
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What is Verification?
- Advantages of Verification
- When to use Verification
- Phases of Verification
- Methodologies of Verification
- Best Practices of Verification
- What is Validation?
- Advantages of Validation
- When to use Validation?
- Testing Involved in the Validation Process
- Phases of Validation
- Methodologies of Validation
- Best Practices of Validation
- Verification vs Validation: What’s the Difference?
Verification vs Validation: Know The Differences
Explore the crucial roles of verification & validation in software quality, their key differences, and best practices to boost reliability.

Nazneen Ahmad
January 13, 2026

In the present era of technological advancement, wherein the pinnacle of software development is reached, the software industry engages in fierce competition to introduce software applications of the utmost quality and reliability. Consequently, a substantial investment is made to keep up with this competition.
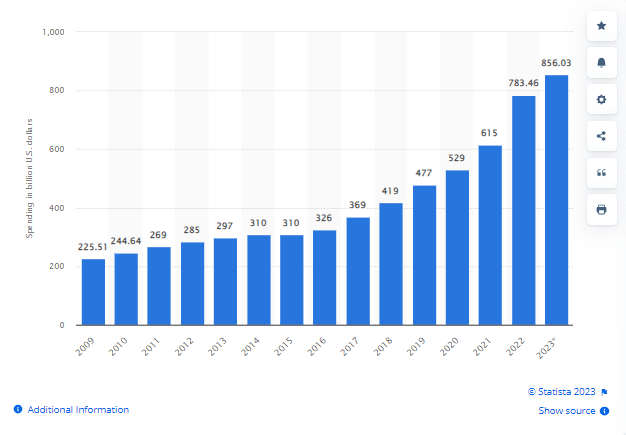
According to Statista, the global expenditure on enterprise software has already surpassed a staggering sum of 783 billion U.S. dollars, showcasing a remarkable growth rate of 7% compared to the preceding year.
Projections indicate an expected investment of 856.03 billion in 2023. These statistics serve as a testament to the ever-expanding and competitive nature of the software development industry, positioning it among the world’s largest and fastest-growing sectors.
In software development, one of the most critical considerations is the assurance of the quality of software applications. This requires the careful integration of two crucial processes: verification and validation. These processes are instrumental in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of software applications in terms of their functionality and performance.
Although these terms may appear synonymous, they represent distinct phases within the Software Development Life Cycle. Thus, knowing the difference between verification vs validation is also important.
The verification process primarily revolves around addressing the fundamental question, “Are we developing the software application correctly?” Its purpose is to ensure the accuracy of the development process itself. Conversely, validation focuses on answering the crucial query, “Are we developing the right software application?” This phase is centered around assessing the efficacy, significance, and overall quality of the software application in question.
Knowing the differences between verification vs validation is crucial for all professionals involved in software development to implement correct strategies and fix errors throughout the Software Development Life Cycle.
In this blog on verification vs validation, we look at the key difference between verification and validation by highlighting its advantages, phases, tests involved, and others. The learnings of this verification vs validation blog will help in your Software Development Life Cycle process.
What is Verification?
Verification is the process in software testing where you check that the software application is developed in the right way and shows correct functionality without any bugs.
In simple terms, verification ensures that developed software applications fulfill the Software Requirement Specification (SRS). Here, the SRS functions as the input for the software development process. Verification ensures that the code logic of the software application is in line with the specification.
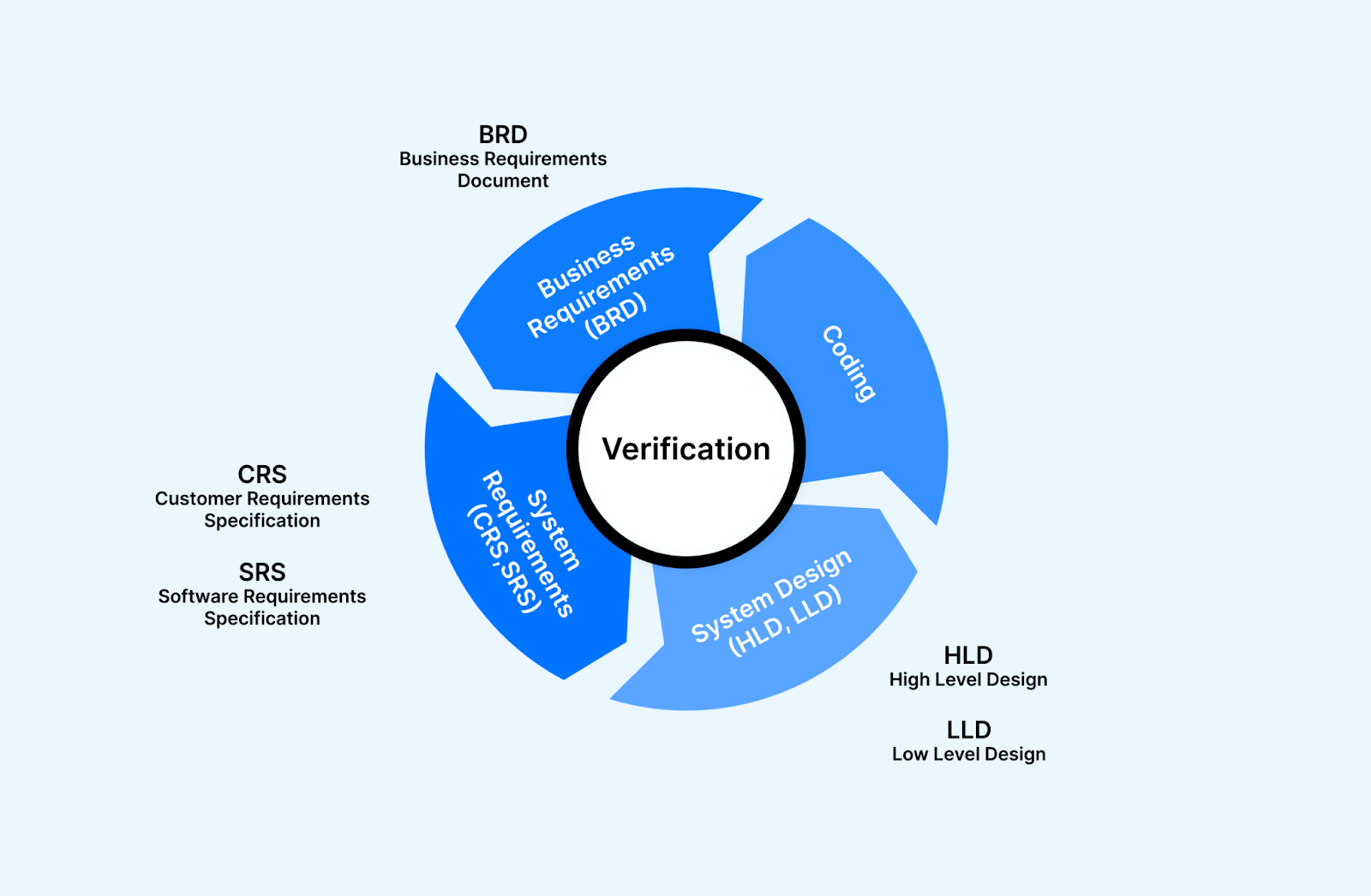
Verification is static testing, which means that the process is focused on verifying the software artifact without running the code or the software application. It is mainly executed by checking documents, designs, and other artifacts. The activities involved here include technical review, code review walk-through, and inspection.
Some of the crucial features of the verification method involve the following:
- The key components of verification include code review, walkthrough, inspection, specification analysis, and design.
- The documents reviewed in the verification method include requirement specifications, database table designs, test cases, test scenarios, traceability matrix, ER diagrams, design blueprints, database table design, etc.
- Verification helps ensure development elements, including software, hardware, documentation, and human resources, align with team-specific standards and protocols.
- It ensures that system design and architecture are correctly architectured and bug-free.
Note: Run your automated tests across 3000+ environments. Try TestMu AI Today!
Advantages of Verification
The verification process in software testing involves several advantages that highlight its significance in Software Development Life Cycle. It is important for you to know about it so that the quality of the software application is maintained. Here are some advantages of the verification process:
- Verification ensures that software applications are developed correctly and in line with specified requirements.
- It helps validate the design and implementation, adhere to the functionality, and meet the desired quality standards.
- This process checks each component and module of the software applications and ensures that software applications work as intended.
- Verification activities are performed early in the software development process; potential bugs are identified and fixed quickly.
- If you perform verification activities at each stage of the development process, you can get timely feedback and insight on the software’s progress and areas that require improvement.
- Verification actions, including testing and analysis, allow you to identify bugs immediately, which gives the team the option to plan for their resolution.
- It helps keep the software application aligned with customer and business requirements at every stage of software development.
- Verification involves assessing software artifacts, such as requirements, designs, and specifications, to ensure they align with the intended objectives and functionality.
When to use Verification
It’s important to run verification tests at each stage before implementing any new feature in the development process.
Let’s take an example of a button called “Proceed to Pay.” Before creating this button, verification tests would examine all the requirements established during the initial idea generation and brainstorming phases.
For instance, the documentation specifies that the button should be yellow with red lettering, no larger than 9mm X 9mm, and always visible in the top right corner of every product page on the website. Additionally, another button with the same text, color, and dimensions should be placed below each product on the page.
Before developing the button, you must review the design and requirements documents and ensure all the specifications are listed. This step is necessary to avoid overlooking guidelines or missing important details.
By performing these verification tests before working on every feature or element on the page, you can ensure that they meet the SRS and follow the agreed-upon design. This helps maintain consistency, adhere to guidelines, and prevent potential issues from arising during development.
In the next section of this blog on verification vs validation, let us understand the phases involved in verification activities.
Phases of Verification
When verifying a software application during its development, there are three main phases of verification testing to go through:
- Requirements Verification: This phase involves confirming that the requirements for the software application are complete, clear, and accurate. Before moving into the design phase, you must very carefully verify the business or end-user requirements to ensure they are correct and detailed.
- Design Verification: In this phase, you have to check whether the design of the software applications aligns with the design specifications provided. They assess various aspects such as layouts, prototypes, navigational charts, architectural designs, and logical database models. The goal is to verify that the design meets both the functional and non-functional requirements specified for the application.
- Code Verification: During code verification, you have to check the code of the software application for completeness, correctness, and consistency. You must review the development artifacts, including the source code, user interfaces, and physical database model, to ensure they align with the design specifications. This phase focuses on validating that the code implementation accurately reflects the intended design.
By going through these three verification phases, you can ensure that the software application meets the specified requirements, adheres to the design specifications, and has complete, correct, and consistent code.
This comprehensive verification process helps identify any potential issues or deviations early on, leading to a higher-quality software application.
The next section of this blog on verification vs validation discusses methodologies of the verification process.
Methodologies of Verification
Verification methodologies include formal reviews, walkthroughs, and inspections of software artifacts. As part of it, code reviews and documentation walkthroughs are performed, allowing for complete verification and identification of errors and inconsistencies. The following are some of the different methodologies used in the verification process, which help ensure the quality of software applications:
- Reviews: The review method may be formal or informal, which mainly depends on the complexity of the software application being reviewed. Here, you must evaluate the software artifacts like source code, requirements, and test cases to give feedback and identify potential issues.
- Walkthrough: In the walkthrough method, you focus on understanding the content, identifying errors, gathering feedback, and gaining insights. In other words, the developers of the software applications guide stakeholders through software code and different artifacts.
- Inspection: It is a formal method of verification that includes a different team of reviewers, mainly experienced testers, SMEs, and others, to verify the software documents and code. This is done to detect defects, design flaws, coding errors, and others.
- Model Checking: It uses formal methods to verify software models against formal specifications, ensuring consistency, correctness, and adherence to desired properties.
Static testing methods like walkthroughs, inspections, model checking, and reviews are essential for verifying software quality. They help identify defects, improve the software design and code, and ensure that the final software applications meet the required standards and expectations. These methods promote collaboration, enhance communication among team members, and contribute to building reliable and robust software systems.
In the next section of this blog on verification vs validation, we will see the best practices of the verification process.
Best Practices of Verification
If you want to verify software artifacts and improve software quality and reliability effectively, you need to follow some best practices. Here are some of those.
- Establishing clear and concise standards, guidelines, and coding practices helps maintain consistency and facilitates effective verification.
- Encouraging collaboration and communication among team members fosters a culture of peer review, where multiple individuals critically assess software artifacts.
- Leveraging automation tools and frameworks for code analysis, test execution, and verification tasks improves the efficiency, accuracy, and repeatability of the verification process.
- Establishing traceability between software artifacts, such as requirements, designs, and test cases, helps ensure that each element is verified and validated against its corresponding requirement.
- Regularly evaluating and enhancing the verification process based on lessons learned, feedback, and industry advancements contributes to continuous improvement and better software quality.
What is Validation?
Validation is the process of checking the developed software application to ensure that it meets the exact needs of the end users. It is usually performed after the completion of the software development process and takes place after the verification process is done.
Here, you only focus on the output and do not consider the internal process and technical complexities involved in the development process. Through the validation process, the team gains valuable insights regarding the development of the software application and ensures its intended functionality within a suitable environment.
It is basically dynamic testing. This indicates that the validation process involves running the software application and monitoring its behavior and functionality in real-time. It mainly addresses the dynamic aspects of the software application, like performance, functionality, and user interaction. Unlike the verification method, it does not validate the static components of the software application, like code or design.
Some of the crucial features of the validation method involve the following:
- The validation verifies that the software application aligns with the intended functionality and purpose.
- It works to ensure that a software application fulfills the end user’s needs and gives the desired outcome.
- It considers the output of the software application to check for its correctness and accuracy.
- It checks for the factors like ease of use, usability, and user interface design of the software application.
- The validation process includes different test methods, such as manual testing, automated testing, user acceptance testing (UAT), and regression testing.
- In the Agile development approach, validation involves repetitive cycles that allow continuous feedback, refinements, and revalidation to check its alignment with requirements.
- Validation involves reporting the validation process, test cases, test results, and any identified issues.
Advantages of Validation
There are several advantages of the validation process in software testing. Some of those include enhanced bug detection, identification of specification inadequacies, alignment with customer demands, and verification of cross browser compatibility.
You can improve the final software application’s quality, reliability, and user satisfaction by incorporating validation into the software development process. Let us learn more about this:
- If you perform a verification process and any bug or error is missed from detection, validation helps uncover those.
- In the software development process, if the specification defined is incorrect or insufficient, validation helps reveal that inefficacy. This enables you to address the shortcoming and avoid potential issues.
- By performing the validation process, you can check whether the development of the software application adheres to the end-user demands, expectations, and preferences in different scenarios like slow connectivity, low battery, and so on.
- Validation is crucial to ensure that the software application functions flawlessly across different combinations of browsers, devices, and operating systems.
- You can identify and fix the defects and bugs in the last phase of the software development process, leading to a reduction of cost and efforts in fixing them after their release in the market.
- It helps ensure that software applications function correctly in real-time conditions, thus lowering the risk of failure.
- It easily identifies any usability issues like confusing workflow and user interface issues.
In the next section of this blog on verification vs validation, we will explore when to use the validation process.
When to use Validation?
The validation process should be executed after the development of each feature of the software application or step of the software development process. It will help you understand the correct functioning of the software application. Let us look at some examples to have clear concepts on this:
One form of the validation process is unit testing, which is performed after creating a unit of code and helps verify that each is functioning as intended before proceeding to the next step. Another form of the validation process is integration testing. It is performed to check how multiple modules or components work together.
A crucial aspect of validation testing is cross browser testing. Quality assurance professionals must check how the software applications render and function on different combinations of browsers, devices, and operating systems.
For instance, they would test if a specific feature, like a “Proceed to Payment” button, works perfectly on different browsers like Google Chrome on a Samsung Galaxy A23 device and Safari on an iPhone 13. By running these tests, the team can identify any issues or discrepancies in the software’s performance across various browser-device-OS combinations.
In the next section of this blog on verification vs validation, we will cover different testing types involved in the validation process.
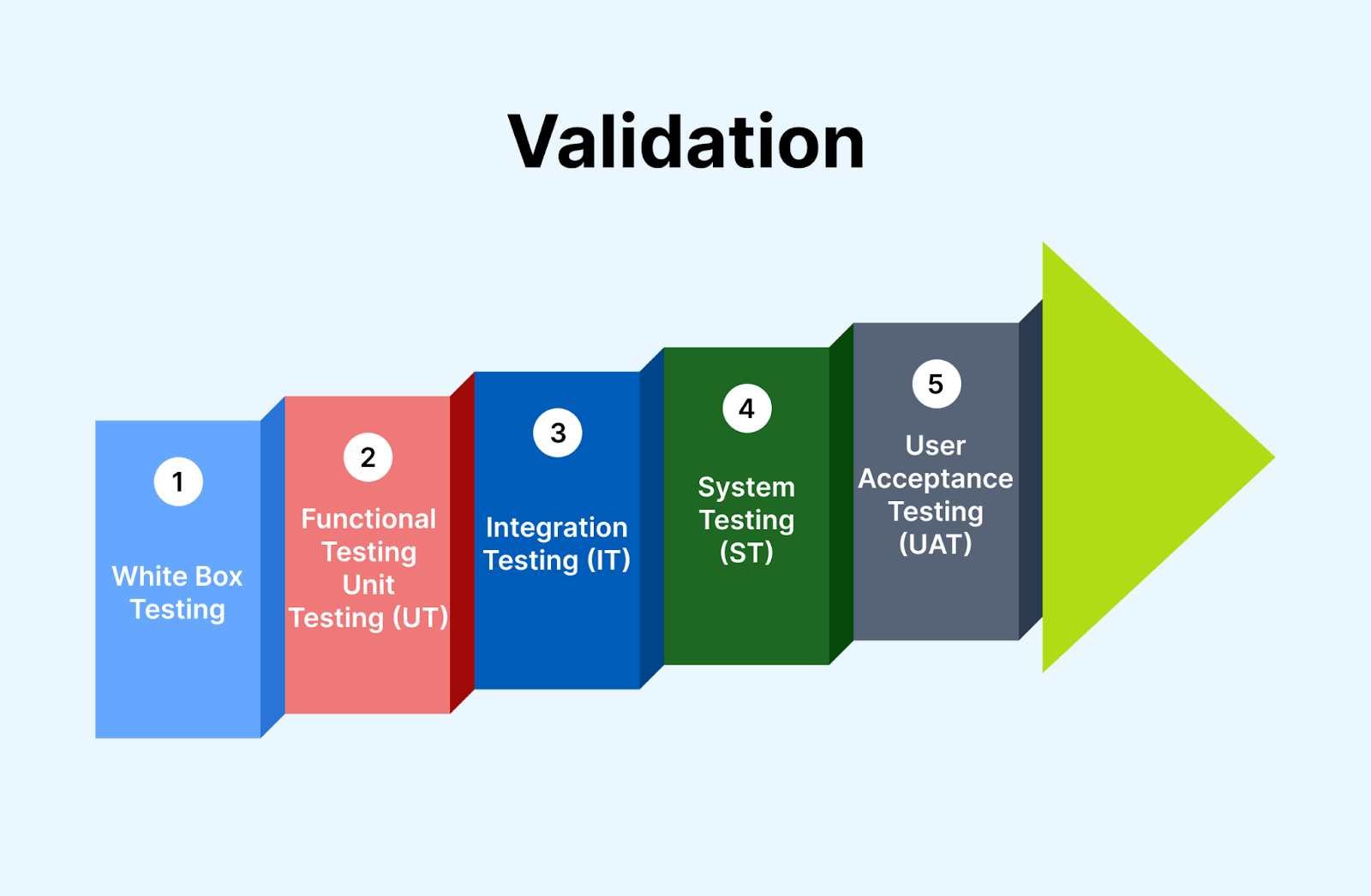
Testing Involved in the Validation Process
Most of the QA forms fall under the category of the validation process. The test from unit testing to user acceptance tests is included as a validation test. Some of the tests involved in the validation of software applications include the following:
Functional Testing
Functional testing verifies that the software application functions correctly according to the specified requirements. Testers execute different scenarios and compare the actual outcomes with the expected results. Here are the different types of functionality tests involved in the validation process.
- Unit testing: It is executed by the developers who are mainly involved in writing test scripts that validate the individual components and units of the software application. It is done to check whether the software application matches the requirements.
- Cross browser testing: This type of test involves validating the behavior and functionality of the software application across different web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and others. It is mainly performed to check for compatibility issues due to variations in browser behavior, HTML interpretation, and CSS rendering.
- Smoke testing: It is typically performed after the release of each build to ensure that software stability is intact and does not encounter any error or bug.
- Sanity testing: It is performed after a smoke test and validates that every major function of the software application is working correctly. It aims to quickly assess whether the specific modifications or fixes have not introduced new issues or affected existing functionalities of the software application.
- Regression testing: This type of test is performed to check or validate the change done to the software application’s codebase; like bug fixes, the addition of new code does not lead to cause any issue or error in the existing working of the software application.
- Integration testing: Integration testing occurs when a software system consists of multiple functional modules that must work together effectively. Integration testing aims to validate that these individual modules interact and function as expected when integrated.
- Beta testing: Beta testing involves releasing the software to a limited group of actual customers or end users in a real or simulated production environment. Beta testing aims to gather feedback and evaluate how comfortable the customers are with the software’s interface, features, and overall usability.
- User acceptance testing: It is performed to define whether a software application meets the requirements and expectations of end users or stakeholders. UAT aims to gain confidence in the software’s readiness for production use by verifying its functionality, ease of use, and alignment with user expectations.
If you want to leverage cross browser testing, you can execute the test in a cloud-based digital experience testing platform like TestMu AI. TestMu AI offers efficient cross browser testing for web and mobile apps to ensure they function seamlessly across a multitude of browsers, versions, and OS.
With real time and automation testing, TestMu AI simplifies the process, saving time and effort. You can deliver a flawless user experience, improve customer satisfaction, and expand your software application’s reach with TestMu AI.
Subscribe to our TestMu AI YouTube Channel to get the latest updates on tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing, and more.
Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing focuses on assessing the attributes of a software system that are not directly related to its specific functionality.
Unlike functional testing, which verifies if the software meets the functional requirements, non-functional testing evaluates aspects such as performance, reliability, usability, security, and compatibility. Here are the different types of non-functionality tests involved in the validation process.
- Performance testing: It validates the performance of the software application under other workload conditions. For example, it measures response time, resource utilization, and throughput.
- Security Testing: In this testing, QA engineers validate the ability of the software application to protect or safeguard against security vulnerability, data breach, and unauthorized access. It includes identifying any potential risk, assessing encryption, and addressing compliance with security standards.
In the next section of this blog on verification vs validation, let us understand the phases involved in validation activities.
Phases of Validation
In software testing, the validation process typically consists of several phases to ensure that the software meets the intended requirements and functions correctly. Here are the common phases of validation:
- Requirement analysis: In this phase, you have to analyze and evaluate the requirements of software applications carefully. This can be done by reviewing the functional and non-functional requirements to get an idea of how it performs.
- Test planning: Here, you make a test strategy and test plan where you identify the key objective, scope, and validation approach. This involves identifying the software testing tools, test cases, and others.
- Test design: Next step is to create detailed test cases based on the identified requirements. Along with this, you also prepare the test data and the required test environment setup.
- Test execution: During this phase, the test cases are executed as per the defined test plan. You can record and report any defects or bugs from the expected behavior, ensuring that all issues are captured and documented for further analysis.
- Defect management: This phase involves managing and tracking the reported defects. In the defect management process, defects are logged, prioritized, and assigned for resolution. Following this, a validation process is closed by analyzing the test result and preparation of the test summary report.
The next section of this blog on verification vs validation discusses methodologies of the validation process.
Methodologies of Validation
When it comes to validating software applications, two methodologies, namely white box testing and black box testing, play a vital role.
- White box testing in the validation process: In validation, white box testing focuses on examining the internal structure and logic of the software application to ensure that all components work together as intended. Testers can design test cases that thoroughly examine different paths and conditions within the code by having access to the source code. This method helps identify potential errors, flaws, or inconsistencies within the software’s internal workings.
- Black box testing in the validation process: On the other hand, black box testing evaluates the software application’s functionality from an end-user perspective. Testers cannot access the internal code or structure but instead evaluate inputs and outputs to ensure that it meets specified requirements and performs as expected.
This method uncovers any deviations from desired behavior, functional issues, or usability problems that users may encounter.
By incorporating white box and black box testing methodologies into the validation process, software developers and testers can cover various aspects of the software application’s quality. This comprehensive approach helps you to identify and address potential issues, resulting in a validated software application that meets the intended requirements and user expectations.
Note: Test reliably and ship applications with confidence. Try TestMu AI Today!
In the next section of this blog on verification vs validation, we will see the best practices to follow when using the validation process.
Best Practices of Validation Activities
To improve or optimize the validation process in software testing, you need to follow some of its best practices, which are explained below.
- Setting well-defined acceptance criteria helps in setting clear expectations and benchmarks for validation.
- Active involvement of end-users throughout the validation process ensures their needs and expectations are accurately addressed.
- Proper management of test data, including realistic and representative data sets, enhances the accuracy and reliability of the validation process.
- Conducting regression tests after making changes to the software or system helps ensure that existing functionality remains intact.
- Maintaining comprehensive documentation of the validation process, including test plans, test cases, and results, facilitates traceability and future reference.
The next section of this blog on verification vs validation discusses key differences in the verification vs validation process.
Verification vs Validation: What’s the Difference?
The difference between the two terms primarily stems from the function of specifications. Verification assesses if the software aligns with specified requirements, focusing on ‘Are we building it right?’ Validation, in contrast, ensures the software fulfills customer needs, addressing ‘Are we building the right thing?
Verification is the process of evaluating work-products of a development phase to ensure they meet the specified requirements. This step is about asking, “Are we building the product right?” It is a quality control process that relies on static methods like reviews, walkthroughs, and inspections, without requiring code execution.
Validation, on the other hand, is the process of evaluating the final product to check whether it meets the business and user requirements. It answers the question, “Are we building the right product?” This step involves dynamic testing methods, including executing the code, to verify the actual product’s performance against the expected outcomes.
Unlike verification testing, validation testing always requires executing code. It involves various types of software testing, such as unit tests, integration tests, regression tests, cross browser and cross device testing, and more.
Both developers and testers perform verification testing to ensure adherence to predetermined standards and expectations. It precedes validation testing in the Software Development Life Cycle. Its focus is on the documentation and assets related to the development process, while validation testing targets the product that customers will use after its public release.
While verification testing does not require specific devices, platforms, browsers, or operating systems for execution, validation testing is best performed using real browsers, devices, and operating systems to ensure the product functions as intended in various environments.
Here are the key differences of verification vs validation for better understanding and comparison.
| Verification Testing | Validation Testing |
|---|---|
| It is the static practice of studying and verifying requirements. | It is the dynamic practice of testing the final product. |
| It does not require executing code. | It always requires executing code. |
| Human verification of required assets. | Human and machine-based checking and approval of software. |
| Document reviews, inspections, walkthroughs, and desk-checking. | Unit tests, integration tests, regression tests. |
| Detects bugs at the beginning of each development phase. | Detects all unnoticed bugs at the verification stage. |
| Targets specification documents, design docs, and test cases. | Targets the product for customer use after the public release. |
| Comes before validation testing. | Follow verification testing. |
| Does not require specific devices or platforms. | Best executed using real browsers, devices, and OS. |
Conclusion
In this blog on verification vs validation, an in-depth discussion on verification vs. validation must have given you a very clear idea of its difference and its related concepts.
Let’s summarize the learnings of verification vs validation. Validation and verification are the two crucial processes in the Software Development Life Cycle, and each has its distinct aim and purpose. Here, verification involves verifying the requirement of the software application where you don’t have to execute the code, pay attention to early identified bugs, and adhere to the pre-determined standards.
However, validation is mainly performed after the development of software applications and involves the execution of dynamic testing to ensure that it meets the end-user requirements. It includes various testing techniques like functional and non-functional tests. It is important for you to understand both verification and validation so that you can ensure the quality and reliability of the software application released.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




