
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What Is CI/CD Pipeline?
- Phases of CI/CD Pipeline
- Why Manual Testing Fails To Suffice in CI/CD Pipelines?
- CI/CD in Automation Testing
- Why Implement CI/CD in Automation?
- Where Do Automation Tests Fit in CI/CD Pipelines?
- How To Choose the Right CI/CD Tools in Automation Testing?
- Best Practices for CI/CD in Automation Testing
- Conclusion
What Is CI/CD in Automation Testing
Learn how CI/CD in automation testing accelerates software development, enables faster release cycles, and helps choose the right CI/CD automation testing tool.

Saniya Gazala
January 13, 2026
Many organizations adopt software development practices like Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) to ensure frequent and reliable product delivery. Regular code commits necessitate continuous testing, as neglecting this can lead to an unreliable infrastructure.
As projects and teams grow, scaling manual processes becomes increasingly challenging. A robust CI/CD pipeline relies heavily on automation testing. Building a sturdy CI/CD pipeline with automation testing is crucial for organizations, and DevOps practices can help address these challenges.
Overview
CI/CD in automation testing is a modern DevOps practice that integrates continuous integration, delivery, and deployment to ensure faster, reliable, and automated software releases. By embedding automated testing within every phase of the CI/CD pipeline, teams can detect bugs early, enhance code quality, and achieve continuous feedback and delivery cycles.
Why Implement CI/CD in Automation?
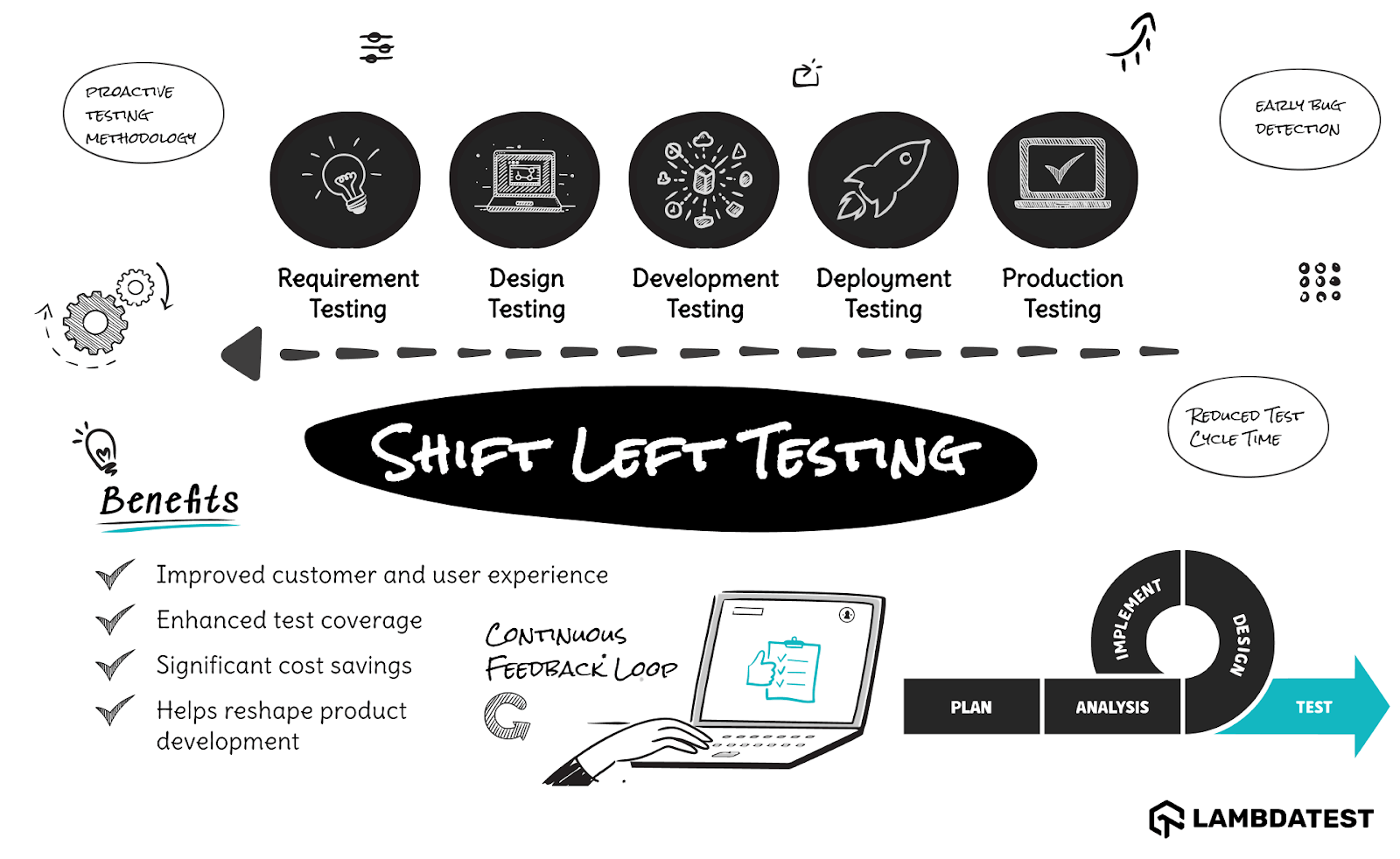
- Shift-Left Testing: Enables early bug detection during the development phase, reducing rework and costs.
- Accelerated Delivery: Ensures continuous testing and validation, improving the pace and consistency of software delivery.
- Efficient Updates: Prevents build failures and delays by automating repetitive validation processes, leading to smoother deployments.
Where Do Automation Tests Fit in CI/CD Pipelines?
Automation tests ensure build consistency, stability, and functionality throughout the CI/CD process.
- Unit Testing: Validates individual components or functions early in development to catch defects quickly.
- Integration Testing: Checks module interactions and data flow across components for reliable functionality.
- Regression & System Testing: Re-runs existing test suites after updates to ensure no new bugs are introduced and that the overall system performs correctly.
What Are the Best Practices for CI/CD in Automation Testing?
- Automate Tests & Builds: Run automated unit, integration, and functional tests for faster feedback.
- Use Version Control & Shared Pipelines: Maintain consistency with single-source builds and collaborative pipelines.
- Adopt Security-First & Parallel Testing: Integrate security checks and run tests concurrently to reduce execution time.
- Monitor Pipeline Health: Continuously measure performance, optimize workflows, and involve the entire team for sustained quality.
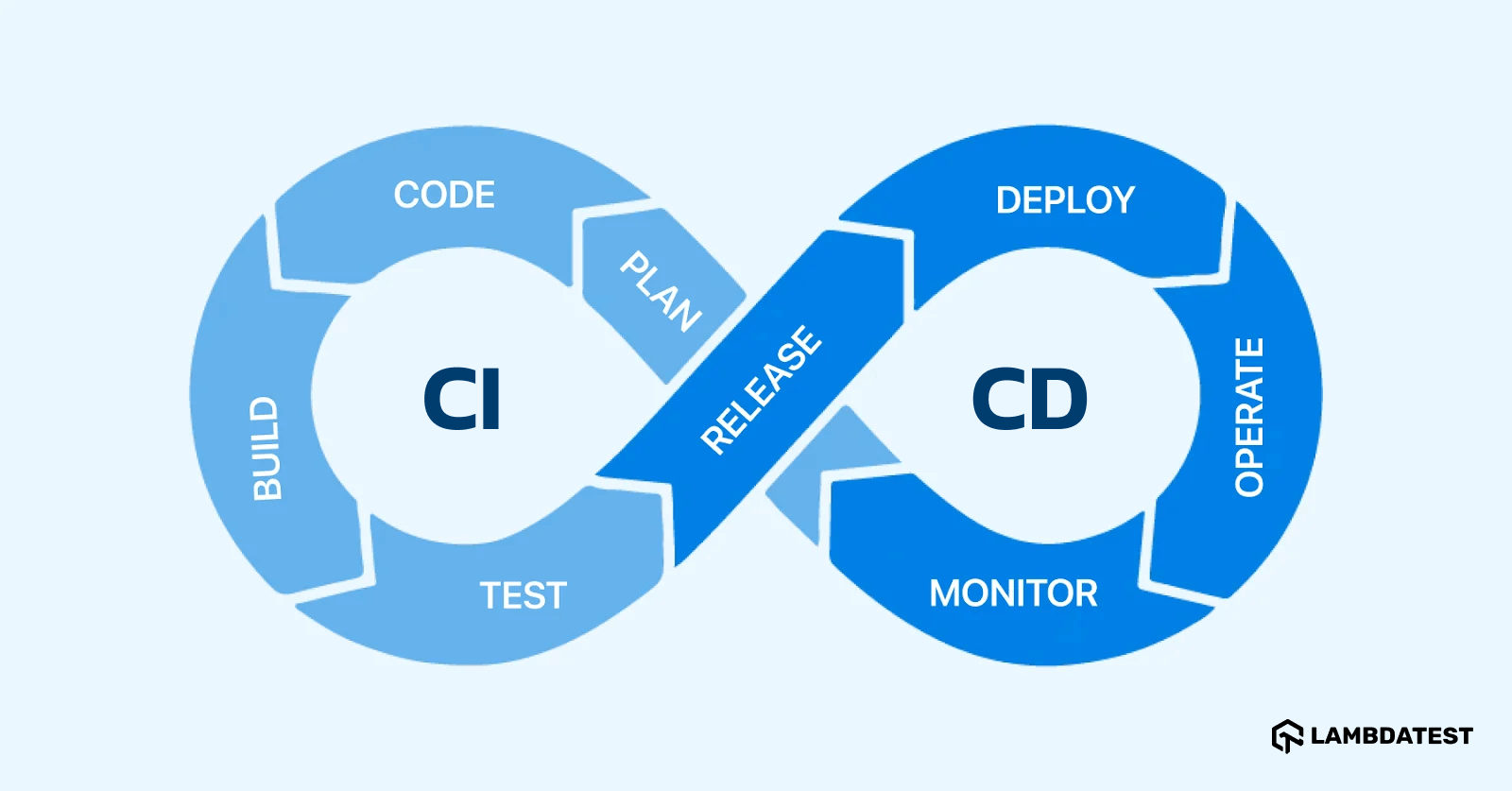
What Is CI/CD Pipeline?
A CI/CD pipeline is a set of practices that allows teams to deliver code changes more frequently. CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, or Continuous Deployment.
In a CI/CD pipeline, code changes go through various stages, such as building, testing, and deploying, where specific events, such as a code commit, trigger each stage. This pipeline helps to catch bugs early and ensure that the code is always functional and ready to be deployed into the production environment.
To learn about CI/CD in DevOps, watch this video tutorial to understand it better.
Phases of CI/CD Pipeline
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines embody the principles of Agile methodology, addressing challenges faced by earlier development models. Understanding the phases of CI/CD is crucial before adopting Agile and implementing test automation.
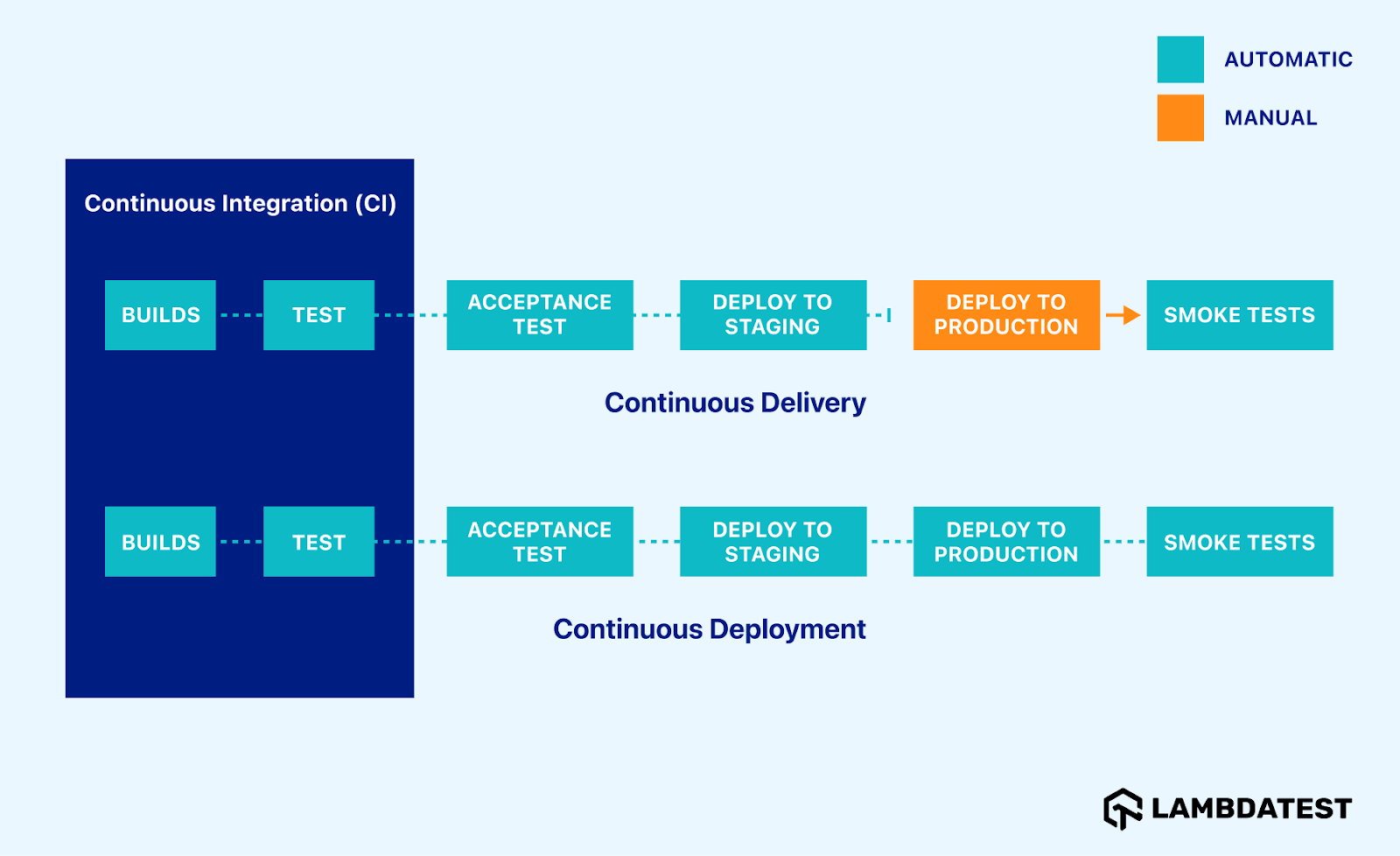
Continuous Integration (CI):
Continuous Integration emphasizes automated testing to ensure the application remains functional whenever new commits are integrated into the main branch.
Phase of Continuous Integration(CI):
- Builds: In this phase, the commits trigger the build process using appropriate CI/CD tools to create a functional module.
- Test: In this phase, regular testing is conducted to verify code changes and ensure the integrity of each build. DevOps engineers typically manage this phase.
Continuous Delivery (CD):
Continuous Delivery (CD) takes Continuous Integration (CI) a step further. While CI frequently integrates code changes, CD manually deploys these changes to testing and production environments after the build stage.
Phase of Continuous Delivery (CD):
- Acceptance Test: In this phase, the developers and testers ensure that the new changes added meet the specified requirements and criteria.
- Deploy to Staging: In this phase, the code is deployed to the staging environment for further testing and validation.
- Deploy to Production: In this phase, the code is moved manually from the staging environment to the production environment.
- Smoke Tests: In this phase, the testers perform a set of tests to check the basic functionality and stability of the application once after deployment.
Continuous Deployment (CD) takes continuous delivery further by automating deployments directly to production environments. Every code change that successfully passes all testing stages is automatically released to your users. By deploying changes directly to production, you get immediate feedback from real users, allowing for quicker iteration and improvement. Eliminating manual deployments frees developers to focus on building new features and fixes.
Why Manual Testing Fails To Suffice in CI/CD Pipelines?
Running unit tests, ensuring code quality, performing security-related tests, etc., and sharing testing information across the operation team necessitates a test-driven infrastructure. While automation testing is the standard for a robust CI/CD pipeline, occasional manual testing may still be necessary.
In CI/CD for automation testing, developers can handle small code integrations or updates more efficiently, consuming less time than manual testing.
Analyzing the pros and cons of a technical approach helps decide which tests should be automated and which ones should be manual. Repeated and labor-intensive tasks should be automated.
Different types of software testing can be automated as part of the CI/CD testing process such as unit, integration, API, functional, regression, and cross-browser testing.
It is beneficial to prioritize and differentiate these tests based on their speed and complexity. Considering this, it becomes necessary to incorporate CI/CD in the automation testing process.
To learn more about adapting your manual skills to automation, follow this detailed guide on how to move from manual testing to automation testing and get valuable insights.
CI/CD in Automation Testing
CI/CD in automation testing focuses on automating the build, test, and deployment of the applications. It adopts practices that use automation to enable the frequent and efficient delivery of applications to end users.
There are three critical components of CI/CD: Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment. These practices collectively streamline application development, ensuring optimal performance and better software quality.
CI/CD in automation testing revolves around implementing effective automation testing strategies. Automation testing is a crucial part of software development for finding bugs, ensuring stable test environment processes, and detecting any environment defects. It involves creating automated test scripts to check if new features work as expected and meet functional requirements.
These scripts can be run during each build to ensure no regressions occur, reducing manual effort and improving overall quality by catching issues early in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
The success of CI/CD in automation testing relies on quick test failure detection, timely feedback to developers, and fast issue resolution.
Here is how automation testing contributes to CI/CD:
- Automates repetitive tasks, reducing manual efforts.
- Identifies potential errors in the latest builds or application sprints quickly.
- Offers high test coverage with greater accuracy.
- Provides quick and timely feedback to developers.
- Generates multiple test results, ensuring product consistency.
- Facilitates collaboration between QA and developers, enabling them to track product development from inception.
Note: Ensure faster, reliable releases by implementing a robust CI/CD pipeline with automation testing. Try TestMu AI Today!
Why Implement CI/CD in Automation?
The objective of CI/CD in automation testing is to facilitate the Continuous Development, Testing, Delivery, and Deployment of applications. The goal is to detect and address issues quickly, allowing for rapid deployment of solutions for real-world use. Once the code is deployed to production, automation testing becomes crucial within the CI/CD pipeline and other toolsets.
Let’s explore the key factors that make CI/CD in automation testing essential:
- Gives A Boost To Shift Left Testing: The CI/CD in automation testing facilitates continuous changes with minimal delays, shortening the testing duration. This advancement supports the shift-left testing approach, which emphasizes the early detection of bugs, starting from the requirement-gathering phase of the SDLC.
According to shift-left testing, bugs discovered early in the SDLC require less cost and resource allocation than those found later. This approach can significantly improve product quality.
- Accelerating CI/CD with Automation Testing: Integrating CI/CD in automation testing enhances continuous delivery. Without it, organizations may fall short and fail to reap the full benefits of DevOps. Automated testing ensures that Quality Assurance (QA) remains continuous, reliable, and Agile, matching the rest of the DevOps automation processes and helping to accelerate DevOps practices.
- Efficient Software Updates with Automation Testing in CI/CD: Frequent software updates in a continuous delivery pipeline can lead to issues if not properly managed. Without automation testing, the testing team may struggle to address bugs quickly, increasing the risk of a polluted build with problematic code. It can impact the readability and maintainability of the code.
Skipping automation testing can also lead to delays in production and updating the build regularly.
With standardized DevOps practices, avoiding irregular and ad-hoc testing approaches is easier. Only planned and random testing with automation and proper planning can streamline the software delivery processes.
- Version Control, Roll-back, & Automated Regression TestingHere are some important aspects of implementing version control, rollback procedures, and automated regression testing within a CI/CD pipeline.
- Version Control System or Central Repository: One of the best CI/CD practices is to use a central repository where developers can push code and pull the latest updates for feature implementations or bug fixes. It keeps the code up-to-date and maintains records of changes to identify differences between versions, ensuring the builds remain maintainable.
- Handling Issues: Developers often encounter issues that need to be fixed in earlier versions or new problems that arise during the latest build. When the latest build differs from what was planned, the quickest solution is often to roll back rather than identify and fix the root causes, which can be time-consuming sometimes.
- Impact of Bugs and Roll-backs: Frequent bugs can disrupt the workflow and compromise the quality of the application. Roll-backs also affect related presentations, documents, and flow diagrams. The version control system’s seamless roll-back feature saves time and effort and mitigates potential that arises during the production or release of a build.
- Preventing Rollbacks with Automated Testing: To maximize the effectiveness of any CI/CD pipeline, it’s crucial to prevent the need for roll-backs. It can be achieved through fully automated software testing and other well-designed pipeline components. Even if a roll-back is necessary to minimize damage to user experience and brand reputation, it’s important to evaluate whether the entire web application functions correctly quickly. Automated testing within the CI/CD pipeline facilitates this quick evaluation, working like magic.
- Parallel Automation Testing in CI/CD Pipeline: The ability to run multiple test cases in parallel is indeed powerful. In an outage, roll-back with automation testing can provide relief. However, running tests sequentially takes significantly longer than parallel testing.
Parallel testing with Selenium can drastically reduce test cycles, ensuring maximum test coverage in a shorter period. Using parallel testing for CI/CD in the automation testing pipeline is crucial for performing large-scale test scripts. Pro-tip: More time-consuming tests should wait for their turn till last; hence, use them just before the code enters production.
- Maintaining Testing Environments Or Staging Environments: Using ephemeral testing environments in containers with minimal state can prevent side effects from affecting subsequent test suite runs. Containerized testing environments are portable, allowing developers to easily replicate configurations for later use in the CI/CD pipeline. They also preserve environmental fidelity, as you can easily spin up and destroy containers.
Unlike ephemeral testing environments, staging environments are meant to be durable, long-lasting replicas of production environments. They are essential for testing every change before pushing it to the live web application. But how do we test websites on different browsers locally?
Selenium plays a pivotal role in the CI/CD pipeline, facilitating the migration of changes between staging environments and ultimately to production after approval. Local automation testing into the CI/CD pipeline can minimize outages and ensure a seamless user interface and experience. This approach provides valuable insights into the appearance and functionality of your website before its official launch.
Development and Testing: Integration of IT operations with the development team forms the basis of DevOps. In this setup, developers communicate with system administrators to deploy software in production, enabling faster delivery with maximum visibility. However, automation testing plays a crucial role in DevOps. It is a prerequisite for optimizing software delivery, allowing development and operations teams to work together seamlessly. Introducing automation testing is essential to realize the true essence of CI/CD, making coordination easier between development and IT operations teams.
- Eliminating Roadblocks: Splitting testing efforts can effectively mitigate the effects of the size and complexity of larger tests, which pose a deployment risk in larger products.
Hence, smaller versions are recommended for a quick release of the build. Once you split these tests, put them in the queue and run them in parallel using automation testing for the CI/CD pipeline. It will help you establish a robust mechanism to find and eliminate tiny roadblocks.
- Better Product Visibility & Feedback: Automated tests, including unit and interface testing, offer better visibility into the product’s state at any time. Test automation for CI/CD enables developers to receive feedback quickly, allowing for prompt fixes to maintain a build in a releasable stage.
- Easy Reconfiguration With Automation Testing In CI/CD Pipeline: CI/CD in automation testing facilitates automatic reconfiguration, allowing for adjusting configurations or frameworks by introducing new technology or changing requirements. This capability contributes to the robustness of the CI/CD pipeline.
Now that we understand the importance of implementing CI/CD in automation testing, let’s learn where automation fits right in the CI/CD process.
Where Do Automation Tests Fit in CI/CD Pipelines?
As we have already learned the role of CI/CD in automation testing, it is clear that CI/CD cannot function effectively without automation.
The testing process involves running automated test scripts to check for build consistency and proper functionality. Multiple tests ensure that builds are error-free before moving them to the production environment.
You might wonder where automation tests fit in CI/CD pipelines when we mentioned that you could perform multiple tests to ensure the builds.
Here are some key tests where automation plays a crucial role in CI/CD pipelines :
- Unit Testing: This type of testing is performed by developers during the development phase. Here, individual units or components of the software application are tested to ensure they are working correctly. It helps identify and fix bugs early in the development process.
Usually, QA teams use either Test-Driven Development (TDD) or Behavioral-Driven Development (BDD) approach for writing test scripts, whereas developers write tests before writing the code to ensure the code meets the requirements.
- Integration Testing: Integration testing is conducted after unit testing. Its focus is on testing the interactions between different modules of the application. Developers and testers ensure that these modules work together correctly and meet the requirements as per the Software Requirement Specification (SRS) document. Integration testing helps identify issues related to the interface between components, data flow, and functionality.
- Regression Testing: This type of testing is performed by developers and testers to ensure that recent code changes have not affected the existing features of the application. This testing type re-runs previously executed tests to verify that the existing functionality works as expected. Regression testing is essential before releasing new application versions to ensure that new features or bug fixes do not introduce new issues.
- System Testing: This type of testing is also known as system-level testing, which involves assessing the interactions of various components within a fully integrated application. This type of testing is performed on the complete system based on functional or design requirements.
How To Choose the Right CI/CD Tools in Automation Testing?
Continuous Integration (CI), a cornerstone technique of DevOps, merges the code updates into the code repositories, but what if code repositories or integration servers transform the future? When the organization decides to change a web app into a hybrid app, similar development changes will take place that will ask for a broad array of frameworks. Adapting to testing solutions that can support the changing needs and maintain the agility of a Continuous Delivery (CD) pipeline will become inevitable.
CI/CD, when augmented by robust tooling, reduces the time to integrate changes, minimizes errors during integration, and increases project velocity. Many tools exist, ranging from free and open-source to commercial. They are all designed to support different testing types and technologies.
You can decide based on your experience, budget, and requirements. Keep looking at the pros and cons of the tool you plan to select, such as how many concurrent builds you require or how much time is needed for your data retention.
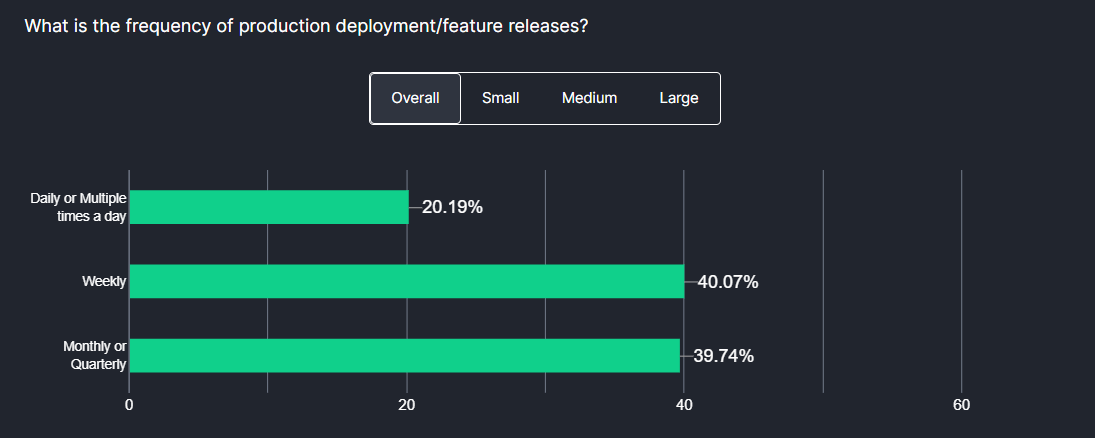
According to the Future of Quality Assurance survey, 88% of organizations have adopted CI/CD tools. These CI/CD tools adaptation enables rapid release cycles, with over 20% of organizations releasing daily and 40% releasing weekly. This is particularly true for small and medium-sized companies, which tend to have more Agile teams.
In contrast, large-scale enterprises, despite adopting CI/CD practices more widely, still have slower release cycles. Nearly half of these organizations release on a monthly or quarterly basis. While release cycles vary significantly from product to product, longer release cycles often indicate a longer turnaround time for fixing bugs.
To enhance the CI/CD process with automation testing, you can run your tests on a cloud-based platform like TestMu AI. It is an AI-native continuous testing platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 10,000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
To further enhance your CI/CD process, you can leverage TestMu AI HyperExecute, an AI-native test orchestration platform designed to accelerate automation testing speed and efficiency. HyperExecute offers intelligent features that automate and optimize the testing process, going beyond traditional cloud-based test execution.
When integrating HyperExecute with your CI/CD process, you can run your tests faster and get quicker feedback on code changes. It allows you to manage and execute large test suites in parallel, optimize resource usage to reduce infrastructure costs and ensure stable and reliable tests across various environments, enhancing software quality.
With HyperExecute in your CI/CD pipeline, you can build a strong, efficient, and scalable testing process, delivering high-quality software faster and more reliably.
Best Practices for CI/CD in Automation Testing
Adhering to CI/CD best practices is crucial for software engineering and operations teams, as it significantly influences every aspect of the development process. These practices enhance quality, increase engineer efficiency, and enable businesses to expedite the delivery of essential features.
Let’s explore how leveraging CI/CD best practices can optimize your engineering organization’s performance.
Cutting-Down Tests of Low ValuesA comprehensive CI/CD in automation testing ensures smooth production deployments by catching unexpected issues early. A fast and reliable pipeline is essential for maintaining development velocity. Scaling the CI/CD infrastructure and optimizing tests can improve efficiency. Over time, it’s wise to reevaluate the value of tests and filter out those with lower values to increase the speed of critical pipelines.
Reliable Performance Validation While performance testing can be complex and sometimes manual testing is necessary, companies often make tweaks to scale automated performance testing. Understanding the difference between performance and functional testing is crucial for tailoring a level-based test plan for automated performance testing.
Stakeholders need to grasp the limitations of performance testing, and realistic expectations can lead to positive results. In automation testing, code moves from testing to production via a staging environment. Unlike functional testing, which checks logic to determine pass or fail, performance testing sets limits based on runtime environment details.
Performance testing requires consistently appropriate infrastructure. However, if the runtime environment doesn’t support the tests’ purpose, it’s counterproductive.
Performance testing cannot occur within the CI/CD pipeline due to time constraints. Therefore, large-scale performance testing is conducted outside the CI/CD pipeline, requiring an environment identical to the production environment. Many CI/CD environments cannot support a production-like runtime environment, leading companies to opt for cloud-based testing services for mission-critical performance testing.
Effective CI/CD Implementation
Implementing CI/CD effectively is crucial for automation testing, ensuring smooth integration and continuous software delivery. By following CI/CD best practices—such as conducting automated tests at every stage of the pipeline, maintaining a comprehensive set of unit, integration, and end-to-end tests, and using reliable version control systems—teams can quickly identify and resolve issues. This approach promotes a consistent and efficient workflow, resulting in higher code quality and faster release cycles.
- Commit Early, Commit Often: Regular commits enable rapid feedback and facilitate easier testing, validation, and rollback of changes.
- Build Only Once: Rebuilding artifacts multiple times can lead to inconsistent test results. Build artifacts once and promote them through environments to ensure consistency.
- Use Shared Pipelines (DRY): Avoid duplicating CI/CD pipelines for each application or microservice. Utilize shared pipelines to reduce duplication and simplify management.
- Take a Security-First Approach: Automate security checks in CI/CD pipelines to identify and fix vulnerabilities early in development.
- Automate Tests: Automate unit, integration, and functional tests to ensure code quality and facilitate faster developer feedback.
- Keep Builds Fast: Speed up builds to provide quick feedback to developers, ideally within 5-10 minutes, to maintain productivity.
- Create Test Environments on Demand: Use on-demand test environments to ensure software reliability, reduce costs, and enable concurrent testing.
- Choose Tools that Support Your Priorities: Select CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, and more based on your specific needs, such as speed, reliability, and debugging capabilities.
- Monitor and Measure Your Pipeline: Regularly monitor and review your CI/CD pipeline performance to identify trends, optimize processes, and prevent productivity bottlenecks.
- Involve the Whole Team in CI/CD Implementation: Make CI/CD a shared responsibility to ensure that all team members understand and contribute to the process effectively.
Conclusion
By adopting your developers with a CI/CD pipeline in automation testing, you can keep up with the rapid demands of modern software testing methodologies such as Agile, Kanban, etc. A CI/CD in the automation testing pipeline empowers you to push code changes live from your Staging environment to your production environment on a monthly, weekly, and even daily basis. Splitting your tests based on complexity and effort is always a wise move. CI/CD in the automation testing pipeline helps you push your code changes from staging environments to production, along with organized version control for roll-back scenarios. If you are running an exhaustive test suite, then parallel testing can help you save a considerable amount of time. Adios!
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



