Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- Types of iOS application testing
- What is Appium?
- Benefits of automating iOS app testing using Appium
- Prerequisites for how to automate iOS app using Appium
- Capabilities setup for real iOS device
- Identifying the iOS elements
- Demo Code for automating iOS app using Appium
- How to automate iOS app using Appium on a real device cloud?
How To Automate iOS App Using Appium
Master iOS app automation with this comprehensive guide on utilizing Appium. Streamline your testing process and enhance app quality.
Sidharth Shukla
January 11, 2026
To ensure that the iOS app runs flawlessly, you must ensure that mobile app testing is planned and executed perfectly. To achieve it, you need to use a framework like Appium to run iOS app testing on real iOS devices at scale. The result is wider coverage and faster execution with utmost quality.
This mobile app testing tutorial on performing Appium testing of iOS devices will help you answer all questions pertaining to how to automate iOS app using Appium. If you are preparing for an interview you can learn more through Appium Interview Questions.
Overview
What Are the Types of iOS Application Testing?
iOS applications can be tested in multiple ways to ensure they function smoothly, perform reliably, and remain secure across devices. Testing can be done on virtual simulators or real devices, covering both functional and non-functional aspects.
- Simulator Testing: Testing the iOS app on a virtual device to quickly validate functionality and UI behavior.
- Real Device Testing: Running tests on actual iPhones or iPads to ensure the app works under real-world conditions.
- Functional Testing: Verifying all app features, buttons, workflows, and user interactions work as intended.
- Performance Testing: Measuring app responsiveness, load times, and stability under different usage scenarios.
- Security Testing: Checking the app for vulnerabilities, data protection, and compliance with security standards.
- Hardware Testing: Ensuring app integrates correctly with device-specific hardware like camera, GPS, or sensors.
What Are the Benefits of Automating iOS App Testing Using Appium?
Appium is a popular choice for iOS automation due to its simplicity, flexibility, and strong community support.
- Cross-Platform Support: Write tests once and execute them on iOS, Android, and Windows devices without modifying the code.
- No Extra Dependencies: Communicates directly with real devices, reducing the need to install additional tools or drivers.
- Compatibility with Major iOS Versions: Supports iOS 9.3 and above using XCUITest, ensuring broad device and version coverage.
- No App Recompilation Needed: Automate testing without changing the app code or opening Xcode, saving time and effort.
- Flexible Execution: Run tests on simulators, emulators, or real device cloud platforms for comprehensive test coverage.
- Easy for Beginners: Provides simple setup and clear documentation, making mobile app automation accessible for new testers.
- Modular Test Design: Allows reusable and maintainable test scripts across different projects and platforms.
How to Automate iOS Apps Using Appium?
Automating iOS apps with Appium requires proper setup of tools, dependencies, and device configurations for smooth execution. Follow these steps to prepare your environment and start automation efficiently:
- Install Java: Ensure JDK is installed and environment variables are set to run Appium with Java projects.
- Install IDE: Use Eclipse or IntelliJ for writing and managing automation scripts efficiently.
- Install Homebrew: Package manager for macOS, used to install dependencies like Carthage, Node, and ios-deploy.
- Install Carthage: Required by WebDriverAgent to build and run tests on iOS real devices.
- Install Node & npm: Appium is Node-based; install Node.js and npm to manage packages and Appium itself.
- Install authorize-ios: Pre-authorizes Instruments, enabling UIAutomation scripts to run on real iOS devices successfully.
- Install ios-deploy: Allows installing and debugging iOS apps on physical devices from the terminal.
- Install ideviceinstaller: A Tool to install, uninstall, and manage iOS apps directly on connected devices.
- Install Xcode: Apple’s IDE for building, testing, and deploying iOS apps and running automated tests.
- Install XCUITest Driver: Enables Appium to automate iOS apps using the XCTest framework and the WebDriverAgent server.
- Install Appium: Core automation server for running iOS tests; use npm install -g appium@version.
- Install Appium Doctor: Checks system and dependencies, ensuring Appium runs without environment issues.
- Install Maven: A Dependency management tool for Java; it helps in building and managing project libraries easily.
- Install TestNG: Test framework to organize, run, and report automated test cases in Java projects.
- Install Appium Desktop: Provides Appium Inspector for identifying app elements and designing test scripts visually.
- Setup Capabilities: Define DesiredCapabilities, including device info, app path, bundle ID, and XCUITest signing details.
- Trust WebDriverAgentRunner: Approve the developer certificate in device settings to allow running automation scripts on iOS.
- Use noReset Capability: Prevents reinstalling the app before every test, saving execution time and improving efficiency.
Is It Possible to Automate iOS Apps on Windows?
You cannot run the official iOS Simulator directly on Windows, as it’s part of Xcode, which only works on macOS. However, you can write automation scripts on Windows and execute them on a macOS machine connected remotely, or use cloud testing platforms like TestMu AI that provide access to real iOS devices and simulators for testing and automation.
Types of iOS application testing
There are specifically two types of iOS application testing, either you can test it using the simulator or by using the real device. In most real-time projects, the team prefers to perform regression testing in the iOS simulator, but simulator testing alone is insufficient for QA sign-off. This is why test (or QA) teams prefer to execute one round of Smoke or Sanity on the real devices.
When teams perform iOS testing, they like to run Functional Testing, Performance Testing, Security Testing, and Hardware Testing. It is important to note that Performance, Security, and Hardware Testing are non-functional testing types.
In this Appium testing tutorial, we will perform functional testing on iOS using a real device cloud.
Many mobile app testing frameworks facilitate automated device testing on iOS. However, my personal choice has always been “Appium.” You will know about the USPs of Appium once you read through this blog on how to automate iOS app using Appium.
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on TestMu AI
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
What is Appium?
Appium is an open source test automation framework , empowers testing for native, web, and hybrid apps across iOS, Android, and Windows platforms. Notably, it offers cross-platform capability, enabling unified testing with a single API across iOS, Android, and Windows devices.
In simple words, it processes the request from the client and forwards it to the simulator and emulator or real devices. The test scripts are automated, and the result is communicated to the client via the server. This emulator vs simulator vs real device testing blog will help you learn more about it.
This enables code reuse between iOS, Android, and Windows test suites. The best part is using programming languages such as JavaScript, Java, Ruby, Python, PHP, and C# for Appium test script design.
As per the official website of Appium, per month, around 416k downloads are done by the users. It has a massive number of users along with community support.
Watch this video to learn about Appium, one of the most popular open-source test automation frameworks for mobile app testing.
Benefits of automating iOS app testing using Appium
As discussed earlier in this blog on how to automate iOS app using Appium, you must have had a little idea about iOS and Appium by now, but the million-dollar question is why Appium?
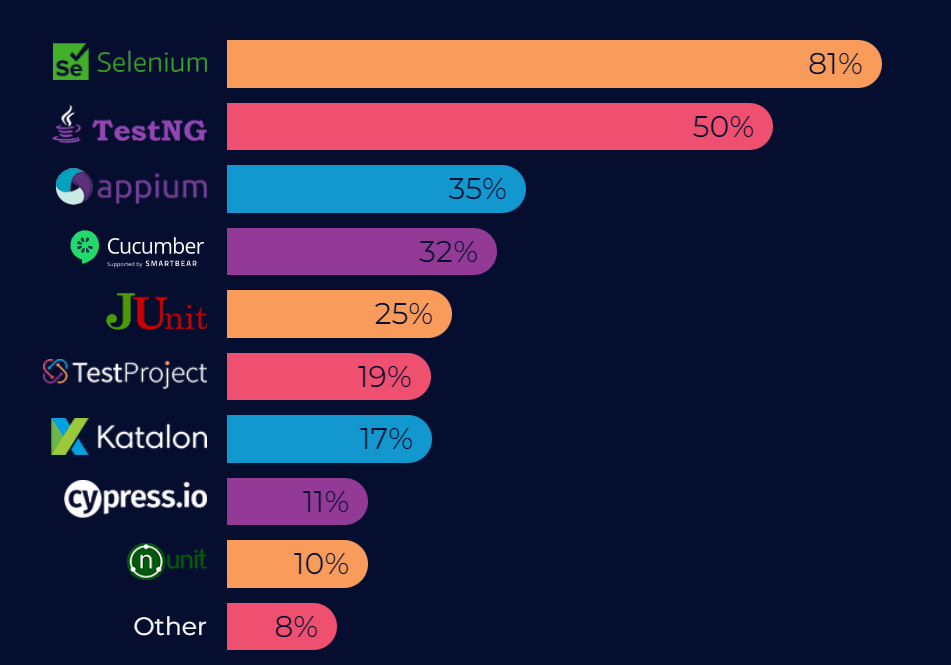
Appium has shown significant progress and is quickly becoming a preferred automation testing tool for mobile applications, with 35% of the organizations choosing it over other free/open source functional testing tools.
So, let’s point out some of the significant benefits of iOS Appium automation testing. We have alternatives for iOS automation, but Appium is easy to use and has extensive community support.
- Cross platform
- Avoid installing extra dependencies
- Support for major iOS versions
- Avoid recompilation of app
- Hassle-free execution
In case you are a beginner to Appium you can learn to perform mobile app testing easily through this tutorial.
As stated on the official website of Appium, the Appium team does not test the XCUITest driver against jailbroken devices, so it cannot be guaranteed that it will work as seen on non-jailbroken devices.
Note: Automate your iOS apps on the Appium cloud of 3000+ real devices. Try TestMu AI Now!
Prerequisites for how to automate iOS app using Appium
Before starting the pre-setup, as per my past experiences, I must tell you that it is quite tedious to do the entire setup, so please stay with us and follow all the steps carefully. Remember that all the steps mentioned below are mainly specific to OS, so follow steps respective to your operating system (i.e., macOS, Windows).
- First, you must have the Java setup done along with an IDE. We can use any IDE, but I recommend using Eclipse or IntelliJ IDE. I would recommend using Eclipse for the first try or practice.
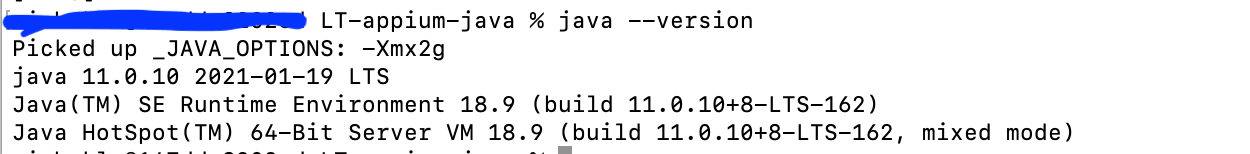
- To set up JDK in the machine, please refer to the official Oracle website. If you already have JDK in your machine, skip this step. Never forget to check your java version in your machine post installation. You can also check the Java version as below once the installation is completed:
- Once your JDK installation along with environment setup is done, the next step is supposed to install Eclipse. For your help, please refer to these blogs on how to install Eclipse and how to install IntelliJ.
You can also subscribe to the TestMu AI YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress E2E testing, CI/CD, and more.
Step 1: Install Homebrew
It is a package management software, and to install, follow the instructions on this page: https://brew.sh/.
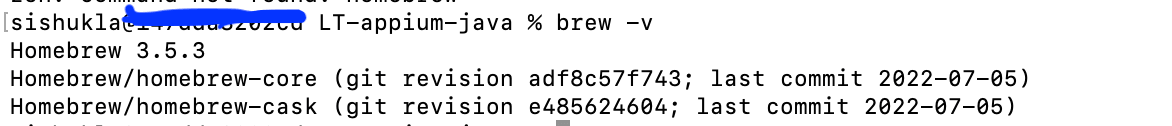
To check the installed details along with the version, we can type “brew -v” as shown below:
Step 2: Install Carthage
The WebDriverAgent requires it. To install it, just type below command:
brew install carthage
If it is already installed in your machine, then you will get a message as below:
“carthage 0.38.0 is already installed and up-to-date.”
Step 3: Install Node & Npm
This step is required because Appium is a node application. To install it, run the below command on the terminal.
brew install node
To verify the installed versions of npm and node, we can use npm -v & node -v as shown below:

Step 4: Install authorize-ios
authorize-ios is a little utility that pre-authorizes Instruments to run UIAutomation scripts against iOS devices. It is required to run tests on real devices.
In the terminal, enter the below command to install authorize-ios:
npm install -g authorize-ios
Step 5: Install ios-deploy
Install ios-deploy via Homebrew by running the below command on the terminal:
brew install ios-deploy
To verify the installation, we can use ios-deploy –version command in the terminal as below:
 Step 6: Install ideviceinstaller
Step 6: Install ideviceinstaller
This is the tool for managing apps on iOS device
brew install ideviceinstaller
To check the installation is completed or not, ideviceinstaller –version command can be used as shown below:
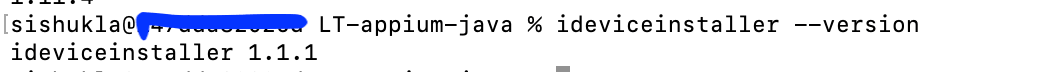
Step-7: Install Xcode
Xcode is a complete developer toolset for creating apps for Mac, iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, and Apple TV. Xcode brings user interface design, coding, testing, debugging, and submitting to the App Store into a unified workflow.
For step-by-step guidance on using Xcode to build, test, and submit apps to the App Store, look at XCode documentation. To verify the Xcode installation, we can use the /usr/bin/xcodebuild -version command as shown below:

Step 8: Install XCUITest driver
Appium XCUITest driver is a combined solution, which allows automated black-box testing of iOS and tvOS native applications and WebKit web views. The native testing is based on Apple’s XCTest framework and the fork of Facebook’s WebDriverAgent server. Web views communication is done via Webkit remote debugger protocol.
The appium-ios-device library ensures real device communication. To install the XCUITest driver, please use the official website. It has the help doc, which can be referred to for common errors or issues faced during the installation.
Step 9: Install Appium and Appium Doctor
To install Appium, please type the below command and use the version of Appium after @ in the below command:
npm install -g appium@version
You can check the version of Appium installed by using the command appium –version on the terminal, refer the below screenshot for reference:

Appium doctor is a mini software that checks all (well, almost all) of the preconditions for appium to run successfully. In the terminal, enter the following:
npm install -g appium-doctor
We can use the command appium-doctor –version to check the installed version:

Step 10: Install Maven
As we all know, Maven is the dependency management tool, type below command in your terminal:
brew install maven
Don’t forget the setup maven path before checking the version, you can do that by using below command:
export PATH=/opt/apache-maven-3.8.6/bin:$PATH
Once installation complete do cross-check by typing below command:
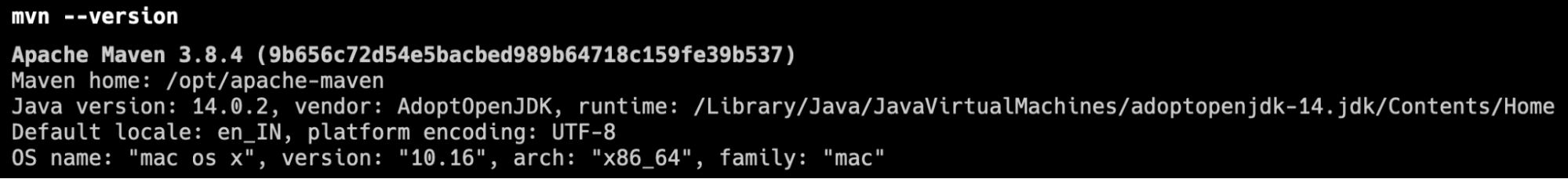
mvn --version
Output will look as below:
Step 11: Install TestNG
TestNG is a testing framework that we’ll be using to manage our automated test suite. Launch Eclipse, select “Help” > “Eclipse Marketplace”–>search for TestNG. Learn more about TestNG through this Selenium TestNG tutorial.
We should be able to see the TestNG for Eclipse option with a button as “Install.” Click on the button and complete the installation. For more help, please go through this Appium with TestNG tutorial.
Step 12: Install Appium Desktop
We need to install Appium Desktop so we can use the Appium Inspector to identify the elements on the iOS app for designing test scripts. You can install the Appium Desktop from the official website.
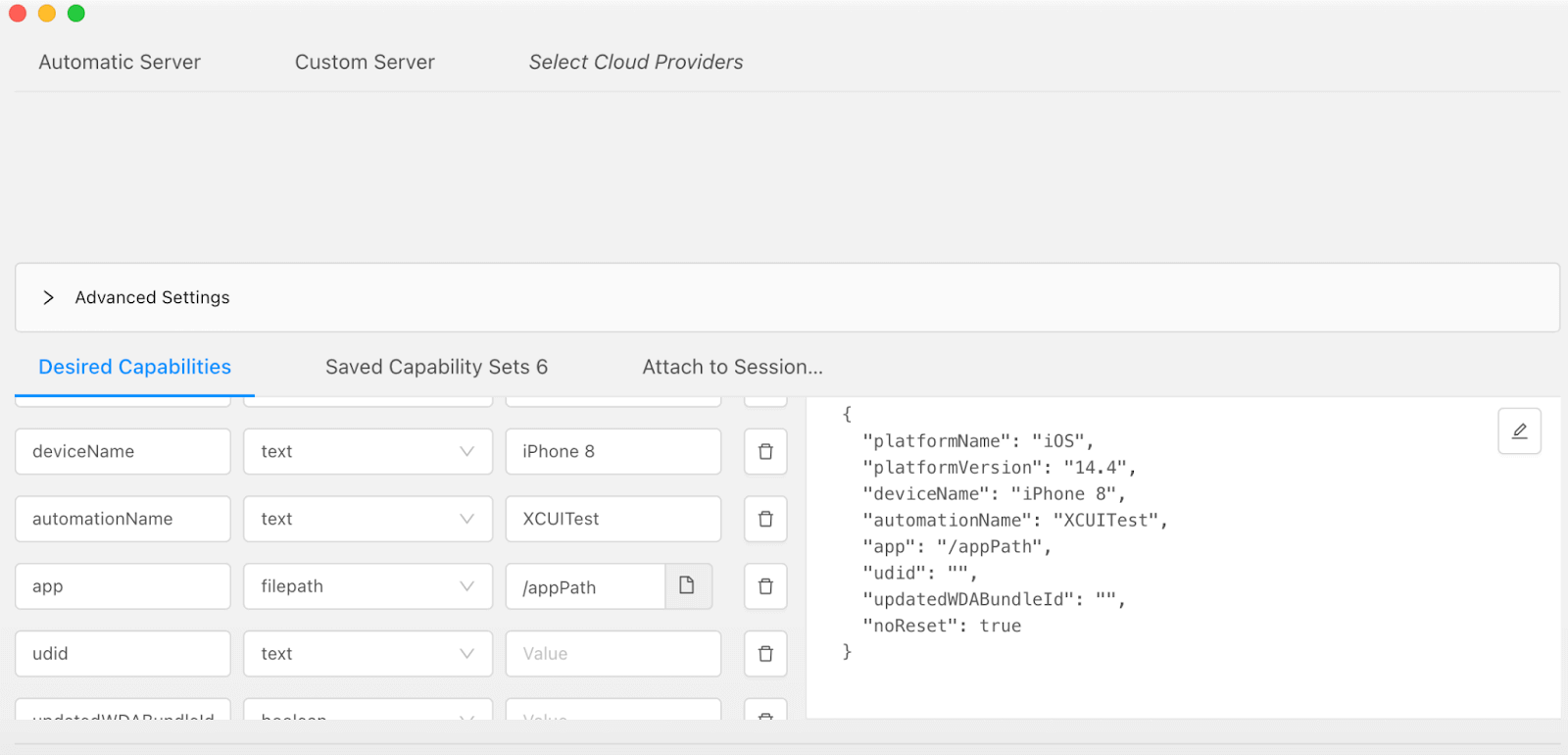
Capabilities setup for real iOS device
This is the most vital step to perform. Below are the mentioned capabilities we require to run our tests.
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("platformName", "iOS");
capabilities.setCapability(MobileCapabilityType.NO_RESET, true);
capabilities.setCapability("useNewWDA", false);
capabilities.setCapability("platformVersion", "12.0.1");
capabilities.setCapability("deviceName", "iPhone 8");
capabilities.setCapability("udid", "auto");
capabilities.setCapability("bundleId", "<your bundle id>");
capabilities.setCapability("xcodeOrgId", "<your org id>");
capabilities.setCapability("xcodeSigningId", "iPhone Developer");
capabilities.setCapability("updatedWDABundleId", "<bundle id in scope of provisioning profile>");
capabilities.setCapability(MobileCapabilityType.APP, "[PATH_TO_YOUR_IPA_FILE]");
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("platformName", "iOS");
capabilities.setCapability(MobileCapabilityType.NO_RESET, true);
capabilities.setCapability("useNewWDA", false);
capabilities.setCapability("platformVersion", "12.0.1");
capabilities.setCapability("deviceName", "iPhone 8");
capabilities.setCapability("udid", "auto");
capabilities.setCapability("bundleId", "<your bundle id>");
capabilities.setCapability("xcodeOrgId", "<your org id>");
capabilities.setCapability("xcodeSigningId", "iPhone Developer");
capabilities.setCapability("updatedWDABundleId", "<bundle id in scope of provisioning profile>");
capabilities.setCapability(MobileCapabilityType.APP, "[PATH_TO_YOUR_IPA_FILE]");
Now the question is how to get the details that have been mentioned in the above code. Let’s go through them one by one:
- platformVersion: is the version of iOS our app is running,
12.0.1in my case. - deviceName: is not required, as we have plugged in a real device and will select that device using the
udiddesired capability. Appium still requires us to supply a value fordeviceName, so we useiPhone 8. To know the device name, in the iPhone, we can navigate to“Settings> General > About > Name.” - udid: is the unique ID of the device we want to run our test on. Now connect your iPhone to your computer by USB and load up iTunes. We could find our device udid by running the command
instruments -sdevicesin the terminal. Still, since we only have a single device plugged in, we can put in auto, and Appium will automatically find the udid of the device for us and use it. If ”auto” doesn’t work, then do provide your udid. - xcodeOrgId & xcodeSigningId: join the Apple Developer Program and locate your apple developer team id; xcodeorgid is the ID of the developer team that signed the certificate used to create the app.
xcodeSigningIdis the first part of the “Common Name” associated with the developer certificate.Since XCode set this up for us, it is almost always
iPhone Developer, but it could be something different for you if you are automating a different iOS device. - bundleID: it is the special iOS-internal name of our app. The easiest way to get the bundleID is by using iTunesConnect. The steps are as below:
- Log into iTunes Connect.
- Click My Apps.
- Click on an app to find the bundle ID.
- The default app page will open, displaying the App ID and bundle ID.
- App: many websites provide the sample apk, which can be used for testing. If you do not have any .apk or .ipa files, you can run your sample tests on TestMu AI using our sample 🔗 iOS app.
- noReset: do not forget to use this capability. This approximately saves 2.9 seconds per test by avoiding app installation before every test run.
- updatedWDABundleId: we need to create a provisioning profile for signing the WebDriverAgentRunner. Launch the Xcode and create a new project, select the team and enter the project name as follows:
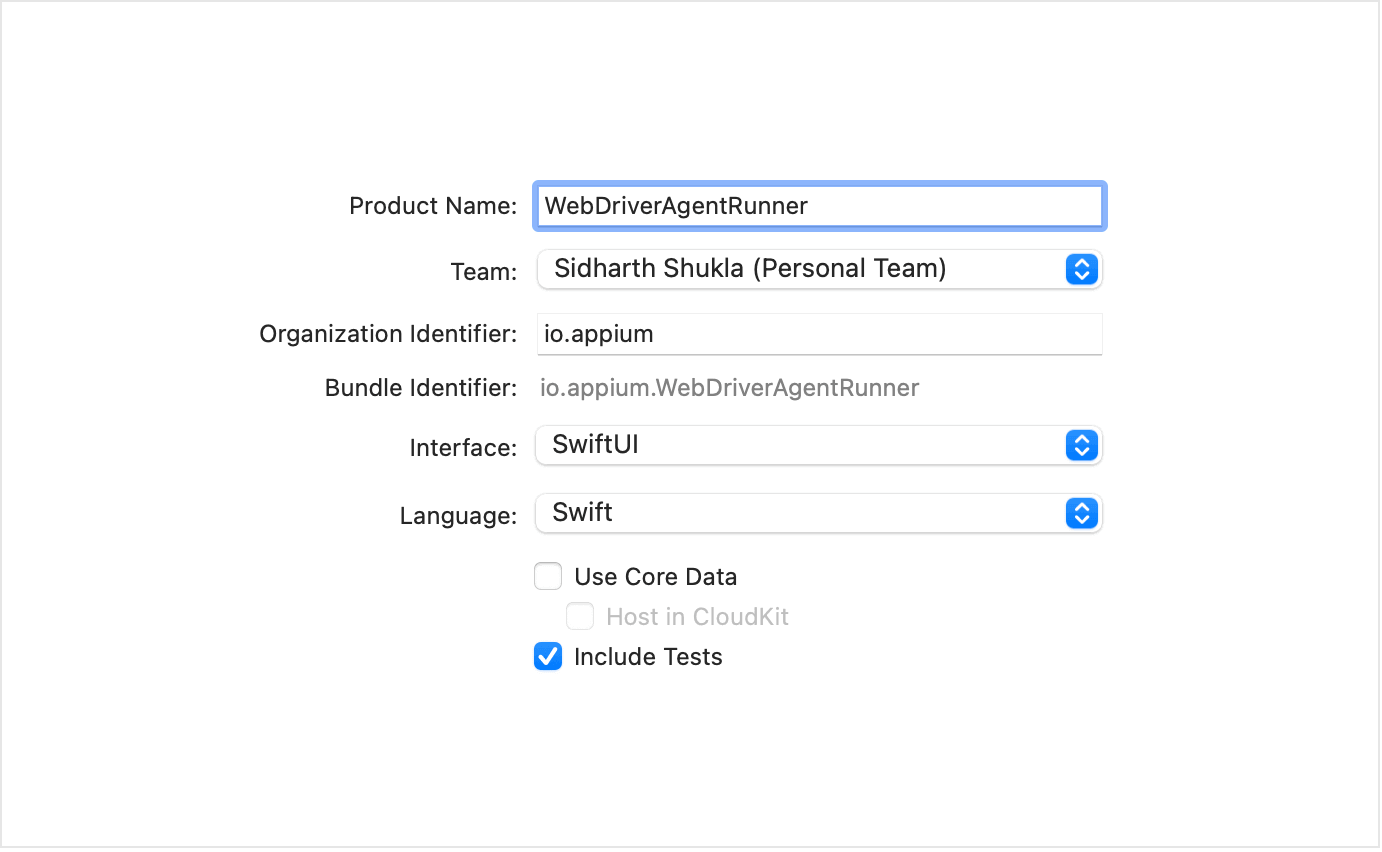
Take a look at the “Project” tab of your project settings to confirm that “Automatically manage signing” is selected, and an Xcode Managed Profile is created.
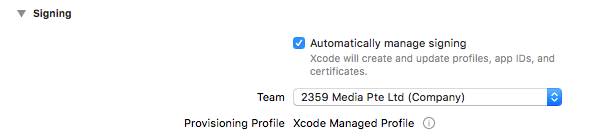
Suppose you manually try to run the WebDriverAgentRunner app on the device. In that case, you will see a popup message:
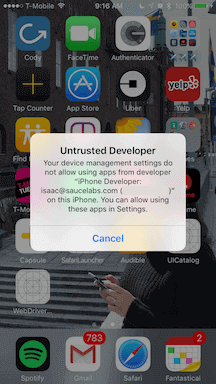
You can go to Settings => General => Device Management on the device to trust the developer and allow the WebDriverAgentRunner app to be run.
Copy your bundleId and add the following capability to your Appium Capabilities setup:
capabilities.setCapability("updatedWDABundleId", "<bundle id in scope of provisioning profile>");
If you are unable to do the above steps, then the manual configuration can also be done. To go through the steps, please refer to this document. It has all the steps along with the screenshots.
Identifying the iOS elements
In this section of this blog on how to automate iOS app using Appium, we will learn how to identify the iOS elements. To identify elements in iOS devices, we need to download and install the Appium Desktop application and use the Appium Desktop Inspector functionality.
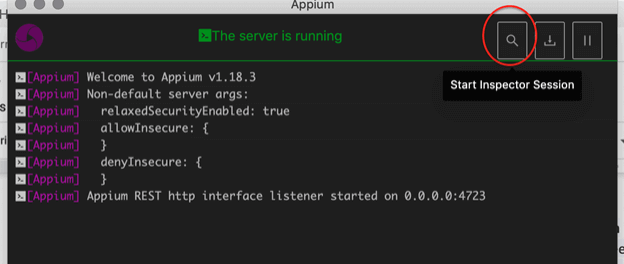
- If you have installed Appium Desktop, then we can start by clicking on the Start Server button inside of Appium Desktop as shown below.
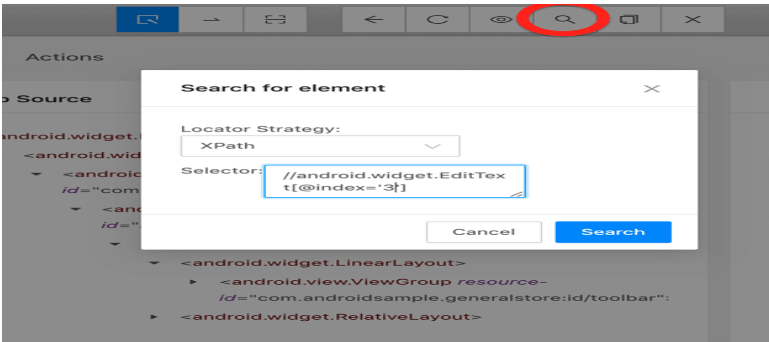
- Click the search icon from the right-up corner.
- Add correct desired capabilities per your device/emulator and application. Then click on the Start Session button.
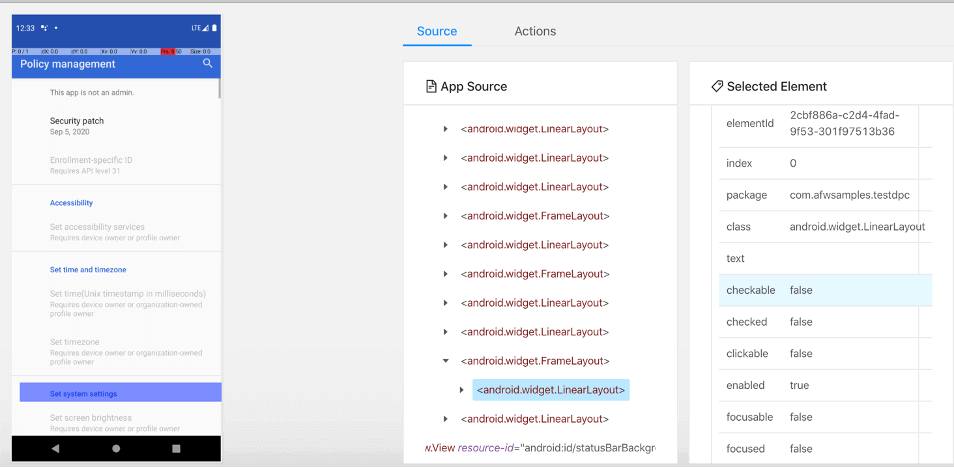
- It will open the App screen, App Source (the hierarchy of elements), and Selected Element Pane (The attributes and associated values of the element). You can use this to create locators which will uniquely identify the element.
- You can provide a .ipa file in desired capabilities inside Appium Inspector, which will install and launch the app. Refer to the screenshots below, which we have used to test .ipa and passed in the value against “app.” Use all the fields of desired capabilities discussed in this blog on how to automate iOS app using Appium. The best thing about the Appium Inspector is that you can verify your written locator on screen. Check the below screenshots.
- If your locator is correct, it will highlight the associated element, which is the same for Android and iOS.

Some of the most used locator strategies are mentioned below.
| STRATEGY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Accessibility ID | Reads a unique identifier for a UI element. For XCUITest, it is the element’s accessibility-id attribute. For Android, it is the element’s content-desc attribute. |
| Class name | For iOS, it is the full name of the XCUI element and begins with XCUIElementType. For Android, it is the full name of the UIAutomator2 class (e.g., android.widget.TextView) |
| ID | Native element identifier. resource-id for Android; name for iOS. |
| Name | Name of element. |
| XPath | Searches the app XML source using xpath (not recommended, has performance issues). |
| Image | Locates an element by matching it with a base 64 encoded image file. |
| iOS UIAutomation | When automating an iOS application, Apple’s Instruments framework can be used to find elements. |
In most real time projects, one public webelement is created, and element identification for Android and iOS is mentioned, as shown below. The nameOfMobileElement mentioned below is just an example. You can replace the same with the name of the locator used to identify the webelement of the targeted mobile app. We have identified the iOS element using iOSNsPredicate.
@iOSXCUITFindBy(iOSNsPredicate = "name=='<nameOfMobileElement>'")
@AndroidFindBy(uiAutomator = "text("<textOf TheMobileElement>")")
public MobileElement elementName;
@iOSXCUITFindBy(iOSNsPredicate = "name=='<nameOfMobileElement>'")
@AndroidFindBy(uiAutomator = "text("<textOf TheMobileElement>")")
public MobileElement elementName;
We can also use XPath as mentioned below for identification in iOS, in-fact all type of axes methods in XPath can be used to identify the element uniquely:
@iOSXCUITFindBy(xpath = "//*[@name='<nameOfMobileElement>']/following-sibling::XCUIElementTypeStaticText")
Though in my past experiences the most used identification I have used is accessibility as below, “GO TO APP” is just an example, it should be replaced with the accessibility for the app used for testing:
@iOSXCUITFindBy(accessibility = "GO TO APP")
While identifying iOS elements, we need to remember that the element should always be unique and try the locators first and give XPath identification the least priority. I would suggest not using XPath locators unless there is no other alternative.
In general, XPath locators might be much slower than other locators like accessibility id, class name, and predicate (up to 100 times slower in some special cases). They are so slow because Apple’s XCTest framework does not natively support the XPath location.
Demo Code for automating iOS app using Appium
Before running the tests, we need to perform below two steps:
Step 1: Make sure the device which will be used for testing is unlocked, and if it asks you to “Trust the Computer”, tap the button to trust our Mac. You’ll need to do this the first time, and it won’t ask for it.
Step 2: Start the Appium server.
import io.appium.java_client.MobileBy;
import io.appium.java_client.MobileElement;
import io.appium.java_client.ios.IOSDriver;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import io.appium.java_client.remote.MobileCapabilityType;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
public class iOS_Test {
private IOSDriver driver;
@Before
public void setUp() throws MalformedURLException {
DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("platformName", "iOS");
capabilities.setCapability("platformVersion", "15.5");
capabilities.setCapability("deviceName", "Sidiphone");
capabilities.setCapability("udid", "auto");
capabilities.setCapability("bundleId", "<your bundle id>");
capabilities.setCapability("xcodeOrgId", "<your org id>");
capabilities.setCapability("xcodeSigningId", "iPhone Developer");
capabilities.setCapability("updatedWDABundleId", "<bundle id in scope of provisioning profile>");
capabilities.setCapability(MobileCapabilityType.APP, "[PATH_TO_YOUR_.IPA_FILE_COMPILED]");
driver = new IOSDriver<>(new URL("http://localhost:4723/wd/hub"), capabilities);
}
@Test
public void testClickAnElement() throws InterruptedException {
//Opens the browser
MobileElement browser = (MobileElement) driver.findElementByAccessibilityId("Browser");
browser.click();
Thread.sleep(3000);
WebDriverWait el7 = new WebDriverWait(driver, 30);
el7.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(MobileBy.id("url")));
driver.findElementById("url").sendKeys("https://www.lambdatest.com/");
//Clicks on the text box
WebDriverWait el = new WebDriverWait(driver,90);
MobileElement el4 = (MobileElement) driver.findElementByAccessibilityId("find");
el.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(el4));
el4.click();
el4.sendKeys("LambdaTest");
//((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=passed");
driver.quit();
}
}
In the above code, the Test method we have used is testClickAnElement(), and the element we are trying to click is from the iOS app shared in this post on how to automate iOS app using Appium.

Troubleshooting Tips
- Make sure UDID is correct by checking it in XCode Organizer or iTunes. It is a long string (approx 20+ chars).
- Make sure the following settings are enabled on your device:
- A. Settings -> Developer -> Enable UI Automation
- Settings -> Safari -> Advanced ->Web Inspector and Remote
- Consider generating a provisioning profile with a .xctrunner identifier if you do not want to generate a wildcard one for manual configuration. The .xctrunner config support has been added since XCode 11.
- Make sure the provisioning profile has an iOS Distribution certificate. An active XCode/xcodebuild connection/session is necessary to interact with WebDriverAgentRunner because of Apple’s security design. The certificate affects the limitation.
- The keyboard preference in the device under test is Apple’s official one, and the input language is set to English to send texts to XCUIElementTypeSecureTextField, as Non-official or non-English keyboards may not be able to send keys to XCUIElementTypeSecureTextField.
Limitations
Given that Appium uses instruments underneath, we have all of the limitations of using Apple’s automation framework. This includes:
- A slower response time between actions, automation that can only run over a USB tether, and only one device can execute automation simultaneously per host.
- Each physical device or simulator requires a separate host running on a Mac to communicate with each device. This is due to the hosts being the one who determines where the commands are communicated, regardless of what parameters are passed into the automation. This may be a bug in the Appium infrastructure or requires a special command to determine the device to execute from the automation code.
- The Instruments log files are not returned as part of the test, and the data given back to the running test is much less than what is seen in a typical Instruments test case.
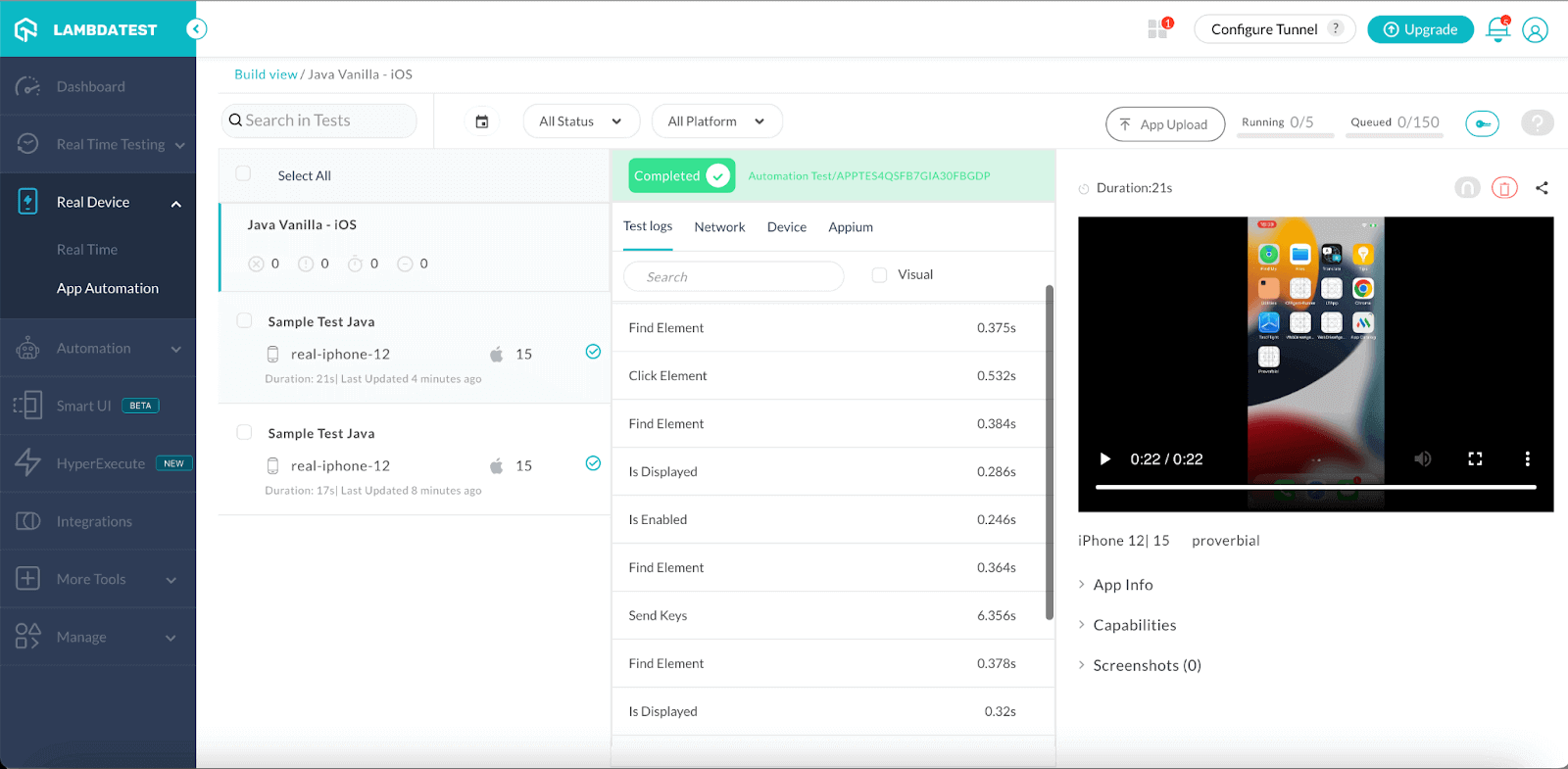
How to automate iOS app using Appium on a real device cloud?
In this blog on how to automate iOS app using Appium, you must have realized that testing on real devices is not a cakewalk, especially iOS real device testing is tedious. The important thing is that real iOS device testing can only take place on a Mac, so we can’t even perform real iOS device testing without a Mac.
As a result, most organizations prefer to use real cloud devices for testing. You can try TestMu AI cloud devices, which are quite easy to use, and we can avoid setting up all the prerequisites on local machines.
TestMu AI provides a cloud-based solution for mobile automation testing. It lets you automate native and hybrid mobile apps on an online device farm of 3000+ real iOS. It is a scalable, secure, and high-performing Appium testing platform that empowers development and testing teams to accelerate their release cycles.
Below we have executed the test suite using TestMu AI real cloud devices. Just use the below code along with your username and password. We used the iPhone 12 for our test run. You can use the model as per the requirement.
import io.appium.java_client.AppiumDriver;
import io.appium.java_client.MobileBy;
import io.appium.java_client.MobileElement;
import io.appium.java_client.ios.IOSDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import java.net.URL;
public class vanilla_ios {
public static String userName = System.getenv("LT_USERNAME") == null ? "sidharth****" //Add username here
: System.getenv("LT_USERNAME");
public static String accessKey = System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY") == null ? "********" //Add accessKey here
: System.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY");
public static final String URL = "https://" + userName + ":" + accessKey + "@beta-hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
public static IOSDriver driver = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try {
DesiredCapabilities caps = new DesiredCapabilities();
caps.setCapability("platformVersion", "15");
caps.setCapability("deviceName", "iPhone 12");
caps.setCapability("isRealMobile", true);
caps.setCapability("app", "******"); //Enter your app url
caps.setCapability("platformName", "iOS");
caps.setCapability("build", "Java Vanilla - iOS");
caps.setCapability("name", "Sample Test Java");
caps.setCapability("devicelog", true);
caps.setCapability("network", true);
driver = new IOSDriver(new URL("https://" + userName + ":" + accessKey + "@beta-hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub"), caps);
Thread.sleep(2000);
//Opens the browser
MobileElement browser = (MobileElement) driver.findElementByAccessibilityId("Browser");
browser.click();
Thread.sleep(3000);
WebDriverWait el7 = new WebDriverWait(driver, 30);
el7.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(MobileBy.id("url")));
driver.findElementById("url").sendKeys("https://www.lambdatest.com/");
//Clicks on the text box
WebDriverWait el = new WebDriverWait(driver,90);
MobileElement el4 = (MobileElement) driver.findElementByAccessibilityId("find");
el.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(el4));
el4.click();
el4.sendKeys("Lambdatest");
//((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("lambda-status=passed");
driver.quit();
} catch (Exception t) {
System.out.println(t);
driver.quit();
}
}
}
In the above script, we have first done the capabilities setup and then automated the iOS app with two steps:
The first one is to open the browser and the second one is to click on the text box and then enter text “TestMu AI” on the text box. For ease of execution, we have used thread.sleep in this blog on how to automate iOS app using Appium. You can ignore the same while executing in your setup.
- To execute the same, you need to use the below two commands on your terminal:
mvn clean install

mvn test -P ios

2M+ Devs and QAs rely on TestMu AI
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
Note: Boost your Testing efficiency by ultimate guide of Appium Commands Cheat Sheet for Developers.
Conclusion
With this, we have concluded this tutorial on how to automate iOS app using Appium. As per my suggestion, we should only consider real iOS devices for Sanity or Smoke suite execution. For regression, it is always advised to use either simulators or cloud devices.
Though we have simulators, we should never release a product without being tested on real devices, so better to prepare an automation suite and run the real devices on the cloud, saving time and ensuring quality.
We can address most app-related issues by ensuring that the app works on a real device. iOS testing with Appium will help provide that confidence in the product and confirm the app’s success when it is released to users.
Happy testing, and do share what should be the next topic you want to learn.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests