
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- Key Salesforce Terminologies
- What Is Salesforce Testing?
- Why Is Salesforce Testing Crucial?
- Types of Salesforce Testing
- How to Perform Salesforce Unit Testing?
- How to Perform Salesforce Testing Using TestMu AI?
- Top Salesforce Testing Services and Tools
- Salesforce Testing Challenges
- Best Practices in Salesforce Testing
- Future Trends in Salesforce Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- An Ultimate Guide to Salesforce Testing
An Ultimate Guide to Salesforce Testing
Check out this complete Salesforce testing guide with practical steps, essential tools, and best practices to ensure reliable CRM performance.

Salman Khan
January 27, 2026
If you rely on Salesforce to manage customer relationships, sales, and operations, testing is no longer optional. Salesforce testing ensures your CRM runs seamlessly, keeps data consistent, and gives users the confidence to work without interruptions.
The platform itself evolves rapidly with seasonal releases, and your own org adds layers of custom logic, automation, and third-party applications. Each new addition raises the risk of workflow breaks, which makes Salesforce testing a critical control point.
Overview
Salesforce testing ensures that your customizations, automations, and integrations work as expected, minimizing risks and maintaining a smooth user experience.
Importance of Salesforce Testing
- Quality Assurance: Catch errors in Apex code, workflows, and Lightning components before deployment.
- Data Integrity: Ensure accurate handling of records and automated processes.
- Seamless Integrations: Validate third-party apps, APIs, and connected systems without disrupting production.
- Compliance and Security: Test permissions, roles, and sharing rules to maintain proper access controls.
- Reduced Risk: Avoid downtime, errors, or business disruptions caused by faulty customizations.
Types of Salesforce Testing
- Unit Testing: Test individual Apex classes, triggers, and components for correct functionality.
- Integration Testing: Ensure smooth interaction between Salesforce and external systems or apps.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Confirm that features meet business requirements from an end-user perspective.
- Regression Testing: Verify that new changes don’t break existing functionality.
- Performance Testing: Check the system handles expected workloads efficiently.
Tools for Salesforce Testing
- TestMu AI: Cloud-based platform for cross-browser testing (manual and automated), supporting Selenium integration for scalable Salesforce testing.
- Provar: Salesforce-native tool with a point-and-click interface, supporting UI and API testing, ideal for both technical and non-technical users.
- Copado: DevOps platform with automated testing, continuous integration, and delivery for reliable Salesforce deployments.
- ACCELQ: No-code AI-powered platform offering codeless UI/API testing, release alignment, and collaboration for Salesforce applications.
- Selenium: Popular open-source tool for automating web browsers, compatible with multiple browsers and operating systems.
Key Salesforce Terminologies
Understanding Salesforce starts with learning its vocabulary. These are the building blocks that shape how data, automation, and user experiences are designed inside the platform.
- Objects: Containers for data in Salesforce, similar to tables in a database. Examples include Accounts, Contacts, and Opportunities.
- Fields: Individual pieces of data within an object, like columns in a table. Can be standard or custom.
- Records: Single entries in an object; each record represents an instance, like one account or contact.
- Page Layouts: Define how fields, sections, and buttons are arranged on a record’s interface.
- Workflows: Automation rules that trigger actions such as email alerts or field updates when conditions are met.
- Process Builder: A tool for building more advanced automation, including multiple if/then actions.
- Flows: Flexible automation for guided screens, approvals, and complex business processes.
- Validation Rules: Rules that enforce data integrity by preventing invalid or incomplete data entry.
- Apex: Salesforce’s proprietary programming language for custom logic and advanced automation.
- Lightning Components: Reusable modules used to build dynamic interfaces in Salesforce Lightning Experience.
- Sandbox: A Copy of a Salesforce environment used for development, testing, or training without affecting live data.
- Salesforce Object Query Language (SOQL): A query language similar to SQL, used to retrieve Salesforce data.
- Chatter: Salesforce’s collaboration tool for posting updates, sharing files, and team communication.
- AppExchange: Salesforce’s marketplace for third-party apps and integrations that extend platform functionality.
By understanding these fundamentals, testers can better design test cases, identify potential issues, and ensure that Salesforce implementations run smoothly. This knowledge also provides a solid foundation for tackling common Salesforce interview questions when preparing for testing or admin roles.
What Is Salesforce Testing?
Salesforce testing is the process of making sure your Salesforce environment works as intended after any change. These changes can be new code deployments, configuration updates, or integrations with external tools. Testing validates that the Salesforce platform continues to perform reliably without introducing errors into daily operations.
The scope of Salesforce testing includes:
- Customizations: Make sure the workflows, automation, and Apex logic you build behave exactly as intended.
- Integrations: Check that your connections with external apps and middleware continue to run without errors.
- Salesforce Updates: After every seasonal release, ensure your existing functionality stays stable.
- Data Consistency: Verify that records, fields, and reports in your org remain accurate and reliable.
- User-Facing Processes: Ensure that the CRM experience you deliver to your teams remains efficient and dependable.
Why Is Salesforce Testing Crucial?
If you rely on Salesforce to manage customer relationships, sales, and operations, testing is essential. Salesforce testing ensures that your CRM functions reliably, data remains accurate, and workflows work without interruption.
Here are the key reasons why Salesforce testing is essential:
- Platform Evolution: Salesforce delivers three major releases each year, and testing confirms that your functionality continues to perform as intended.
- Complex Customizations: With proper validation, workflows, automation, and Apex code function together without conflict.
- Data Reliability: Consistent testing supports accurate reports and dashboards that leadership can trust for decision-making.
- User Productivity: A reliable CRM environment empowers your teams to work efficiently and stay focused on outcomes.
- Third-Party Integrations: Testing ensures applications and middleware exchange data accurately to keep processes running without any interruptions.
Note: Test your Salesforce websites across 3000+ desktop & mobile browsers. Try TestMu AI Now!
Types of Salesforce Testing
Testing Salesforce isn’t just about meeting a deployment requirement. Because the platform combines custom code, configurations, and integrations with external tools, you need a layered approach to ensure stability and trust.
Below is a clear framework that covers the major testing types, when to use them, and why they matter.
Unit and Component Testing
This is where quality starts. Developers perform unit testing for Apex code, Lightning Web Components, and Flows.
- Apex tests check triggers, classes, and batch jobs. Salesforce enforces at least 75% code coverage before anything moves to production.
- Lightning Web Component tests use Jest to verify rendering, data binding, and user interactions.
- Flow tests validate automation logic. Complex Flows should be tested with multiple input variations.
Purpose: Catch defects early and validate that the smallest building blocks of your solution work as intended.
Business Process and Functional Testing
Once the pieces are in place, you need to see how the system supports real business operations.
- Functional testing ensures page layouts, validation rules, workflows, and approvals work according to requirements.
- Regression testing re-checks existing functionality after updates or deployments.
- Smoke testing provides a quick confidence check that core actions (like creating a record or running a report) still function.
Purpose: Ensure that day-to-day processes remain reliable and consistent.
Integration and Data Testing
Salesforce rarely stands alone. It often connects with ERP, billing, or marketing platforms, and these connections must be verified.
- Integration testing checks APIs, middleware, and event-driven processes.
- End-to-end testing validates workflows that cross system boundaries.
- Data migration testing ensures clean imports, accurate mapping, and complete reconciliation when moving data from legacy systems.
Purpose: Ensure that information flows correctly across systems and data quality remains intact.
Non-Functional Testing
Beyond “does it work,” you need to ask “does it perform, scale, and stay secure?”
- Performance testing evaluates response times and scalability under load.
- Security testing validates access permissions, authentication, and data protection.
- Resilience testing simulates failures (like API outages) to confirm the system can recover gracefully.
Purpose: Ensure Salesforce meets expectations for speed, safety, and reliability.
User Acceptance and Production Testing
Finally, testing comes back to the people who actually use Salesforce.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) allows business users to validate that Salesforce supports their real-world tasks.
- Production verification testing takes place after go-live to ensure deployments succeeded.
- Seasonal release testing is critical because Salesforce delivers three updates each year (Spring, Summer, Winter). Running regression tests during these windows helps prevent unexpected disruptions.
Purpose: Build confidence among end users and maintain stability through Salesforce’s continuous evolution.
How to Perform Salesforce Unit Testing?
Consider you run a store and want to give discounts. If a customer buys something worth 1000 and you give a 10% discount, the final price should be 900.
Let’s write a unit test in Salesforce that calculates this correctly and then test it.
Code to Test (Apex Class):
This is the class that calculates the discount.
public class DiscountService {
public static Decimal applyDiscount(Decimal amount, Decimal percent) {
if(amount == null || percent == null) {
throw new AuraHandledException('Amount and percent are required');
}
return amount - (amount * (percent / 100));
}
}Code Walkthrough:
- Takes two numbers: amount and percent.
- If either is missing, it throws an error.
- Otherwise, it subtracts the discount and gives back the final price.
The Unit Test (Test Class):
Now we create a test class to check if the above method really works.
@isTest
public class DiscountServiceTest {
@isTest
static void testApplyDiscount() {
// Step 1: Set up input values
Decimal amount = 1000;
Decimal percent = 10;
// Step 2: Call the method we want to test
Decimal result = DiscountService.applyDiscount(amount, percent);
// Step 3: Verify the result is what we expect
System.assertEquals(900, result, '10% discount on 1000 should return 900');
}
}Code Walkthrough:
- @isTest tells Salesforce this is a test class.
- Give the method inputs (1000 and 10).
- Run the discount method.
- Check if the output is exactly 900.
If the method works, the test passes. If not, it fails.
Test Execution:
1. Go to Setup > Apex Test Execution.
2. Select DiscountServiceTest.
3. Click Run.
4. Look at the results:
- Green = test passed.
- Red = test failed.
How to Perform Salesforce Testing Using TestMu AI?
For manual and automated testing, you can opt for cloud testing platforms like TestMu AI. It lets you test your Salesforce websites and web applications across more than 3000 desktop and mobile browsers without the need to maintain local infrastructure.
TestMu AI provides a scalable Salesforce testing cloud where you can run both manual tests (for real-time cross-browser checks and responsive validation) and automated tests (using Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, or Salesforce-specific frameworks).
Manual Salesforce Testing
1. Log in to TestMu AI and click Real Time.
2. Pick the browser, browser version, OS, resolution, or mobile device you want to test.
Enter your Salesforce URL (sandbox, production, or login page). If your org is behind a firewall, use the TestMu AI Tunnel to connect securely.
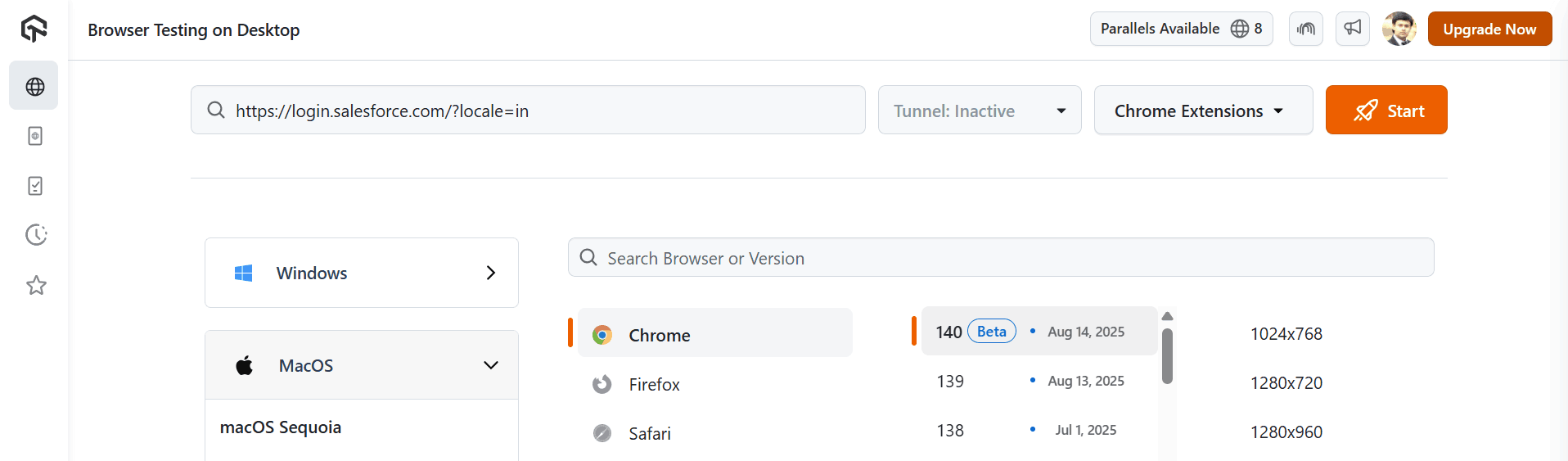
3. Run interactive tests by navigating across Salesforce modules, validating Lightning components, dropdowns, modals, and custom UIs. You can also check workflows for different user roles and verify responsiveness across devices and screen sizes.
For instance, the below snap shows testing of the Salesforce Login page.
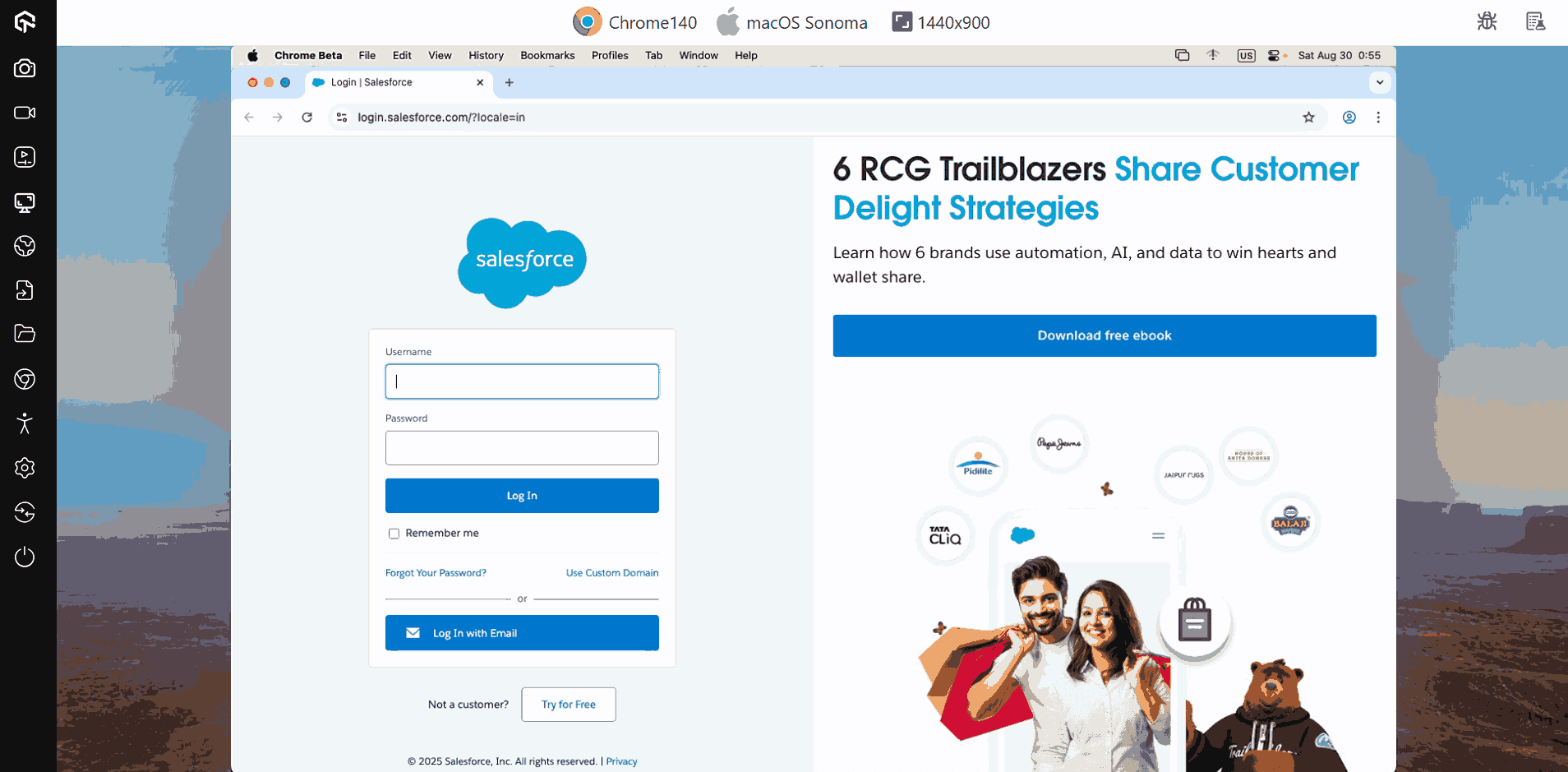
You can capture screenshots, mark bugs, or record videos directly within TestMu AI and push them to tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana.
In addition, you can perform UAT of Salesforce websites with real device cloud and test websites in real-world environments.
For more information on real-time testing features, check out this guide on desktop browser testing with TestMu AI.
Automated Salesforce Testing
TestMu AI provides a scalable automation testing cloud purpose-built for Salesforce websites and web applications. As your teams and projects grow, the platform grows with you, letting you run tests in parallel at any scale.
With TestMu AI, you can automate Salesforce testing using automation testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright and more.
Before you can run automation tests on TestMu AI:
- Get your Username and Access Key from your TestMu AI Profile > Account Settings > Password & Security. These credentials allow your test scripts to authenticate and connect securely to the TestMu AI cloud.
- Next, you need the Hub URL and automation capabilities. The Hub URL follows this format:
https://<username>:<access_key>@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hubIn addition, you need to define the automation capabilities in your test script, specifying details such as the browser, operating system, browser version, build name, and test name. These capabilities tell TestMu AI what environment to provision before initializing the RemoteWebDriver for your Salesforce web tests.
You can generate these capabilities from the TestMu AI Automation Capabilities Generator.
Here is the Selenium test script for the Salesforce Login page that validates the page loads successfully in the specified browser, OS, and version on TestMu AI.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class SalesforceLoginTest {
public static final String USERNAME = "YOUR_LT_USERNAME";
public static final String ACCESS_KEY = "YOUR_LT_ACCESS_KEY";
public static final String GRID_URL = "https://" + USERNAME + ":" + ACCESS_KEY + "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ChromeOptions browserOptions = new ChromeOptions();
browserOptions.setPlatformName("Windows 10");
browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("latest");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", USERNAME);
ltOptions.put("accessKey", ACCESS_KEY);
ltOptions.put("project", "Salesforce Login Test");
ltOptions.put("selenium_version", "4.0.0");
ltOptions.put("w3c", true);
browserOptions.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(GRID_URL), browserOptions);
driver.get("https://login.salesforce.com/?locale=in");
driver.findElement(By.id("username")).sendKeys("[email protected]");
driver.findElement(By.id("password")).sendKeys("Tvh123");
driver.findElement(By.id("Login")).click();
System.out.println("Login Error Message: " + driver.findElement(By.id("error")).getText());
driver.quit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}To get started, check out this guide on Selenium testing with TestMu AI.
Top Salesforce Testing Services and Tools
Selecting the right testing tool is crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of your Salesforce applications. Below are some of the top Salesforce testing tools widely used in the industry:
- TestMu AI: It is a cloud-based platform offering cross browser testing (both manual and automated) on over various real browsers and OS combinations. It supports integration with tools like Selenium, enabling scalable automated testing for Salesforce applications.
- Provar: It is a Salesforce-native test automation tool that offers a point-and-click interface, making it accessible for both technical and non-technical users. It supports UI and API testing and integrates seamlessly with Salesforce metadata.
- Copado: It is a comprehensive DevOps platform for Salesforce that includes automated testing capabilities. It supports continuous integration and delivery, ensuring that your Salesforce applications are always in a deployable state.
- ACCELQ: It is a no-code, AI-powered test automation platform optimized for Salesforce. It offers codeless UI and API testing, real-time release alignment, and collaborative features, enhancing test efficiency and collaboration.
- Selenium:It is one of the popular Salesforce automation testing tools for automating web browsers. While it requires programming knowledge, it offers flexibility and is compatible with various browsers and operating systems.
Looking to get started? Check out this guide on what is Selenium.
Salesforce Testing Challenges
Testing Salesforce applications presents unique challenges due to its complex workflows, customizations, and cloud-based architecture. Ensuring quality requires targeted strategies and attention to platform-specific limitations.
Here are the main challenges you may face during Salesforce testing:
- Customization Complexity: Salesforce orgs often have extensive custom objects, fields, and triggers. Testing needs to account for both standard and custom logic to prevent unexpected issues.
- Integration Dependencies: Salesforce frequently integrates with external systems. These connections can cause delays, failures, or data inconsistencies, making testing more complicated and requiring mock services or sandbox testing.
- Data Volume and Quality: Testing with realistic datasets is critical. High data volume can affect performance, while incomplete or inconsistent data may lead to false test results.
- Limited Test Execution in Sandboxes: Salesforce sandboxes may not perfectly mirror production, and some processes like workflow rules, email alerts, or third-party integrations might behave differently, introducing risk during deployment.
- Automated Testing Constraints: Tools like Salesforce DX or Selenium have limitations, especially for UI automation in Lightning components. Test automation scripts must be carefully maintained to avoid brittleness.
- Release Management Challenges: Frequent Salesforce updates and seasonal releases require regression testing. Failing to test thoroughly can break existing functionality.
- Security and Access Controls: Profiles, permission sets, and sharing rules complicate testing. Testers must ensure different roles can access only appropriate data and workflows.
Best Practices in Salesforce Testing
Implementing effective testing practices in Salesforce ensures higher quality releases, fewer defects, and smoother adoption of new features. Following structured strategies can help mitigate platform-specific challenges.
Here are some key best practices to follow in Salesforce testing:
- Use Sandbox Environments Effectively: Leverage full, partial, and developer sandboxes for different testing needs. Keep sandboxes updated with relevant metadata and representative data to mirror production scenarios.
- Prioritize Automated Testing: Implement automated test scripts using Salesforce DX, Selenium, or other compatible tools for repetitive regression and integration tests. Automation improves consistency and accelerates testing cycles.
- Maintain Test Data Management: Use anonymized, masked, or synthetic datasets that reflect production data patterns. Ensure tests cover edge cases, large data volumes, and data integrity scenarios.
- Focus on Integration Testing: Test all connected systems thoroughly. Use mock services when real integrations are unavailable to validate workflows and data flows across platforms.
- Leverage Declarative and Programmatic Testing: Combine declarative testing (flows, validation rules) with Apex unit tests. Maintain high code coverage without relying solely on automated scripts.
- Monitor Releases and Regression Risks: Track Salesforce seasonal releases and apply regression testing proactively to catch potential breaks before deployment.
- Implement Role-Based Testing: Verify security, profiles, and permission sets. Ensure different user roles have appropriate access to data and functionalities.
Future Trends in Salesforce Testing
Salesforce testing is evolving rapidly as new technologies and methodologies emerge. Staying ahead of these trends helps organizations maintain high-quality applications, improve efficiency, and adapt to complex Salesforce environments.
Here are some key trends shaping the future of Salesforce testing:
- AI Testing: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly used to automatically generate, execute, and maintain test scripts, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy across Salesforce workflows.
- Shift-Left Testing: Testing is moving earlier in the development lifecycle. Continuous integration pipelines now incorporate Salesforce testing from the earliest stages, helping catch defects sooner and reduce deployment risks.
- Low-Code and Codeless Automation: Codeless testing tools are gaining traction, allowing non-technical users to create and run tests efficiently. This trend democratizes testing and accelerates release cycles for Salesforce applications.
- Enhanced Test Data Management: Advanced strategies like synthetic data generation, masking, and automated refreshes will become standard to ensure realistic, secure datasets for Salesforce testing without relying directly on production data.
- Cloud-Native and Cross-Browser Testing: As Salesforce continues expanding on cloud platforms, testing across multiple browsers, devices, and geographies will become more automated and integrated within cloud-based testing platforms.
- Integration of DevOps and Continuous Testing: DevOps practices will further merge with Salesforce testing, enabling seamless CI/CD pipelines, automated regression testing, and faster feedback loops to support Agile development.
- Focus on Security and Compliance: With increasing data regulations, automated checks for security, privacy, and compliance will become an integral part of Salesforce testing, ensuring protection and regulatory adherence.
For instance, Generative AI testing tool like TestMu AI KaneAI allows users to plan, author and evolve end-to-end tests using natural language commands, helping non-technical stakeholders to get started with Salesforce automation testing.
Conclusion
Effective Salesforce testing is essential for ensuring high-quality releases and reliable application performance. By following best practices, leveraging the right tools, and understanding unique platform challenges, teams can significantly reduce defects and deployment risks.
Embracing trends like AI test automation, low-code test automation tools, and robust test data management helps organizations stay ahead. A strategic testing approach ensures smoother releases, stronger user confidence, and a more stable Salesforce environment for business-critical processes.
Citations
- Salesforce : https://www.salesforce.com/in/
- Salesforce Smart Testing Best Practices : https://appexchange.salesforce.com/image_host/7c1bb965-eea7-40c6-a0be-7132760e36f9.pdf
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




