
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What is Severity?
- What is Priority?
- What is Defect Triage?
- Bug Severity and Bug Priority in Software Testing
- Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Key Differences
- Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Who Does What?
- Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Conceptual Examples
- Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Real-Time Examples
- Insights on Bug Severity and Priority Considerations
- Guidelines for Identifying Severity and Priority in Software Testing
- Bug Reports Can Take You A Long Way!
- How to Perform Debugging and Report Bugs Over the Cloud
Bug Severity and Priority: Its Difference With Examples
Learn about bug severity and priority and understand its differences, guidelines, and real-time examples. Explore insights on bug reports and more.

Nazneen Ahmad
January 13, 2026
When conducting software testing, encountering bugs is common. Understanding the severity and priority of a bug is crucial in determining its impact on the software and the user experience. Critical bugs may cause the software to crash or prevent users from accessing essential features, requiring immediate attention from the development team. On the other hand, less severe bugs may be cosmetic issues or minor inconveniences that can be addressed in future updates.
This blog aims to differentiate between bug severity and priority using real-time examples. We will cover the definitions of the terms and the significant differences between bug severity and priority with real-time examples, their types, and more.
Let us start by first understanding “severity and priority.”
What is Severity?
Severity in software testing refers to the degree of impact a bug has on the software’s functionality. It indicates how critical the bug is and its potential to impact the software or its users.
These bugs can vary in severity, from minor issues to critical problems that affect the software’s functionality or performance. Some bugs may be straightforward to understand and fix, while others can be more complex and challenging to diagnose. For example, a bug that causes the software to crash would be considered highly severe, while a minor visual glitch may be classified as low severity.
When evaluating the severity of a bug, testers consider factors such as the extent of the impact on the software, the likelihood of the bug occurring, and the ease of avoiding or recovering from the bug. Based on these factors, bugs are typically classified into several severity categories, such as
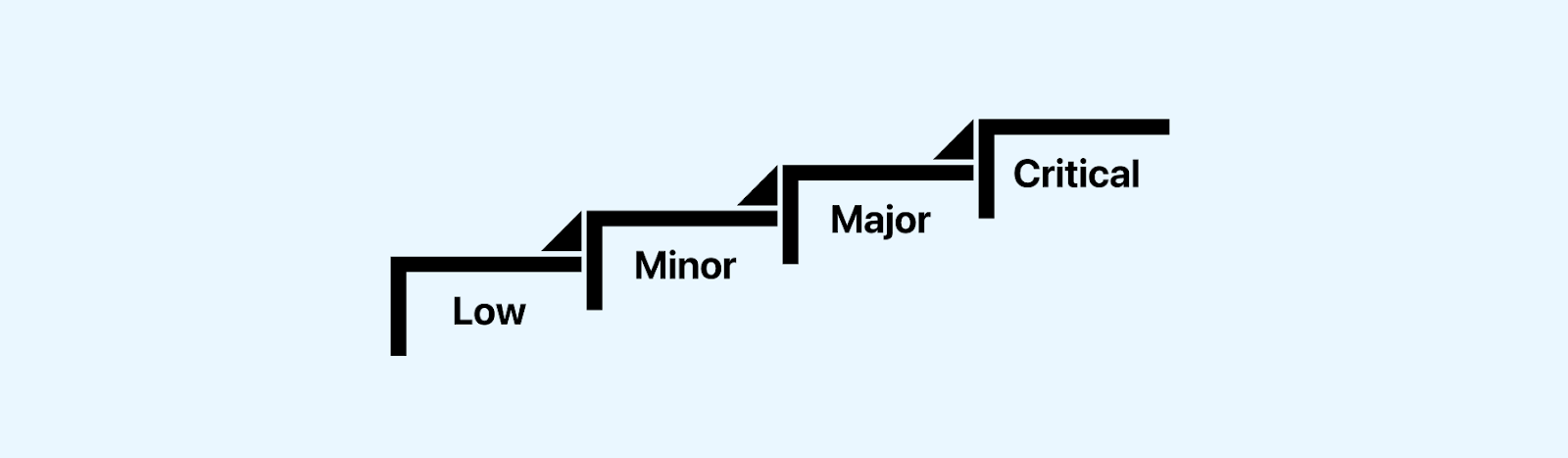
- Critical: A bug with critical severity completely halts the functionality of an application, making it inaccessible for users or testers.
- Major: When a bug impacts important system functionalities without affecting the entire application, it is classified as a bug with major severity. Unlike critical severity bugs that can cause a complete system shutdown, major severity defects do not result in such severe consequences. However, they still hinder significant and sometimes basic application functionalities from working correctly.
- Minor: Minor severity bugs deviate the application’s behavior from what is expected, but this deviation does not affect the overall functionality. Unlike major severity bugs, minor severity bugs often have a workaround, allowing functionality to continue. These bugs can usually be deferred until the next release since they do not impede the application’s functionality.
- Low: Low severity bugs are similar to minor severity bugs, which are cosmetic and do not impact application functionality or user experience (UX). Despite not affecting functionality or UX, these bugs are still considered valid and should be addressed to maintain the overall quality of the application. Examples of low severity bugs include typos, alignment issues, or color inconsistencies.
Understanding the severity of a bug is crucial for risk assessment and management. There are five severity levels, with level 1 being the highest priority:
- Level 1 – System Down/Critical Impact: Indicates a complete system failure.
- Level 2 – Significant Impact/Severe Service Downgrade: This represents a severe impact on service, although it does not cause a complete system failure.
- Level 3 – Minor Impact/Most of the System is Operational: Suggests a minor impact where most of the system remains operational.
- Level 4 – Informative/Low Impact: Denotes an issue with the low impact that is more informative.
- Level 5 – Cosmetic: Refers to cosmetic bugs that do not impact functionality or user experience.
In addition to severity, testers also consider the priority of a bug when reporting issues. Bug priority indicates the urgency with which a bug needs to be fixed, considering factors such as its severity, user impact, and business priorities. It helps ensure that critical bugs are addressed promptly while less severe issues are tackled orderly. Understanding the distinction between severity and priority in the testing process is crucial.
To effectively assess and manage risk, developers can use intelligent test generation and planning tools to quickly categorize bugs by their impact, from Critical to Low severity.
Let’s understand priority in detail in the next section.
What is Priority?
Priority in software testing refers to how quickly a bug should be fixed and erased from the website or application. Bug priority indicates the urgency for dealing with a bug based on its impact on the website or application’s functionality.
For example, consider a scenario where the organization name is misspelled on the homepage of a website. While this issue may have a low severity as it does not affect the website’s functionality, the priority for fixing it becomes high due to its visibility and potential impact on the organization’s image.
Bug priority can be classified under different categories, including the following:
- Catastrophic: Catastrophic bugs significantly impact every functionality the product offers. When such a bug occurs, it requires immediate attention and collaboration among the development team, testing team, and product managers to find the root cause and minimize further business loss.
- High: Bugs impacting the bottom line or user experience (UX) are considered high priority. These bugs can affect the entire application, requiring prompt resolution to minimize their impact. Assigning a high priority to these bugs ensures a swift resolution time, as they can significantly impact the business and user satisfaction.
While major severity bugs often correspond to high priority, this is not always true. There may be situations where a bug is of major severity but does not directly impact the bottom line or user experience, leading to a lower priority. It is essential to evaluate each defect based on its impact and prioritize accordingly.
- Medium: Bugs that do not significantly impact business or customers are classified under medium priority. These bugs are less urgent than high-priority bugs and can be addressed when the development team can handle them. They may be resolved either in the same release or the subsequent one.
- Low: Bugs with the lowest priority for resolution are addressed after all high and medium-priority bugs are fixed. The resolution for low-priority bugs is typically provided along with fixes for some high or medium-priority bugs.
Buggy software can severely impact the project’s timeline and resource allocation, leading to a re-evaluation of risk and priorities. This is why shift-left testing is gaining popularity, aiming to identify and address risks and bugs early in development. In shift-left testing, website testing begins as early as the requirement-gathering phase. Correctly prioritizing bugs is crucial for effectively planning the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
What is Defect Triage?
In software testing, triage is often associated with defects or bugs, and this process is applied to defects identified during testing to prioritize them based on their severity, risk, and other factors.
Defect triage becomes necessary when there are limited resources available to manage defects. For example, when the number of defects exceeds the available resources, triage helps resolve as many defects as possible by prioritizing them based on their severity and other factors.
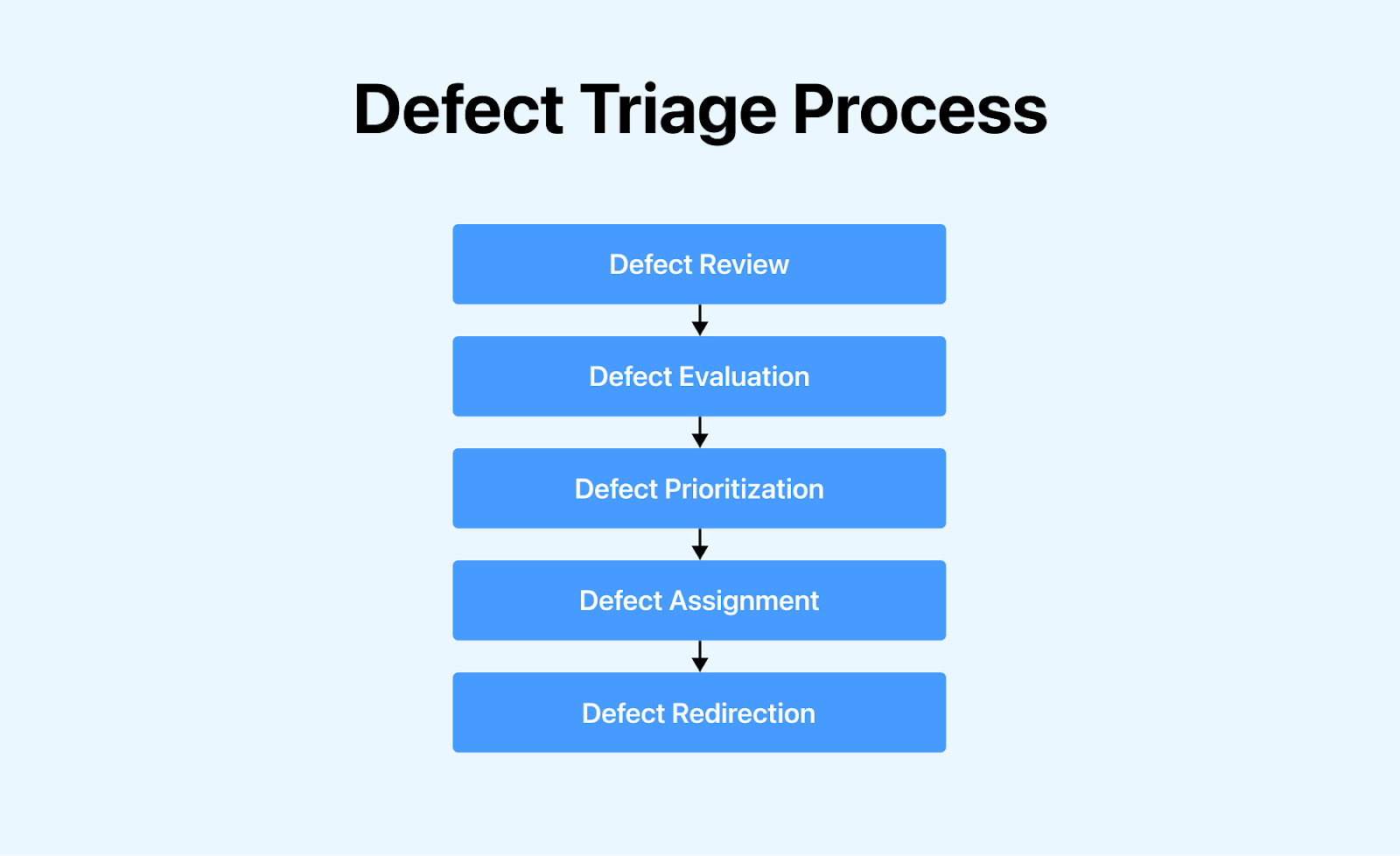
The defect triage process typically includes the following steps:
- Defect Review: Reviewing all defects, including those rejected by the team.
- Defect Evaluation: Conducting an essential evaluation of defects based on their content, priority, and severity.
- Defect Prioritization: Prioritizing defects based on the provided inputs.
- Defect Assignment: Assigning defects to the appropriate release under the guidance of the product manager.
- Defect Redirection: Redirecting defects to the relevant owner or team for further action.
By following the defect triage process, teams can enhance customer satisfaction by resolving critical defects quickly and uncovering hidden bugs in their software.
Now, let’s learn more about the severity and priority of bugs in software testing.
Bug Severity and Bug Priority in Software Testing
Bug severity, or defect severity in software testing, refers to the extent of a bug or defect’s impact on the software application under test. It measures how much the fault deviates from the expected behavior. A higher impact on application functionality results in a higher severity level. Determining the severity level of a bug or defect is typically done by a Quality Assurance (QA) Engineer, who assesses the technical aspect of the problem.
Bug priority, or defect priority, on the other hand, establishes the sequence in which bugs should be addressed. It determines whether a bug should be addressed immediately or if it can be postponed. Testers communicate the priority status to developers, specifying a timeframe for resolving the bug or defect. Higher-priority bugs or defects require immediate attention from developers. The priority status aligns with user requirements and helps prioritize bug fixes based on business impact, project timelines, and customer needs.
Both severity and priority are crucial in efficiently allocating resources and promptly addressing critical issues. By considering these factors, project managers and developers can effectively manage bugs and deliver a high-quality product to users.
Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Key Differences
In this section, let us learn more about severity and priority by highlighting their fundamental differences.

| Aspects | Bug Severity | Bug Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degree of impact a bug has on the system | Order of severity impacting the system |
| Relation | Related to standards and functionality of the system | Related to scheduling |
| Examination Criteria | Assesses the seriousness of the impact | Assesses whether the bug should be resolved promptly or can be delayed |
| Operation | Operated by functionality | Operated by business value |
| Change Likelihood | The level of severity is less likely to change | Priority may differ |
| Assessment Perspective | Technical perspective of web-application workflow | User-experience perspective of web application usage |
Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Who Does What?
Bug severity and priority are crucial in determining the importance and urgency of fixing bugs in software development. Here’s a breakdown of who does what:

- Bug Severity: Determined by Quality Analysts and Test Engineers, bug severity reflects the impact of a bug on the system’s functionality. It is assessed based on the bug’s impact on the system’s functionality, ranging from critical to low.
- Bug Priority: Assigned by Product Managers or Clients, bug priority determines the order in which bugs should be fixed based on severity and other factors. Business needs, project timelines, and user impact often influence priority.
While Quality Analysts and Test Engineers assess the severity of bugs, Product Managers or Clients determine their priority, ensuring that critical issues are addressed promptly and aligned with business goals.
Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Conceptual Examples
Below are some conceptual problems that will help you understand the concepts of severity, priority, and the actions needed:
- Problem Statement 1: Customers of an e-commerce website are experiencing issues during the checkout. After adding items to their cart and proceeding to checkout, some customers report that the total amount is incorrect or that their orders are not being processed correctly. This issue is causing customer frustration and leading to lost sales for the website.
- Severity: High (Lost sales, customer frustration).
- Priority: High (Core functionality of the website impacted, significant impact on revenue).
- Action: Investigate and fix the checkout process immediately to prevent further revenue loss and ensure a seamless shopping experience for customers.
- Problem Statement 2: Users accessing the application on older Internet Explorer versions like IE8 experience improper page loading, causing overlapping fields and text and impacting the entire application.
- Severity: High ( Improper page loading impacting the application’s usability).
- Priority: Low (Few users utilize IE8 or older versions).
- Action: Schedule a fix for the issue to align with future updates or when resources permit. Consider providing alternative solutions or workarounds for users until the fix is implemented.
- Problem Statement 3: A website’s help section or FAQ section has a theme or font style that doesn’t match the rest of the page.
- Severity: Low (Doesn’t affect the website’s functionality).
- Priority: Low (Not many users access this specific section).
- Action: The fix can be delayed as it is a low priority. Consider aligning the theme or font style with the rest of the page during a future website update.
- Problem Statement 4: There is a typo on a school website where ‘Admission Form’ is misspelled as ‘Admission From.’
- Severity: Low (No functional impact, only a typographical error).
- Priority: High (Critical for maintaining business reputation and user perception).
- Action: Immediate correction of the typo is required to uphold the professionalism and credibility of the school website.
Now that we better understand how to identify severity. Let’s discuss the critical differences between bug severity and priority with real-time examples.
Bug Severity vs. Bug Priority: Real-Time Examples
Let’s clarify the key differences between bug severity and priority with real-time examples from the perspective of a tester performing cross-browser testing. Cross-browser testing involves evaluating how a website appears and functions across various desktop and mobile browsers and their versions.
High Severity vs. High Priority
Real-Time Scenario: Imagine you’re a tester in a SaaS company, testing your site on Chrome without any issues. However, when you switch to Internet Explorer, you notice that the text iframes on the pricing page look distorted. The buttons for buying the plans and pricing information are missing based on different features. This issue makes it difficult for customers to understand the offerings and prevents them from purchasing.
- High Severity: The pricing grid is not presented to the customer, leading to a blocker in product purchase.
- High Priority: The issue needs to be resolved urgently as it is a blocker for product selling.

Prevention: Performing visual and cross-browser testing is essential to avoid such functionality and inconsistencies. Visual testing helps capture any website appearance inconsistencies across different browsers.
On the other hand, cross-browser testing ensures that the website functions correctly and appears as intended across various browsers and their versions. Combining these two testing approaches can help identify and fix browser-related issues, such as the one described in the scenario, before they affect the user experience.
High Severity vs. Low Priority
Real-Time Scenario: Imagine your website’s home page renders poorly in legacy browsers, with text overlapping or the logo failing to load. It significantly hampers the product’s functionality and user experience, indicating a high-severity bug.
- High Severity: The issue is considered high severity because it significantly impacts the functionality and user experience of the website.
- Low Priority: However, since legacy browsers account for a small percentage of visitors, resolving this issue may be considered a low priority regarding resource allocation and urgency.
For example, wix.com may not render correctly in IE8, as shown below.
Prevention: To prevent compatibility issues with legacy browsers like IE8, one practical approach is to incorporate routine compatibility checks and automated cross-browser testing by leveraging automation testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright. Conducting thorough code reviews and using feature detection techniques to adjust website behavior based on browser capabilities.
Use user-agent detection to provide specific instructions or workarounds for legacy browsers. These strategies can help catch and address compatibility issues early, ensuring a smoother user experience across browsers.
Low Severity vs. High Priority
Real-time scenario: While testing the website’s login functionality in the latest version of Google Chrome and Ind, the form fields are slightly misaligned. Although they are still editable, the visual representation is compromised.
- Low Severity: The issue is considered low severity because it does not impact the functionality of the form fields, and users can still interact with them as intended.
- High Priority: However, since it affects the visual appearance of the website, it is considered a high priority to maintain a positive user experience.
For example, the below comparison is for the login page of reddif.com, where the input fields are slightly misaligned based on the two browsers, Google Chrome with browser version 118 and Internet Explorer version 110 version. The difference is highlighted with the pink border.
Prevention: Implementing automated visual regression testing using cloud-based platforms to help catch visual issues, such as overlapping buttons, early in development. Such platforms allow you to compare visual snapshots of your website across different browser versions and screen sizes, highlighting any differences that may indicate a problem. By integrating visual regression testing into your testing strategy, you can ensure a smoother user experience and faster bug resolution.
Low Severity vs. Low Priority
Real-time scenario: You are testing a website’s home page and notice a typo error.
- Low Severity: The issue is considered low severity because it does not impact the website’s functionality. Users can still access the content and navigate the site.
- Low Priority: Since the issue is minor and would not be noticed by most users, it can be considered a low priority for resolution.

(The examples mentioned above are for demonstration purposes only. It is up to the team only to decide the severity or priority of the bug.)

Prevention: To prevent and catch typos and inconsistencies in font color, regularly review and manually inspect all text content and design elements. Use spell-check tools in content management systems for automatic correction.
Implement manual and automated testing, including visual regression and cross-browser testing, to ensure font style and color consistency across browsers and devices. Additionally, conduct accessibility testing to meet accessibility standards.
When creating a software application, it is crucial to adhere to accessibility standards to ensure it is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities. To maintain compliance with these standards, it is essential to use various accessibility testing tools. These tools help identify and fix accessibility issues, ensuring everyone, including those with disabilities, can use the application.
Insights on Bug Severity and Priority Considerations
Strategic insights are crucial to managing bugs effectively. Critical considerations for seamless bug resolution and collaborative testing efforts:
- Priority Over Severity: Communicate to the development team that high-priority defects should be addressed before high-severity ones. It ensures that critical issues impacting users are resolved promptly.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Empathize with customers and consider bugs from their perspective. Understand how a bug affects their experience and prioritize accordingly.
- Time Consideration: Evaluate the time required to fix a bug based on its criticality and the verification time needed. It helps in planning bug resolution and testing efforts efficiently.
- Understanding System Impact: Testers should understand how a bug affects the overall system functionality before assigning severity. Collaboration between development and testing teams is crucial for this.
- The Clarity in Terminology: Ensure the team understands the distinction between severity and priority. Avoid using these terms interchangeably and maintain consistency in their usage.
- Utilize Bug Tracking Tools: Use bug-tracking tools to effectively organize and manage bug reports. These tools help in tracking the status of bugs and ensure timely resolution.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Perform cross-browser testing using cloud-based platforms like TestMu AI to ensure your website works seamlessly across different browsers and versions. It helps in identifying and fixing browser-specific issues.
Guidelines for Identifying Severity and Priority in Software Testing
Some guidelines you must consider when selecting the severity in testing:
- Evaluator Roles: The Tester assesses severity while the Product Manager or Defect Triage team determines priority. This distinction is crucial for effective defect prioritization in web application or website testing, preventing confusion within the development team.
- Clear Understanding: Ensure a clear understanding of priority and severity concepts. Severity reflects the impact of a defect on the software, while priority determines the urgency of fixing it.
- Issue Type Impact: Assign severity based on the type of issue and its direct impact on priority. For example, a defect that causes a system crash would be assigned a higher severity and priority.
- End-User Impact: Understand the potential impact of a scenario or test case on the end-user. It helps determine the severity level, especially for issues affecting user experience.
- Fix Time and Complexity: Consider the time and complexity required to fix the defect and the verification time. This information helps determine the severity level, especially for defects requiring significant resources.
Note: Quickly identify, prioritize, and resolve bugs, ensuring high-quality software delivery. Try TestMu AI Today!
Severity and priority are two essential aspects of defect management in software testing.
Bug Reports Can Take You A Long Way!
Bug reports are invaluable in improving your application. Even the most successful apps receive less-than-perfect ratings. Zero-bug development is a myth. Despite rigorous testing, you can’t control the execution environment, so bugs can still occur. Therefore, collecting and analyzing user-reported bugs and assigning appropriate severity and priority levels can help you prioritize and plan future sprints more effectively.
You can use bug-tracking tools integrated with your development environment to report bugs to your team members effectively. You can use cloud-based platforms like TestMu AI, which offers seamless integration with bug-tracking tools, enhancing the process for development teams. TestMu AI is an AI-native test execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 5000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations. You can use Mark as Bug feature while performing Real Time Testing and log bugs onto your favorite project management and bug-tracking tools.
This platform allows you to easily capture screenshots, record screen videos, and provide detailed descriptions of the bug, including steps to reproduce it. Additionally, you can set the severity and priority levels directly in the bug tracking tool, ensuring that critical issues are addressed promptly. Collaborating with your team through TestMu AI streamlines the bug reporting and resolution process, leading to a more efficient development cycle.
For testers & QA looking to streamline bug reporting or generate better test cases, exploring these ChatGPT Prompts for Software Testing can greatly improve clarity, speed, and consistency in test documentation.
Benefits of Fixing Bugs with Cloud-Based Platforms
Detecting and resolving bugs is feasible in conventional software development settings and cloud-based platforms. Opting for TestMu AI can enhance the bug-fixing process in software development. Here are practical reasons for selecting TestMu AI:
- Accessibility: It enables easy access to bug-tracking tools from any location, fostering collaboration with team members and simplifying bug reporting and tracking. In contrast, traditional software development environments necessitate physical access to the bug-tracking system, restricting accessibility and impeding team collaboration.
- Scalability and Updates: It benefits from seamless updates and scalable options, allowing organizations to adapt effortlessly to evolving bug management needs. Resource scaling is also possible, ensuring effective bug tracking and resolution, even in scenarios involving a high volume of bugs. Conversely, manual updates and resource allocation are necessary in a traditional environment, complicating bug management.
- Automation Integration: It seamlessly integrates with automation tools, streamlining the detection and resolution of bugs. In contrast, conventional methods rely more on manual testing, which is less efficient and effective for bug detection and resolution.
How to Perform Debugging and Report Bugs Over the Cloud
To demonstrate how to report bugs, capture screenshots, or record sessions to identify and fix inconsistencies across various browsers and operating systems, we will perform real-time testing on TestMu AI.
To do so, we must follow some steps:
- Create a free account on TestMu AI and log in. Upon logging in, you will be redirected to the dashboard.
- Navigate to the left side of the menu and click on Real Time to begin real-time testing.
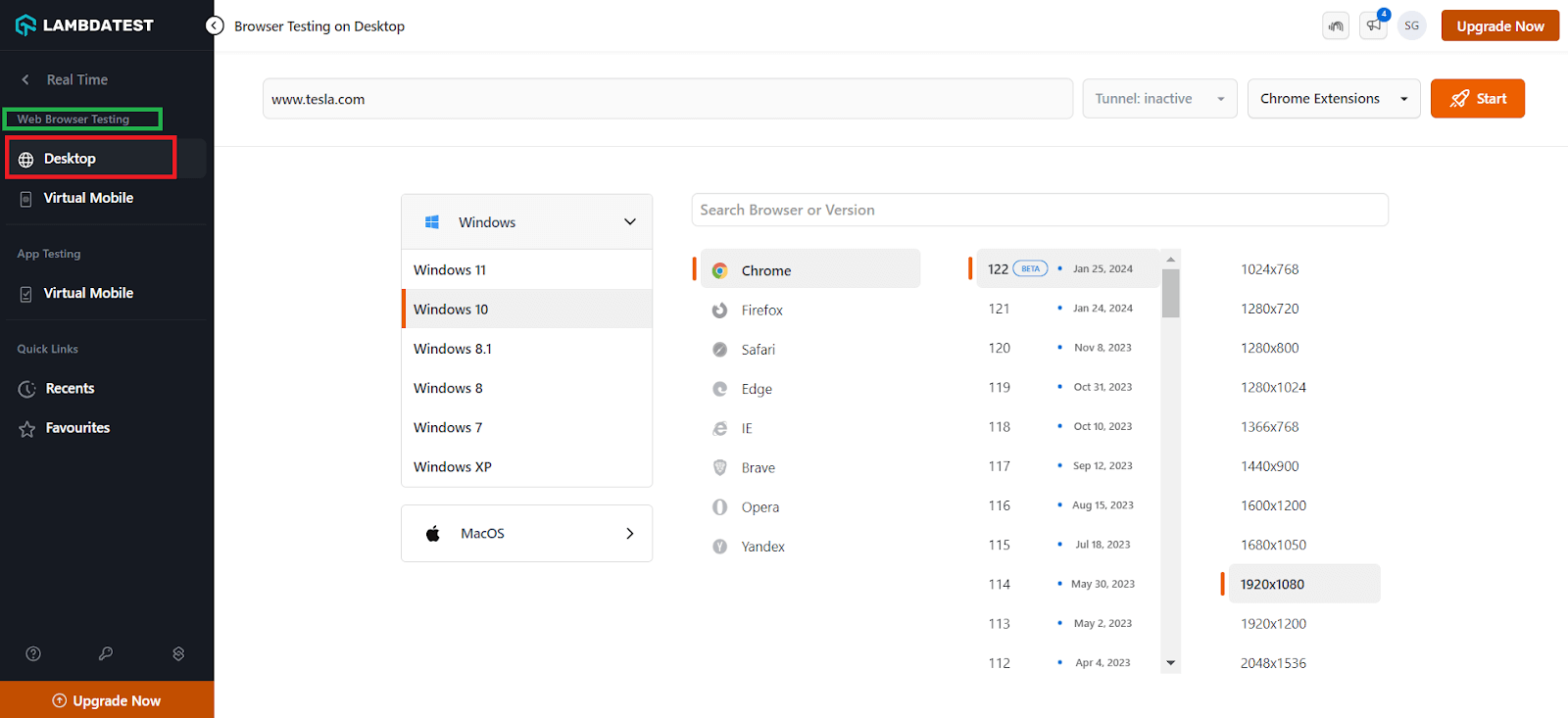
- Select the Desktop option under the Web Browser Testing menu to proceed with the real-time testing.
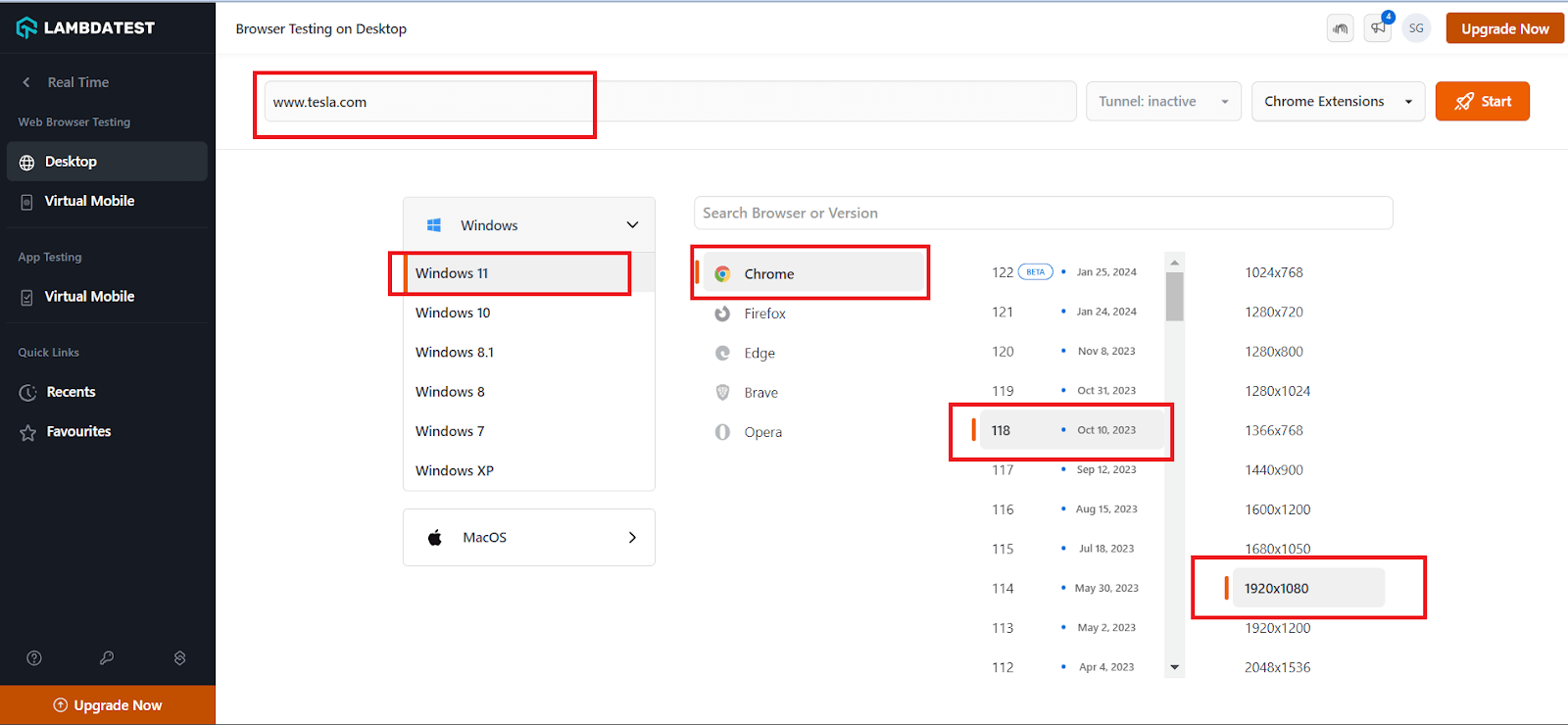
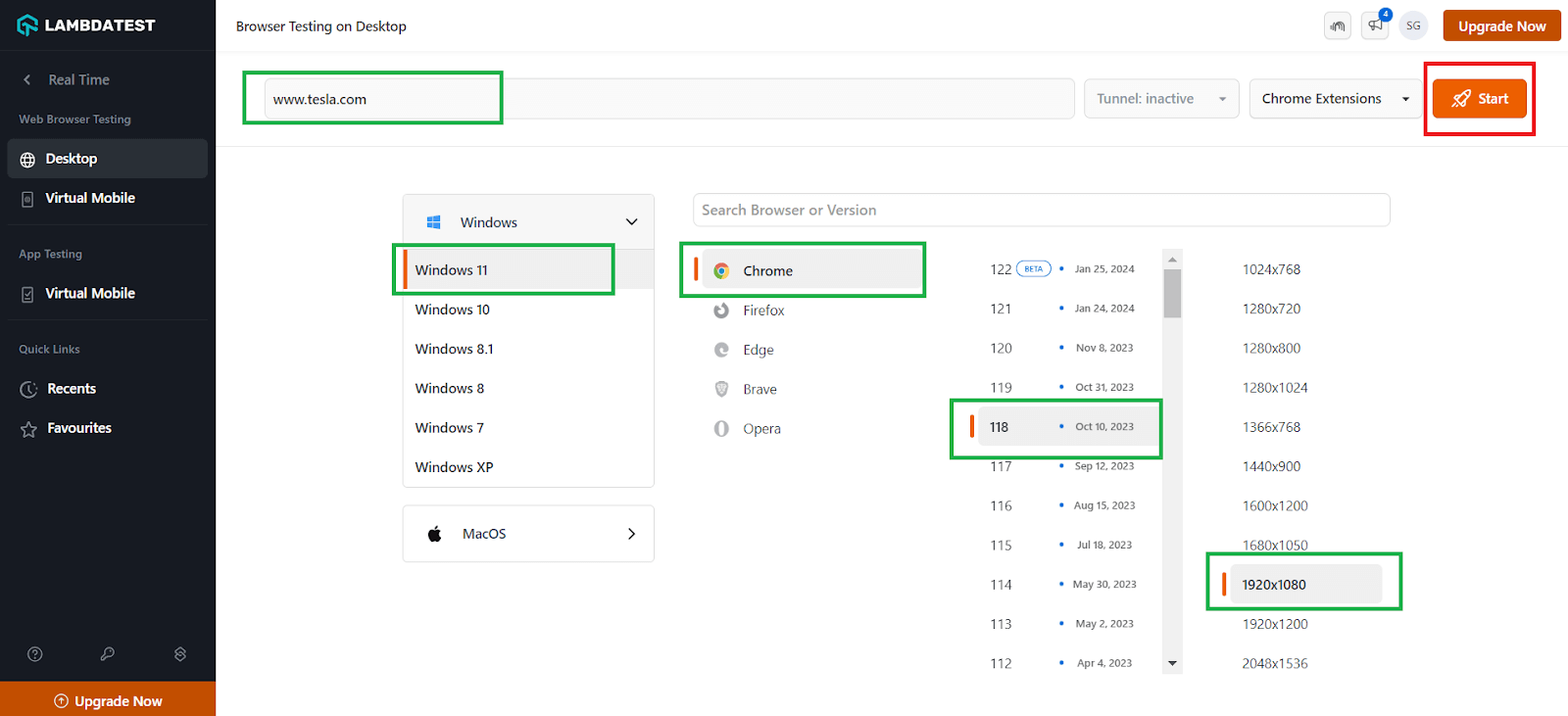
- On the right side of the panel, enter the site URL you want to test. Then, select the operating system (e.g., Windows 11), browser (e.g., Chrome), browser version (e.g., 118), and resolution (e.g.1920×1080).
- Click the Start button to launch the application on the selected configurations.
- Utilize the options in the left tool panel for testing and debugging efficiently. Explore the Mark as bug option to highlight and share bugs with the team immediately.
Allow some time for the application to launch based on your configuration. Once launched, you will see the website loaded.
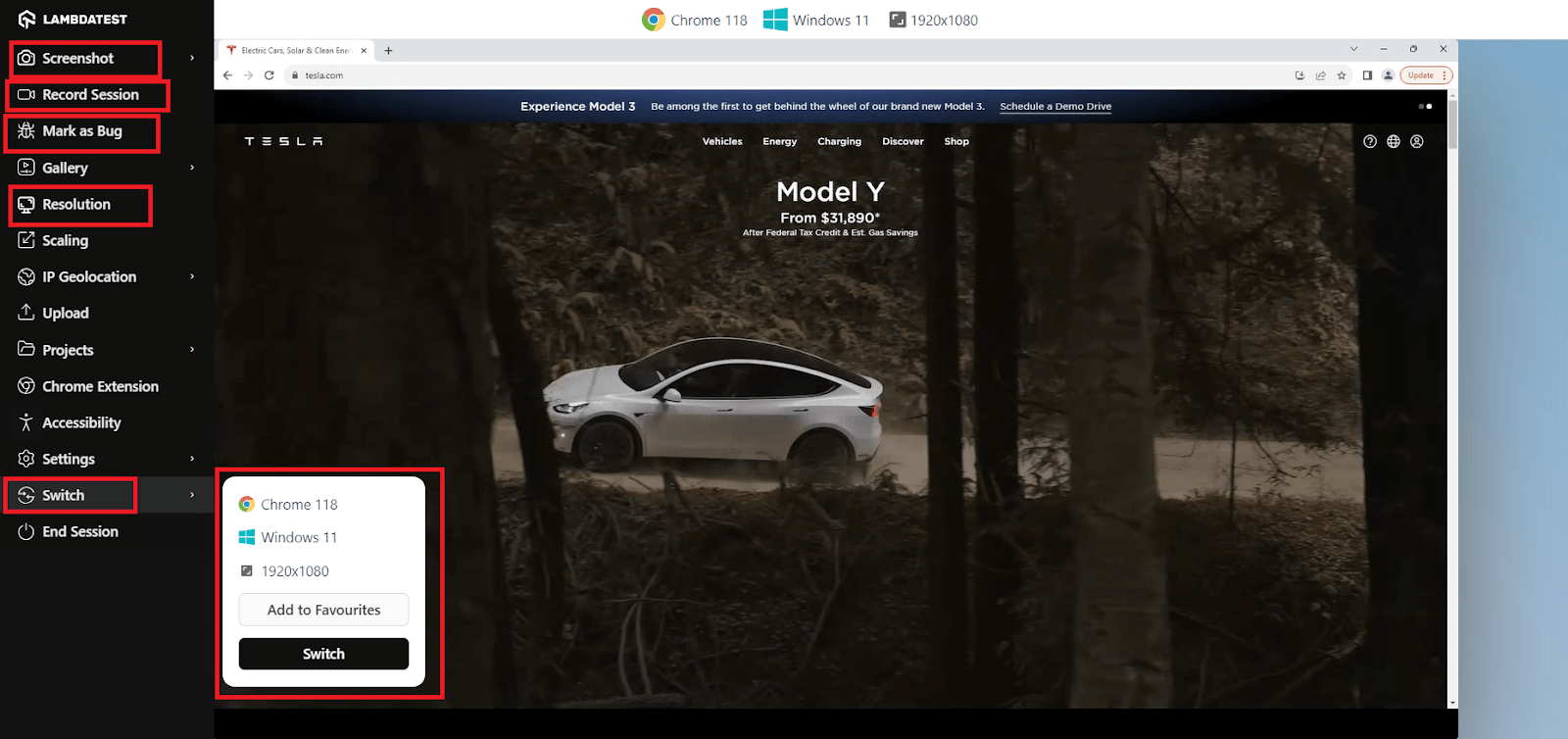
Use the Screenshot option to capture screen issues. You can also use the Record Session feature to record all your actions on the website for a better visual representation. Use the Resolution option to change the resolution on the go, helping you identify any overlapping UI elements or content. Lastly, use the Switch option to choose different operating systems, browser versions, and resolutions for testing.
With all the flexibility, TestMu AI offers features like LT Browser and LT Debug, making work easier for developers and testers.
- LT Browser: Developed by TestMu AI, LT Browser is specifically designed for testing and debugging mobile websites. The latest version of LT Browser offers enhanced debugging capabilities with multiple developer tool options. This next-generation browser enables developers to test website responsiveness on over 53+ device viewports, taking responsive testing to the next level.
To try LT Browser, simply click the button below to download the .exe file. After downloading, run the .exe file to install LT Browser and start using its features.
Check out this video tutorial for a quick start with LT Browser. It will guide you through its functionalities and make the debugging process more accessible.
- LT Debug: LT Debug by TestMu AI is a powerful free developer tool that streamlines the debugging process. It allows you to manipulate headers, whether they are request or response headers, by adding, removing, or modifying them.
Additionally, it enables actions such as blocking HTTP requests, network throttling, switching between different user agent strings, simulating web page experiences, and executing cross-domain AJAX website requests. Installing LT Debug is easy; just go to the LT Debug Chrome Extension page and add the extension. Once installed, you can start using its features without any hassle.
Learn more about the TestMu AI platform, functionality, and features to enhance your testing strategy and efficiency. Get started with a video tutorial on using the platform and making your testing journey more efficient!
Subscribe to the TestMu AI YouTube channel for more videos on Selenium testing, Playwright testing, Cypress testing, automation UI testing, and more.
Conclusion
In website development, the selection process of severity and priority can drastically affect the overall performance of the software application and, thus, should be chosen wisely. It is vital to incorporate the two terms separately in your bug-tracking process. When you have new teammates on board, they need to communicate the difference in detail so they don’t get confused later on.
I hope this article helped you determine the difference between bug severity and bug priority in detail.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




