Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What are Software Defects?
- What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Software Testing?
- Types of Root Causes
- 3Rs of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- How to Perform Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Software Testing?
- Popular Techniques of Root Cause Analysis
- Benefits of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Common Challenges Faced in Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Performing Root Cause Analysis on the Cloud
- Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Testing: ‘Detect,’ ‘Analyze,’ and ‘Improve’
Unlock the reasons behind software defects through Root Cause Analysis in testing, to elevate software’s reliability and performance.

Ayush Mishra
January 11, 2026
Bugs or Defects are common challenges in software development. Detecting bugs or defects is vital, and delving into the reasons behind their occurrence is equally important. Identifying the underlying cause of issues is important for preventing their recurrence. It allows developers to implement potential solutions rather than applying temporary fixes.
This article will go through Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in testing, a strategic approach that delves deep into the core of software bugs or defects to ensure high-quality deliverables.
What are Software Defects?
Software defects refer to the deviation from the expected behavior to the actual behavior of a software application. These deviations can occur at any software development life cycle stage, from data collection to coding, testing, and deployment.
Eager to understand more about software bugs? Take a walk through the bug life cycle in software testing – where glitches become tales!
Causes of Software Defects
Some of the causes of software defects are:-
- Inadequate Requirements: Software defects often arise from incomplete requirements, giving rise to misunderstandings and implementation errors during the development process.
- Limited Test Coverage: Software defects may arise due to poor test coverage, where more testing is needed to sufficiently explore and validate different aspects of the software, leaving potential defects undetected.
- Lack of an Effective Defect Management Process: Inadequate defect management processes can lead to the prolonged existence of software defects, hampering the overall quality and user experience due to delayed resolutions and untracked issues.
- Communication gap: Software flaws occasionally result from poor communication between developers, testers, and other stakeholders.
Learn how to get practical details from PMs to reduce defects and missing requirements and work effectively with product managers.
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Software Testing?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in software testing is an effective process to identify the root causes of software defects or problems during the software development life cycle. It identifies the underlying causes of the issues over the surface-level syntax and apparent anomalies in the system.
Types of Root Causes
There are three types of root causes that can have a potential impact on a problem
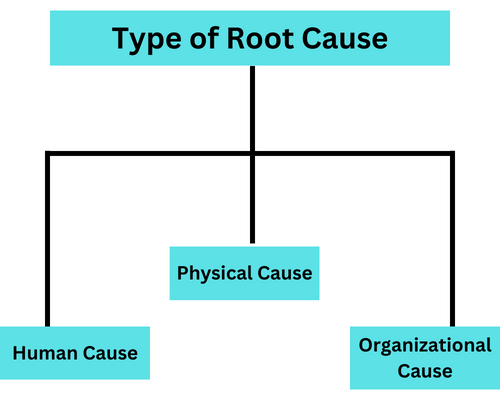
- Human Cause: Factors attributed to human actions, decisions, or knowledge. For example, Data entry error in the Database.
- Physical Cause: Factor related to malfunctioning or breakdown of hardware. For Example, hard disk failure.
- Organizational Cause: Factor that arises from problems within organizations. For Example, poor communication and weak policies.
3Rs of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 3R’s of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) are “Recognize,” “Rectify,” and “Replicate“. They are the key steps in Root Cause Analysis used to identify and address the underlying causes of a problem.
- Recognize: This initial step involves acknowledging a problem or defect in the software. It requires keen observation and effective communication between team members to ensure that issues are identified and not overlooked.
- Rectify: After identifying the issue, the next step is to take corrective action to deal with the underlying causes. This entails implementing fixes that won’t just address the current problem but also stop it from happening again.
- Replicate: This phase ensures the identified root cause is effectively rectified and allows thorough software testing to prevent any future recurrence of issues.
How to Perform Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Software Testing?
The essential steps to perform the Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in software testing are:-
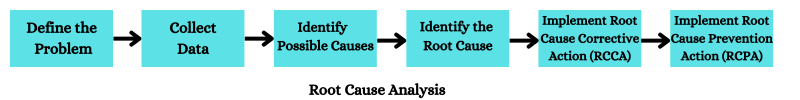
- Define the Problem: The first step is identifying and defining the problem or defect during software testing.
- Collect Data: After finding the problem, collect problem evidence, such as problem test cases, logs, screenshots, and reports.
- Identify Possible Causes: List all potential causes contributing to the problem or defects.
- Identify the Root Cause: Employ various Root Cause Analysis (RCA) techniques to identify the underlying issue accurately.
- Implement Root Cause Corrective Action (RCCA): After identifying the root cause, implement corrective action to address identified root causes and proactively prevent the recurrence of issues.
- Implement Root Cause Prevention Action (RCPA): After resolving the root cause, implement preventive measures such as improved testing procedures or process enhancements to avoid similar issues in the future.
Popular Techniques of Root Cause Analysis
Some of the most popular techniques of Root Cause Analysis are:-
The 5 Whys Technique
The “5 Whys” is a Root Cause Analysis technique involving iterative questioning to uncover the fundamental cause of a defect in the software development phase. Asking “why” multiple times helps identify underlying issues rather than just addressing surface-level issues.
Let’s see the example of how the “5 Whys” technique will be applied to investigate a user login failure of an e-commerce application.
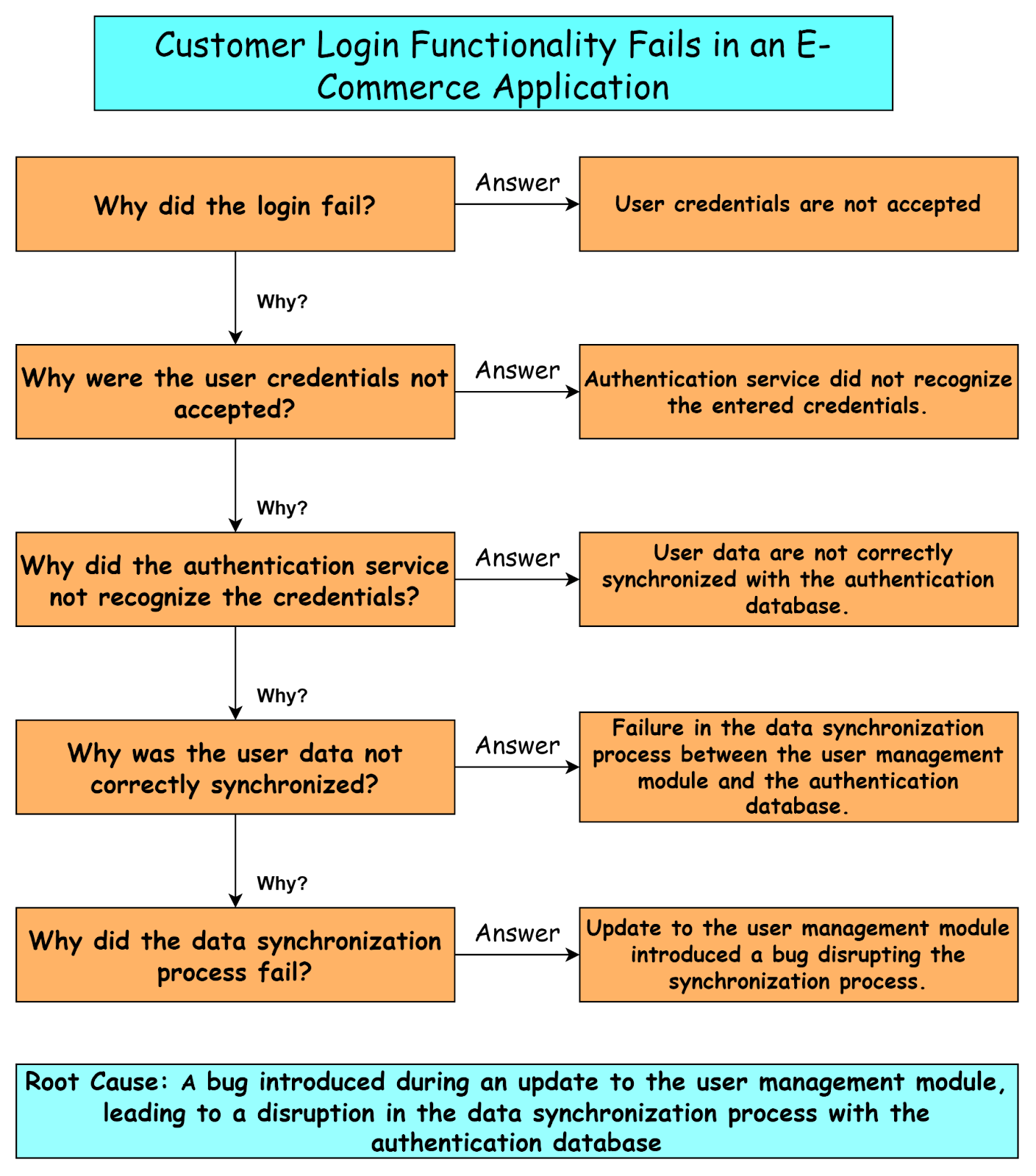
Advantages of using the 5 Whys technique:
- Finding Deeper Causes
- Avoiding Superficial Fixes – It avoids dealing with a problem’s superficial origins or symptoms, which could cause it to repeat.
- Encourages Critical Thinking
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a deductive technique that utilizes boolean logic such as AND, OR, and NOT and a graphical representation, the “Fault Tree,” used to find critical events concerning fault introduction in the software development process. It helps analyze logical relationships leading to undesirable events, helping in effective risk mitigation and software reliability enhancement.
The Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) involves three key stages:-
- Develop a Fault Tree Diagram.
- Examine the diagram by examining failure events, initiating events, and contributing factors.
- Examine the connections between failures and initiating events (or contributing factors).
A fault tree diagram uses symbols known as events, conditions, or states that can occur at any point in time during system operation. Lines connect these symbols to illustrate how one issue might lead to another, eventually resulting in a problem, or “fault,” in the system. The faults represent what can go wrong in our system. Below is a general example of how these diagrams can look.
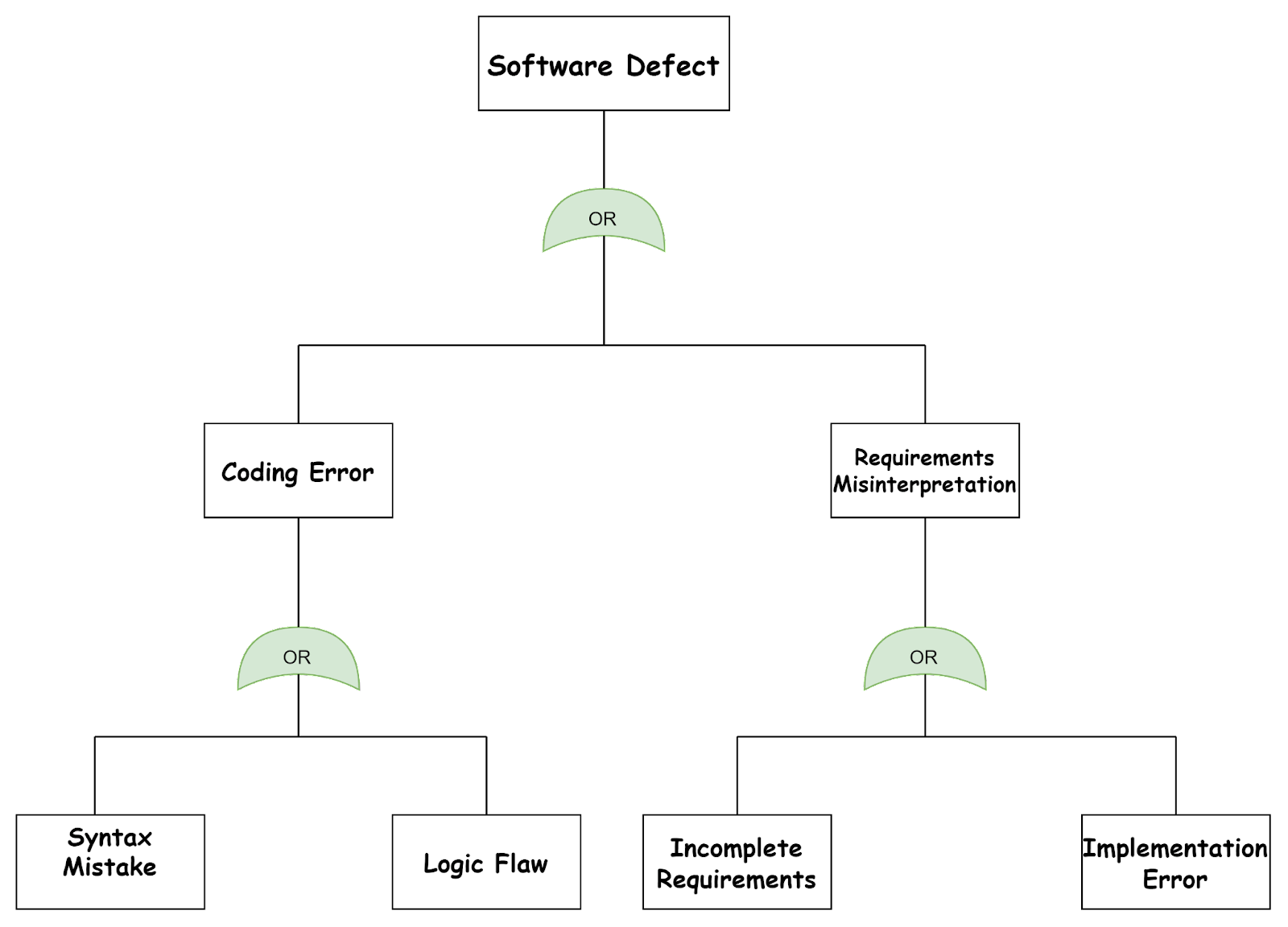
In the fault tree diagram above, the top event is a Software Defect that arises from initiating events like “Coding Errors” or “Requirements Misinterpretation” by the developer in the Software Development phase. To the left of the fault tree diagram is “Coding Errors,” and we can see “syntax mistakes” or “logic flaw“ events failure. Similarly to the right “Requirements Misinterpretation,” we can see “Incomplete Requirements” or “Implementation Errors.”
Advantages of using the Fault Tree Analysis:
- Structured Analysis for problem isolation: The Fault Tree offers a structured visual representation of the analysis process, helping teams systematically investigate the causes of an event leading to failure.
- Action Prioritization: The analysis helps prioritize action items, assisting teams in determining which aspects require immediate attention for problem resolution.
The Fishbone Diagram
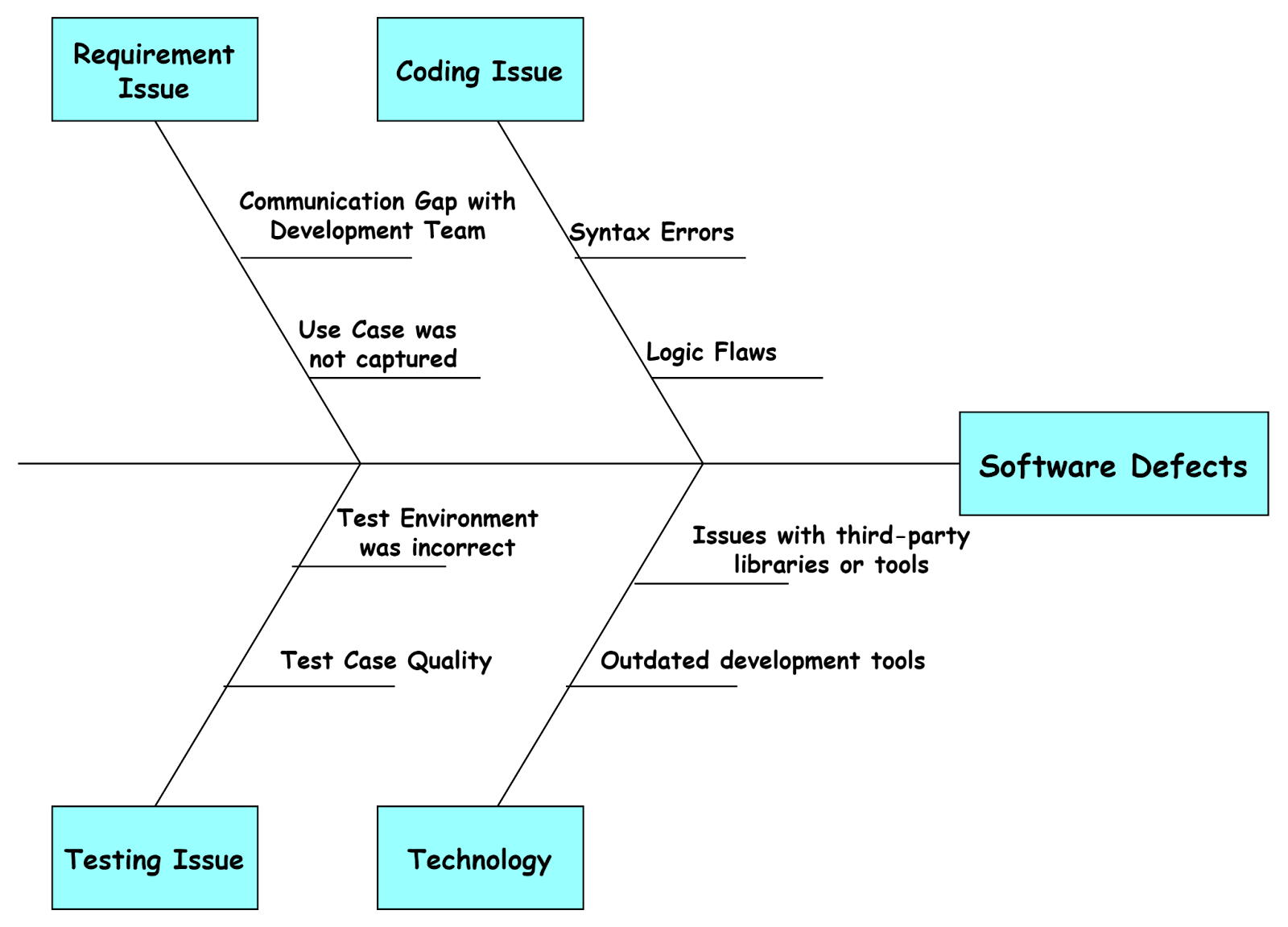
The Fishbone Diagram called the Ishikawa Diagram or the Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a visual representation of a problem’s potential causes. Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese expert in quality control, created it. It is widely used for Root Cause Analysis(RCA) in testing to pinpoint the root causes of a persistent performance issue, identifying factors related to code, hardware, network, database, and configuration.
It resembles the structure of a fish’s skeleton, where the problem serves as the fish’s head, the category of cause is written at the end of the bone, and the causes under each category are at the spines of the fish.
For example, in the diagram below, the fish head represents the Software Defects, the main problem. Causes of software defects include requirement issues, coding issues, testing issues, and environmental issues at the end of the bone. Factors attributed to all the causes of software defects are represented in the spins of the fish.
Advantages of using the Fishbone Diagram:
- Display relationships clearly and logically: The Fishbone Diagram presents a clear and organized depiction of the connections between potential causes and their corresponding outcomes. A logical categorization makes the correlations between cause and their outcomes easily understandable.
- Clarity in Communication: It enhances communication by presenting complex issues clearly and organized, helping in effective discussions and decision-making.
Scatter Diagram
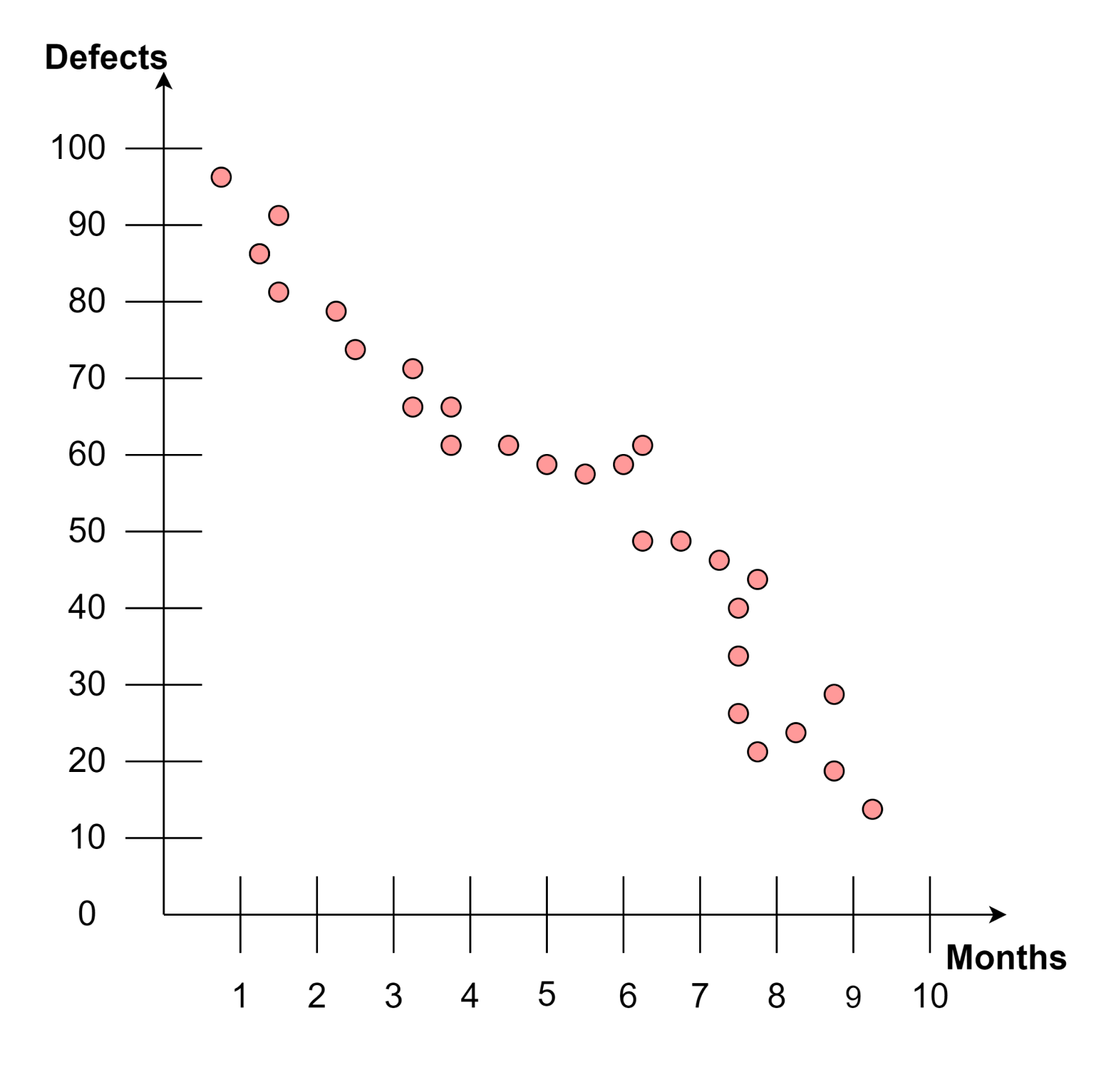
The scatter diagram, also known as the correlation diagram, is a graphical representation that shows the relationship between two variables that may cause a problem. It helps us to test hypotheses, identify outliers, and discover potential root causes.
In software testing, a scatter diagram helps identify the process parameter (independent variable) causing issues with the system (dependent variable). The x and y axes represent these variables, enabling a visual analysis to pinpoint the root cause of problems.
For example, in the scatter diagram below, the y-axis represents the number of defects in software, and the x-axis represents the time allocated to testing. Each data point on the scatter diagram represents a specific module. Analyzing the above scatter diagram allows us to determine whether testing time and the number of defects are correlated. This helps in making well-informed decisions regarding resource allocation and refining testing strategies.
Advantages of using the Scatter Diagram:
- Facilitates Data Interpretation: The scatter diagram assists in data interpretation by visually displaying the distribution and clustering of data points, allowing a deep understanding of the root cause.
- Supports Informed Decision-Making: It helps understand the impact of one variable on another, thus providing informed decisions about which variables to investigate further to find the root cause.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
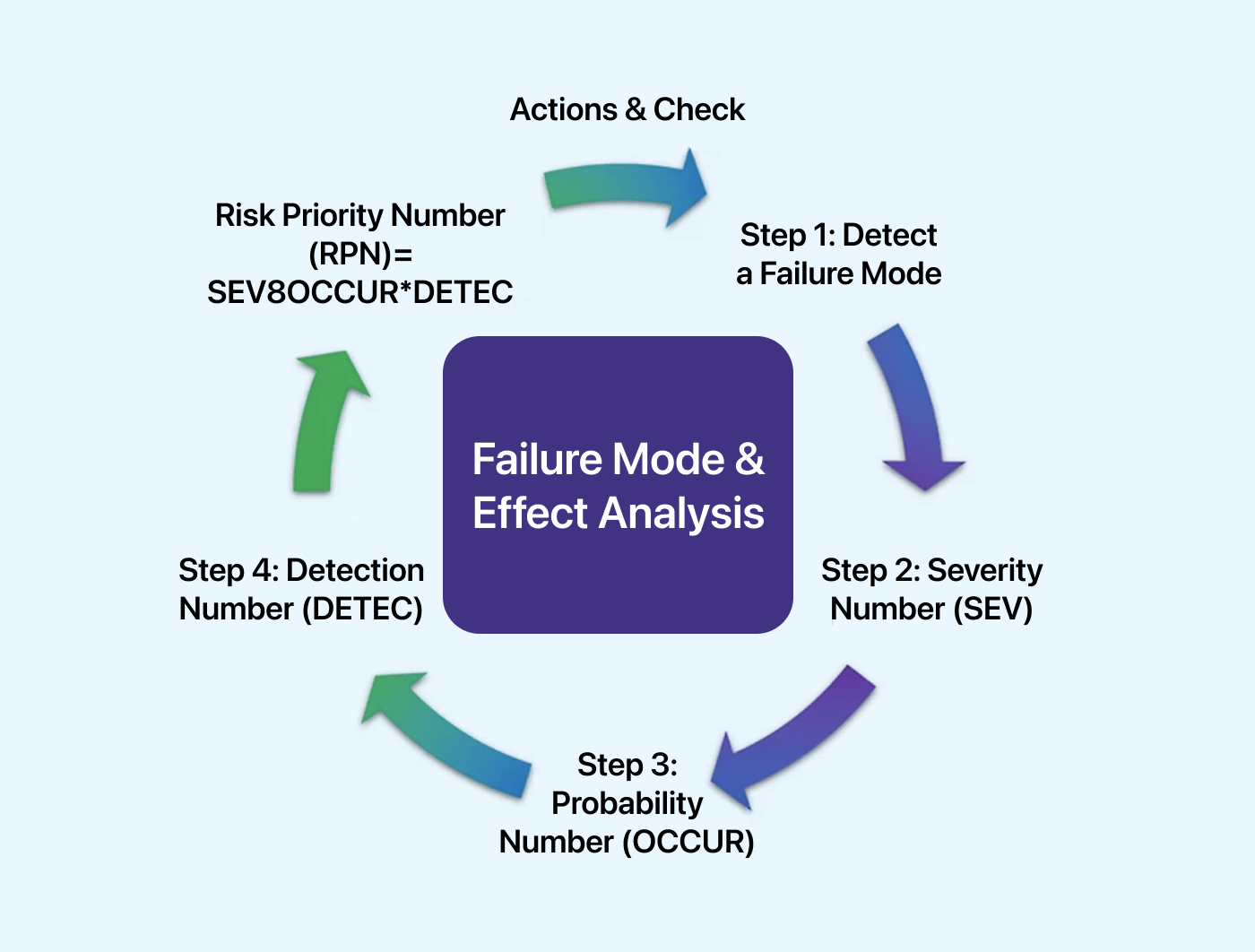
In software, “Failure Mode” encompasses potential issues such as bugs, errors, crashes, and security vulnerabilities, and “Effects Analysis” examines the consequences of these failures, assessing their severity and impact on end-users, system reliability, data integrity, and business operations.
In this method, each failure mode is assessed for:
- Severity (S)
- Occurrence (O)
- Detection (D)
A Risk Priority Number (RPN) is generated using the Severity, Occurrence, and Detection. The RPN is then given a rating system to determine which issue needs more priority. The lesser the RPN number, the greater the risk and vice-versa.
Advantages of using the Failure Mode and Effective Analysis:
- FMEA systematically identifies and evaluates potential failure modes in software, helping teams proactively mitigate risks before they impact software quality.
- FMEA provides justification for not doing certain tests i.e. where the probability of failure is least.
Affinity Diagram
Affinity Diagram, also called KJ Diagram, is a technique to arrange and classify various aspects that contribute to problems methodically. This can help provide a thorough understanding of the underlying problems and guide successful problem-solving techniques.
The diagram below shows how an affinity diagram can be applied to group the defects in the software development process according to their nature. It helps teams visualize and understand the commonalities among different defects, leading to more targeted and effective improvements in the defect management process.
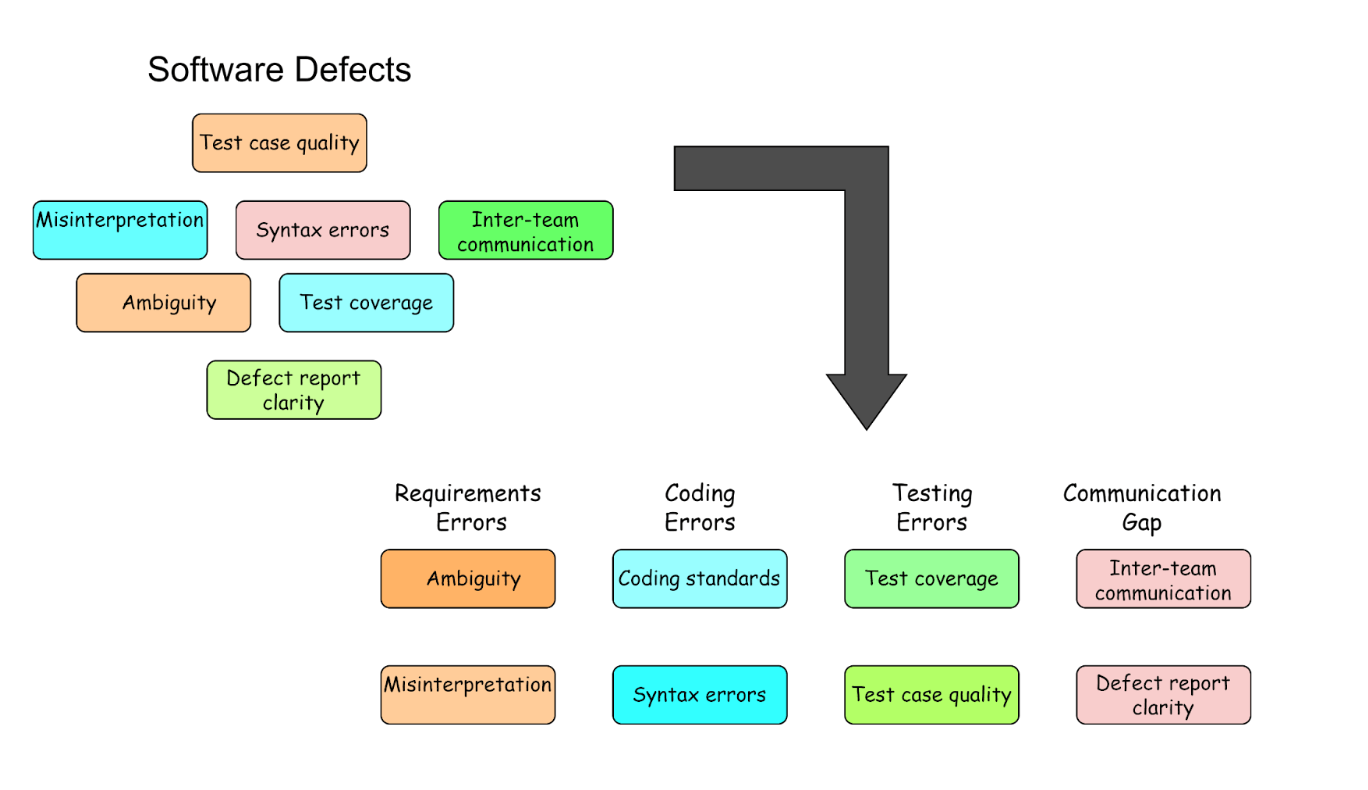
Advantages of using the Affinity Diagram:
- Visual Representation: It provides a visual representation of the information, allowing for a clear and structured view of the problem, which helps better understand and analyze the root cause.
- Promotes Collaboration: It encourages team members to work together in categorizing and prioritizing ideas or potential causes, fostering a collaborative problem-solving approach.
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Some of the benefits of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) are:-
- Improved Software Quality: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) improves software quality by eliminating systemic problems and enhancing the effectiveness of software testing processes.
- Risk Reduction: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in testing mitigates future incidents by pinpointing and rectifying core causes, thus reducing associated risks. This is especially important in fields where dependability and safety are top priorities.
- Prevention of Recurring Defects: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps to prevent the recurrence of similar issues by identifying and addressing the root causes of defects. This reduces the need for repeated debugging and fixes, saving time and resources.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) employs data and evidence to find the underlying reasons. This encourages decision-making and problem-solving that is more informed and objective.
Note: Test your Web and Mobile Applications across 3000+ combinations of browsers, real devices, and OS. Try TestMu AI Today!
Common Challenges Faced in Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Some common challenges faced in Root Cause Analysis (RCA) are:-
- Limited Data Availability: Sometimes, it can take time to gather complete and reliable data. This may obstruct the exhaustive investigation for Root Cause Analysis (RCA). Ensure that data-gathering procedures are reliable and all pertinent information is available.
- Complex Systems and Interactions: Finding the precise root cause in complicated systems can be complex. The interactions between different elements could make it challenging to identify the precise cause of the issue. For an accurate Root Cause Analysis (RCA), it is imperative to comprehend these interactions.
- Time Constraints: Conducting a thorough Root Cause Analysis (RCA) requires dedicated time and effort, especially for complex or multifaceted issues. So, balancing the need for a comprehensive analysis with time constraints is challenging. Prioritizing tasks and allocating resources effectively is crucial.
- Human error and factors: The Root Cause Analysis (RCA) process may contain flaws brought by human error during data gathering or processing. Additionally, the results may be impacted by assumptions or prejudices held by participants. An effective Root Cause Analysis (RCA) must address human aspects and ensure strict technique.
Root Cause Analysis(RCA) is a critical aspect of software development, as it’s essential to find out why there was a deviation from the intended behavior of the feature. However, as applications grow in size and complexity, finding the root cause of the issue becomes laborious. This is where cloud-based testing platforms come into play. The process becomes smoother with the help of cloud-based testing platforms. These platforms offer flexible and scalable setups, making it easier for teams to collaborate in real time. They also provide insightful analytics that help teams identify and fix problems quickly. So it’s like having a fully equipped toolbox that speeds up testing and increases the software quality with every release.
Performing Root Cause Analysis on the Cloud
TestMu AI is an AI-driven test orchestration tool that offers a Test Intelligence platform. This platform aids in Root Cause Analysis (RCA) by utilizing artificial intelligence to identify and address underlying issues within software testing processes quickly.
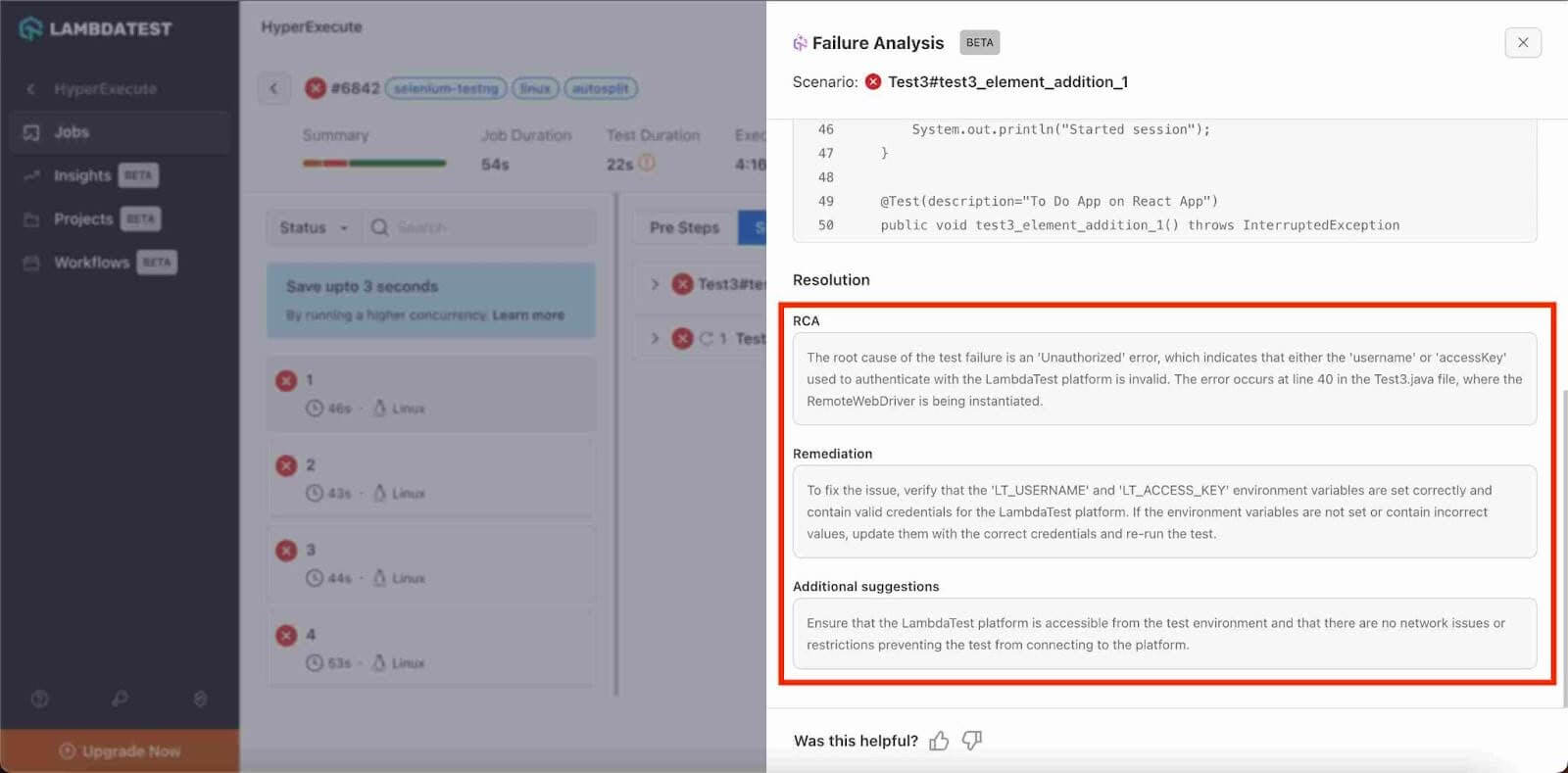
TestMu AI lets you run manual and automated tests at scale on over 3000 real devices, browsers, and OS combinations. We can optimize testing workflows with TestMu AI’s Root Cause Analysis (RCA), ensuring reliable user applications.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Testing is the cornerstone of effective defect resolution in software testing. It enables teams to find the root causes of faults rather than only fix the visible ones. Testers can lead a continuous improvement culture using RCA Techniques like the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagrams, Fault Tree Analysis(FTA), etc. These techniques enhance product quality and help prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests