Creating a Website Using HTML Without a Framework
You can create a fully functional HTML website using just a simple code editor and a web browser. This approach is perfect for beginners to understand the basics of HTML structure and styling before moving on to frameworks.
Prerequisites:
- Code Editor: A code editor like VS Code, Sublime Text, or Notepad++ to write your HTML and CSS.
- Web Browser: A modern browser like Chrome to preview and test your website.
- HTML/CSS Knowledge: Basic understanding of HTML and CSS is helpful but not required.
Once you have the prerequisites in it’s place now you can get started with writing your first HTML code.
Steps to create a website using pure HTML and CSS:
- Project Folder: Create a project folder on your computer (e.g., my-website) to organize all your website files.
- HTML File: Create an HTML file inside the folder (e.g., index.html) to write your webpage content.
- Open in Editor: Open the HTML file in your code editor to start writing HTML and CSS.
Let’s build a basic webpage with a header, some text, and a simple 3-column layout using only HTML and CSS.
Code Implementation:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Simple HTML Site</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 0; padding: 0; }
header { background: #333; color: white; padding: 20px; text-align: center; }
.container { display: flex; justify-content: space-around; margin: 20px; }
.column { flex: 1; padding: 10px; margin: 5px; background: #f0f0f0; border: 1px solid #ccc; text-align: center; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
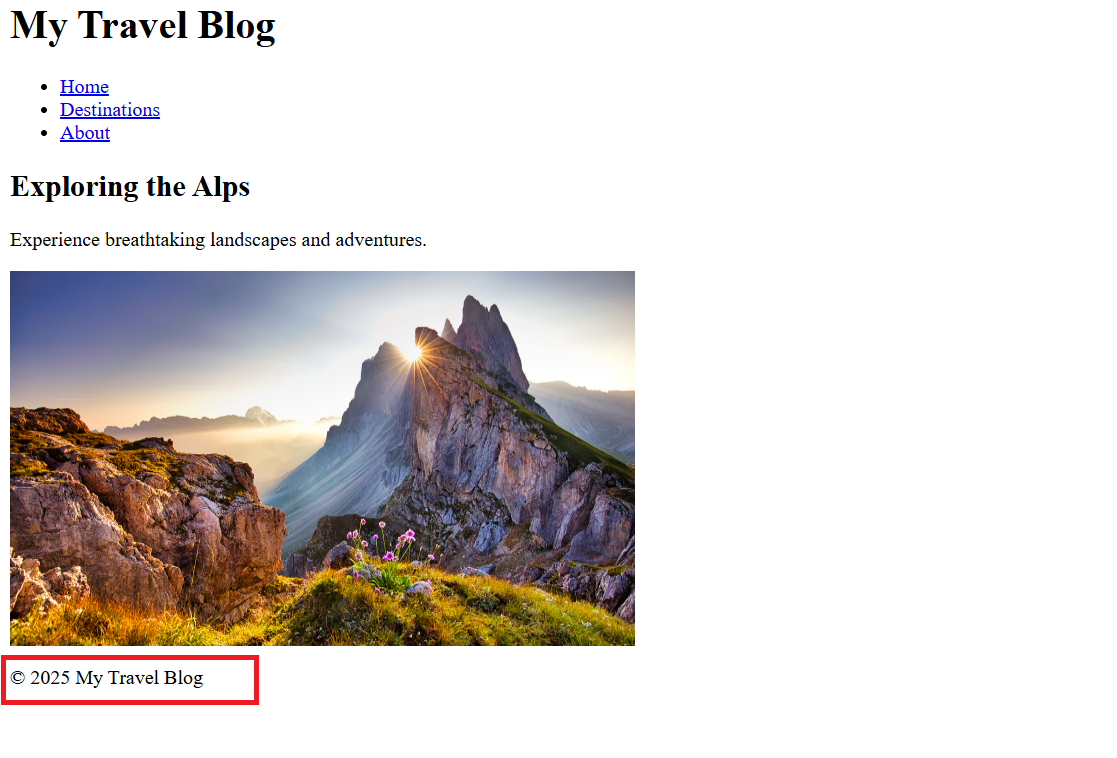
<h1>Welcome to My Simple Website</h1>
</header>
<div class="container">
<div class="column">Column 1</div>
<div class="column">Column 2</div>
<div class="column">Column 3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Code Walkthrough:
- Header: The <header> tag adds a top section with a background color and centered text.
- Container: The .container class uses display: flex to arrange child divs side by side.
- Column: The .column class adds padding, margin, background, border, and centers the text inside each box.
- Inline Styles: All CSS styles are written inside the <style> tag in the <head>, so no external CSS or libraries are needed.
Result:To view your results of your HTML, open the file in Chrome by double-clicking it or right-click > Open with > Chrome.
Creating a Website Using HTML With a Framework
When building websites, writing all CSS and JavaScript from scratch can be time-consuming. Frameworks like Bootstrap provide pre-written, ready-to-use components and styles that make development faster and more consistent.
They save you time, ensure your design is responsive, and follow modern best practices. Popular web development frameworks include Bootstrap, Tailwind CSS, and Foundation.
Frameworks like Bootstrap make building websites faster and easier by providing ready-made styles, responsive grids, components like buttons, navigation bars, forms, and even Bootstrap themes that help you create professional-looking layouts without starting from scratch.
Prerequisites: The requirements are the same as mentioned in the previous section.
For this demonstration, we’ll explore how to create a website using HTML with Bootstrap, so you can see how a framework simplifies layout, styling, and responsiveness.
Steps to create an HTML website using Bootstrap:
- Create a project folder: Make a new folder on your computer (e.g., bootstrap-demo).
- Create an HTML file: Inside the folder, create a file named index.html.
- Include Bootstrap: Add Bootstrap using its CDN (Content Delivery Network) link. This lets you use Bootstrap without downloading anything.
- Set up a structure: Add a <head> and <body> section to organize your webpage.
Let’s build a basic webpage with a navigation bar and a 3-column responsive grid using Bootstrap.
While CSS Grid allows precise layout control with pure CSS, Bootstrap’s grid system provides pre-built, responsive classes that make creating multi-column layouts faster and easier, especially for beginners or projects that need consistency across devices. Learn more about the difference between CSS Grid vs Bootstrap and get deeper insights.
Code Implementation:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Bootstrap Demo</title>
<!-- Include Bootstrap -->
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<!-- Navigation Bar -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark">
<div class="container-fluid">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">My Website</a>
</div>
</nav>
<!-- Page Content -->
<div class="container mt-5">
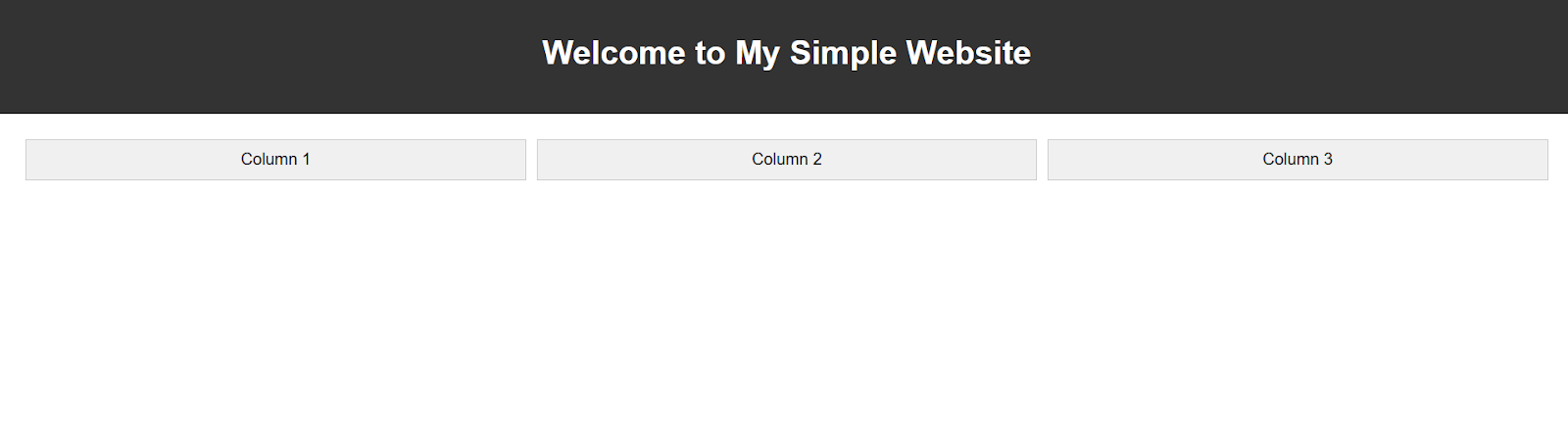
<h1 class="text-center">Welcome to Bootstrap!</h1>
<p class="text-center">This is a simple responsive layout using Bootstrap framework.</p>
<!-- Responsive Grid -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4 bg-light p-3 border">Column 1</div>
<div class="col-md-4 bg-secondary text-white p-3 border">Column 2</div>
<div class="col-md-4 bg-light p-3 border">Column 3</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Bootstrap JS -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Code Walkthrough:
- Include Bootstrap: The <link> tag pulls in Bootstrap styles from a CDN.
- Navbar (navbar): Creates a top navigation bar with branding.
- Container (container): Adds margins and centers content.
- Row + Columns (row + col-md-4): Creates a responsive 3-column layout.
- Utility Classes (bg-light, p-3, border): Quickly style elements without writing CSS.
Result:
After building your website, the next step is to ensure it works seamlessly across all devices before going live. Testing on various devices helps identify issues in functionality, UI, and responsiveness. According to StatCounter, most web traffic today comes from mobile devices, making a mobile-first approach essential.
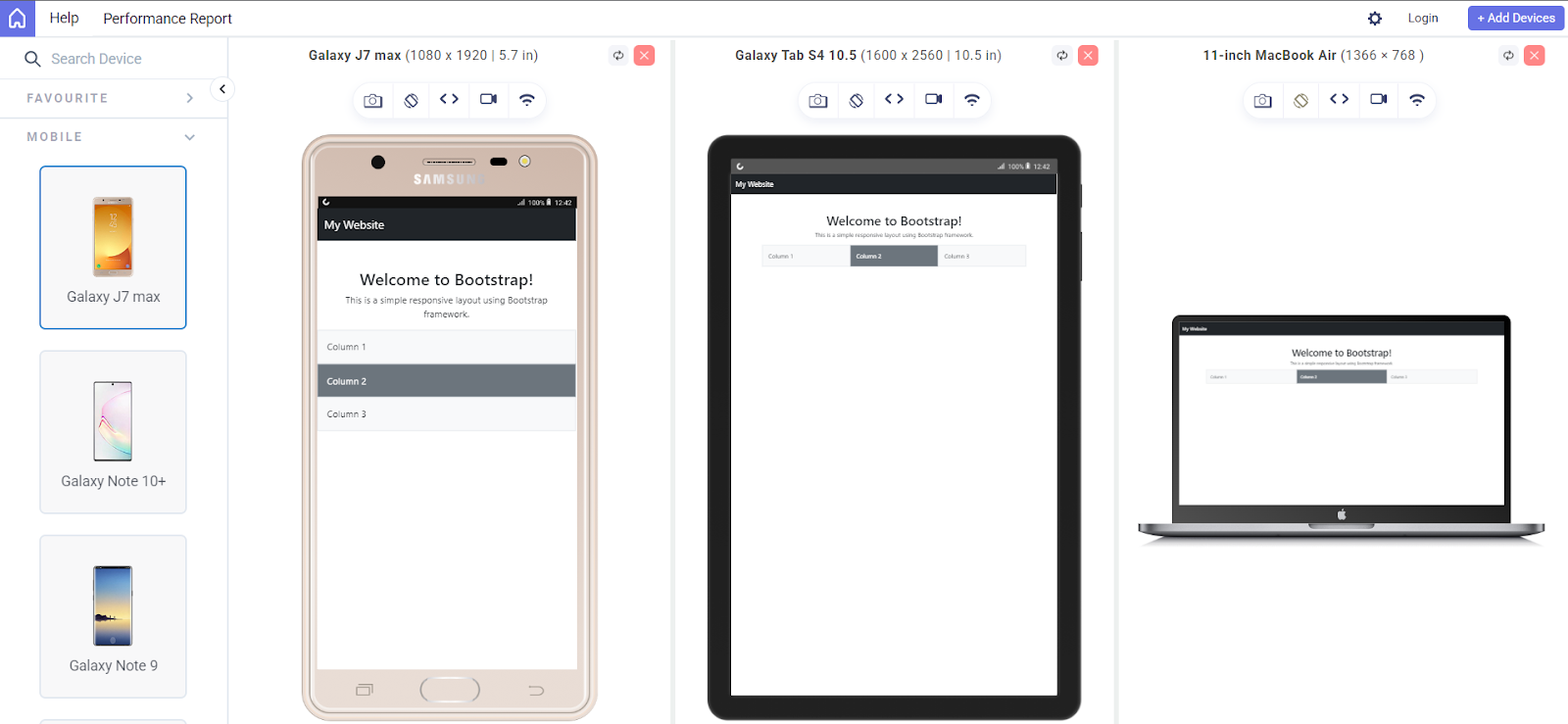
To showcase the results, I have used LT Browser by TestMu AI to simplify responsive testing. LT Browser makes mobile-friendly testing simple by providing over 53+ pre-installed viewports that cover a wide range of standard resolutions. It also includes powerful developer tools to enhance the testing process.
Some of the standout features include device sync, which lets you scroll two devices at the same time, and network throttling to simulate various internet speeds. You can capture full-page screenshots, generate performance reports powered by Google Lighthouse, and even record video sessions of your tests to share with your team.
If you wish to try LT Browser, click on the download link below:

With these capabilities, LT Browser helps you quickly identify layout or performance issues and ensure your HTML website is responsive, fast, and user-friendly across all devices.