
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Integration Testing vs Functional Testing: Key Differences
Explore the two testing methodologies, Integration Testing and Functional Testing and their key differences.
Upendra Prasad Mahto
January 11, 2026
Software Testing plays an essential role in the world of software development. It connects the bridge between innovation and reliability. It ensures that the software meets industry standards and exceeds user expectations. With the advancement in technology and the increasing demands of users, software testing has become a fundamental and indispensable practice.
The main objective of this blog is to explore key differences between Integration Testing and Functional Testing. We will look at its workflow, advantages, disadvantages, when to use it, key differences, and use cases.
What is Integration Testing?
Integration testing is software testing where software modules are gradually integrated and then tested as a unified group. This testing ensures that all modules interact correctly and without flaws and errors. The modules must be tested independently before being tested together; hence, unit testing must be performed before integration testing.
Integration testing uses grey box testing techniques, combining white box testing and black box testing. There are various ways to perform integration testing, such as top-down, bottom-up, sandwich, big-bang, and incremental approaches.
The main objectives of integration testing are:
- Interaction Check: It verifies that different modules of the software work as expected when combined.
- Issue Discovery: It looks for hidden problems arising when these modules interact.
Learn more about integration testing in detail.
Workflow
The integration testing workflow is visually represented in the image below.
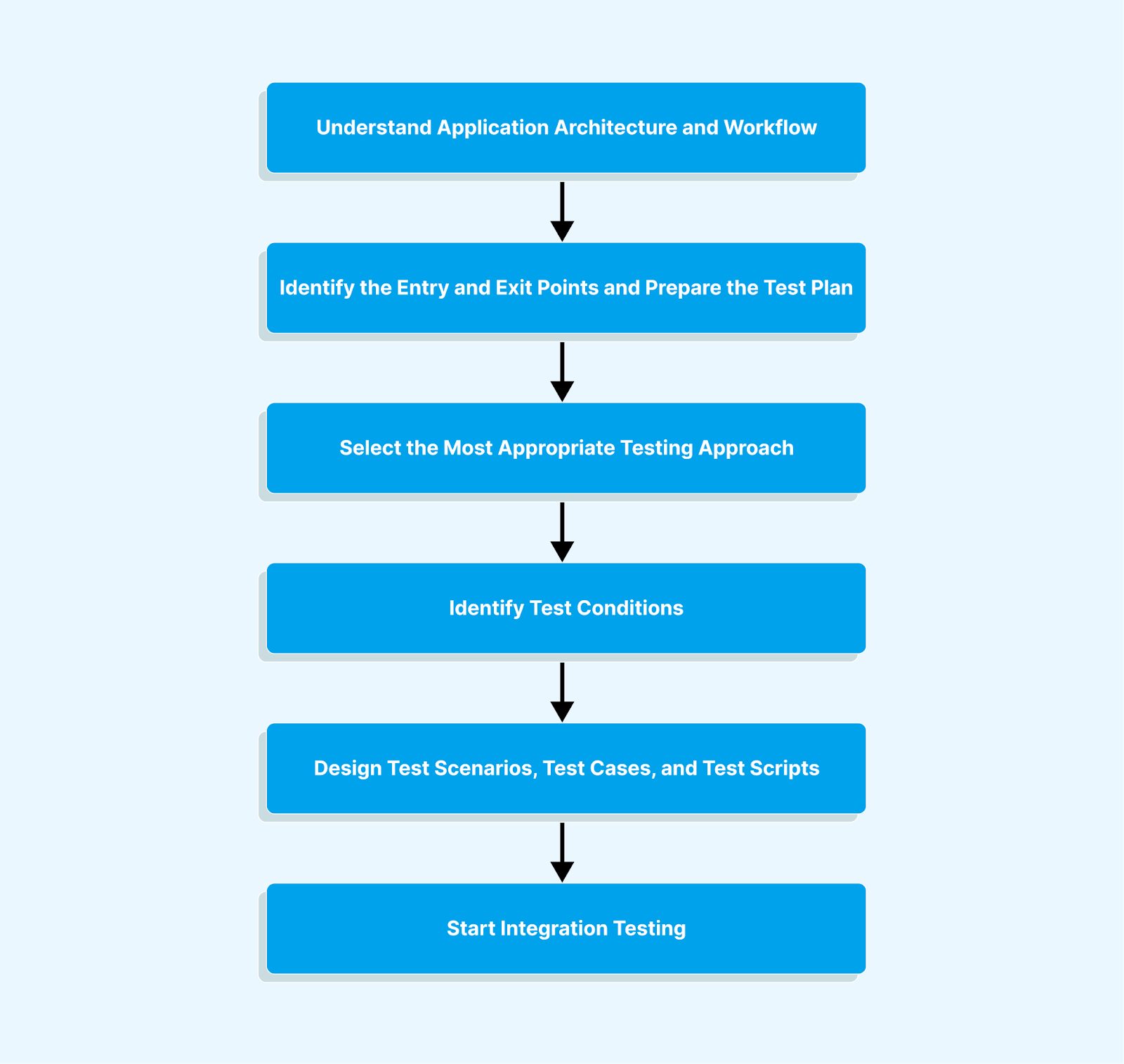
From the above image, we may conclude the workflow as follows:
- Understand and verify the requirements and specifications.
- Prepare a test plan by identifying entry and exit points.
- Create a traceability matrix through analysis and planning.
- Select the best testing approach based on application needs.
- Design various test cases and scripts for integration testing.
- Compare actual results with expected output for validation.
Advantages of Integration Testing
The following are the advantages of integration testing:
- Integration testing allows you to test important scenarios that can only be verified when all system modules are combined.
- Integration testing provides a structured approach to assembling a software system and running tests, efficiently uncovering errors related to component interactions.
- You don’t have to wait for all individual modules to complete unit testing before integration testing can begin.
- It is important to confirm whether software modules work cohesively and in unity, which is crucial for seamless system functionality.
Disadvantages of Integration Testing
The following are the disadvantages of integration testing:
- Integrating different modules can be complex and time-consuming, especially for large and complicated systems.
- It can delay development, especially when integration problems require extensive troubleshooting.
- Identifying the root cause of integration problems can be more challenging than unit testing, where problems are usually limited to a specific component.
- It may require substantial hardware, software, and test environments, making it resource-intensive.
Use Cases of Integration Testing
The following are the uses of integration testing:
- It ensures that APIs work seamlessly together, enabling data exchange and communication between software services.
- It helps to check the interaction between the software and the database.
- It helps to test the integration of third-party APIs and services, such as payment gateways or social media logins. Also, it ensures that they work smoothly with the main application.
- It helps test the software performance on different platforms like mobile devices, web browsers, or operating systems.
When to Perform Integration Testing
Integration testing is performed after unit testing and before functional testing. Unit testing involves isolating individual modules to ensure their correctness and acceptance. The integration test is done once the module unit tests are completed. Integration testing examines how modules interact when combined to form a unified group. After successful integration testing, functional testing is the next phase. It assesses the entire software system to ensure it meets user requirements and functions correctly in real-world scenarios.
Let’s take a real-world scenario as an example.
Suppose you’re building an e-commerce platform with various interconnected modules – a product catalog, a shopping cart, and a payment gateway. Each module is developed independently, ensuring they work flawlessly in isolation.
To guarantee a smooth shopping experience, you want to ensure these modules work correctly. The workflow should be: a customer browsing the product catalog, adding items to the shopping cart, and successfully making a payment.
This involves checking whether the product details are correctly transferred from the catalog to the cart. The payment gateway securely processes the transaction if the cart accurately matches the costs. Integration testing ensures that these modules interact correctly without any error.
Note: To ensure your application never BREAKS, test it with an infrastructure that won’t break either. Try TestMu AI Today!
What is Functional Testing?
Functional testing is a black-box testing technique in which the software is tested to verify that it works as expected in real-world situations. It evaluates a software system by examining whether it meets all specific requirements and expectations, such as user interface, database, APIs, client/server communication, security, and other crucial components. It includes various tests such as smoke testing, acceptance testing, sanity testing, regression testing, etc.
The main objectives of functional testing are:
- Verify Correctness: Ensure software functions according to documented requirements and performs tasks accurately and effectively.
- Detect Defects: Identify deviations from expected behavior or software functionality errors.
Learn more about functional testing in detail.
Workflow
The functional testing workflow is visually represented in the image below.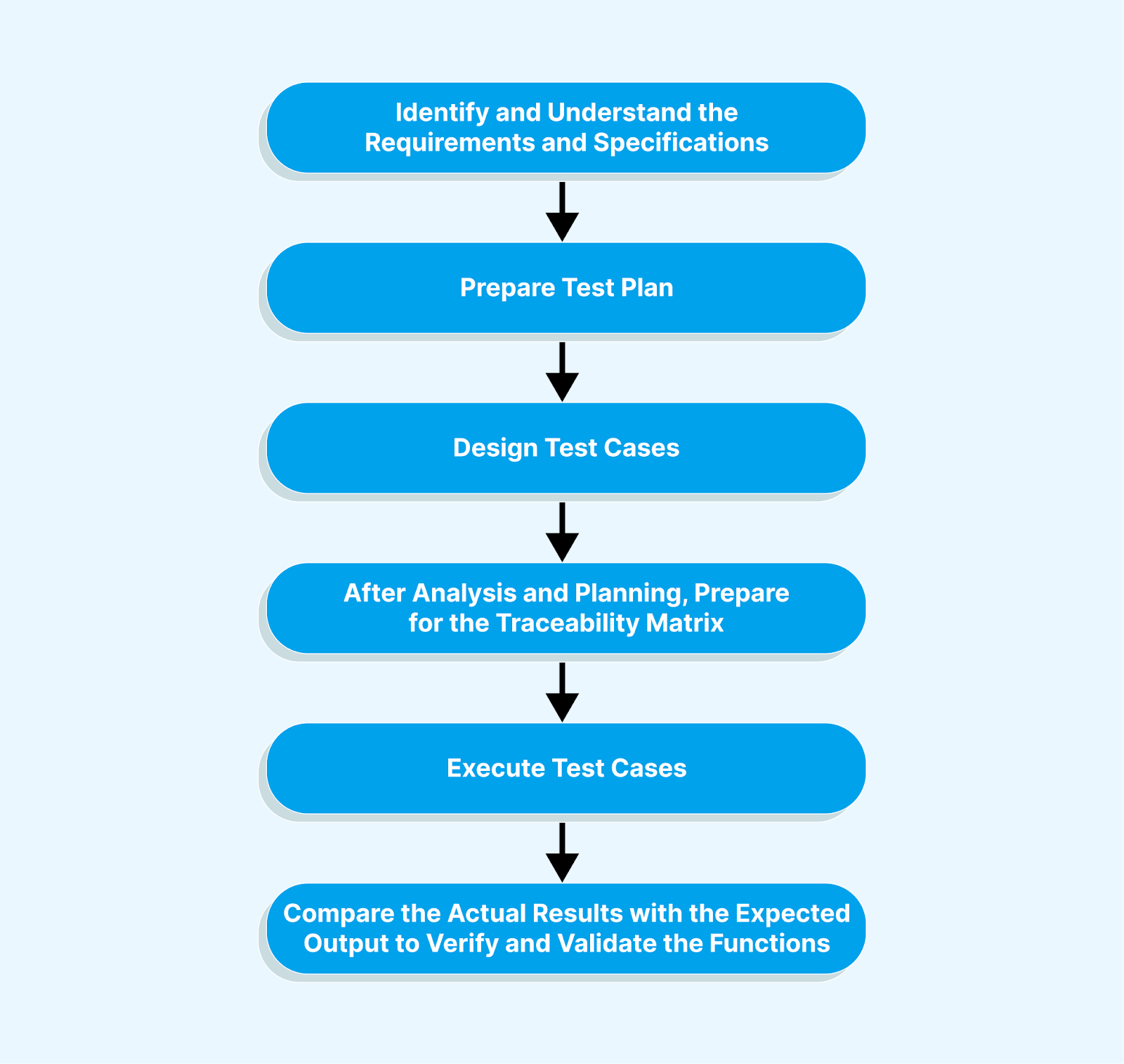
From the above image, we may conclude the workflow as follows:
- Identify and understand the requirements and specifications.
- Prepare and design test cases.
- Create a traceability matrix through analysis and planning.
- Execute the test cases.
- Validate the results by comparing actual results with expected output.
Advantages of Functional Testing
The following are the advantages of functional testing:
- Functional testing ensures software meets user expectations by testing individual functions against specified requirements.
- It reduces and resolves software defects and prevents problems before they become critical.
- It verifies that each software function performs as intended, resulting in a more reliable and bug-free product.
- It saves costs by detecting functional issues early and preventing defects from propagating through later stages of development.
Disadvantages of Functional Testing
The following are the disadvantages of functional testing:
- This may only cover some lines of code or all possible scenarios, leaving some parts of the software untested.
- It mainly focuses on what the software is supposed to do and generally neglects non-functional aspects such as performance, security, and scalability.
- With functional testing, it can be difficult to discover all problems.
- It can be resource-intensive, requiring time, effort, and a range of test scenarios.
Use Cases of Functional Testing
The following are the uses of functional testing:
- It helps identify and fix software deficiencies, bugs, and errors to improve reliability and quality.
- It helps verify software performance under various configurations, loads, and environments to ensure reliable functionality.
- It helps in testing the software to prevent new problems when implemented changes or updates are introduced.
When to Perform Functional Testing
Functional testing after integration testing may coincide with system testing, depending on the software development methodology. Functional testing occurs after unit testing, which evaluates individual modules in isolation, and integration testing, which verifies the interactions between those modules.
Let’s take a real-world example of functional testing by considering a mobile banking application.
- User Authentication: In this, you want to check whether you securely log in to their mobile banking accounts. Here, the testers validate that the login credentials are correctly verified and ensure users can access their accounts securely.
- Balance Inquiry: In this, you want to check account balances and transaction history. Here, the testers perform balance inquiries, verifying that account balances and transaction histories are accurately displayed and any transactions are updated immediately.
What makes TestMu AI the right testing partner for you?TestMu AI is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000 real devices, browsers, and OS combinations thus complementing functional testing needs with its cloud-based infrastructure.
For a smooth and efficient functional testing experience you can leverage TestMu AI’s capabilities for efficient cross-browser testing, comprehensive test coverage and real-time collaboration.
Key Differences : Integration Testing vs Functional Testing
The key differences between integration testing and functional testing are important for effective software quality assurance. Knowing these differences helps testing and development teams choose the right testing approach and effectively allocate resources across development phases.
| Parameters | Integration Testing | Functional Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Testing Techniques | Grey-Box Testing | Black-Box Testing |
| Testing Complexity | It is less complex as the software modules are integrated logically and tested as a group. | It is more complex than integration testing as it tests the whole functionality of the application. |
| Focus | Interaction between integrated modules. | Issues that stop applications from performing their functionality. |
| Scope | It examines how integrated modules work as a whole. | It tests specific functions, features, or use cases. |
| Aim or Goal | Find integration issues and ensure system modules work together. | Verify that individual software features are reliable and meet user needs. |
| Testing Items | Components or modules integrated into a system. | Individual functions, features, or interfaces. |
| Level of Testing | Typically conducted after unit testing. | Often performed after unit and integration testing. |
Note: Turn Testing Complexity into Simplicity: Automate your tests across 3000+ browsers, real devices, and OS combinations. Try TestMu AI Today!
Conclusion
We have explored two testing approaches, namely integration testing and functional Testing. Integration testing mainly focuses on the harmony of software modules, and functional testing ensures user-oriented functionality. These are two indispensable pillars of quality assurance. We have examined their workflows, advantages, and disadvantages and shed light on the nuances that determine their application. At the end of this article, it is clear that a deep understanding of integration testing and functional testing enables you to create solutions that stand up testing with time.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests


