions from the data.
- Integrate the models into the framework: Incorporate the analytical models with the framework by either writing custom code that integrates them into your software system or implementing third-party software solutions. This vital step will help bridge the gap between the models and the Data Driven Framework.
- Test and validate the models: Validating and testing the models is crucial to guarantee their accuracy. To accomplish this, it is necessary to analyze the predictions against actual data and uncover any inconsistencies.
- Implement data visualization and reporting: Once the models are integrated into the framework and validated, it is important to implement data visualization and reporting tools. This helps to make the insights derived from the data accessible and understandable to a broader audience.
- Train and educate users: One crucial aspect of adopting a data-driven approach is to ensure that users are properly trained and educated. This means imparting knowledge about both the tools and strategies utilized within the framework, as well as educating them on the particular business challenges that the framework aims to address.
- Evaluate and refine the framework: Lastly, it’s important to continuously evaluate and refine the Data Driven Framework. This may include monitoring the model’s accuracy, adjusting the data inputs or algorithms used in the model, or sometimes identifying new sources of data that can be used to improve the model’s predictions.
Advanced Features of a Data Driven Framework
A data-driven Selenium framework, a powerful tool for automating web application testing, can be enhanced with several advanced features. Here are some of them that can be added to a data-driven Selenium framework:
- Parallel execution: One of the most important advanced features of a data-driven Selenium framework is the ability to execute test cases in parallel. This can greatly increase the speed of the testing process and allows more efficient use of resources.
- Test case management: A data-driven Selenium framework can be enhanced with test case management tools allowing better organization and management of test cases. This can contain features such as test case prioritization, grouping, and filtering.
- Integration with test management tools: A data-driven Selenium framework can be integrated with test management tools, such as Jira or HP ALM, to facilitate better collaboration and good communication between testers and developers.
- Test data management: A data-driven Selenium framework can be enhanced with test data management tools allowing better management and control of test data. This includes features such as test data generation, data masking, and data obfuscation.
- Reporting and analytics: A data-driven Selenium framework can be enhanced with reporting and analytics tools that allow for better visibility into the testing process. This can include features such as test case coverage reports, defect tracking, and performance metrics.
- Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) integration: A data-driven Selenium framework can be integrated with CI/CD tools such as Jenkins or Bamboo to facilitate the automated testing process as part of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
- Cloud-based testing: A data-driven Selenium framework can be enhanced with cloud-based testing tools that allow testing on various devices and platforms. This can include features such as cross browser testing, mobile device testing, and accessibility testing.
Keyword Driven Framework
A Keyword Driven Framework in Selenium is a technique that testers implement to define test steps using keywords or actions. This approach separates the logic of test scripts from the test data, resulting in more readable and reusable test cases. It allows for greater flexibility and ease of maintenance during the testing process.
We will look at the Keyword Driven Framework in the light of the following parameters:
- Concepts and Benefits
- Components
- Designing
- Advanced features
Concept and Benefits of a Keyword Driven Framework
In a Selenium-based Keyword Driven Framework, test cases are organized into a set of keywords that represent actions which may include opening of a web page, entering text into a text box, clicking a button, verifying if an element is present or not, and so on. Each keyword is associated with a function or method that performs the corresponding action using the Selenium API. This framework proves to be easy to understand and maintain, even for non-technical team members.
Keyword Driven Framework also includes a test script that uses the keywords to define the test steps. The test script is typically written in a tabular format, with columns representing different domains of the test, such as keywords, data values, and
expected outcomes. The test script can be written in various formats, which include a spreadsheet, CSV file, or a database table.
The Keyword Driven Framework offers several benefits for test automation:
- Reusability: By organizing and dividing tests into keywords and functions, the framework promotes reusability. Thus reducing duplication of code and enhancing maintainability.
- Modularity: The framework’s modular nature helps testers to create and maintain tests at a granular level. Each keyword represents a specific action, making it easier to understand and update each individual test step without affecting other parts of the test case. This improves maintainability and reduces the effort required in making changes.
- Abstraction of Technical Details: Testers, even without strong programming skills, can design and maintain tests using keywords, as they do not have to deal with the underlying technical implementation. This abstraction helps testers to focus on test design and validation rather than involving in the intricacies of the automation code.
- Clarity of Test Case: The use of keywords in test scripts enhances the clarity and most importantly, the readability of test cases. Testers can write test scripts using a simple, business-readable language that aligns with the application’s domain. This makes it easier for stakeholders, including non-technical team members, to understand the tests and provide feedback.
- Scalability: The Keyword Driven Framework helps in providing a scalable approach to test automation. New tests can be easily created by combining the existing keywords, and the framework can accommodate changes in the application under test by modifying or sometimes extending the keyword library.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: The Keyword Driven Framework facilitates collaboration among testers, domain experts, and developers. Testers work closely with domain experts to define meaningful keywords that accurately explain the desired behavior of the application. Developers focus on implementing the underlying functions or methods related to the keywords, while testers generally focus on test case design and execution.
- Test Coverage and Maintainability: With the modularity provided by the framework, it becomes easier to achieve test coverage without sacrificing maintainability. Testers can create a comprehensive set of reusable keywords that include various aspects of the application’s functionality. As a result, new test cases can be created by existing keywords, improving both efficiency and effectiveness in test automation.
Components of a Keyword Driven Framework
The Keyword Driven Framework in Selenium framework consists of the following listed components:
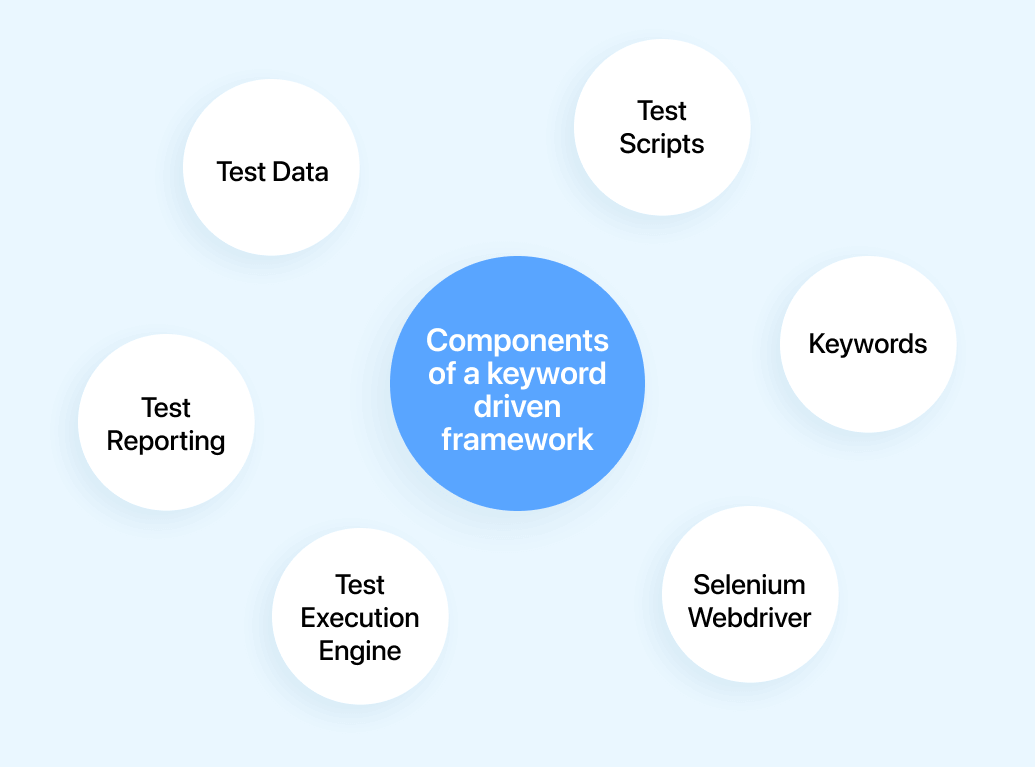
- Test Scripts: Testers create test scripts using a tabular format. Each test script represents a sequence of actions or steps that needs to be performed on a web application.
- Keywords: Keywords represent specific actions that can be performed using Selenium WebDriver. Some examples of keywords include “openBrowser,” “navigateTo,” “clickElement,” “enterText,” “verifyElementPresent,” and so on. Test scripts are written using these keywords to define the desired test steps.
- Test Data: This refers to the input values required for executing the test steps. For example, input data may include URLs, login credentials, search terms, form field values, and so on. Test scripts include columns for test data, also allowing testers to provide input values for each step.
- Test Execution Engine: The test execution engine is generally responsible for interpreting the keywords in the test script and executing the relative Selenium commands. It reads the test script, identifies the keywords, and calls the appropriate Selenium WebDriver methods or functions to perform the desired actions on the web application.
- Selenium WebDriver: Selenium WebDriver is the underlying API that interacts with web browsers. The test execution engine makes use of Selenium WebDriver to control the browser, perform actions like clicking elements, entering text, navigating through pages, and also validating the application’s behavior.
- Test Reporting: A Keyword Driven Framework may include test reporting capabilities to generate detailed reports on test execution results. These reports generally help testers and stakeholders understand and process the test outcomes, identify any failures if caused, and track the overall test progress.
Designing a Keyword Driven Framework using Selenium and Java
- Identify Keywords: Start by identifying the keywords that represent the actions you want to perform in your tests. Examples of keywords in a Selenium framework could include “OpenBrowser,” “login,” “searchProduct,” “addToCart,” etc as mentioned above. Consider the actions required to test your application and create suitably appropriate keywords.
- Create the Keyword Library: Implement the functions corresponding to each keyword in the keyword library. These functions make use of the Selenium API to perform the desired actions. For example, the “searchProduct” keyword would have a function that finds the product using appropriate locators.
- Design the Test Scripts: Create test scripts in a tabular format (e.g., using a spreadsheet) or in a format of your choice. Each row represents a test step and contains columns for keywords, input data, and expected results. Populate the test scripts with the appropriate keywords and associated data for each test case.
- Build the Execution Engine: Develop an execution engine that reads the test scripts, interprets the keywords, and invokes the corresponding functions from the keyword library. The execution engine should execute the test steps in sequence, passing any required data from the test script to the keyword functions. This can be achieved using programming constructs such as loops and conditionals.
- Set Up the Selenium WebDriver: Initialize the Selenium WebDriver in the execution engine. This involves configuring the desired browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox), setting up browser options, and specifying the WebDriver executable path.
- Execute Test Scripts: Run the execution engine, which reads the test script row by row, identifies the keyword, and executes the associated function from the keyword library. The execution engine should handle any exceptions or failures that occur during test execution and report the results appropriately.
- Reporting and Logging: Enhance the framework by adding reporting and logging capabilities. Capture the execution results, including pass/fail status, errors, and any additional relevant information. Generate test reports in a format that is easy to understand, such as HTML or PDF.
- Maintain and Extend the Framework: Regularly review and maintain the keyword library, test scripts, and execution engine as your application evolves. Add new keywords or update existing ones as needed. Ensure that the framework remains robust, flexible, and scalable over time.
Example:Test Script:
| Keyword | Input Data | Expected Result |
|---|
| openBrowser | URL | Browser opened |
| login | username, password | Success |
| searchProduct | product name | Results |
| addToCart | item | Item added |
| verifyCart | item | Item in cart |
| checkout | | Order placed |
In this example, the test script defines steps of actions to be performed on a web application. The execution engine reads and processes each row of the test script, identifies the keyword, and invokes or calls the corresponding function or method to perform the action.
public class KeywordDrivenTest {
public static WebDriver driver;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="Mention the path for test script";
CSVReader reader = new CSVReader(new FileReader(filePath));
String[] nextLine;
while ((nextLine = reader.readNext()) != null) {
String keyword = nextLine[0];
switch (keyword) {
case "OpenBrowser":
openBrowser(nextLine[1]);
break;
case "Login":
login(nextLine[1], nextLine[2]);
break;
case "SearchProduct":
searchProduct(nextLine[1]);
break;
case "AddToCart":
addToCart(nextLine[1]);
break;
case "VerifyCart":
verifyCart(nextLine[1]);
break;
case "Checkout":
checkout();
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid keyword: "+keyword);
break;
}
}
reader.close();
}
public static void openBrowser(String url) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver”,
"C:\chromedriver.exe");
driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get(url);
}
public static void login() {
WebElement usernameField = driver.findElement(By.id("username"));
WebElement passwordField = driver.findElement(By.id("password"));
WebElement loginButton = driver.findElement(By.id("loginButton"));
usernameField.sendKeys(username);
passwordField.sendKeys(password);
loginButton.click();
}
public static void searchProduct() {
//code for SearchProduct
}
public static void addToCart() {
//code for addToCart
}
public static void verifyCart() {
//code for verifyCart
}
public static void checkout() {
//code for checkout
}
}
Advanced features of a Keyword Driven Framework
In a keyword-driven Selenium framework, several advanced features can be implemented to enhance the functionality and effectiveness of the framework. These features include:
- Dynamic Test Execution: The framework supports dynamic test execution by allowing the selection and execution of specific keywords or test cases based on various criteria. This flexibility enables testers to execute specific subsets of tests based on factors like test coverage, priority, or environment.
- Non-Linear Test Execution: In a Keyword Driven Framework, the order of test execution is not fixed. Testers have the flexibility to define the sequence of keywords based on the test scenario, allowing for non-linear test execution. This is particularly useful when dealing with complex test cases or when executing tests in parallel.
- Keyword-level Error Handling: A Keyword Driven Framework enables error handling at the keyword level. Testers can define exception-handling mechanisms specific to each keyword, allowing for granular control over error management. This feature enhances the robustness and reliability of the tests.
- Test Case Independence: In a Keyword Driven Framework, each test case is independent of others. Testers can easily add, modify, or remove test cases without affecting the overall test suite. This independence allows for more flexibility in test case management and execution.
- Test Environment Configuration: The framework facilitates the configuration and management of test environments. It provides the ability to define and switch between different test environments, such as development, staging, or production, with associated configuration settings, browser types, or platform variations.
- Test Execution Control: The framework offers granular control over test execution. Testers can pause, resume, or stop the execution of test cases at any given point, providing more flexibility during test debugging or investigation of failures.
- Integration with test management tools: A keyword-driven Selenium framework can be integrated with test management tools, such as TestRail, Jira, or Zephyr, to synchronize test cases, track test execution results, and generate comprehensive test reports.
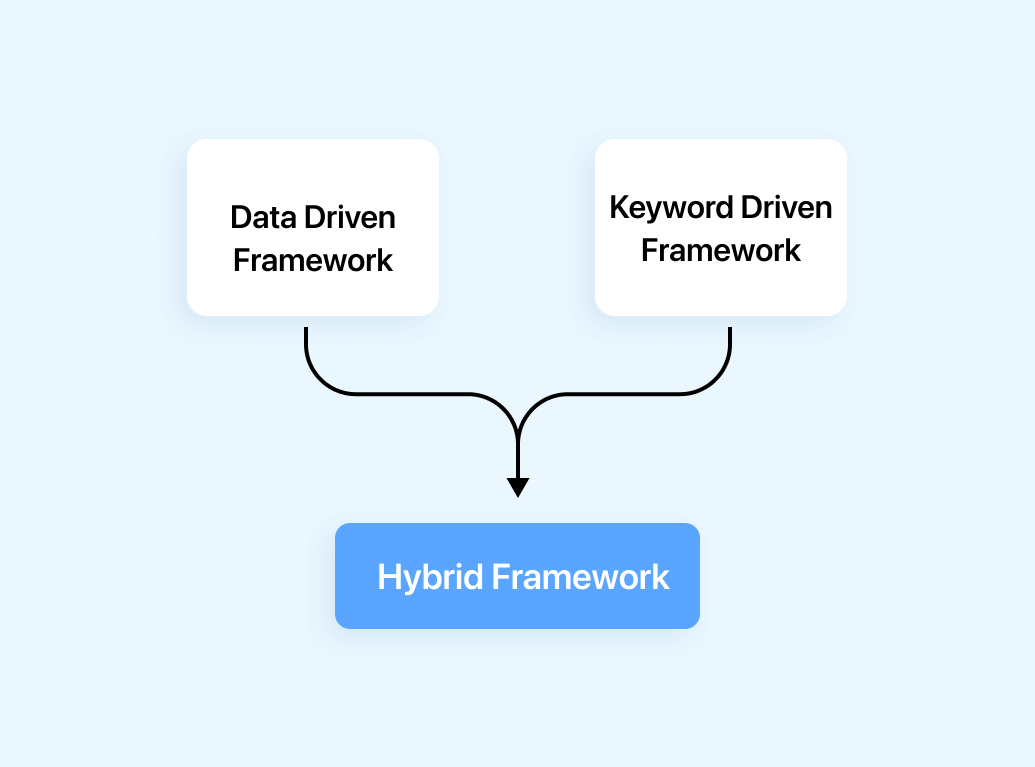
Hybrid Framework
The hybrid framework seamlessly merges data-driven and keyword-driven testing methods, fostering flexibility. Test data and keywords reside externally, enhancing efficiency. Keywords are organized within a dedicated Java class file, while test data can be managed through Properties or Excel files.
By combining the strengths of multiple frameworks, testers gain the advantage of enhanced flexibility and efficiency in their test automation processes, enabling them to create more robust and adaptable tests.
We will look at the Keyword Driven Framework in the light of the following parameters:
- Concept and Benefits
- Integration
- Designing
Concept and Benefits of a Hybrid Framework
Hybrid framework includes elements of both data-driven and Keyword Driven Frameworks. This allows testers to create automation solutions that are flexible and scalable and can handle a variety of testing scenarios.
The hybrid framework emphasizes modularity, data-driven testing, and the use of keywords to represent actions. It also promotes flexibility of test case design, centralization of test scripts, and also the reporting and logging mechanisms. The hybrid framework can be integrated with continuous integration and deployment tools, making it an adaptable approach to test automation in the Selenium framework. Overall, a hybrid framework provides a balanced approach to test automation, offering the best of multiple frameworks to create a powerful and effective solution.
Integration of the Strengths of Data Driven and Keyword Driven Frameworks
The integration of the strengths of Data Driven and Keyword Driven Frameworks in a hybrid framework offers several benefits and enhances the effectiveness of test automation. Here’s how the strengths of both frameworks can be combined:
- Separation of Test Data: Data Driven Frameworks excel in separating test data from test scripts. This separation allows for easy management and modification of test data without changing the test scripts. By integrating this strength, a hybrid framework can incorporate external data sources, such as spreadsheets or databases, to provide dynamic and reusable test data for test cases defined using keywords.
- Abstraction and Readability: The Keyword Driven Framework promotes abstraction and readability by using keywords to represent actions or operations. This approach enhances the understandability of test cases for stakeholders who may not have a technical background. By integrating this concept, the hybrid framework provides a business-readable language for test case design, making it easier for non-technical team members to review and contribute to the testing process.
- Flexibility in Test Case Design: Keyword Driven Frameworks offer flexibility in test case design, allowing testers to create test scenarios using a combination of keywords. This flexibility can be integrated into a hybrid framework, where keywords can be parameterized to accommodate different test data sets from external sources. Testers can design test cases that incorporate both modular components representing specific functionalities and keywords representing common actions, enabling comprehensive and flexible test case design.
- Modularity and Maintainability: Both Data Driven and Keyword Driven Frameworks emphasize modularity and maintainability. In a hybrid framework, modular components representing specific functionalities or features can be combined with keywords to create test cases. This combination promotes modular and maintainable test scripts, where testers can easily update or modify specific modules or keywords without impacting the entire test suite.
- Scalability and Test Coverage: Data Driven Frameworks excel in handling large amounts of test data and increasing test coverage by executing test cases with various data sets. By integrating this strength, a hybrid framework can leverage the data-driven approach to execute test cases with different combinations of data while utilizing keywords to perform common actions. This integration allows for scalable and comprehensive test coverage, ensuring the application is tested with a wide range of data inputs.
Designing a Hybrid Framework using Selenium and Java
To design a hybrid framework using Selenium and Java, let’s take an example of testing a login functionality in a web application. Here are the steps to design the framework:
- Identify Modules and Functionalities:
- Module 1: Login functionality
- Define Keywords:
- Keyword 1: openURL – Opens the application URL
- Keyword 2: enterText – Enters text in a text field
- Keyword 3: clickElement – Clicks on a web element
- Keyword 4: verifyText – Verifies text on a web element
- Keyword 5: login – Combines the above keywords to perform a login operation
- Test Data Management:
- Store test data, such as usernames and passwords, in an external source like a spreadsheet or properties file.
- Test Case Design:
- Design test cases using a combination of keywords and modular components.
- For example, a test case for login functionality may look like:
- Centralized Test Scripts:
- Create a central repository for test scripts where modular components, keywords, and test data are stored separately.
- Store reusable functions and utilities in separate Java classes.
- Reporting and Logging:
- Implement a reporting mechanism to generate detailed test execution reports.
- Capture relevant information such as executed keywords, test case statuses, execution time, screenshots, and any encountered errors or exceptions.
- Use logging frameworks like Log4j or the built-in Java logging API to capture important events and actions during test execution.
- Integration with CI/CD:
- Integrate the hybrid framework with a CI/CD pipeline, such as Jenkins or Bamboo.
- Configure triggers to execute tests upon code commits or build deployments for continuous testing.
- Maintainability and Extensibility:
- Keep the framework modular and organized for easy maintenance.
- Use object-oriented programming principles to create reusable components and functions.
- Allow for the addition or modification of test cases, keywords, or modules to accommodate changes or new functionalities.
- Error Handling and Exception Management:
- Implement error handling mechanisms at both the keyword and test case levels.
- Use try-catch blocks or custom exception handling to handle exceptions gracefully and report meaningful error messages.
- Test Execution Control:
- Provide granular control over test execution.
- Implement mechanisms to pause, resume, or stop test execution at any point.
- Use test frameworks like TestNG or JUnit to manage test execution flow.
| Step 1: openURL [Application URL] Step 2: enterText [Username field, TestData.username]Step 3: enterText [Password field, TestData.password]Step 4: clickElement [Login button]Step 5: verifyText [Welcome message, “Welcome to LAMBDATEST!“] |
|---|
Setting up Selenium Framework
Here’s a step-by-step installation guide for Selenium:
- Choose a programming language: Select a programming language of your choice. Popular options include Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript.
- Set up an Integrated Development Environment (IDE): Install an IDE to write and manage your Selenium scripts. Some popular options are Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, and Visual Studio Code. Download and install the IDE of your choice from their respective websites.
- Install the programming language-specific dependencies:
a. Java:
- Download and install Java Development Kit (JDK) from the Oracle website.
- Set up the JAVA_HOME environment variable and make sure you add the JDK’s bin directory to the system’s PATH variable.
b. Python:
- Download and install Python from the official website of Python.
- Add Python to the system’s PATH variable during the installation process.
c. C#:
- Install Visual Studio, including the necessary components for C# development.
d. JavaScript:
- No additional installation is required as JavaScript is a built-in language in web browsers.
- Install Selenium WebDriver: Selenium WebDriver is the core component of Selenium. You need to install the WebDriver specific to the browser you want to automate. For example, if you want to automate Chrome, you need to download ChromeDriver.
a. Chrome:
- Download ChromeDriver from the ChromeDriver downloads page: download
- Place the downloaded ChromeDriver executable in a directory accessible from the system’s PATH variable.
b. Firefox:
- Download GeckoDriver from the Mozilla GitHub repository: download
- Place the downloaded GeckoDriver executable in a directory accessible from the system’s PATH variable.
c. Edge:
- Download the appropriate Microsoft Edge WebDriver from the Microsoft WebDriver downloads page: download
- Place the downloaded Edge WebDriver executable in a directory accessible from the system’s PATH variable.
Note: For other browsers like Safari and Opera, WebDriver is pre-installed, and you don’t need to download any additional drivers.
- Test Framework: Choose a test framework like TestNG or JUnit (for Java) or pytest or unittest (for Python) to organize and manage your tests effectively. Install the test framework and set it up in your project.
- Set up the project:
- Create a new project in your IDE or use an existing one.
- Configure the project with the necessary dependencies, such as Selenium WebDriver and your chosen programming language’s testing framework (e.g., TestNG, JUnit).
- Start writing Selenium tests:
- Import the necessary Selenium libraries into your required project.
- Write your test scripts using the programming language and testing framework you’ve chosen.
- Execute Selenium tests:
- You can execute your Selenium tests from your IDE or use build automation tools like Maven or Gradle to execute them from the command line.
- Make sure you have the appropriate web browser installed on your machine for Selenium to interact with.
- Version Control System: Set up a version control system (such as Git) to manage your source code, test scripts, and any other project-related files. This helps in collaboration, versioning, and tracking changes.
- Continuous Integration (CI) Tool (optional): If you want to integrate your tests into a CI/CD pipeline, choose a CI tool like Jenkins, Bamboo, or CircleCI. Configure the CI tool to execute your tests automatically whenever there are code changes or on a scheduled basis.
That’s it! You’ve now installed Selenium and are ready to start automating tests using the framework. Remember to refer to the Selenium documentation and resources specific to the chosen programming language for further guidance.
Configuring Selenium with the chosen Framework
To configure Selenium with the chosen framework, follow these general steps:
- Add Selenium WebDriver dependencies: In your project’s build configuration file (e.g., pom.xml for Maven or build.gradle for Gradle), include the Selenium WebDriver dependencies specific to your programming language and testing framework. Here are some examples:
For version 3.x.x
- For Java with TestNG:
- For Python with pytest:
- For C# with NUnit:
- Configure the WebDriver in your test setup: Depending on your chosen framework, you need to configure the WebDriver to instantiate the desired browser and set up any necessary configurations. This step typically involves creating a setup method or annotation in your test framework.
- For Java with TestNG:
- For Python with pytest:
- For C# with NUnit:
- Write Selenium tests: With Selenium and the WebDriver configured, you can start writing your tests using the provided APIs and methods. Refer to the Selenium documentation and resources specific to the programming language and framework for guidance on writing tests.
- Run Selenium tests: You can now run your Selenium tests using your chosen test framework’s command-line interface or IDE integration. Ensure that the necessary WebDriver executable (e.g., chromedriver) is accessible and compatible with the browser you’re targeting.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>3.x.x</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>7.x.x</version>
</dependency>
pip install selenium pytest
Install-Package Selenium.WebDriver
Install-Package NUnit
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
public class MyTests {
private WebDriver driver;
@BeforeTest
public void setup() {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "/path/to/chromedriver");
driver = new ChromeDriver();
}
}
from selenium import webdriver
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def setup():
driver=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="/path/to/chromedriver")
yield driver
driver.quit()
using NUnit.Framework;
using OpenQA.Selenium;
using OpenQA.Selenium.Chrome;
[TestFixture]
public class MyTests {
private IWebDriver driver;
[SetUp]
public void Setup() {
driver = new ChromeDriver("/path/to/chromedriver");
}
}
For version 4.9.x
We dont have to explicitly download install drivers for specific browsers. Instead, selenium-manager will do it automatically as soon as you try to instantiate the driver object. For this you simply need to add selenium-manager to the dependency.
Configuration of Selenium WebDriver version 4.9.x with the TestNG framework using Java.
Step 1: Set up your project:
Create a new Java project in preferred IDE.
Step 2: Add Selenium WebDriver and TestNG dependencies:
Add the following dependencies to your project’s pom.xml file for Maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>4.9.x</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-manager</artifactId>
<version>4.9.x</version>
</dependency>
Step 3: Create a test class:
Create a new Java class in the project created to serve as test class.
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class MyTest {
private WebDriver driver;
@BeforeMethod
public void setUp() {
// Set up WebDriver instance
driver = new ChromeDriver();
}
@Test
public void myTest() {
// Write test logic using WebDriver
driver.get("https://example.com");
// Perform actions and assertions
}
@AfterMethod
public void tearDown() {
// Clean up and quit the WebDriver instance
driver.quit();
}
}
Step 4: Next step is to set up WebDriver instance:
- In the setUp() method, set up the WebDriver instance, specifying the browser-specific driver path (for e.g., chromedriver for Chrome).

Step 5: Start writing test methods:
- Write test methods using the @Test annotation provided by TestNG. You can create multiple annotations as well.
- Utilize the WebDriver instance (driver) to interact with web elements, perform actions, and also verify the expected behaviors.

Step 6: Run the tests:
- Run your tests using TestNG’s test runner, either do it through your IDE or by using the TestNG CLI.

Getting Started with Automation Testing Using Selenium Framework on TestMu AI
Now that you have Selenium setup on your local system and assuming you are in a position to write your first automated test for web applications, you may consider to know how TestMu AI helps in running the test scripts.
TestMu AI provides a helpful solution for individuals who are new to the Selenium framework and are embarking on their initial journey of writing automated tests. It offers a user-friendly cloud-based platform that allows easy execution of Selenium based test scripts. With its seamless integration, wide range of supported browsers and devices, TestMu AI assists beginners in running their tests across different environments, enabling them to gain valuable experience and proficiency in automated testing.
If you are keen to explore, then here is a tutorial on running the first automated test on TestMu AI. I would encourage you to first choose a framework for yourself as discussed above and write a basic automation test and run it on TestMu AI grid by following the guide.
Benefits and Results Achieved by Using Selenium Framework
Here are some benefits and results achieved by companies through successful implementations of the Selenium framework:
- Booking.com:
- Booking.com implemented Selenium for their web application testing, resulting in significant improvements.
- They achieved faster feedback cycles by automating repetitive tests, reducing the time required for testing.
- Selenium allowed them to scale their testing efforts and achieve better test coverage across multiple browsers and platforms.
- The framework helped them identify and fix issues earlier in the development process, leading to improved overall quality and customer satisfaction.
- Salesforce:
- Salesforce, a leading CRM platform, leveraged Selenium for their web application testing needs.
- They achieved faster test execution times, enabling quicker feedback on the application’s quality.
- Selenium facilitated parallel test execution, allowing them to run tests concurrently on multiple browsers, reducing testing time significantly.
- The framework helped them identify and fix issues earlier, resulting in improved software stability and reliability.
- Etsy:
- Etsy, the popular e-commerce marketplace, adopted Selenium for their web application testing.
- Selenium’s cross browser testing capabilities enabled them to ensure consistent user experience across different browsers and platforms.
- By automating repetitive tasks, they reduced the testing effort and increased test coverage.
- Selenium allowed them to catch critical issues early in the development cycle, resulting in improved software quality and faster time-to-market.
- ThoughtWorks:
- ThoughtWorks, a global software consultancy, utilized Selenium for their web application testing projects.
- They achieved improved collaboration between testers and developers through the use of Selenium.
- Selenium’s compatibility with various programming languages allowed for seamless integration with their existing tech stack.
- The framework enabled efficient test execution and quick identification of bugs, leading to faster delivery cycles and improved client satisfaction.
These case studies demonstrate the benefits of using the Selenium framework, including faster feedback cycles, improved test coverage, enhanced software quality, and cost savings. These successes highlight the versatility and effectiveness of Selenium in various industries and organizations.
Future of Selenium Framework and Test Automation
The future of the Selenium framework and test automation is expected to continue evolving to meet the changing needs of software testing and development.
- Enhanced AI and Machine Learning Integration
As AI and machine learning technologies advance, they can be leveraged to improve test automation processes. This includes intelligent test case generation, predictive analytics for identifying high-risk areas, and self-healing capabilities to adapt tests to evolving application changes.
- Shift Towards Headless and Browserless Testing
With the increasing popularity of headless browsers and API-driven testing, Selenium may see further advancements in supporting headless execution modes and extending its capabilities to facilitate browserless testing approaches.
- Integration with Containerization and Cloud Technologies
The adoption of containerization technologies like Docker and cloud-based testing platforms continues to rise. Selenium is likely to enhance its integration with these technologies, enabling seamless test execution in distributed environments and providing scalability and parallelization options.
- Focus on Mobile and IoT Testing
As the use of mobile applications and IoT devices expands, Selenium may place more emphasis on improving support for mobile automation and IoT testing. This includes frameworks like Appium for mobile automation and extending Selenium’s capabilities for testing IoT devices and applications.
- Robust Reporting and Test Management
Test reporting and management are crucial aspects of the testing process. Future developments may include improved reporting capabilities, integration with test management tools, and enhanced visibility into test results and coverage.
- Security and Performance Testing
With security and performance being critical aspects of software quality, Selenium may see advancements in integrating security and performance testing capabilities. This includes features for automating security scans, load testing, and stress testing.
- Collaboration and Community-Driven Enhancements
Selenium has a vibrant community of users and contributors. Future developments will likely be driven by community feedback and collaboration, with enhancements addressing common pain points, improving documentation, and expanding resources for learning and support.
It’s important to note that the future of Selenium and test automation is subject to technological advancements, industry trends, and community contributions. Staying updated with official Selenium documentation, participating in relevant forums, and exploring emerging testing technologies will help professionals stay at the forefront of these developments.