Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Selenium RC: A Look Back At Its Influence on Test Automation
Explore Selenium RC's impact on test automation — understand its legacy and how it paved the way for current testing frameworks.

Ayush Mishra
January 11, 2026
Ensuring that apps work smoothly across several platforms and browsers is crucial in software development. If entrusted alone to humans, this task requires enormous effort. This is where automation testing steps in as a game-changer.
When it comes to automating web application testing, there are many frameworks to consider, such as Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, Puppeteer, etc. Among these, Selenium stands out as a widely adopted test automation framework. It specializes in automating web browsers and offers compatibility with various programming languages such as Java, Python, C++, Ruby, etc.
We will look at what Selenium RC (Remote Control) is and briefly look at its components. After examining the limitations of Selenium RC, we will focus on the improvements made by Selenium WebDriver and see what makes it better. Finally, we’ll go over the main differences between WebDriver and Selenium RC to provide readers with an in-depth understanding of these essential components in automated testing.
If you’re looking to improve your Selenium interview skills, check out our curated list of Selenium interview questions and answers.
Overview
Selenium RC (Remote Control) is an early Selenium tool for automating web testing. It allows scripts in multiple languages to control browsers remotely, simulating user actions and enabling flexible cross-browser testing.
What are the Components of Selenium RC?
Selenium RC consists of two main elements, the Server and Client Libraries, each enabling automated browser testing effectively.
- Selenium Server: Selenium Server functions as a bridge between test scripts and browsers. It injects Selenium Core into browsers, interprets commands, executes them, and returns results efficiently.
- Client Libraries: Client libraries enable test scripts to run Selenium commands in various languages. They communicate with the Server, receive execution results, and pass them back for processing.
Why Is Selenium WebDriver Better Than Selenium RC?
Selenium WebDriver is faster, more efficient, and reliable than Selenium RC. It directly interacts with browsers, supports complex user actions, and uses a simpler API for accurate, maintainable test automation.
- Smaller and Compact API: Selenium WebDriver’s API is more object-oriented than Selenium RC API, making it easier to work with Selenium WebDriver.
- Improved Emulation of User Interactions: Selenium WebDriver prioritizes simulating user interactions more closely than Selenium RC. It uses native events whenever possible, providing a more accurate simulation of how users interact with websites and applications.
- Advanced User Interaction APIs: Selenium WebDriver offers advanced user interaction APIs compared to Selenium RC, enabling the modeling of complex interactions with websites. This allows for more comprehensive and realistic testing scenarios.
- Strong Support from Browser Vendors: Major browser vendors like Opera, Mozilla, and Google actively contribute to WebDriver’s development. This leads to built-in support for WebDriver within the browsers themselves, ensuring tests run efficiently and stably.
What is Selenium RC?
Selenium RC, or Remote Control, is an essential component of the Selenium. To automate web UI tests, testers and developers can write automated test scripts in various programming languages, such as Java, Perl, C#, Python, etc.
Setting up Selenium can be tricky, but don’t worry! You can follow this Guide To Download Selenium and set it up on IDEs like Eclipse and IntelliJ.
Learn how to automate tests with Selenium IDE.
Components of Selenium RC
Selenium RC Architecture has two key components: Selenium Server and Client Libraries. Let’s see how both the components operate and the role each plays in running the test scripts.
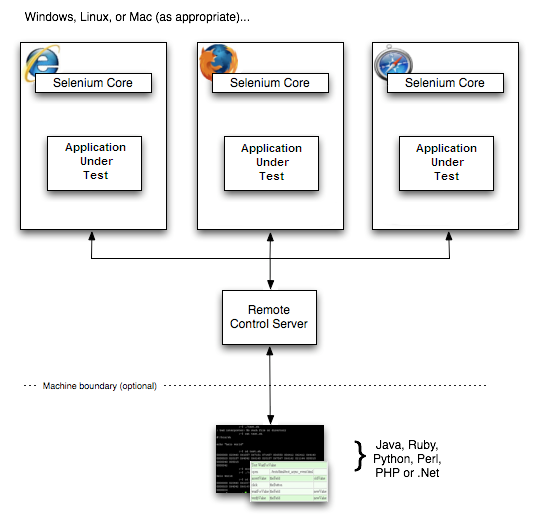
- Selenium Server: The Selenium Server acts as a bridge between test scripts and the browser. It interprets and executes the test scripts and returns the results. It automatically injects Selenium Core, a JavaScript program, into the browser. This allows for the interpretation and execution of a set of Selenium commands using the browser’s built-in JavaScript interpreter. The Server communicates with the test scripts through basic HTTP GET/POST requests, enabling automation in various programming languages that support HTTP requests.
- Client Libraries: Client libraries provide the programming support to run Selenium commands from the test scripts. Each supported language has its client library. These libraries provide API for running Selenium commands. They send these commands to the Selenium Server for execution on the Application Under Test (AUT), receive the result, and return it to the test scripts. A program then processes the result, stores it, and takes appropriate action based on the success or failure of test scripts.
Limitations of Selenium RC
Some limitations of Selenium RC are:-
- Slower Execution: Selenium RC relies on JavaScript injections(Selenium Core) for interaction with the browser, which delays the execution of commands.
- No Support for Headless Browsers: Selenium RC lacks built-in support for headless browsers, which are increasingly essential for server-side testing and continuous integration tasks.
- No Support of Parallel Testing: Selenium RC did not support parallel testing. It cannot run multiple tests on different browsers in parallel on the same machine.
- Limited Features: Selenium RC provides limited support for dragging-and-drop actions on web elements. So, automating scenarios involving dragging and dropping an element onto another is complex in Selenium RC.
- Lack of Switching between Multiple Instances of Same Browsers: In Selenium RC, handling multiple instances of the same browser (e.g., two Chrome windows) and switching between them programmatically is very complex.
Find out how Headless Browser Testing works and why it’s useful by diving into the world of it.
However, Selenium RC has been deprecated with the emergence of Selenium WebDriver due to its more efficient and stable browser automation features.
Understanding the Selenium WebDriver Architecture, which makes it the most efficient and stable browser automation tool, is important to understand why developers are switching to Selenium WebDriver.
What Makes Selenium WebDriver Better Than Selenium RC?
Selenium WebDriver superseded Selenium RC as the preferred choice for automation testing due to several key advantages it offered:
- Smaller and Compact API: Selenium WebDriver’s API is more object-oriented than Selenium RC API, making it easier to work with Selenium WebDriver.
- Improved Emulation of User Interactions: Selenium WebDriver prioritizes simulating user interactions more closely than Selenium RC. It uses native events whenever possible, providing a more accurate simulation of how users interact with websites and applications.
- Advanced User Interaction APIs: Selenium WebDriver offers advanced user interaction APIs compared to Selenium RC, enabling the modeling of complex interactions with websites. This allows for more comprehensive and realistic testing scenarios.
- Strong Support from Browser Vendors: Major browser vendors like Opera, Mozilla, and Google actively contribute to WebDriver’s development. This leads to built-in support for WebDriver within the browsers themselves, ensuring tests run efficiently and stably.
Selenium Grid, the third component of the Selenium suite, empowers parallel test execution across multiple machines and browsers, optimizing efficiency and reducing testing time. However, managing and scaling your own Selenium Grid infrastructure can be complex. With TestMu AI, you can effortlessly leverage the power of Selenium Cloud Grid without the infrastructure management overhead. TestMu AI is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale on over 3000 real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
Difference Between Selenium RC and Selenium WebDriver
Let’s see some differences between Selenium RC and Selenium WebDriver based on their architecture, browser support, browser interaction, etc.
| Factors | Selenium RC | Selenium WebDriver |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | It is based on Client-Server architecture and requires a Selenium Server. | It directly interacts with browsers using the built-in capabilities provided by the browsers. |
| Browser Support | It has limited support for newer browsers and features. | It has broad support for all modern browsers. |
| Browser Interaction | It relies on JavaScript injections for interaction. | It utilizes the browser’s built-in functionalities directly. |
| Drag and Drop | It has limited support for drag-and-drop actions. | It provides better support for drag-and-drop interactions. |
| Object-Oriented APIs | It is less object-oriented compared to WebDriver. | It offers a more structured, object-oriented approach. |
| Handling Multiple Windows/Tabs | It is challenging to switch between them programmatically. | It efficiently handles multiple browser tabs/windows. |
| Speed | It is slower due to JavaScript injections. | It is faster due to direct communication with the browser. |
Note: Selenium RC has an advantage over Selenium WebDriver for report generation as the results will be generated automatically as HTML files. Selenium WebDriver does not have this feature.
Conclusion
One of Selenium’s first web application testing components, Selenium RC, was a server and client library that supported several programming languages, including Java, Perl, C#, Python, and others. It was used for automated cross-browser testing.
It had limitations like browser compatibility issues and security obstacles. The introduction of Selenium WebDriver emerged as an improved solution, offering direct and efficient browser automation, which led to the deprecation of Selenium RC. It’s like transitioning from an older model to a swifter, more dependable one.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests