
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Mobile Testing Pyramid For Agile Teams
The Mobile testing pyramid provides a basis for organizing website tests for optimum speed and accuracy. This quick guide to Mobile testing pyramid discusses how it can help agile teams in their Mobile app testing approach.
Harish Rajora
January 11, 2026
This article is a part of our Content Hub. For more in-depth resources, check out our content hub on Mobile App Testing Tutorial.
A great website is the backbone of a successful business. This means top-quality mobile websites and apps with impeccable user experiences. While ensuring that your website works on all devices and platforms might seem easy, it is not. Users do not tolerate sites with bugs or errors simply because they have alternatives.
According to Statista, more than 50% of worldwide web traffic comes from mobile devices. The number of people who access websites via a mobile device is only growing, so website owners must do everything they can to ensure that their websites run flawlessly on mobile devices. However, the mobile landscape is constantly evolving, creating challenges for web developers. With so many platforms and devices available today, it can be challenging to know which platforms to focus on first.
This is where a testing pyramid comes into the picture. Just like the test automation pyramid, the Mobile Testing Pyramid is an organized approach for carrying out automated testing on mobile devices. It was designed specifically for today’s applications, with a growing number of mobile platforms to support.
This post on the Mobile Testing Pyramid discusses how it can help agile teams in their Mobile app testing approach.
What is the Mobile Testing Pyramid?
The Mobile Testing Pyramid is a strategy to test apps on Mobile devices in an efficient way. It was first introduced by Kwo Ding in 2017.
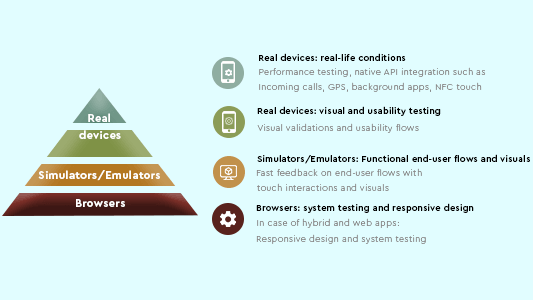
The Mobile Testing Pyramid is divided into three segments – real devices, simulators/emulators and browsers. Their order in the pyramid is decided by the number of tests they should cover under them. The broader a section is, the more tests it should cover. As we see, Ding prefers larger tests to be executed when dealing with browsers (desktop browsers). The reasons for it are explained in their specific segments.
But that’s just what we see and not what we would be using in our testing career. So to understand these sections deeper, we need to understand the inspiration behind the Mobile Testing Pyramid.
Also, Read– Mobile App Testing Basics
Inspiration behind the Mobile Testing Pyramid
Ding’s inspiration behind designing the Mobile Testing Pyramid is the challenges a tester faces with Mobile app testing. Currently, there are 3.5 billion smartphones active globally, and many of them differ from each other in a number of ways.
Initially, we don’t need to worry about that. We just take the list of most used smartphones and probably test ten out of it and release our application. The issue here is that it is not as easy as web testing. Mobile app testing is not just about UI and responsiveness but covers other broad parameters like network conditions, hardware, operating system and much more. Check out our blog on Mobile app testing challenges and solutions.
All of these factors make Mobile app testing more difficult. Exploring various devices without direction and structure can result in adverse user reactions. Furthermore, even if you only started with ten devices at first, you will gradually receive feedback from users about app glitches when used on their devices. So you’d have to increase the number of devices gradually, and your traditional method would fail in such cases. Agile can also burden you in subsequent version releases over time.
A mobile app testing strategy and a mobile app testing checklist are needed to test mobile applications effectively. Hence, what comes to mind is how we have structured our test automation. A slight modification can also help us in Mobile app testing, and hence Kwo Ding modifies the original pyramid to the Mobile Testing Pyramid.
Read More – How To Test Mobile Applications Manually
Focus Areas of the Mobile Testing Pyramid
The following section explains the focus areas of the Mobile Testing Pyramid. The section is arranged in the bottom-to-top order for the testing pyramid.
Desktop browsers
The bottom-most section of the testing pyramid states “browsers,” corresponding to testing the mobile app on the desktop browsers. Since it is the broadest section, it has the maximum number of tests.
Mobile testing on desktop browsers is not a hard job. Just run the web app on the browsers, rescale them for responsive design test and UI glitches, and you are good to go. It is the best choice to start with when dealing with hybrid applications or pure web apps.
Read – Difference Between Web vs Hybrid vs Native Apps
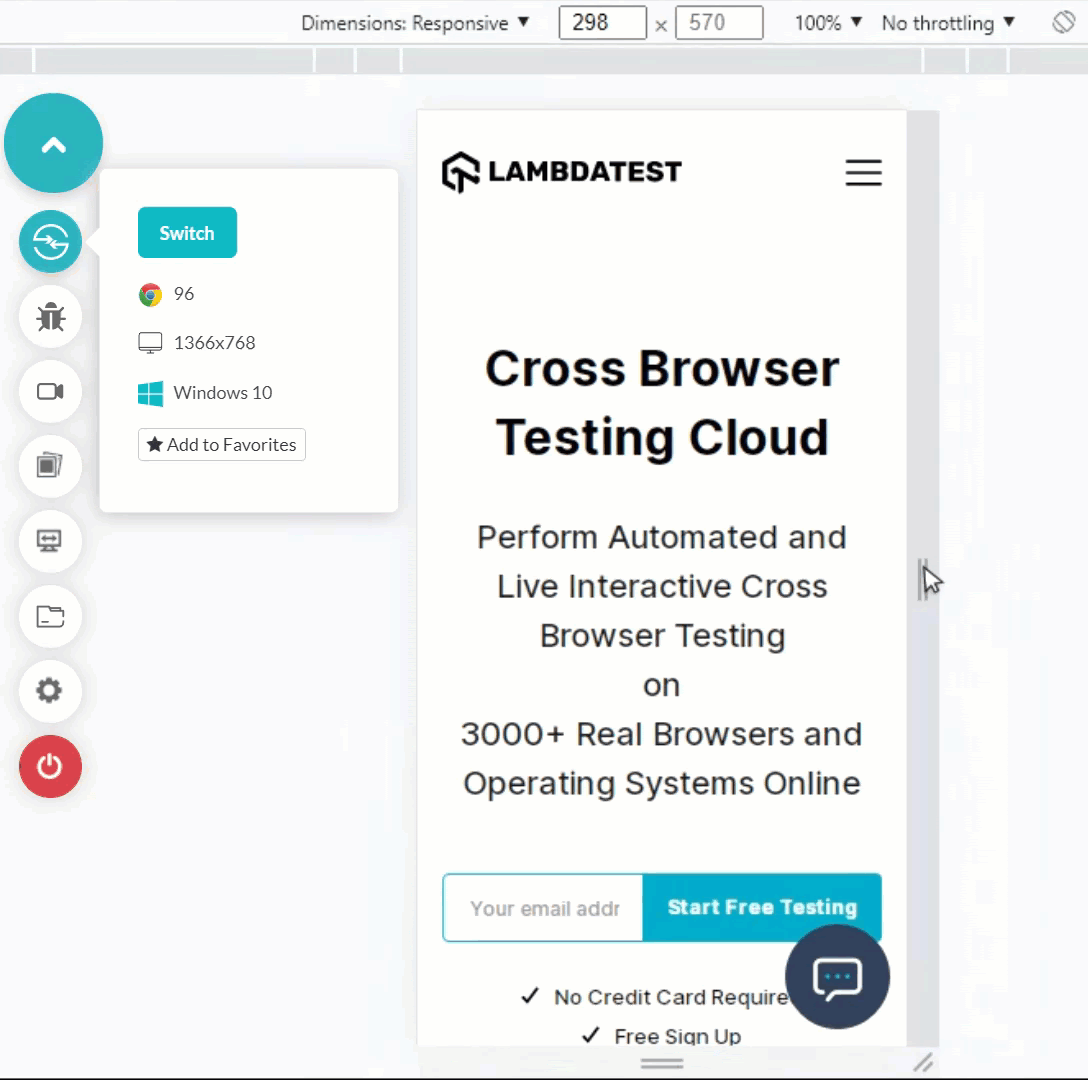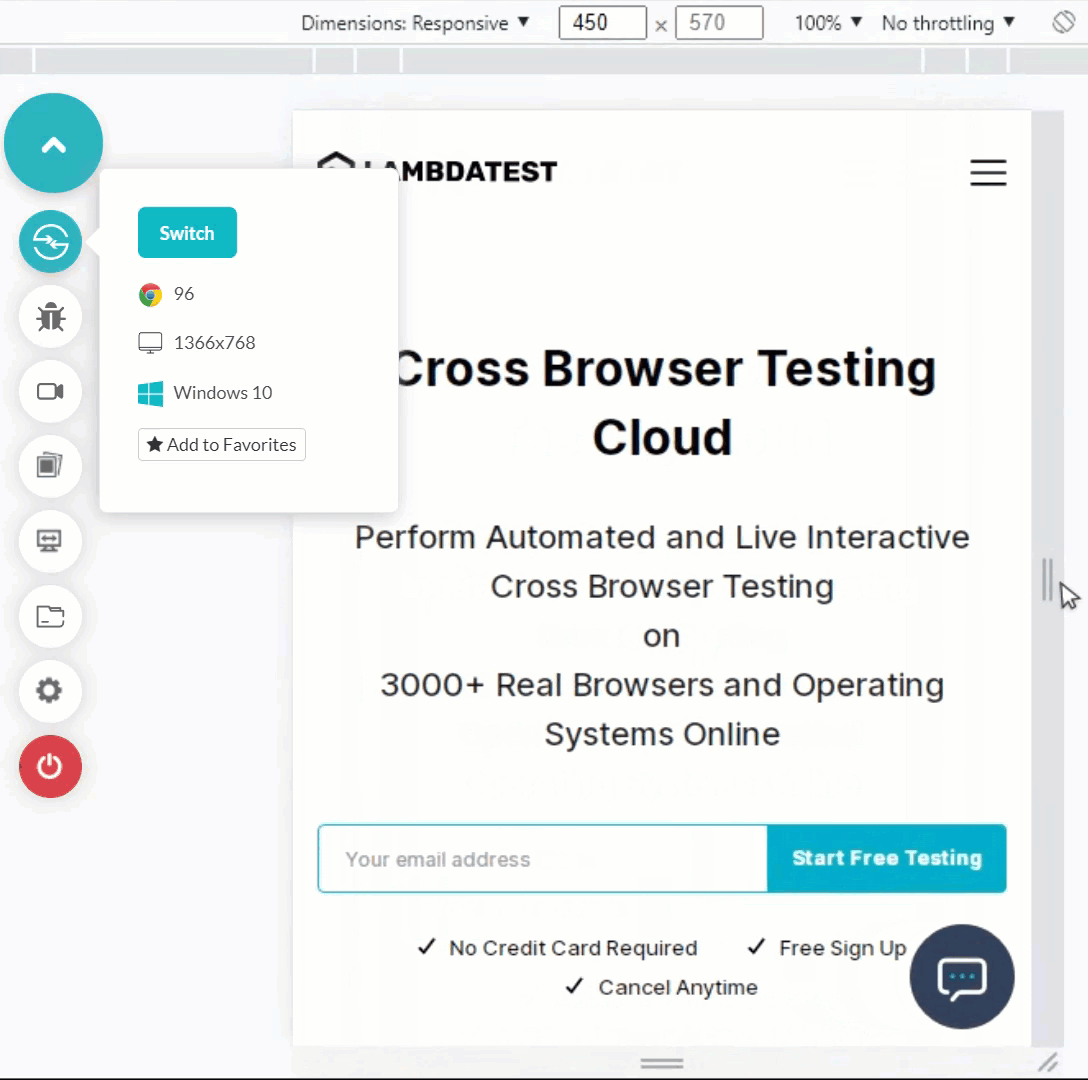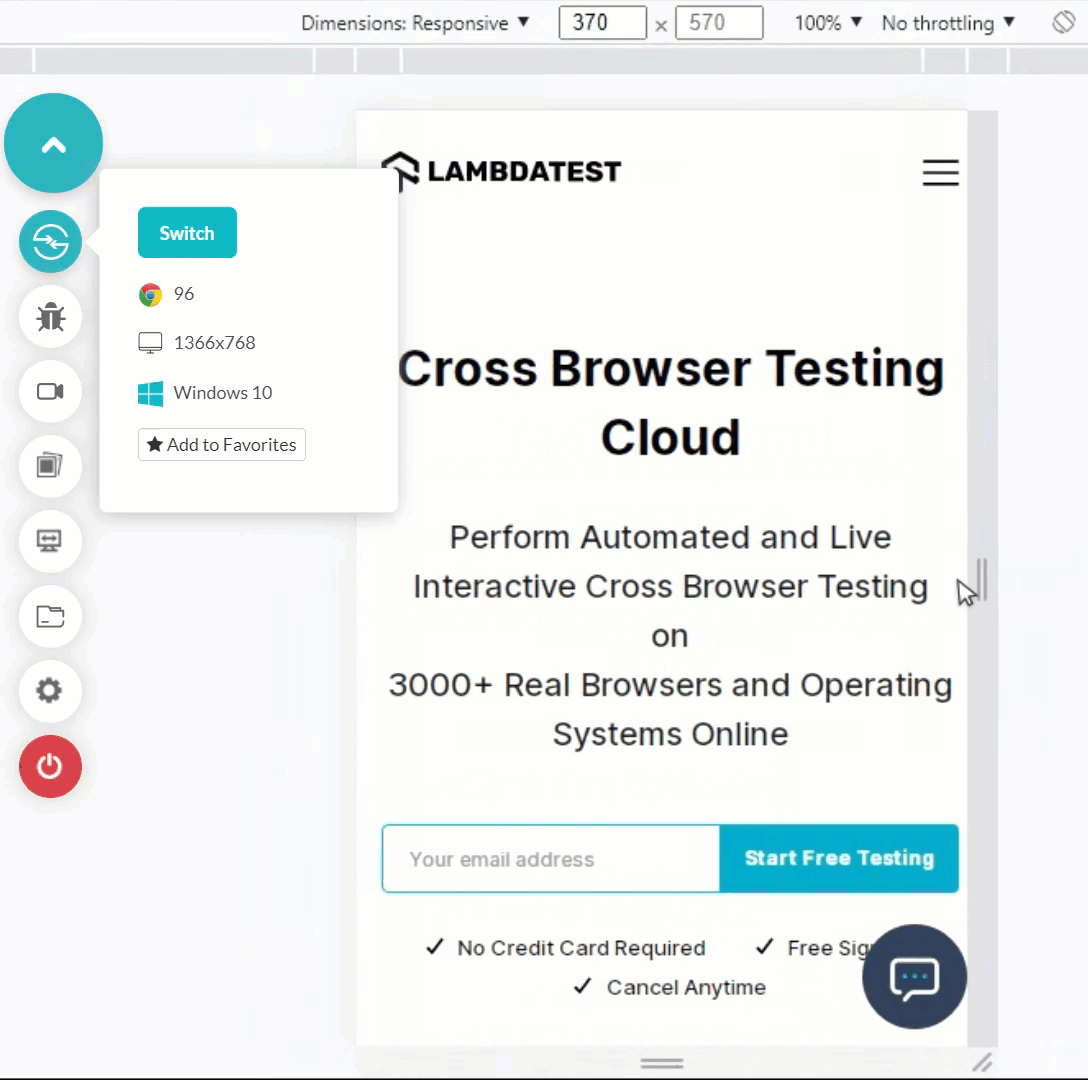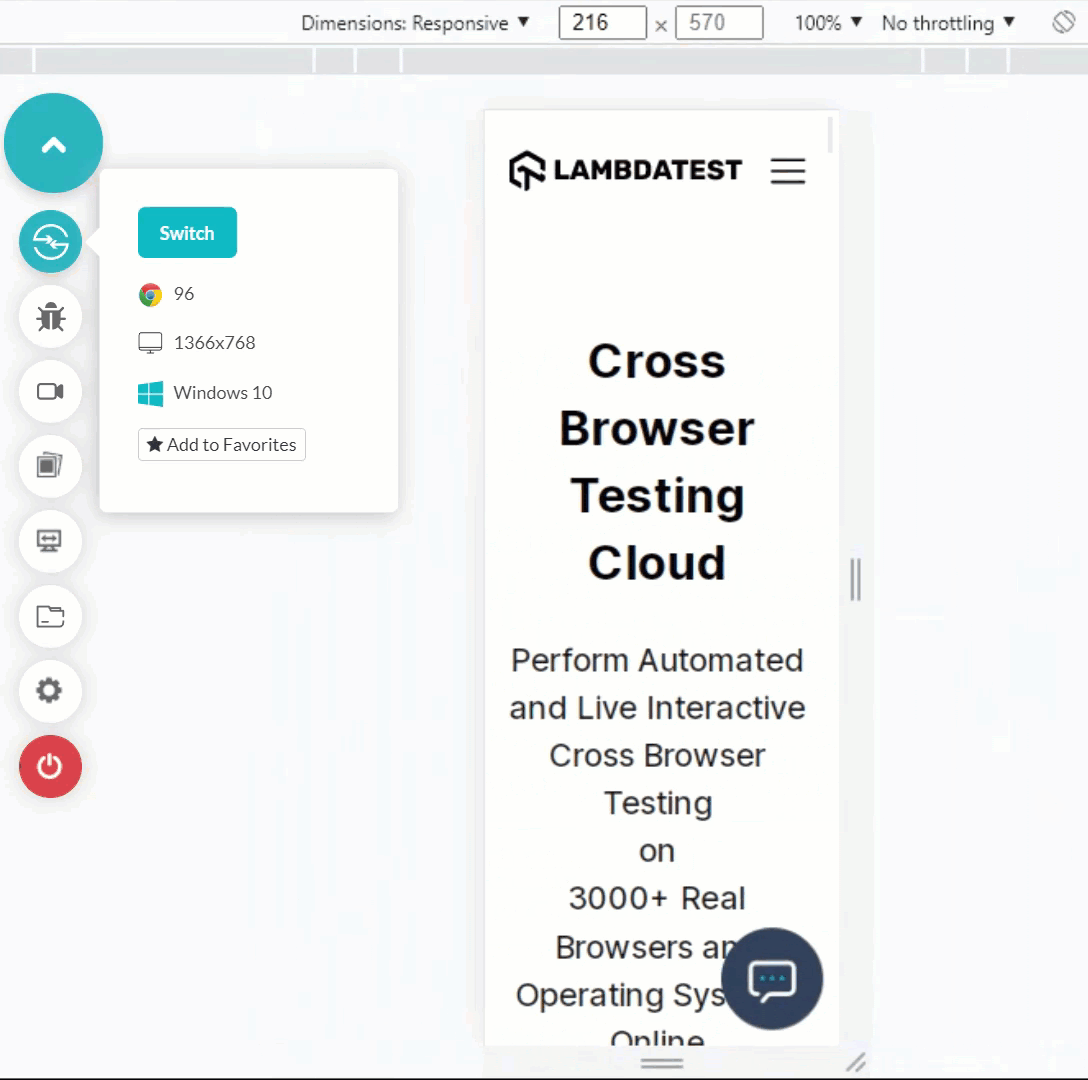
Shown below is an example of resizing a web app on a desktop browser.
Advantages
- Extremely fast: Using desktop browsers for testing is a speedy job. Using the best automation testing frameworks like Selenium, you can run thousands of parallel test cases and use the headless approach. Refer to our page to know what is Selenium?
- Scalable: As mentioned in the previous point, you can use Parallel testing to cut down test execution time by leveraging a like TestMu AI. New browsers are also easy to acquire as they are available readily.
- Easy for cross-platform: Desktop browsers are easy to work with because you don’t need to install a completely new OS as you would do on a native app. You can use cloud-based cross browser testing platforms to launch browsers from a single platform.
- Feasible and Easily available: Desktop browsers are readily available and are free to use. So you need very little investment to start with.
Disadvantages
- Whatever you do, you are still on a desktop – No matter how rigorously you test on mobile on the desktop browsers, the fact that you are using desktop resources won’t change. This affects how your results appear on the reports and the app’s performance.
- No “mobile-like” behavior – When you use a desktop browser to test an application. There are no network variations, including blockages, no incoming calls in between, no sudden freezing of devices due to lack of resources etc. These things are necessary when performing app testing on mobile as these are normal mobile behavior. Any crash due to these can affect your viewership.
- “Just not a device” – A self-explanatory sentence as said by Kwo Ding – “this is just not a device”.
Also, Read – Best Mobile App Testing Frameworks For Android and iOS Apps
The above-discussed analyses are true. Still, since browsers secure a place in the Mobile Testing Pyramid, they are unique and need to be considered in the testing.
The following focus areas are important while testing mobile apps on desktop browsers.
- Functional System testingDesktop browser tests efficiently perform functional system testing, which could be considered a primary testing method.
- Responsive designOne of the most important outputs of desktop browser tests for mobile apps is to check its responsive web design. Responsiveness is an important characteristic and should be applied in every application you build using a browser.
Also Read: Why Responsive Web Design Is Important?
The following image reflects a responsive web app rendered across two different sized screen devices on LT Browser.
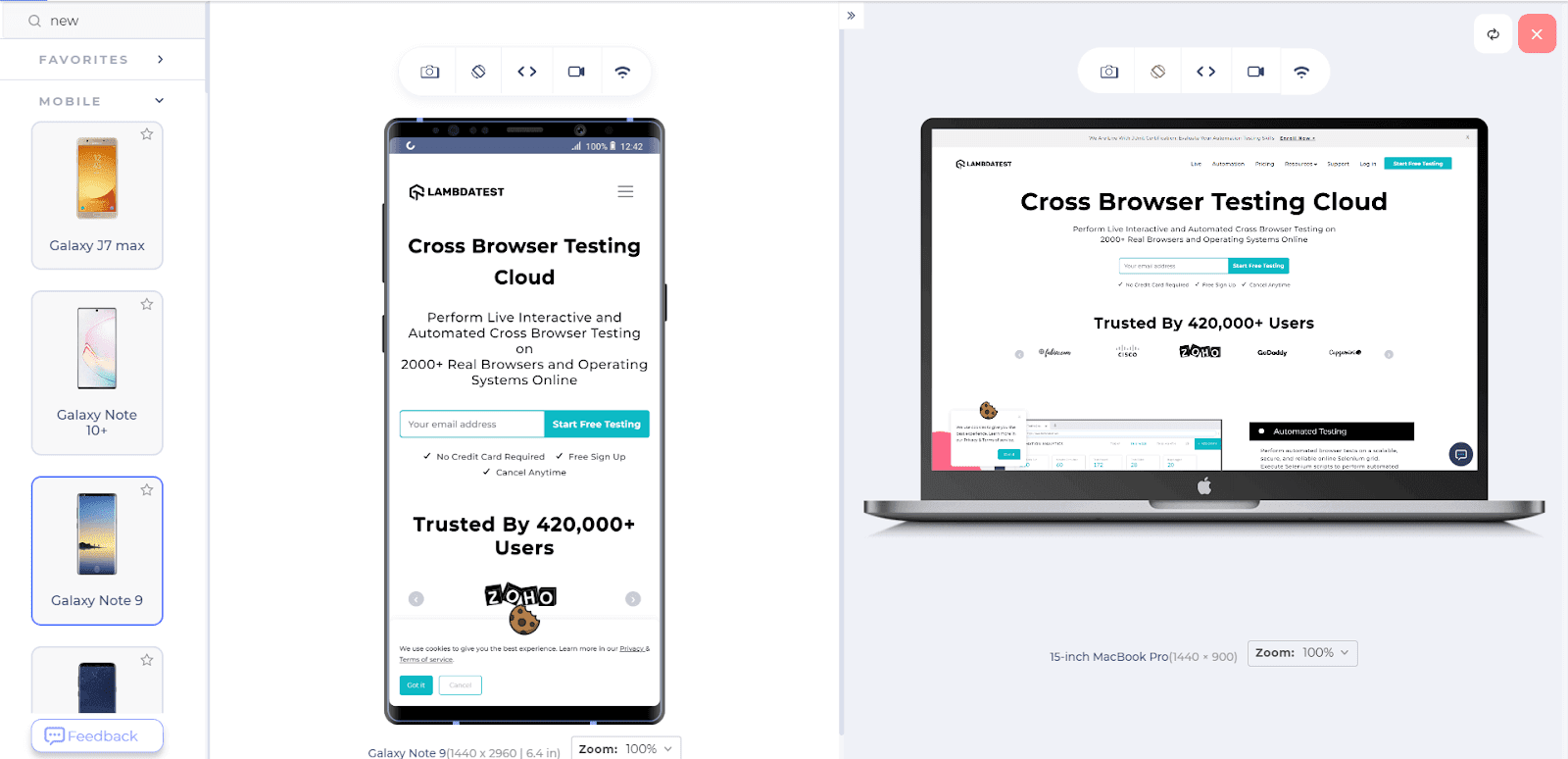

Here is the quick rundown of LT Browser.
- Cross Browser TestingCross browser testing ensures the cross browser compatibility property of your mobile app across numerous browsers and operating systems.
- Overall Visual layoutPerforming Visual regression testing on desktop browsers can also help verify the overall visual layout of the mobile app. Kwo Ding ensures to focus on the word “overall” here. This is because desktop browsers cannot be trusted to deliver the accurate UI layout that you would get on a mobile screen. You can get a big picture but not the specifics or minute nuances of the UI elements.
Read More – All You Need To Know About UI Testing
Emulators and Simulators
After reading the desktop browser section, anyone can be convinced that they are probably an excellent way to go through and launch our app without caring too much. If you think of the same question, let’s test an Android app on a mobile app emulator.
Output
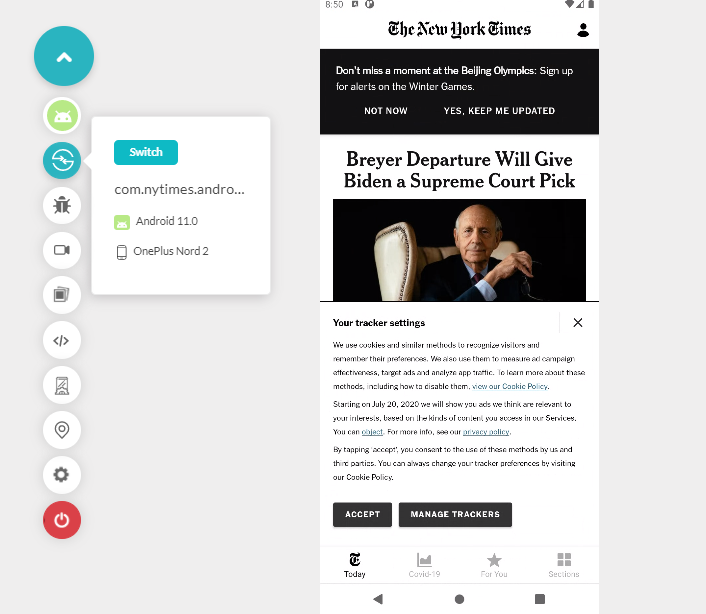
Shown below is the mobile web tested application. It shows glitches in navigation when rendered on a mobile emulator. Such occurrences can happen with you, too, if you rely on desktop browser testing entirely for the mobile app.
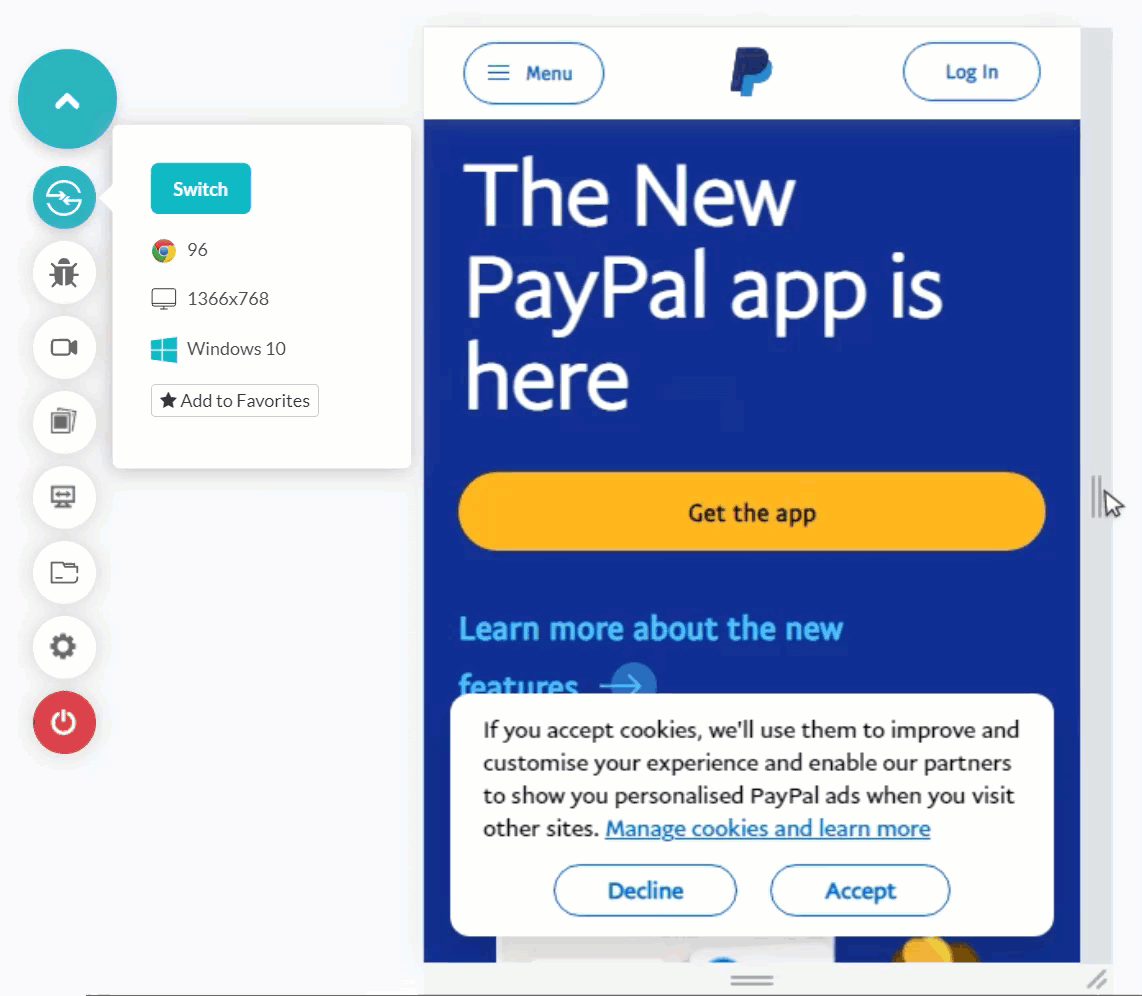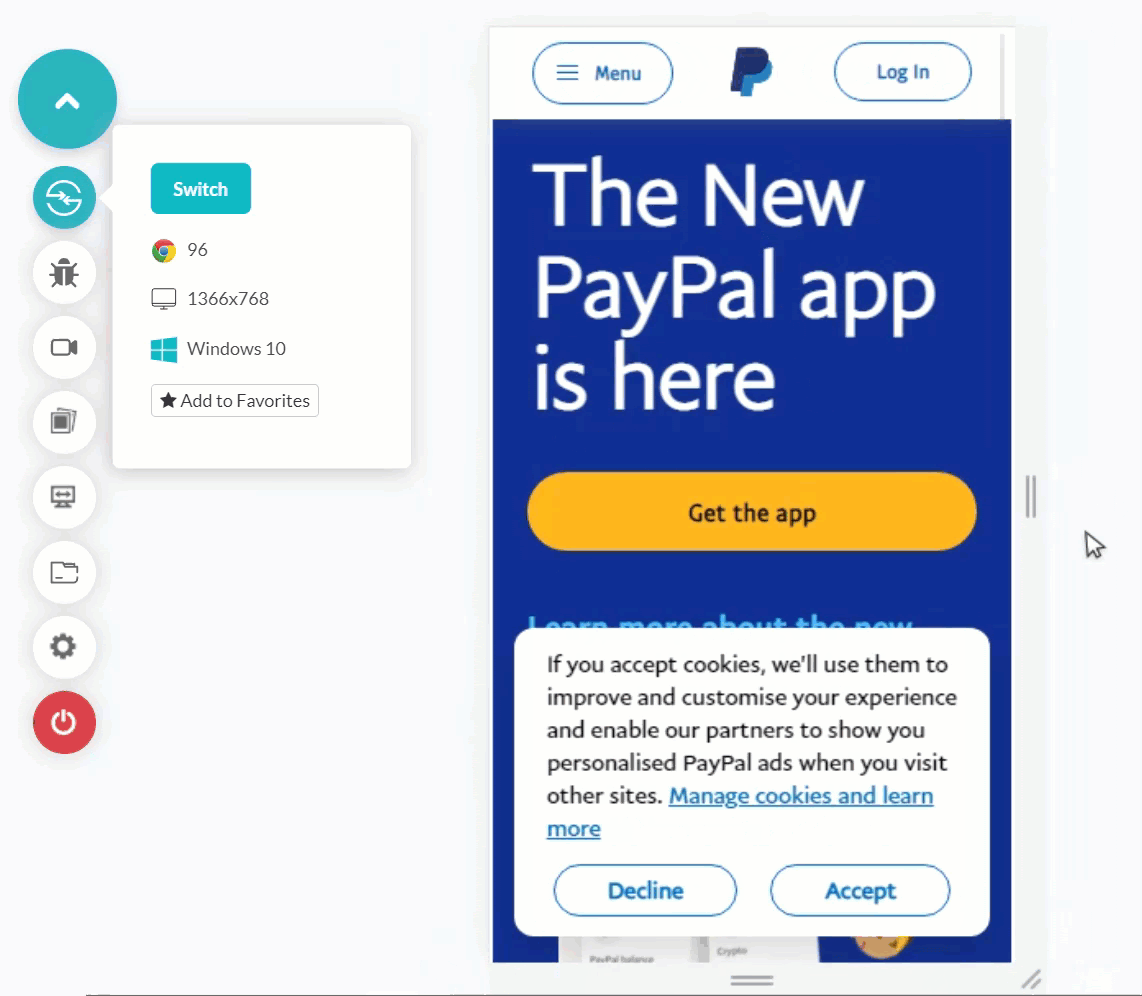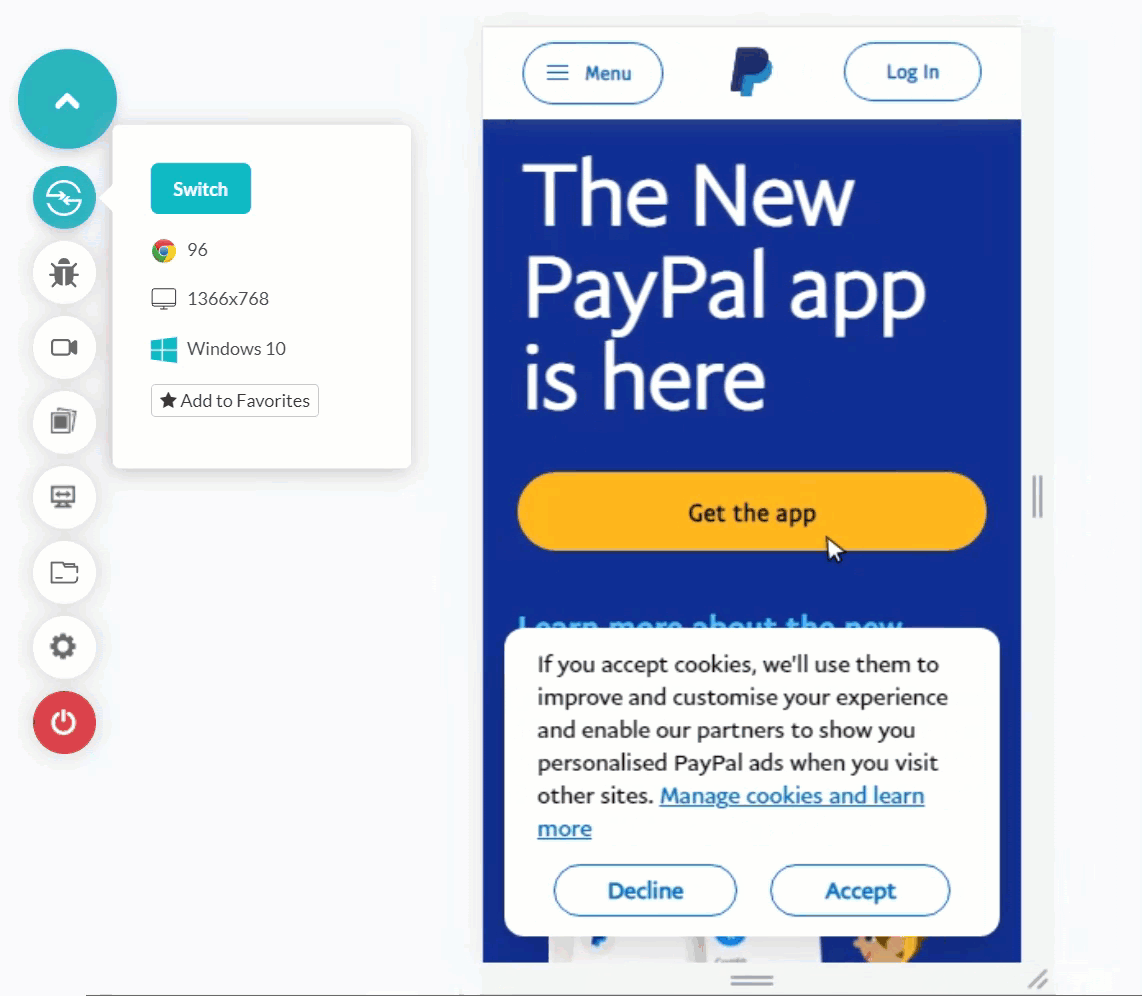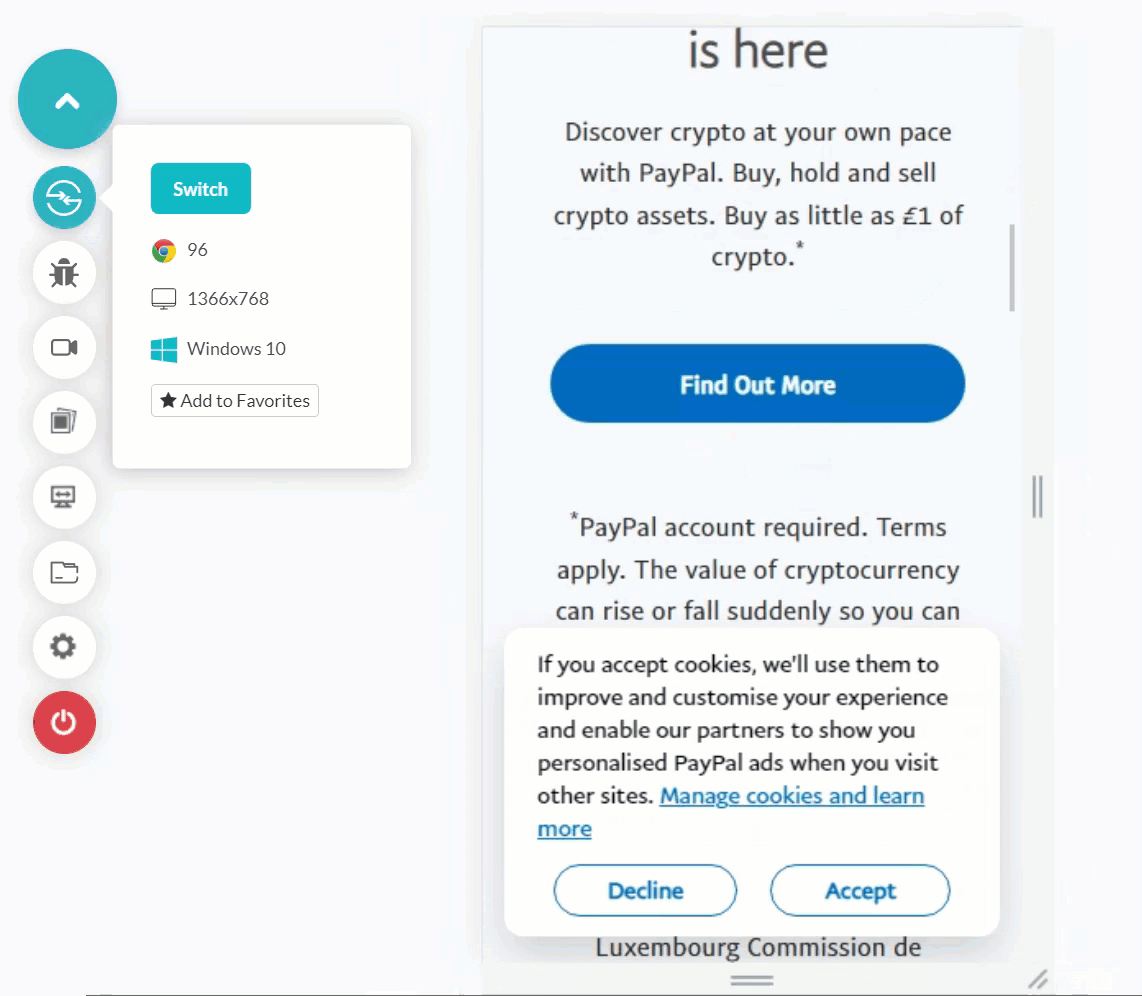
Testing Mobile apps on Emulators and Simulators is more inclined towards mobile devices’ reality (especially the emulator) than desktop browsers. This is because emulators consider hardware while rendering a mobile application or a mobile web. Recent emulators can also mimic certain functionalities of mobile devices like incoming calls and network variation. This provides a better idea of our mobile app execution for the end-user.
Also, Read – Why Android Application Testing Is Important?
Since it is the next segment to browsers, it should be performed after you are convinced with desktop browser tests. If an error is found in a desktop browser, it will reflect different processes. However, its vice versa is not true.
Advantages
- Quick to use: The emulators are straightforward to set up, and you can quickly start testing.
- Scalable: Emulators are easily scalable as you just need to install a new device when it is launched. You don’t need to worry about procuring one.
- Bring a few native functionalities: Emulators bring a few native functionalities into the testing environment, such as receiving calls and messages.
- Debugging facilities: Tests run on emulators are easy to debug as you use a desktop screen to work. In addition, the logs can be saved and analyzed quickly.
- Fast to execute: Emulators are faster to execute the test as you just upload a native binary file or enter a URL to see quick results. You can also use parallelization in emulators to execute tests faster.
- Gives you a head-start: The emulators are available as soon as the device is announced. Sometimes it is available based on rumoured specifications too. So testing on emulators can give you a head start to those waiting to receive the real device when it comes to the market.
Disadvantages
- Can’t imitate each device: Emulators cannot mimic each device in the market. You would find a lot of skins for many devices, but they run on a fixed stock underneath.
- Inaccurate resource usage: Emulators do not accurately picture the resource usage such as CPU, GPU, memory, or others. They provide the metrics, but that is hardly comparable due to the absence of real hardware.
- Absence of native mobile behavior: Emulators are better than desktop browsers in bringing a few mobile-like behaviors to the testing environment. However, it cannot mimic a lot of native mobile device APIs such as camera behavior, Bluetooth behavior, other wireless connections such as NFC etc.
- ARM-based emulators are slow: Kwo Ding mentions that almost all Android devices work on the ARM architecture. But, emulators working on ARM architecture are slower in execution. Therefore, they do not give a precise output from the tests.
Practically, emulators play a vital role in Mobile testing, and therefore, a tester should focus on the following areas while working with the emulators:
- Functional end-user flowsFunctional end-user flows determine whether your application works from path A to path B when navigated like an end-user. Again, emulators are an excellent choice to confirm that.
- Native API integrationA tester can focus on native API integration available in the emulator to verify their correctness with respect to the application. These may include call features, message features, GPS features etc.
- Visuals testingA tester can check the visuals but not go too deep into a device-specific UI. The high-level visuals can be verified here.
- Touch interactionsEmulators are an excellent primary choice to test for touch interactions of the mobile application. Even though it is not as accurate as a real device, it can give an idea about the high-level interaction and mobile app performance.
Real device
Kwo Ding describes the real device section as “the real thing” in his introduction to the Mobile Testing Pyramid. He is right in this statement. The benefit of real devices is that you can test crucial mobile app testing scenarios in real-user conditions.
Read More – Real Device Cloud For Native App Testing.
Looking to perform Android and iOS app testing on Real Device Cloud, check out our video below –
But that does not mean they lack any downside. Let’s compare its pros and cons.
Advantages
- All native APIs – A real device has all the native APIs and can be used along with the Mobile app testing.
- Real conditions – A real device presents real conditions to the tester that an actual end-user would face. This gives an accurate idea of the behavior of our mobile application.
- Faster ARM (Android) tests – As discussed earlier, ARM-based emulators are slow in test execution which majorly corresponds to Android devices. Therefore, real device test execution is much faster in Android.
- Everything is real – Ding does not let it slip again that the fact here is that they are real devices, and hence every metric here is accurate. So you get real CPU usage, real battery metric, real GPU usage, real logs etc.
Disadvantages
- Huge costs- Real devices are not easy to acquire as an emulator. They are too costly and can be a significant part of your overall testing budget. The current average cost of one device globally is close to USD 300. Acquiring 100 devices can put USD 30,000 just for procurement which can be a big deal for startups.
- Heavy maintenance – Another major factor in real device testing is the continuous maintenance it asks for from a user. A significant factor here is the continuous release of mobile phones. In 2021, 47 new mobile devices were released worldwide, a below-average number if you follow over the years. As a tester, you need to keep acquiring new devices to raise costs.
Except for cost and maintenance, real devices hardly bring any disadvantages to the table. But, I have a solution to eradicate this anomaly too. Why not try cloud-based real device labs that give you real devices for testing without actually purchasing even a single device.
TestMu AI platform offers a real-device lab with top-notch features integrated into it. With 3000+ screens to test on, TestMu AI real devices provide accurate metrics, device usage and logs in their detailed performance report. Along with it, you get network throttling, screen recording, sharing options and a debugger integrated into the platform. Once done, you can make use of tons of TestMu AI integrations that can facilitate your testing from a single place.
In the Mobile Testing Pyramid image below, notice that the real device section is distributed to two-segments instead of one, like emulators and browsers.
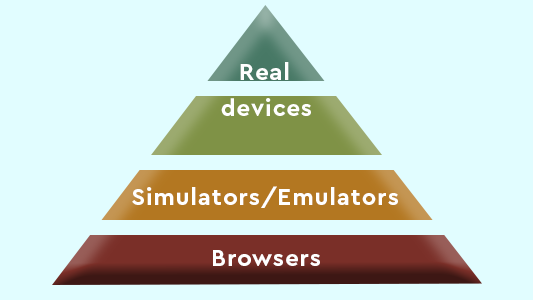
The lower segment containing the word “devices” denotes the usability or functional testing part of the real devices. The upper segment is for the non-functional testing part.
These will also reflect in the following focus area of real devices.
- Usability
The usability of the mobile application can be tested thoroughly and most efficiently in a real device. This may include touch interaction connections such as Bluetooth, NFC and more.
- CPU
Focus on CPU usage and the metrics it generates as they will be accurate according to the device in use.
- Visuals
Kwo Ding refers to this section as the “leftover visuals” you could not see in other testing (segments). Desktop browsers and emulators can clear out most of the visual stuff for your application. But for confirmation, you can focus on this here with lower priority.
- Manufacturer’s sauce
A few manufacturers put up their UI environment on Android. For example, Samsung has its own One UI that comes on top of Android’s UI engine. This could affect your mobile application UI and therefore is a good focus area for a tester.
- Specific built-in browsers
A few device manufacturers also release their devices with specific built-in browsers, such as Samsung with Samsung Internet. They may contain a tiny percentage of users, but it is always a good practice to account for everyone and every scenario before releasing the mobile app.
This was all about the Mobile Testing Pyramid and the detailed exploration of its various segments. The Mobile Testing Pyramid is an excellent reference for structured testing and good performance. A brief analysis can be therefore dictated here for the agile teams.
Effect of the Mobile Testing Pyramid on Agile teams
Agile is the most well-received and adopted SDLC methodology across the world today. It expedites the process and aims at software delivery within four weeks (it can also be 15 days or 45 days, depending on the organization). However, testers are especially under pressure once the development part completes, and there is very little time left for conducting testing and moving the feedback cycle. Some may argue that in-sprint testing is a suitable method but that sometimes puts more pressure if the sprint cycle is not reduced.
Can the Mobile Testing Pyramid help the agile teams in any way? Definitely!
The Mobile Testing Pyramid gives a structure to the testing team. Without a proper structure, you can start testing on real devices first and discover that a few things could have been done much faster if you had chosen desktop browsers before. This is true and therefore determines their place in the testing pyramid.
The Mobile Testing Pyramid describes that testers should always start with browser tests (as many as you can) because they are quick to execute and fast to achieve. If tests do not need real devices, they can be quickly wrapped up as per the testing pyramid’s principle.
The Mobile Testing Pyramid also describes focus areas for each segment. They can prove to be essential when a tester is lost in configuring hundreds of tests and determining which one to use. If a section defines a focus area, that can be a foundation for creating or dividing tests around that. This can help you quickly execute the tests, which is ultimately the goal in an agile environment.
Also, Read – Enabling Agile Software Testing With Automation
What are your thoughts on the Pyramid?
This brings us to the end of this section. Kwo Ding’s testing pyramid represents structured testing that speeds things up and gives clear direction. It is indeed a new thing when it comes to testing mobile apps. As a tester, you would see some differences in your app when run on a desktop browser, emulator and a real device. The challenges we face during Mobile device cloud testing has been the foundational thinking behind devising the testing pyramid based on the automation testing pyramid designed by Mike Cohn.
This post combines my and Ding’s thoughts on the testing pyramid. Either being a tester or a developer, you can incorporate this in practice. I would love to hear your thoughts on the same.
I hope to see some great comments and suggestions in the comment section below.
Thank you for reading, and have a nice day!
To further strengthen your expertise in mobile app development and mobile testing, be sure to check out our comprehensive guide on top asked mobile testing interview questions. This resource will equip you with the knowledge needed to excel in this dynamic field.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests





