
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Testing Microservices: A Quick Start Guide
In this testing microservices guide, you will learn what microservices architecture involves, how it compares to other software architecture models, and the technologies that make it possible.
Jolive Hodehou
January 21, 2026
During the last few years, applications have grown to host millions of users and produce a large volume of data. People using these applications expect fast responses and 24/7 availability. For applications to be fast and available, they must respond quickly to the increased load.
One way to do this is to use a microservices architecture because, in a monolithic application, the main problem is the difficulty of scaling the application. The resulting application has a very large code base and poses maintainability, deployment, and modification problems.
Testing today’s environments is more complex than a few years ago. The transition to distributed environments such as microservices has created complexity, overhead, and friction in testing. Testing requires a lot of preparation, infrastructure building, and maintenance because many services communicate asynchronously.
In this testing microservices guide, you will learn what microservices architecture involves, how it compares to other software architecture models, and the technologies that make it possible. You’ll also learn about the challenges you’ll face when testing microservices in how best to evaluate their merits.
What is Microservices architecture?
Basically, microservice architecture is a software development method that aims to break down an application to isolate key functions, each of which is called a “service”.
These services are designed to be responsive to a specific and unique business need, for example, order management, shipping service, payments, or notifications. In addition, they are independent and modular, allowing each to be developed and deployed without affecting the others.
This type of architecture is the opposite of monolithic architecture, built as a single autonomous unit. Microservices are more and more used in companies, including the largest ones.

How does Microservices architecture work?
Microservice applications are composed of several small applications, each of which handles an individual application function. The services communicate with other services as necessary to perform their functions.
Today, most cloud applications that expose a REST/GraphQL interface are built using microservices.
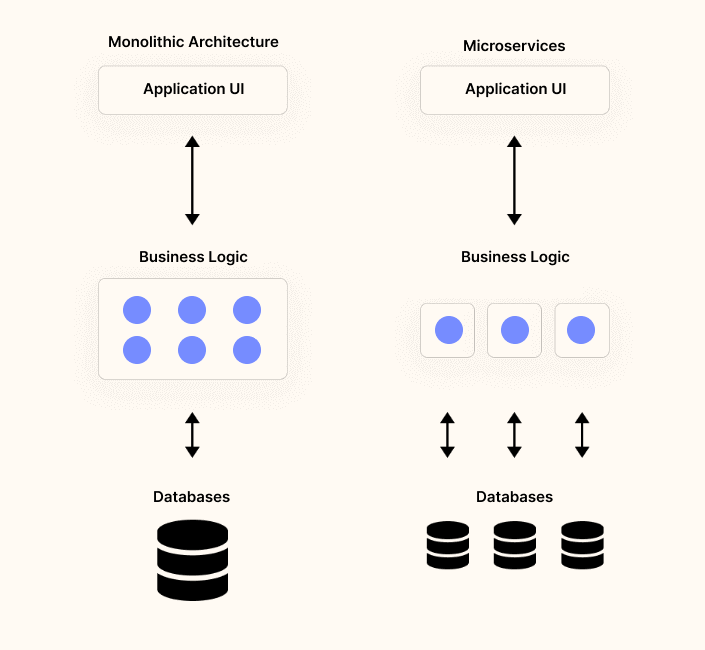
Monolithic vs Microservices architecture
The monolithic architecture versus the microservices architecture has two major differences at a high level:
- Monolithic architecture is a single, large, executable application.
- Microservices is a set of loosely decoupled services to support larger application deployments.
Microservices architecture offers a different approach to software development. With cloud deployment technologies, API management, integration technologies, and microservices monitoring, microservices provide an agile and efficient way to deploy large, complex enterprise applications.
The big difference is that your monolithic application is disassembled into a set of independent services, which are developed, deployed, and maintained separately.
Note: Test microservices application component on the cloud. Try TestMu AI Now!
Test microservices application component on the cloud. Try TestMu AI Now!
Monolithic architecture
When starting a project, it is easy to use this architecture because it is easy to develop. It is easy to test, and deployment can be done very simply. But this simple approach has a limit in terms of size and complexity. As the size of the application increases, there are many disadvantages.
The size of the application can slow down the start-up time. You have to redeploy the whole application with each update, and continuous deployment is also difficult.
As far as reliability is concerned, monolithic applications have significant problems. If one of the components has a bug, it will halt the whole application and process.
As technologies develop rapidly and new technologies are invented, these applications have a high barrier to adoption. As changes in frameworks or languages affect the whole application, they are extremely costly and time-consuming.
Microservice architecture
Microservices architecture represents a paradigm shift from monolithic architecture. Microservices decentralize software development and allow agile methodologies to be applied, which speeds up testing and deployment.
Let’s look at the benefits of microservices to help you understand what makes microservices so attractive.
- Performance: Microservices allow for the development of language-independent applications. This means that teams can build applications in the language best suited to that type of application. One team may use a more suitable language to build an order management application’s backend, while another may use a different language for a payment microservice. This improves the performance of the whole system.
- Independency: As each service can be built by a dedicated team, each team only has to worry about one part of the system. In a microservices architecture, teams are autonomous in building and deploying their service. This allows teams to work independently without fear that their changes will greatly impact the system’s overall state. It also fits well with the agile philosophy of continuous testing and delivery.
- Reusability: Microservices allow parts of the service to be reused in other applications: if a payment functionality has already been created for one application and another need this functionality, the same microservice can be used in the latter.
- Scalability: Microservices are infinitely scalable horizontally, and their lightweight nature allows each service to better adapt to incoming requests. As load is introduced into the system, additional servers can be added to balance the load.
- Maintainability: Microservices are highly fault-tolerant. Even if one service fails, the inherently isolated nature of the architecture means that other services can be largely unaffected. Because individual services are relatively small, downtime can often be remedied quickly, as it is immediately clear which part of the service is causing the problem.
Despite the benefits, microservices architecture has certain challenges. Let’s look at the challenges associated with microservices architecture.
- Complexity: While each service is simpler, the system as a whole is more complex. As a distributed system, care must be taken to select and configure all services and databases and then deploy each of these components independently. All the challenges of a distributed system must be considered.
- Testing: Having many independent services can make test writing more complex, especially when there are many dependencies between services. A mock should be used for each dependent service to test a service as a unit.
- Data integrity: Microservices have a distributed database architecture, which is a challenge for data integrity. Some business transactions, which require the update of several business functions in the application, need to update several databases belonging to different services. This requires eventual data consistency, which is more complex and less intuitive for developers.
Getting started with testing Microservices
The testing process of a microservice architecture is very different from the usual one. The particularity of a microservice architecture is that the software is provided by several services running on the backend.
As a result, we need a different and broader approach to testing, as it can be challenging to perform integration testing or to walk through the main flows during development.
However, we can quickly update an individual microservice and test it without affecting the others.
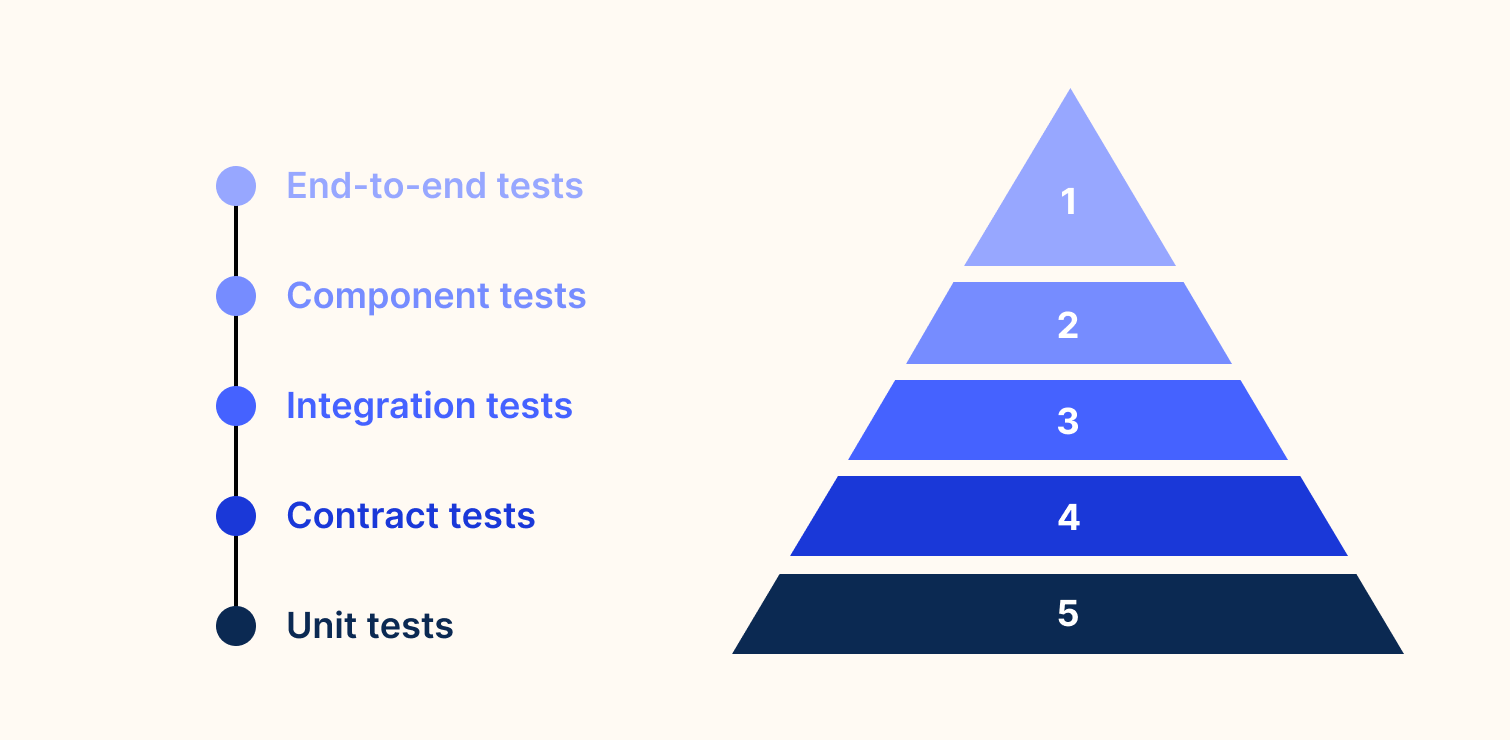
The microservices pyramid adds two new types of tests:
- Component tests.
- Contract tests.
The challenges of testing Microservices
Microservices require additional steps, such as managing multiple repositories and branches, each with its database schema.
But the testing challenges related to microservices architecture can be more profound than that.
Here are some key challenges associated with testing microservices:
- Availability: Since different teams may manage their microservices, it is difficult to secure the availability of a microservice (or, worse still, to try to find a time when all microservices are available at the same time).
- Fragmented and holistic testing: Microservices are designed to work alone and with other loosely coupled services. This means that developers must test each component in isolation, as well as test everything together.
- Knowledge gaps: Especially with integration testing (which we’ll discuss later in this article), whoever is doing the testing will need to understand each service well to write test cases effectively.
Types of tests while testing Microservices
Now, let’s take a closer look at all the microservices testing type
Unit tests
Unit testing is a type of software testing that allows you to check the accuracy of individual modules or software components. The goal is to verify that each unit of code works correctly.
At the feature development stage, developers write unit tests independently because each developer knows and understands the workings of their code better and can perform this task better than the testers.
This allows you to quickly check whether the next code change has led to a regression, i.e., the appearance of errors in previously tested parts of the code. It also makes it easier to detect and eliminate such defects.
Contract tests
It is a test at the border of an external service, verifying that it meets the contract expected by consumer service.
Contract testing is a technique for testing an integration point by isolating each microservice and checking whether the HTTP requests and responses that the microservice transmits conform to a common understanding documented in a contract.
In this way, contract testing ensures that microservices can communicate.
Integration tests
Integration testing checks the interactions between different modules (or classes), usually belonging to the same subsystem, to ensure that they work together as intended when providing high-level functionality.
Integration tests also check that all the communication paths taken by the subsystem are correct and detect any incorrect assumptions that each module may have about how its peers are supposed to act. This type of test is considered the most critical test of the whole architecture.
Component tests
A component is a microservice or set of microservices that accomplishes a role within the larger system. Component testing allows you to independently validate and evaluate the performance of each component of a microservice application without integrating other services.
Generally, it is easier and faster to run component tests than to evaluate microservices.
Since it is difficult and slow to test microservices, you need to simulate other microservices or dependencies. You can isolate the dependencies by replacing them with test duplicates or dummy servers.
Modern teams adopt cloud-testing solutions like TestMu AI to perform component testing through browser testing.
platforms like TestMu AI allow you to perform automated testing of components at scale over an online browser farm of 3000+ browsers and operating systems. TestMu AI provides your team with a cloud-based virtual machine running a real operating system. You can perform real-time component testing of your websites or web applications.
End-to-end tests
End-to-end testing builds on integration testing, which in turn builds on all the other forms of testing you have learned. As the name suggests, E2E tests the business logic as an integration test process, not in isolation, but as part of the whole system.
They should, in theory, simulate a real user of your application or at least perform the actions of a real user. These tests are usually the most difficult to write and consume the most development time.
Final Thoughts
Microservices architecture is a software architecture model in which each task of a larger application is presented as an independent application.
Microservices offer many advantages over other architectures, including easier deployments and better scalability. However, they also come with some challenges, including testing.
When it comes to testing microservices, there are advantages and disadvantages to consider. On the one hand, microservices can be tested independently, making finding and fixing bugs easier. On the other hand, microservices must be tested in concert with each other, which can be more complex and time-consuming.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




