
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

32 Top Java Frameworks For 2026
Check out top 32 Java Frameworks to use in 2026. Elevate your web development with top Java frameworks such as JUnit, Spring, Hibernate, Play, Apache Struts, Blade, Grails, and more.
Daniel Mascarenhas
February 7, 2026
In today’s world, quality is the key to success for any product software. Human mistakes by programmers are inevitable, but the cost of not correcting them in time can be costly and lead to debts. Technical debt is way riskier than financial debt! Unaddressed technical debt can destroy the product.
One bibliometric study published in August 2022 at the University of Maribor showed that the research publications related to software quality are currently following an exponential growth trend and that the software quality research community is growing tremendously. Quality today is at the forefront of product development.
In this article on top Java frameworks, let’s delve into the various Java testing frameworks and discuss some of the most popular Java frameworks used for web development with their salient features.
Introduction
Automation testing has been there for a while and is widely adopted by small-scale startups to large enterprises. Automating the test cases for AUT (Application Under Test) is essential to get a quick quality assessment before any new release. Delivering new features without compromising on quality needs good test automation coverage. And to achieve that, we must make good use of some test frameworks readily available on the Internet. Chosen automation testing framework should align well with the internal test processes.
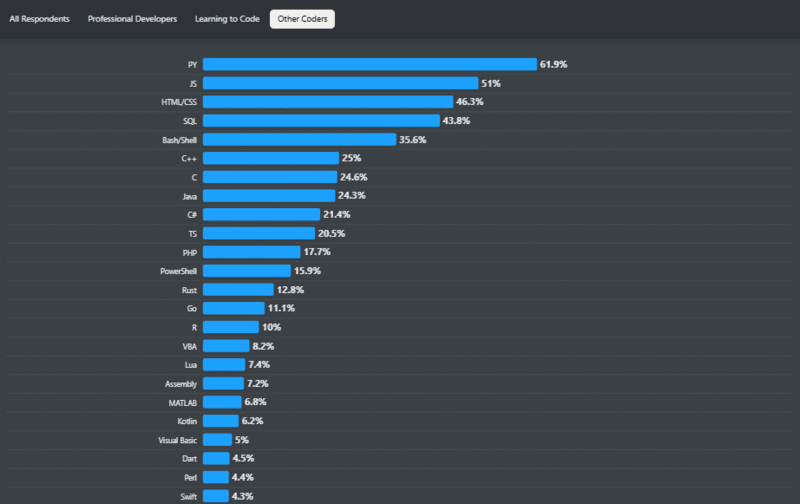
According to the StackOverflow 2024 survey, C++ holds the top 6th position, with 25% of people successfully using it. It is a reliable programming language that can be harnessed to its full potential with Java testing frameworks. There are many Java frameworks in the market to cater to different needs. It’s not easy to pick and choose one.
What is Framework in Java?
A Java framework is a pre-written set of classes, interfaces, and methods providing reusable components and guidelines to simplify application development.
In Java, a framework is a pre-written set of classes, interfaces, and methods that provide a structure to build applications. It offers a foundation for developers to create software by providing reusable components, libraries, and guidelines. Frameworks simplify development by offering ready-made solutions for common tasks, allowing developers to focus more on application-specific logic rather than reinventing the wheel. They often enforce certain design patterns, best practices, and conventions, which can enhance productivity and maintainability of Java applications.
What Are the 9 Best Java Testing Frameworks?
Top Java testing frameworks include JUnit, Selenium, TestNG, JGiven, Selenide, Gauge, Geb, Cucumber, and Serenity BDD for various testing needs.
Java testing frameworks are essential for ensuring the quality of software applications. Several popular Java frameworks are available that cater to different testing needs. Here are some of the commonly used Java testing frameworks in detail.
1. JUnit
JUnit is a Java framework for automating unit tests. Usually, a developer who builds a unit or API must ensure detailed unit testing. JUnit has various test guidelines, which can help developers build reliable unit tests. As application development advances, the volume of APIs will grow exponentially.
It helps to manage all these unit tests effectively. Also, since it’s about testing a single unit, tests are incredibly reliable and would help us build a firm test bed as the code grows. When writing this blog, the JUnit version referred to is 5.6.2.
In earlier JUnit versions, we must import a single monolithic jar with the whole JUnit architecture. For example, APIs for writing and running tests were part of the same jar. JUnit 5, however, allows us to import what is necessary. The API for writing tests using JUnit is called JUnit Jupiter. And the API for managing and running tests is called JUnit Platform.
Why is JUnit One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
JUnit offers a wide range of features that facilitate the creation and execution of effective unit tests. Some of the key features that make JUnit one of the best Java frameworks are:
- Support for AnnotationsJUnit 5 has a wide range of annotations that programmers can use in their code. It improves the readability of code. Below are some of the most used JUnit Annotations.
- Assertions for testing particular conditionsJUnit Assertions are used to test a particular condition that must be evaluated to be true for the test to continue. Adding plenty of positive and negative boundary-level unit tests is an important part of the JUnit test suite. Assertions such as assertEquals, assertNotEquals, etc., help implement positive and negative test scenarios.
Here are some of the most used assertions of JUnit 5
- Test Runner for resultsFor running unit tests developed using JUnit 5, we need to import the JUnit Platform. For IDEs such as IntelliJ IDEA 2016.2 + and Eclipse Oxygen.1a (4.7.1a +). We can also explicitly import libraries of the JUnit Platform into Maven and Gradle to run the tests. Once desired libraries are imported into Maven or Gradle repositories, we can use commands to perform JUnit testing.
For the Maven command, we can use:
mvn clean test
For Gradle, we can use:
gradle clean test
| Annotations | Usage |
|---|---|
| @Test | Denotes that a method is a test method. |
| @DisplayName | User-friendly method name, which would be displayed in the report. |
| @BeforeEach | Methods with this annotation will be executed before each test. |
| @AfterEach | Methods with this annotation will be executed after each test. |
| @BeforeAll | Methods with this annotation will be executed before all tests. |
| @AfterAll | Methods with this annotation will be executed after all tests. |
| @RepeatedTest | Allows a test method to be repeated a specified number of times during test execution. |
| @Disabled | Methods with this annotation will not be executed. |
| Assertion Type | Usage |
|---|---|
| assertEquals(expected, actual) | Asserts that expected and actual values are equal. Both expected and actual values should be of the same data type. |
| assertNotEquals(unexpected, actual) | Asserts that expected and actual values are not equal. Both expected and actual values should be of the same data type. |
| assertTrue(boolean condition) | Asserts that the supplied condition is true. |
| assertFalse (boolean Condition) | Asserts that the supplied condition is not true. |
| assertAll(Executable… executables) | Asserts that all supplied executables do not throw exceptions. |
| assertSame(Object expected, Object actual) | Asserts that expected and actual reference to the same object. |
| assertArrayEquals(expected[], actual[]) | Asserts that expected and actual arrays are equal. An array could be of any datatype, e.g., Char, String, Boolean, etc. |
| assertNotNull(Object actual) | Asserts that actual is not null. |
| assertNotSame(Object unexpected, Object actual) | Asserts that expected and actual do not refer to the same object. |
With JUnit 5, you can use multiple test runners simultaneously to run your tests. This helps us distribute tests for faster test execution. Furthermore, you may also check out our comprehensive guide on JUnit 5 extensions.
To enable parallel testing with JUnit 5 and Selenium, we must create a junit-platform.properties file in the src/test/resources folder. We can enable the parallelization feature by adding the following line in the file as mentioned above:
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled = true
We can also add the below lines in the above file to enable multithreading at the class and module level.
| To run tests parallel within a particular class in separate Thread | junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.default = concurrent |
|---|---|
| To run tests parallel within a particular module in separate Thread | junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.classes.default = concurrent |
Usage of JUnit Framework
Now that we have looked into the key features of JUnit 5, let’s see this popular Java framework in action!
Add these entries to the POM file to use JUnit 5 Platform and Junit 5 Jupiter.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>5.6.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-runner</artifactId>
<version>1.9.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-console-standalone</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Sample JUnit Code snippet with different JUnit annotations and assertions:
package com.lambadatest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Nested;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNotEquals;
@DisplayName("Tests with different types of assertions")
public class SampleJUnit5Test {
Integer ExpectedInstance = 5;
Integer ActualInstance = 5;
Integer ExpectedEvents = 4;
Integer ActualEvents = 9;
@BeforeEach
void init(TestInfo testInfo) {
String BeforeEachTestDoThis = testInfo.getTestMethod().get().getName();
System.out.println(BeforeEachTestDoThis);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Positive test: Instances should be equal")
void shouldBeEqual() {
assertEquals(ExpectedInstance, ActualInstance);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("Negative test: Events should not be equal")
void shouldNotBeEqual() {
assertNotEquals(ExpectedEvents, ActualEvents);
}
@Disabled
@Test
@DisplayName("Test is not more valid.")
void eventsshouldBeGreaterThanInstances() {
assertTrue(ActualEvents > ActualInstance);
}
}
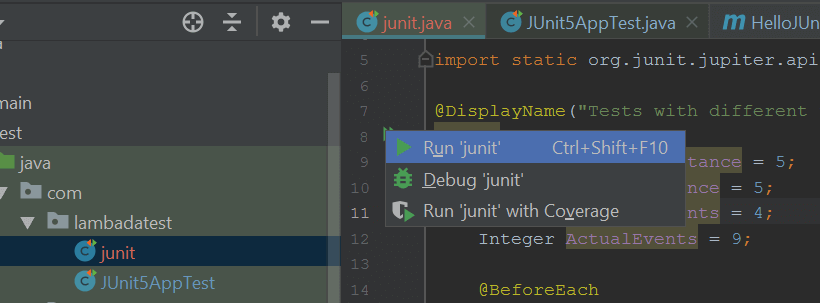
Let’s now see how to run JUnit 5 tests using IntelliJ (2020.2 version).
Right-click on the test and select the ‘Run ‘junit’’ option as shown below.
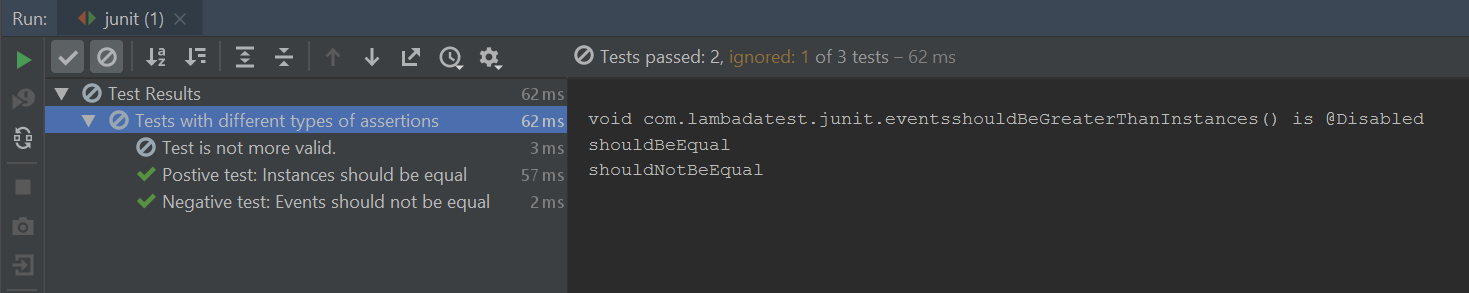
After execution, it would show test results as shown below.
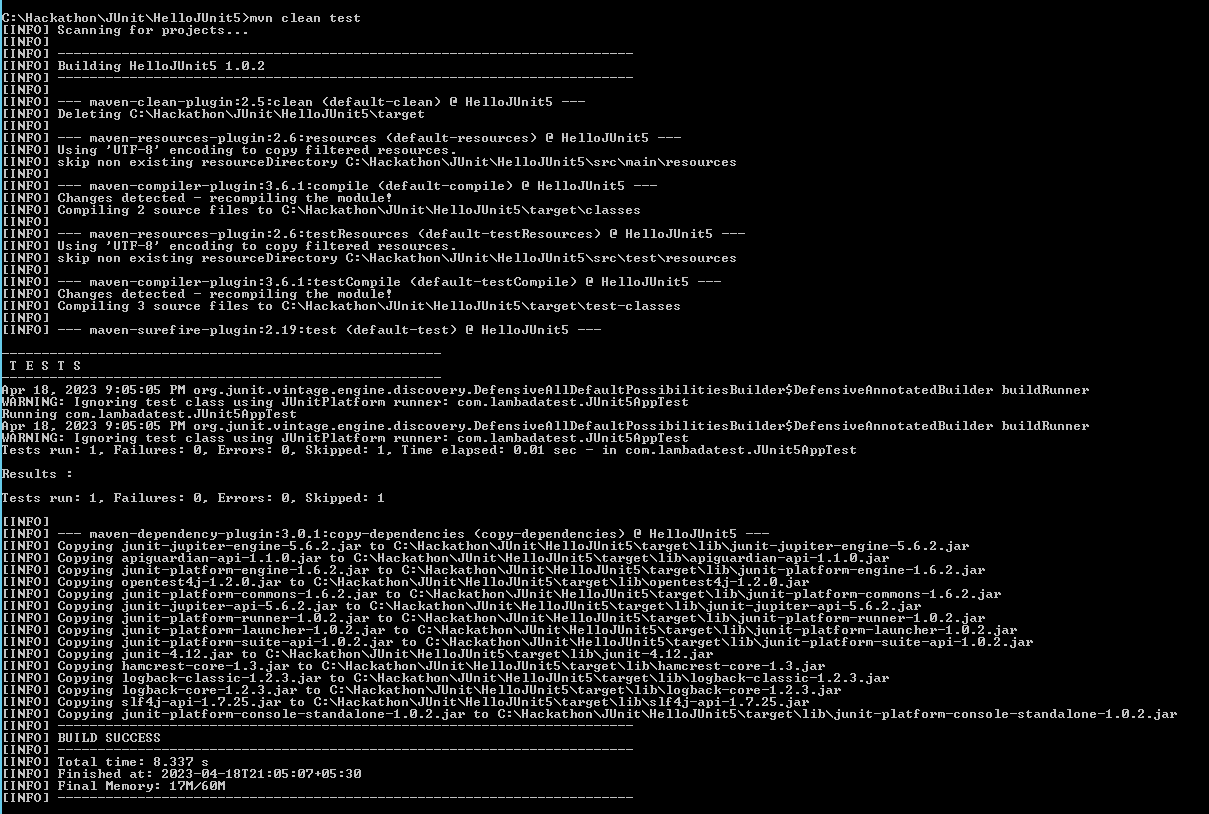
For running JUnit tests using Maven, open a command prompt (Windows), navigate to the directory where you have the JUnit test project copied, and enter the following command:
Once executed, it should show output as below.
When to Opt for the JUnit Framework?
- For building a unit test suite right from the initial development phase.
- For testing the behavior of a particular unit.
- For better coordination between developers and testers.
2. Selenium
Selenium is a browser automation tool for web-based applications. It is the most popular open-source automation testing tool for integration test cases. It is used mainly for the UI automation of test cases.
Selenium comes with Selenium WebDriver, Selenium Grid, and many other useful features essential for building efficient automation tests on any browser. You can also perform Selenium automation testing with Selenide framework.
It has a good online presence, making it easy for automation engineers with beginner-level experience to adapt. When writing this blog on Java frameworks, the Selenium version is 4.8.3.
Why is Selenium One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
Let’s delve into the salient features of Selenium and uncover why is it one of the prominent Java frameworks:
- Selenium WebDriver with strong web supportSelenium WebDriver is the API that establishes the communication between the test script and the browser. Each browser would have its corresponding WebDriver. WebDriver supports a wide range of methods to interact with browsers. Below are some of the most common WebDriver methods used.
- Support for multi-browser testingSelenium interacts with UI via a web browser. Using a browser with native support, it can perform any operation just like an end user would. It supports most of the popular browsers. The list includes Chrome, Safari, IE, Opera, Firefox, Edge, etc. Features like the Page Object Model in Selenium Java (POM) can help maintain automation code with minimal effort.
- Support of multiple programming languagesSelenium supports all the major programming languages like Java, Python, JavaScript, PHP, Perl, Ruby, etc. We can write automation scripts in any language we are comfortable with.
- Selenium IDESelenium IDE provides a record and playback feature for building automation scripts. This tool comes in handy for those with limited programming skills. This IDE comes as a browser add-on. It is available for major browsers like Firefox, Chrome, etc.
- Better integration optionsSelenium can be easily integrated with frameworks like Ant and Maven for source code compilation. It can also be integrated with TestNG for generating effective reports for Selenium test execution.
- A mature tool for UI automationSelenium has been around since 2004 now. It has evolved into a tool with good features for automating any web UI test case. Also, being an open-source and widely used tool has resulted in a good online presence. Several communities can help users with any day-to-day automation challenges.
| Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|
| driver.get("https://www.lambdatest.com/blog/") | To open any URL. |
| driver.navigate().to("https://accounts.lambdatest.com/login"); | To navigate to another URL. |
| driver.navigate().refresh(); | To refresh the page. |
| driver.findElement(By.id("login-button")).click(); | To locate any UI element. |
| driver.switchTo().frame("iframeName"); | To switch to any nested iframe. |
| driver.navigate().back(); | To navigate back in the browser. |
| driver.navigate().forward(); | To navigate forward in the browser. |
| driver.switchTo().window("Child Window name"); | In case of multiple browser windows, to switch to a specific window. |
Usage of Selenium Framework
Let’s now assume a simple test case. If one wants to check if the TestMu AI account has been logged in successfully or not. He can write a script for the same using Selenium as below.
POM Entry
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.seleniumhq.selenium/selenium-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>4.8.3</version>
</dependency>
Sample Code
package com.lambadatests;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class lambadatest {
public WebDriver driver;
public static String USERDIR = "user.dir";
String userName = "//input[(@id='username') or (@name='username')]";
String password = "//input[(@id='password') or (@name='password')]";
String submit = "//button[text()='Login']";
String verifyAfterLogin = "//a[@class='lambda__logo']";
public void sampleTest() {
// Initialization of chromedriver
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", chromeDriverLocation);
driver = new ChromeDriver();
//Launching url of the lambda test application
driver.get("https://accounts.lambdatest.com/login");
driver.findElement(By.xpath(email)).sendKeys("[email protected]");
driver.findElement(By.xpath(password)).sendKeys("Password");
driver.findElement(By.xpath(submit)).click();
//Verification of actual test step
if (driver.findElement(By.xpath(verifyAfterLogin)).isDisplayed()){
System.out.println("Login to Lambda test is passed.");
}else {
System.out.println("Login to Lambda test is failed.");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
lambadatest obj = new lambadatest();
obj.sampleTest();
}
}
When to Opt for the Selenium Framework?
Here are some scenarios where opting for Selenium would be appropriate:
- To build a robust UI automation suiteWith a comprehensive set of features, one can build a robust UI automation. As applications tend to change over time, we need to update test scripts. Selenium provides all support to build a suite that is easy to maintain.
- To get more accurate UI test resultsUI tests tend to be flaky and unreliable due to numerous factors such as – application sluggishness and ever-changing application functionality. Selenium provides multiple methods to wait dynamically for a particular element to load. It also provides concepts such as Page Object Model (POM) to organize your tests.
3. TestNG
TestNG is a JUnit-based framework. It is one of the best Java frameworks for testing. However, it does have particular distinctions. Unlike JUnit, TestNG is designed for unit, integration, and end-to-end tests. In an enterprise organization, where we have a large set of automated test cases, we face the following challenges:
- How to create a subset or full set of tests for Build Verification tests (BVT), Sanity tests, Regression tests, etc.?
- How to run tests in the multi-threaded manner for quick execution?
- How to run specific test cases against a varied set of test data?
- How to make some tests dependent on other tests?
- How to disable tests owing to any open defects?
- How to generate good reports with all key execution details?
TestNG helps us solve the above crucial challenges. It helps us manage test execution better and more effectively. At the time of writing, the TestNG version referred to is 7.7.1.
Why is TestNG One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
Let’s dive into the special features of TestNG and discover why testers consider it as one of the best Java frameworks for testing:
- Multiple annotationsTestNG supports a wide range of annotations. These annotations can be used to set test execution patterns. Here is the list of the most commonly used TestNG annotations.
In addition to this, you may refer to our complete guide on TestNG annotations.
- Grouping of testsTestNG helps you form ‘test groups’. And it can be configured separately in the configuration file. This means we can create test suites outside test scripts as per our needs.
For e.g., in a script, we can group test cases as shown below:
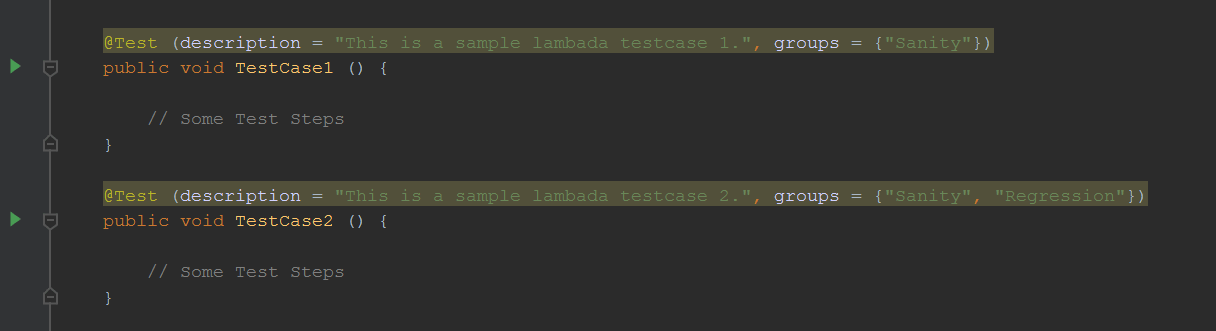
During run time, in TestNG.xml, we can specify the group that needs to run.
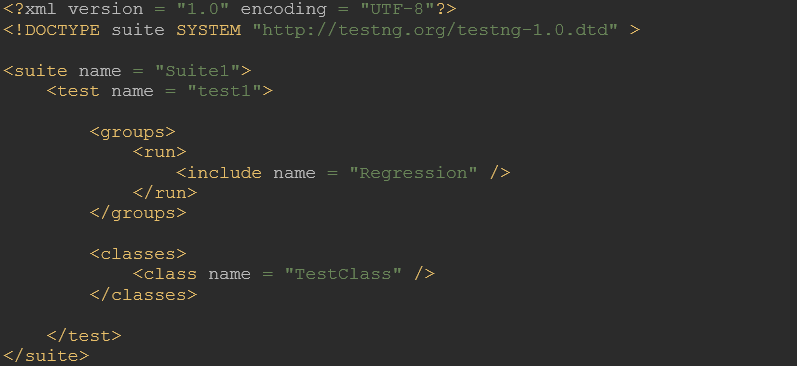
The above file will run only ‘TestCase2’ from the above class.
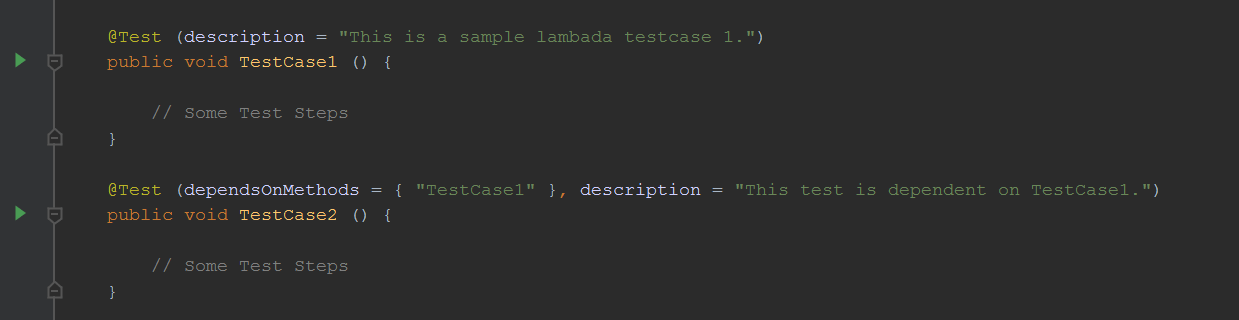
- Easy to configure dependent testsSometimes, we must ensure the execution of certain tests before other tests. We can ensure that by introducing dependency between such tests. TestNG provides an easy way to accomplish that.
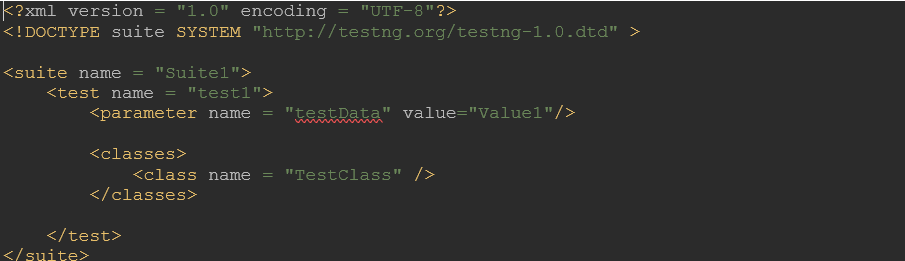
- Parameterized testsIt’s a common requirement where we want to run the same tests against different sets of test data. TestNG provides us with a cleaner way to do that.
We can define parameterized tests using TestNG, as shown below.
In test script:

In the test suite file, TestNG.xml
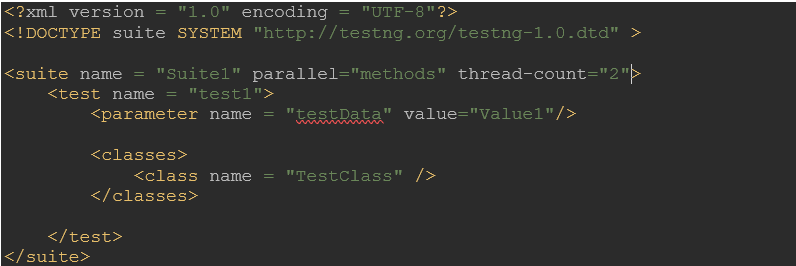
- Multi-threaded executionTest cases run in parallel for quick execution. We can have multithreading at method, test, and class levels. Accordingly, the TestNG.xml test suite file can be configured as below. Based on the level of multithreading, we can pass parallel values as ‘methods,’ ‘tests,’ and ‘classes.’ If we have dependent tests, we must be careful in introducing multithreading as it might not work as expected. Accordingly, the TestNG.xml test suite file can be configured as shown below.
- A retrial of failed test cases:Every time tests fail in a suite, TestNG creates a testng-failed.xml file in the output directory. This XML file contains the necessary information to rerun only those methods that failed. It allows users to quickly reproduce the failures without rerunning all the tests.
- Support for test reportsReporting is a key data point for any test execution. TestNG, by default, generates an HTML and an XML report. The report gets generated in the target folder of the project. TestNG also allows us to generate our reports. For that, we can make use of either org.testng.ITestListener or org.testng.IReporter interface.
| Annotations | Purpose |
|---|---|
| @BeforeSuite | Methods with this annotation will run before the execution of all the test methods in the suite. |
| @AfterSuite | Methods with this annotation will run after the execution of all the test methods in the suite. |
| @BeforeTest | Methods with this annotation will be executed before the execution of each test method from that class. |
| @AfterTest | Method with this annotation will be executed after the execution of each test method from that class |
| @BeforeClass | Methods with this annotation will be executed before the first method of the current class is invoked. |
| @AfterClass | Methods with this annotation will be invoked after the execution of all the test methods of the current class. |
| @BeforeMethod | Methods with this annotation will be executed before each test method runs. |
| @AfterMethod | Methods with this annotation will run after the execution of each test method. |
| @BeforeGroups | Methods with this annotation will run only once for a group before the execution of all test cases belonging to that group. |
Here is a sample snapshot of an HTML report in TestNG:
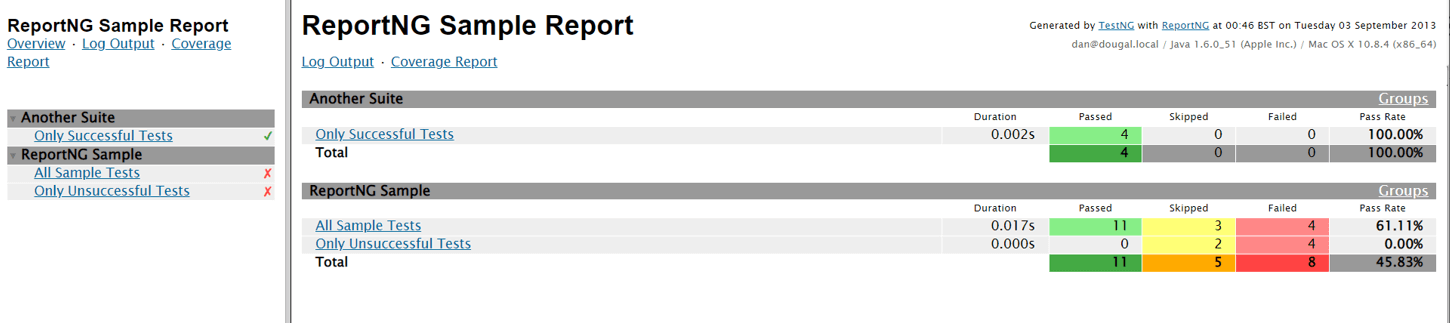
Usage of the TestNG Framework
To use TestNG, add the entry below to your pom file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>7.7.1</version>
</dependency>
With TestNG, the script looks like below. As you can see, the main function is no longer required. TestNG will execute the test method with @Test annotation.
package com.lambadatests;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.*;
public class lambadatest {
public WebDriver driver;
public static String USERDIR = "user.dir";
String email = "//input[@id='email']";
String password = "//input[@id='password']";
String submit = "//button[@type='submit']";
String verifyAfterLogin = "//a[@class='lambda__logo']";
@Test (description = "This is a sample lambada test.")
public void sampleTest() {
// Same code as earlier
}
}
We can also create a test suite file using TestNG, as per our needs.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd">
<suite verbose="2" name="Full Suite" parallel="classes" thread-count="1">
<listeners>
<listener class-name="com.lambadatests.Listener"/>
</listeners>
<test name="Lambada Test Suite">
<classes>
<class name="lambadatest">
</class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
When to Opt for the TestNG Framework?
As the test suite grows in size, management of tests could get tedious if not handled properly. Test execution is completely different from test development and has its own challenges. TestNG helps address most of it.
4. JGiven

JGiven is considered one of the best Java frameworks for testing. Sometimes, even though we have thousands of automated tests, it doesn’t give confidence in the quality of the test scripts written. Business Analysts who draft the requirement can’t read through test scripts to understand the actual test coverage. JGiven is the Java framework for automating Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) tests.
Unit testing, Integration, and end-to-end of any type of use cases can be implemented in BDD using JGiven. The BDD approach forces testers to be in the customer’s place. Since test scripts are written in Gherkin format, even a non-coder can read the test script and find out what it is doing. Thus, reducing the communication gap between expected business features and their actual implementation. At the time of writing, the JGiven version referred to is 1.2.5.
Why is JGiven One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
JGiven offers several key features that aim to enhance the tests. Below are some of the notable ones:
- Aligns product development with Business valuesBusiness Analysts (BAs) draft requirements or scenarios in plain English. Product development translates it into code & further moves ahead for testing. This process does create problems. During development, some key details highlighted by BAs can get lost in translation. JGiven helps us overcome that.
Scenarios are written in plain Java by BAs with a fluent Java framework API. Business Analysts thus dictate the structure of the final automated test case and not the automation engineer. Automation engineers just have to fill in the code in the structure. This helps in reducing the communication gap between the two ends.
For e.g., the Login scenario will be defined by BAs as shown below.
- Integration support for JUnit, TestNGJGiven Scenarios can be executed using either JUnit or TestNG. No extra test runner is required. JGiven works well with existing IDEs such as Eclipse, IntelliJ, etc.
- Test reportAfter the test scenario is executed, reports are generated by converting the scenario into plain English. Since Business Analysts originally draft the scenario, the test report becomes a living documentation.

For aforementioned scenario, the report in the plain test will look like this:
Test Lambdatest login
Given open URL: https://accounts.lambdatest.com/login
When login to LambadaTest
Then, verify login is successful
With the above report, JGiven can also generate an HTML report.
- Pass percentage gives more accurate quality perceptionBusiness Analysts define scenarios in plain Java, and they hand it over to the test team. Testers have to implement each method defined by Business Analysts. This ensures good test coverage and instills discipline in the test script. The execution report of such a test suite will also give the correct quality perception.
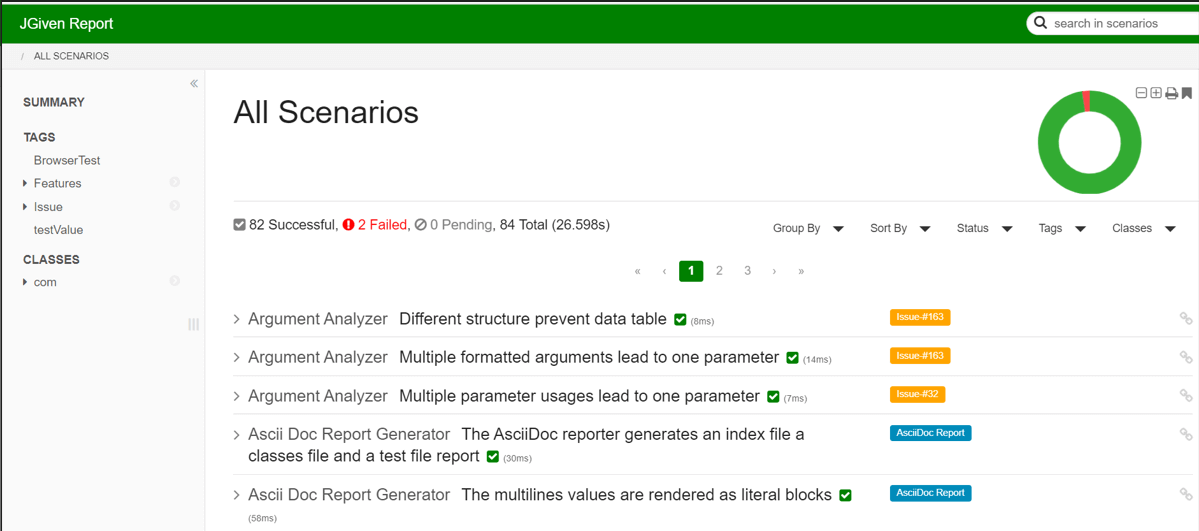
Usage of the JGiven Framework
For using JGiven with TestNG, add the below entry to the POM file.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.tngtech.jgiven</groupId>
<artifactId>jgiven-testng</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Initially, Business Analysts will give use case drafted as below:
import org.testng.annotations.*;
import com.tngtech.jgiven.junit.ScenarioTest;
public class LambadaTestJGivenTest
extends ScenarioTest<GivenLambadaTestState, WhenLambadaTestState, ThenLambadaTestState> {
@Test
public void test_lambadatest_login() {
given().open_url();
when().login_to_lambadaTest();
then().verify_login_is_successful();
}
}
You can see the division of the test above into three stages: Given, When and Then. This allows the separation logic of the test into individual classes. Each stage is a class-expanding stage. Testers must write stage classes for Given, When, and Then as below,
import com.tngtech.jgiven.Stage;
public class GivenLambadaTestState extends Stage<GivenLambadaTestState> {
public GivenLambadaTestState open_url() {
// Detailed code declaration
return self();
}
}
import com.tngtech.jgiven.Stage;
public class WhenLambadaTestState extends Stage<WhenLambadaTestState> {
public WhenLambadaTestState login_to_lambadaTest() {
// Detailed code declaration
return self();
}
}
import com.tngtech.jgiven.Stage;
public class ThenLambadaTestState extends Stage<ThenLambadaTestState> {
public ThenLambadaTestState verify_login_is_successful() {
// Detailed code declaration
return self();
}}
When to Opt for the JGiven Framework?
JGiven is a difficult Java framework to adopt, let’s face it! However, it solves an important problem of ensuring good test coverage. We can use it to automate a few but ‘must-work’ critical business use cases.
We have explored some of the Java frameworks in detail. Certainly, some more frameworks offer efficient approaches and enable developers to improve overall software quality. Let’s have a brief walkthrough.
5. Selenide

Selenide is one of the best Java testing frameworks created on top of Selenium WebDriver. It focuses on business logic rather than resolving browser, AJAX, and timeout issues. It is also used in creating UI test cases for a Java application that is reliable, specific, and descriptive. It majorly avoids ongoing minor problems and concentrates on business logic.
Why is Selenide One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
- Smart Wait is one of the main features in Selenide that helps keep your testing steady. It will wait up to 4 seconds for each piece to ensure it is visible and intractable.
- Finding elements in Selenide is as simple as typing $ or $$. Thus, you are no longer required to drive.findElement.
- Selenide offers a variety of practical techniques to simplify your daily automation.
- Selenide uses chainable commands to help make tests more understandable. It allows each command to be chained with others rather than having to type it out separately every time.
- Selenide offers more locator strategies. You can findElement bytext, byValue, and in many other ways.
- It also can automatically take screenshots when a test fails without requiring any settings.
6. Gauge
Gauge is an open-source Java framework for testing launched by ThoughtWorks. The Gauge framework is renowned as an outstanding testing framework for conducting cross browser testing. It requires less maintenance, less code, and more acceptance testing. It also develops understandable and maintainable tests in your preferred languages.
Why is Gauge One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
- Gauge has a strong plugin architecture and ecosystem, making it simple to add support for IDEs, drivers, data sources, and text execution events.
- Accelerate your tests and use your infrastructure best with Gauge’s out-of-the-box parallelization support.
- Gauge takes a screenshot to see exactly what went wrong when a test fails. Reports are accessible in XML, JSON, and HTML formats.
- Provides integrations with a cloud-based platform like TestMu AI for solving the cross browser testing objectives and enables you to construct scalable tests through parallel execution.
- Maintain extremely understandable specifications while testing massive data sets with ease. It supports data driven testing.
- It supports the command line, facilitating the best CI/CD tool integration.
7. Geb

Geb is also one of the best Java frameworks for testing. It combines the strength of WebDriver, the grace of jQuery content selection, the sturdiness of Page Object Modeling, and the expressiveness of Groovy language. Geb uses the WebDriver library to automate browsers. Geb is compatible with every browser that WebDriver is compatible with, and that number keeps expanding.
Why is Geb One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
- Tests are readable to the point where they almost resemble plain English with the help of Geb’s Page Objects and Groovy DSL.
- Saves time and cost by running the tests quickly.
- It is compatible with a variety of browsers, including HTMLUnit, Firefox, IE, and Chrome.
- The tests are executed in the real browser. It is similar to conducting testing in a real-world environment that the user would experience.
- It makes regression testing simple. To see if any existing functionality is broken following a fix or change to the application, run the Geb for automated test cases.
- It offers maximum test coverage within a single script.
8. Cucumber
Cucumber is an automation testing framework commonly used for Behavior Driven Development. The test cases are written in Gherkin language, which anybody can understand, irrespective of their technical proficiency.
Why is Cucumber One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
- User experience is the main focus of Cucumber.
- The way tests are written makes it simpler to reuse code in the tests.
- Easy and quick to set up and execute.
- Non-technical stakeholders are easily engaged.
- Lower maintenance costs and associated hazards result from the code quality enhancement.
- Lowers the need for writing the same code repeatedly by supporting step reuse.
9. Serenity BDD
Serenity is an open-source Java framework emphasizing acceptance testing and Behavior Driven Development (BDD). It is intended to make creating and running automated tests for web applications simpler and more efficient. This testing helps you to produce tests with a structured layout.
Why is Serenity BDD One of the Best Java Frameworks for Testing?
- Tests can be written easier for non-technical stakeholders to comprehend and understand.
- Serenity offers a selection of utilities and annotations that make it simple to automate tests. Serenity also supports REST API testing and database testing.
- Serenity produces test reports that include test reports, execution times, screenshots, error messages, and other relevant data. The reports are produced in HTML format, making them easy to examine.
- It can be used for automated web testing.
- Serenity offers data driven testing, which enables you to execute a single test scenario using various test data sets.
We have discussed the different Java frameworks in detail. However, once you have built your websites or web applications, ensuring they function correctly across different browsers, devices, and platforms is important.
AI-native test orchestration and execution platforms such as TestMu AI lets you perform Java automation testing to test your websites or web applications to ensure it delivers a consistent user experience across various browser, device, and operating system combinations. With TestMu AI, you can get the best experience to test with confidence on the scalable cloud Selenium grid of 3000+ browsers and operating systems.
Note: Ensure flawless digital experiences across 3000+ real environments. Try TestMu AI Now!
In conclusion, Java testing frameworks play a vital role in ensuring the quality and reliability of Java applications. By leveraging these Java frameworks, developers can automate testing processes easily. However, there are also well-known Java frameworks for web development that are readily accessible, each with a unique set of capabilities. Here are some popular Java frameworks for web development:
What Are the 12 Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
Best Java web frameworks include Spring, Hibernate, Play, Apache Struts, Dropwizard, GWT, JSF, Vaadin, Blade, Grails, Jakarta Faces, and MyBatis.
Java-based web development framework provides a basis for building a reliable and scalable online application using the Java programming language. They provide an organized approach with libraries and tools to streamline the development process, improve productivity, and foster code reuse. There are several Java frameworks available for web development. Here are some popular ones.
1. Spring
Spring is a robust and widely used Java framework that supports developing enterprise-level Java applications. It provides various modules and libraries for different purposes, such as web development, data access, security, and messaging. These modules integrate seamlessly, allowing developers to choose the components and easily extend the functionality of their applications. Netflix, LinkedIn, Yahoo, and Amazon are some top companies using the Spring framework.
Why is Spring One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Spring is a lightweight framework. The complexity of application code can be reduced with a lightweight framework.
- Spring provides powerful transaction management capabilities. Developers can define transaction boundaries using annotations or XML configurations.
- It streamlines the creation of web applications by providing a structured architecture for managing HTTP requests and responses using Spring MVC.
- Allows developers to modularize cross-cutting concerns, such as logging, security, and transaction management, using Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP).
- Spring uses Dependency Injection (DI) that facilitates loose coupling between components.
2. Hibernate
Hibernate is a well-known Java framework for Object-Relational Mapping (ORM). It provides a suitable way to interact with relational databases using Java objects. Hibernate untangles the process of retrieving data from a database by eliminating the need for writing complex SQL queries. It also offers various features that make database operations more efficient and developer-friendly.
Why is Hibernate One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Hibernate supports various inheritance strategies for mapping object hierarchies to database tables.
- It supports mapping between entities, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships.
- It also supports levels of caching, such as first-level cache, second-level cache, and query caching. Hibernate allows developers to map Java objects to database tables.
- It provides built-in support for performing Create, Retrieve, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations.
3. Play
Play is a well-known Java framework that follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern. It provides a robust set of features and tools to simplify the development of web applications. Play is useful for creating Scala and Java applications and web applications. It provides various features and capabilities, making it the best choice for building modern and scalable web applications.
Why is Play One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Play provides a flexible and expressive routing mechanism that helps developers to define URL patterns.
- It allows developers to separate the presentation logic from the application code with a template engine.
- Play follows a reactive programming model, which enables it to handle high loads and concurrent requests efficiently.
- It includes security features to help protect web applications.
- Play supports data access approaches, including object-relational mapping (ORM) frameworks like Hibernate.
4. Apache Struts
Apache Struts is an open-source Java framework for enterprise applications. It provides a set of reusable components and tools for developers to build scalable, maintainable, and secure web applications. It also follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern to separate the application’s business logic, user interface, and data manipulation.
Why is Apache Struts One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Developers can depend on naming conventions to reduce the configuration required.
- It supports declarative validation through XML configuration or annotation-based validation in Java code.
- Struts provides custom tag libraries that ease the generation of HTML content in JSP views.
- It uses a configuration file, struts-config.xml, to construe the application’s behavior.
5. Dropwizard
Dropwizard, commonly used Java frameworks designed to simplify the development of lightweight and high-performance RESTful web services. It combines several well-known libraries to provide a cohesive development experience and promote best practices for building productive applications. Dropwizard is often chosen for its simplicity, speed, and opinionated approach to development.
Why is Dropwizard One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- It allows developers to run their applications without needing external web servers using Jetty.
- It handles RESTful API development.
- Dropwizard supports monitoring and collecting application metrics using the Metrics library.
- Dropwizard provides a convenient configuration framework based on YAML files.
- It has support for a variety of independent and open-source libraries.
6. Google Web Toolkit (GWT)

Google Web Toolkit (GWT) is an open-source Java framework by Google that helps developers to build web applications using Java programming language. GWT supports tools, libraries, and APIs to streamline the development process and allows developers to write client-side web applications that can be compiled into optimized JavaScript code.
Why is GWT One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- It pulls the developers’ Java code and converts it into optimized JavaScript code.
- GWT integrates well with other web technologies and frameworks.
- It has built-in support for internationalization and localization.
- It eases the process of sending requests from the client side to the server-side and receiving responses.
- The GWT compiler produces optimized JavaScript code that allows the application to run consistently across different browsers without developers having to write code.
7. Java Server Faces (JSF)
JSF stands for JavaServer Faces. It is a Java framework that untangles the development of user interfaces for Java EE (Enterprise Edition) applications. It has strong API and tag libraries that provide a well-defined programming model. JSF offers many built-in features for handling common web application tasks.
Why is JSF One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- It offers a wide range of tools for designing attractive user interfaces.
- It is an important component of Java EE.
- Using Java Server Faces, existing backend Java code may be expanded with a web interface without requiring a new framework to be added to the original program.
- JSF has a well-defined lifecycle that governs the processing of requests and the providing of responses.
8. Vaadin

Vaadin is also one of the best open-source Java frameworks. It provides a server-side architecture where the UI is entirely developed in Java. It allows the development of UI code on the server and automatically renders on the client side.
The Vaadin Java framework consists of two main parts: the server-side API and the client-side engine. The server-side API includes pre-built UI components, functionalities, and security features.
The client-side engine renders the UI components on the client side, communicating with the server via AJAX requests and updating the UI based on server-side changes.
Why is Vaadin One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Applications are deployed to any Java Servlet container or application server.
- It supports a flexible layout system for arranging UI components on the screen.
- Developers can use pre-built layouts like VerticalLayout and HorizontalLayout, or create custom layouts to achieve the desired structure.
- It includes basic input and advanced components for complex use cases.
- Vaadin includes powerful data binding capabilities, allowing developers to bind UI components directly to data models.
9. Blade

Blade is a lightweight Java framework used to facilitate web application development. It is an open-source framework that was first released in 2014. Its simplicity, ease of use, and fast performance have gained popularity.
One of the key features of Blade is its minimalist approach to building web applications. It is easy to learn and use, with a streamlined API that allows developers to build web applications quickly.
Why is Blade One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- It is fast and efficient, ideal for building high-performance web applications.
- Blade provides support for dependency injection, which makes it easy to manage complex object graphs and dependencies.
- Blade uses a simple configuration file format, making it easy to configure and customize your application.
- It makes it easy to build APIs and other RESTful services.
- Blade has a robust plugin system that allows developers to easily extend the framework’s functionality.
10. Grails
Grails is a dynamic Java framework that operates on the Java platform and exhibits excellent compatibility with the Java syntax. It combines the power of the Groovy programming language with established Java frameworks, such as Spring and Hibernate, to provide a productive and efficient development experience.
Why is Grails One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Seamless integration with Groovy and Java libraries for leveraging existing code and resources.
- Extensive plugin ecosystem to easily extend and enhance application functionality.
- Testing support with integrated frameworks for unit testing, integration testing, and functional testing.
- MVC architecture for organizing application code and separating concerns.
- Support for RESTful APIs and web services.
11. Jakarta Faces (JF)
Jakarta Faces is an open-source Java framework for developing user interfaces in web applications. It provides a set of reusable UI components that can be easily integrated into web applications. It allows developers to create rich and dynamic user interfaces with minimal effort. The Jakarta Faces framework is based on the MVC architectural pattern. It helps to separate application logic from the presentation layer.
Why is JF One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- It is also easy to develop and maintain complex web applications.
- Reduced code complexity and improved code reusability.
- Developers can create complex UI elements by combining simple building blocks or components.
- Easy to build accessible web applications.
12. MyBatis
MyBatis is a popular Java framework used for data persistence that simplifies the development of database-driven applications. It provides a simple way to map SQL queries to Java objects, reducing the amount of boilerplate code required for database access. It allows developers to write SQL queries directly in the code or define them in external XML files.
Why is MyBatis One of the Best Java Frameworks for Web Development?
- Flexible and configurable approach to working with databases.
- Easily maintained and reused across different parts of an application.
- Supports advanced features such as caching, transaction management, and batch processing features.
- Reliable choice for high-performance web applications.
What Are the 5 Best Java GUI Frameworks?
Top Java GUI frameworks include Swing, JavaFX, Apache Pivot, SWT (Standard Widget Toolkit), and Qt Jambi for building desktop applications.
In the dynamic world of Java frameworks for GUI development, various frameworks offer unique features and tools to create user-friendly and visually appealing interfaces. These frameworks cater to a range of needs, from building traditional desktop applications to sophisticated modern interfaces. Here, we explore five such frameworks that stand out in the Java frameworks ecosystem.
1. Swing
Swing, a cornerstone in Java’s GUI framework arsenal, offers a robust set of components and tools for building traditional desktop applications. It stands out with its ability to create highly interactive and customizable user interfaces. Swing’s architecture, built atop the Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT), facilitates the creation of complex windows and dialogues, offering developers a wide array of components like buttons, toolbars, and menus to enhance the user experience.
Why is Swing One of the Best Java GUI Frameworks
- Swing offers a rich set of widgets and components, allowing for intricate and comprehensive GUI development.
- It supports a look-and-feel feature that can mimic various platforms, enhancing user experience.
- Swing’s MVC architecture ensures a clear separation of design and logic, streamlining application development.
2. JavaFX
JavaFX represents the next step in the evolution of Java GUI frameworks, offering a modern suite of features for creating rich client applications. It is particularly notable for its support of advanced graphics, animation, and media, catering to applications that require a high level of visual appeal and interactivity. JavaFX’s scene graph-based framework and support for 3D graphics set it apart as a choice for building sophisticated user interfaces.
Why is JavaFX One of the Best Java GUI Frameworks
- JavaFX provides a modern and feature-rich platform for creating visually appealing and responsive UIs.
- It supports CSS for styling and FXML for defining user interfaces, facilitating easier design and layout management.
- JavaFX’s property binding mechanism simplifies the development of dynamic, event-driven applications.
3. Apache Pivot
Apache Pivot merges the capabilities of a web-centric GUI toolkit with those of a full-fledged application framework, making it uniquely suited for building interactive web applications using Java. This framework provides a rich set of components, enabling developers to create applications that are both visually appealing and highly functional. Pivot’s emphasis on easy data binding and event handling makes it an excellent choice for developers looking to bridge the gap between web and desktop development paradigms.
Why is Apache Pivot One of the Best Java GUI Frameworks
- It offers a wide array of widgets and data binding capabilities, useful for rich internet application development.
- Apache Pivot provides a more web-like development model for desktop applications, bridging the gap between web and desktop interfaces.
4. SWT (Standard Widget Toolkit)
Developed by the Eclipse Foundation, the SWT is a powerful framework designed for creating high-performance, native GUI applications in Java. Its direct use of the native widgets provided by the operating system ensures that applications built with SWT integrate seamlessly into their respective environments, offering a native look and feel. This focus on performance and consistency makes SWT a popular choice for developers building applications that require a high degree of responsiveness and integration with the underlying operating system.
Why is SWT One of the Best Java GUI Frameworks
- SWT’s use of native widgets ensures that applications have a look and feel that users are accustomed to on their respective platforms.
- It is known for its performance and responsiveness, crucial for resource-intensive applications.
5. Qt Jambi
Qt Jambi brings the comprehensive features of the Qt application framework to the Java world, allowing developers to create cross-platform GUI applications with native performance and capabilities. This framework is known for its extensive range of tools and features, suitable for building everything from simple GUI applications to complex, multi-platform software systems. With its emphasis on cross-platform compatibility, Qt Jambi is a go-to framework for developers aiming to deploy applications across various operating systems without compromising on performance or user experience.
Why is Qt Jambi One of the Best Java GUI Frameworks
- Qt Jambi facilitates the development of applications that can run seamlessly across different operating systems while maintaining native performance.
- It provides a wide range of tools and features, making it suitable for both simple and complex application development.
What Are the 6 New Java Frameworks for 2026?
New Java frameworks for 2026 include Micronaut, Quarkus, Helidon, JHipster, Vert.x, and QuantumJava for modern cloud-native and microservices development.
Java continues to evolve, and 2026 has brought forward exciting new Java frameworks that cater to the growing demands of modern application development. These frameworks not only enhance Java's robustness but also introduce innovative features to keep pace with emerging technologies and environmental concerns.
1. Micronaut
Micronaut is a modern, JVM-based, full-stack Java framework for building modular, easily testable microservice and serverless applications. Designed to be lightweight and fast, Micronaut aims to avoid the downsides of framework reflection and proxying, resulting in faster startup and runtime performance. It’s particularly suitable for building microservices where efficient resource usage and quick startup times are essential. Micronaut also offers a cloud-native experience with native integration with popular cloud platforms and tools1. Micronaut was first released in October 2018 and the latest version is 3.0.1, released in August 20212.
Why is Micronaut One of the Best New Java Frameworks for 2026
- Micronaut’s minimal use of reflection and proxies reduces memory consumption and increases startup speed, making it ideal for cloud-native applications.
- It supports Dependency Injection and Aspect-Oriented Programming, simplifying application development and maintenance.
- The framework’s built-in tools for building HTTP servers and clients, as well as support for various cloud configurations, make it versatile for microservices and serverless applications.
2. Quarkus
Quarkus is a commonly used Java framework that optimizes Java for containerized environments, such as Kubernetes and GraalVM. Quarkus offers a fast boot time, low memory footprint, and live reload capabilities. Quarkus also provides a unified development model with over 200 extensions that integrate with popular Java libraries and standards3. Quarkus was first released in March 2019 and the latest version is 2.2.3, released in September 20214.
Why is Quarkus One of the Best New Java Frameworks for 2023
- It significantly reduces the footprint of Java applications, making it highly effective for microservices architecture in cloud environments.
- Quarkus offers live coding features, enabling developers to see changes in real-time without the need for lengthy rebuilds and restarts.
- With its integration with GraalVM, Quarkus allows ahead-of-time compilation of Java code, drastically reducing startup time and memory usage, a critical feature for serverless computing.
3. Helidon
Helidon is a set of Java libraries for writing microservices that run on a fast web core powered by Netty. Developed by Oracle, it comes in two versions: Helidon SE and Helidon MP. Helidon SE offers a reactive, non-blocking programming model for high-performance applications, while Helidon MP aligns with MicroProfile standards, offering a more familiar model for Java EE/Jakarta EE developers. Helidon was first released in September 2018 and the latest version is 2.3.1, released in August 2021.
Why is Helidon One of the Best New Java Frameworks for 2026
- It provides a lightweight, fast foundation for microservices, suitable for modern cloud-native applications.
- Helidon’s reactive web server offers efficient resource utilization, crucial for handling high-load applications.
- The framework is designed for simplicity and quick development, making it user-friendly for Java developers diving into microservices.
4. JHipster
JHipster, short for “Java Hipster,” is an application generator used to develop and deploy modern web applications and microservice architectures. JHipster combines a range of tools and technologies like Spring Boot, Angular, React, and Vue.js, offering a comprehensive platform for full-stack development. JHipster also provides tools for testing, documentation, continuous integration, and deployment. JHipster was first released in October 2013 and the latest version is 7.2.0, released in August 2021.
Why is JHipster One of the Best New Java Frameworks for 2026
- It accelerates the development process by generating boilerplate code, allowing developers to focus on business logic.
- JHipster supports both monolithic and microservices architectures, making it versatile for different project requirements.
- The framework integrates front-end technologies seamlessly with backend Java development, ensuring a smooth full-stack development experience.
5. Vert.x
Vert.x is a prominent Java framework that enables the creation of reactive and distributed applications on the Java Virtual Machine. Vert.x supports a variety of languages, such as Java, Kotlin, Groovy, and Scala. Vert.x also offers a rich set of features, such as event bus, clustering, web server, web client, and reactive streams. Vert.x was first released in December 2011 and the latest version is 4.1.5, released in September 2021.
Why is Vert.x One of the Best New Java Frameworks for 2026
- Vert.x is known for its lightweight, high performance, and scalability, making it ideal for handling a large number of concurrent connections, typical in modern web applications.
- It offers a simple concurrency model, avoiding the complexities of traditional multi-threaded development.
- The framework’s event-driven, non-blocking nature allows for building highly responsive and resilient applications.
6. QuantumJava
QuantumJava introduces a pioneering approach to integrating quantum computing capabilities with traditional Java development. This framework provides an intuitive platform for Java developers to explore and harness the power of quantum algorithms and simulations, a domain that was once reserved for specialized researchers. QuantumJava is ideal for applications requiring complex computations and problem-solving techniques that are beyond the scope of classical computing.
Why is QuantumJava One of the Best New Java Frameworks for 2026
- It opens up quantum computing to a wider range of developers, fostering innovation in fields like cryptography, optimization, and simulation.
- QuantumJava maintains Java’s simplicity while introducing quantum computing concepts, making it easier for developers to transition into this advanced computing paradigm.
- The framework facilitates the development of hybrid applications, blending quantum and classical computing methods for enhanced performance and capabilities.
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on TestMu AI
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
Conclusion
Java is a highly popular language in the realms of testing and development. However, it is vital to conduct a thorough evaluation of various factors before selecting the appropriate framework.
While a test framework can bring significant advantages, it is crucial to consider the team’s technical expertise to ensure successful implementation. Additionally, factors such as time and cost should be meticulously assessed for each framework. The chosen framework should play a role in establishing and maintaining software product quality. By leveraging these Java frameworks, developers can streamline the automation of testing processes.
It is important to acknowledge the presence of well-established Java frameworks that cater specifically to web development. These Java frameworks have gained popularity and widespread usage due to their robust features, extensive functionalities, and ability to address the diverse needs of web development projects.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



