
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

What Is Autonomous Testing: A Detailed Guide
In this guide, learn about autonomous testing and how it automates test creation, execution, and maintenance, reducing manual effort.
Harish Rajora
February 15, 2026
Overview
What Does Autonomous Testing Mean?
Autonomous testing uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to run software testing activities with minimal human involvement. Instead of relying heavily on manual effort, intelligent systems handle testing tasks independently.
What Are the Core Elements of Autonomous Testing?
Autonomous software testing depends on a set of tools and frameworks that replicate user behavior, provide input data, and validate expected results without manual control. The main components include:
- Test Case Design: Test scenarios are structured to reflect real user interactions. They may be written manually or generated automatically by examining the application’s interface or underlying code.
- Test Script Creation: Scripts are developed using languages such as Python, Java, or C#. These scripts automate execution by interacting with the application through testing frameworks.
- Test Execution: Scripts run automatically through a test engine or within a CI/CD workflow, continuously validating the application as new changes are introduced.
- Test Result Analysis: Actual outputs are compared with expected results. AI techniques can detect recurring failure patterns and use those insights to improve future testing cycles.
- Debugging and Reporting: Intelligent tools pinpoint defects, examine likely root causes, and recommend fixes. Findings are shared with development teams through dashboards or alerts for faster resolution.
Which Tools Support Autonomous Testing?
Several AI-driven tools help teams implement autonomous testing across different stages of the software lifecycle. Some notable options include:
- KaneAI: It is a Generative AI testing tool built for fast-moving quality engineering teams. It allows users to plan, author and evolve tests using natural language, lowering the barrier to starting test automation.
- Functionize: It uses AI and machine learning to simplify how tests are created, executed, and maintained. It supports natural language–based test generation and includes self-healing features that reduce maintenance when applications change.
- SeaLights: It focuses on quality intelligence and risk-based optimization. It identifies areas of code that lack sufficient testing and helps teams prioritize efforts to avoid unnecessary runs.
- Worksoft: It is designed for large-scale enterprise environments and supports end-to-end testing of complex systems such as ERP and CRM platforms. Its no-code interface allows broader team participation
Testers often deal with complex software applications requiring extensive coverage, handling flaky tests, and meeting tight release deadlines. Also, limited skilled resources and high test maintenance overhead add to the pressure, making it hard to scale traditional testing methods.
Autonomous testing is an approach that helps overcome the challenges associated with traditional testing methods using AI/ML technologies. These tasks include automating test creation, execution, and maintenance. Autonomous testing speeds up the test process, cutting down on manual work and offers smart features like self-healing, test generation, and even more.
What Is Autonomous Testing?
Autonomous testing refers to the use of AI, machine learning, and other advanced technologies to enable software testing processes to function independently without significant human intervention.
It is the concept of having an autonomous testing infrastructure, i.e., an infrastructure where tools and frameworks are so intelligent that they can take complete control over the testing cycles. The processes included involve test case creation, modification, optimization, execution, and generation of final test reports.
Such a testing technology can only be successful if intelligent decision-making is included. For this, artificial intelligence and machine learning are incorporated into autonomous testing with algorithms that can perform actions such as predictive analysis and self-healing. Using this set of algorithms, the software is expected to make not only correct choices but choices that are according to the software application and its behavior and in the most optimum way possible.
Benefits of Autonomous Testing
The integration of autonomous testing into the existing infrastructure can be helpful in multiple ways. Some of them are as follows:
- Improves Efficiency: Autonomous testing saves a lot of time by taking over all the testing processes from testers. This time can now be invested in activities such as enhancing the testing cycles, optimizing, expanding, and filling all the loopholes and vulnerabilities.
- Ensures Faster Testing and Delivery: Autonomous testing does not require any manual intervention and is achieved through fast algorithms that can perform a task in a fraction of the time as compared to conventional testing. Hence, the team can get tested software faster, which can initiate subsequent processes such as production upload much faster than before.
- Boosts Software Quality: Artificial intelligence and machine learning, when used correctly with high-quality training datasets, can produce algorithms that can detect failures, generate high-quality test cases, and increase test coverage by covering all the functionalities and probably all lines of code. In short, if all the gaps and weaknesses are covered, the result of such accurate testing is high-quality software with minimum bugs.
- Minimize Errors: Finally, when autonomous testing takes over, the chances of human errors are brought down to 0. If everything goes as planned, we may be able to bring production bugs to a minimum and, ideally, 0.
- Improves Test Reporting: Artificial intelligence, when integrated with test reporting, brings out deep insights and rich patterns that are hard to derive manually. It helps in making better decisions in the future and getting a healthy insight into the existing test infrastructure, ultimately saving future maintenance costs.
- Reduces Costs: The processes that AI handles are traditionally done by a team of testers. This team will take more time to complete all the processes and then more people are hired for expansion and handling other tasks. All this is extremely costly for the organization which makes autonomous testing an even more desirable feature for them.
Note: Leverage the potential of autonomous testing with the cloud. Try TestMu AI Today!
Key Components of Autonomous Testing
Autonomous software testing uses tools and frameworks to simulate user actions, input data, and expected results, all without any human involvement. Here are its key components:
- Test Case Design: Test cases are created to mimic how users interact with the app. These can either be manually written or automatically generated by analyzing the app’s code or user interface.
- Test Script Creation: Developers write test scripts using programming languages like Python, Java, or C#. These scripts automate the execution of test cases, using testing frameworks to interact with the application.
- Test Execution: The test scripts run automatically through a test engine or as part of a Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline. It simulates user interactions and continuously checks the app as updates are made.
- Test Result Analysis: The testing framework compares the actual results with what was expected. AI can help identify patterns in failures, making future tests smarter and more efficient.
- Debugging and Reporting: AI tools automatically identify defects, analyze their causes, and suggest fixes. The results are reported to the development team through dashboards or notifications, helping them quickly address issues.
All these stages cover all the tasks associated with a Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) without any human involvement. It brings out an efficient infrastructure, taking minimum time for execution.
From Manual to Autonomous Testing
This journey from manual to autonomous testing represents a great shift in testing software applications, where the degree of automation is slowly increased in order to make it more efficient, accurate, and fast. Throughout this process, the role of human involvement gradually decreases, and that of the intelligent systems takes over.
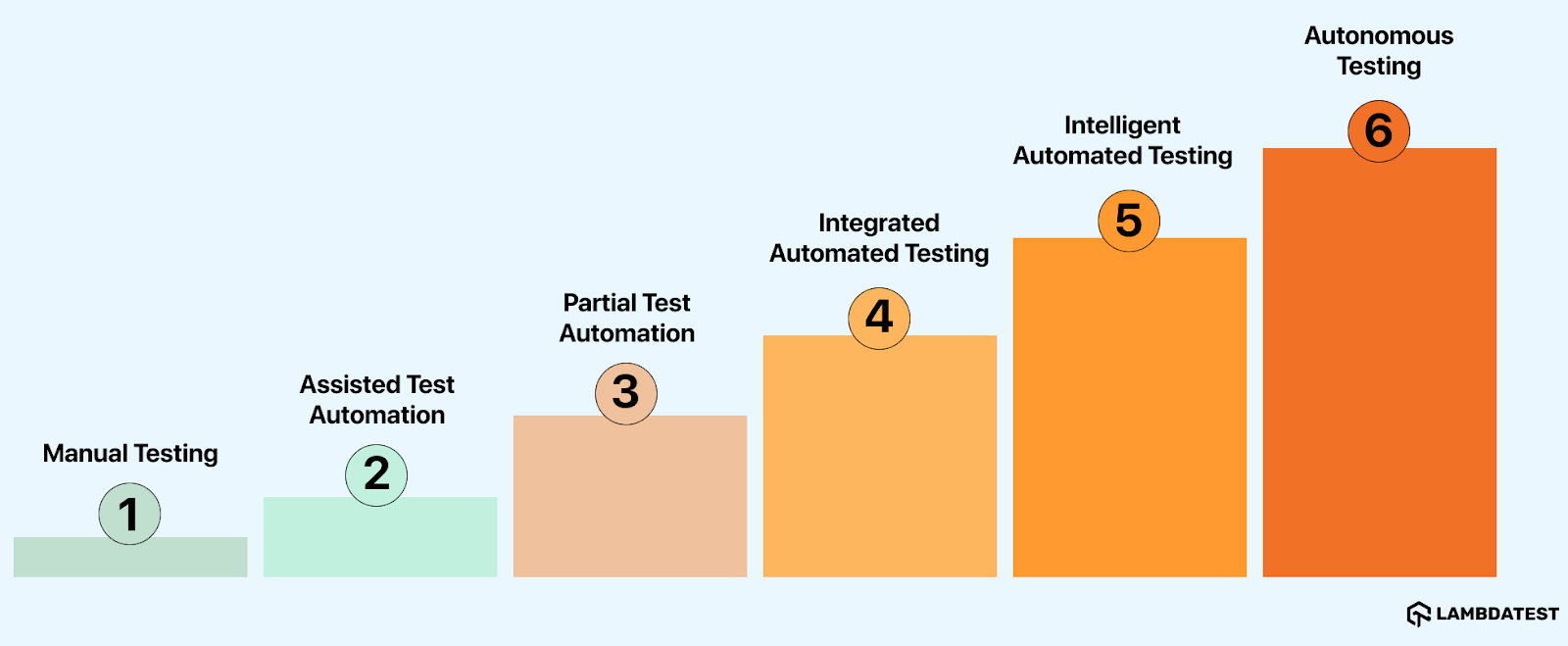
The following are six key stages that outline this transition of progress from manual testing to fully autonomous testing:
- Manual Testing: Testers make all decisions and handle every aspect of testing.
- Assisted Test Automation: Automated testing tools help testers, but testers still create and maintain the test scripts. At this level, testers are heavily involved in test design and management.
- Partial Test Automation: Both testers and automated testing tools contribute to testing, with the majority of decisions still made by testers.
- Integrated Automated Testing: Automated testing tools with AI capabilities generate suggestions or insights and can be used only after the tester’s approval.
- Intelligent Automated Testing: AI testing tools generate, evaluate and run tests. Tester involvement is optional but still possible if needed.
- Autonomous Testing: AI testing tools take full control over the testing process, including decision-making and execution, without testers.
Autonomous Testing Tools
While testing software applications, here are some of the autonomous or AI testing tools you can consider.
KaneAI
KaneAI by TestMu AI is a GenAI native QA Agent-as-a-Service platform for test authoring, management, and debugging, designed specifically for high-speed quality engineering teams. With KaneAI, users can create and refine complex test cases using natural language, drastically reducing the time and expertise needed to begin test automation.
Features:
- Intelligent Test Generation: Simplifies test creation and evolution using NLP-based instructions.
- Intelligent Test Planner: Generates and automates detailed test steps from high-level objectives.
- Multi-Language Code Export: Transforms automated tests into various languages and frameworks.
- Smart Show-Me Mode: Converts actions into natural language instructions for creating reliable tests.
With the rise of AI in testing, it’s more important than ever to stay ahead by enhancing your skills. The KaneAI Certification validates your practical expertise in AI-powered testing and positions you as a future-ready, high-value QA professional.
Functionize
Functionize is an AI-driven testing platform leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to streamline test creation, execution, and maintenance. It offers intelligent test generation using natural language and self-healing capabilities for robust test automation.
It also supports cross-browser and cross-platform testing for modern software applications. With its cloud-based architecture, Functionize ensures scalability and fast deployment.
SeaLights
SeaLights is an AI-powered test optimization platform focused on quality intelligence and risk-based testing. It identifies untested code and helps prioritize testing efforts, reducing unnecessary executions.
It can also integrate with CI/CD pipelines that ensure continuous feedback on test quality. SeaLights also offers AI-driven insights to enable teams to make data-informed decisions and optimize testing efficiency.
Worksoft
Worksoft is an AI-infused test automation tool designed for enterprise-scale business applications. It lets you perform end-to-end testing of complex software applications, including ERP and CRM applications.
With a no-code interface, Worksoft empowers teams to automate testing without extensive technical skills. Its AI-driven analysis ensures high accuracy and reduced test maintenance.
Challenges With Autonomous Testing
Autonomous testing is a process with many complex technologies working together to make a lot of things work. Certainly, such a process will pose a few challenges to the team before, during, and post its integration.
Following are some of the challenges that you can come across while performing autonomous testing.
- Training AI for All Projects: Traditional testing generates test scripts for each project depending on its requirements, functionality, goals, etc. However, autonomous testing tools have to be generic where it is expected from the tool to change its testing method according to the project. This is a complex and difficult task to achieve. Even if the team gets vanilla algorithms, training them with respect to each project is cumbersome and time-consuming.
- Incompatibility With All Phases: A testing cycle will consist of many phases, each deployed for a specific goal. Most of the time, the team focuses on functional requirements, which are easier to convert to AI-based techniques.
However, certain phases are more human than robotic which does not necessarily work on intelligence due to challenges in AI incorporation. These phases could be user experience-focused, such as UX or exploratory testing.
- Doubts on AI Accuracy: Autonomous infrastructure works independently and presents an output at the end of execution. While the theoretical accuracy of the infrastructure is always provided to the team by the tool provider, doubts over its correctness in different situations are always lingering among the team.
Since too much depends on the outputs received by an autonomous system, it becomes a challenge to verify them every time without wasting any time.
- Integration With Other Tools: Integration with third-party tools is an essential part of software testing. However, there is always a security threat if this application (which is to be integrated) allows anyone to integrate and transfer data across applications.
Therefore, only authorized tools are allowed to access a tool out of its space most of the time. But since there are so many integrations available today and nobody is sure about which one will be used by which team in which organization, all of them will hardly be supported by any autonomous tool. It becomes a major challenge for the testing.
- Lack of Standardization Authority: Testers often go through IEEE 829 to learn about the standards for software testing. However, these do not consider autonomous testing as of now. For that, currently, the teams and businesses have to analyze the impact themselves. This lack of standardization can often lead the testers to make a wrong decision when it comes to autonomous testing elements.
- Frequent Maintenance: Autonomous testing goes through frequent changes, or rather advancement, in a very short period. This is because the technology is new and undergoes extensive research and innovation every day.
Hence, the adoption of autonomous technology would mean frequent maintenance and update work, which can incur additional time and costs. However, this challenge can be settled if a cloud-based tool is adopted, given that they do not change the testing behavior and the way testing is executed.
- High Production and Costs: Autonomous testing tools require expert and expensive testers with world-class infrastructure to execute everything at a faster speed. On the other hand, if the production costs are high, it ultimately gets trickled down to its customers and they are the ones who have to pay a heavier price in the end.
It is the reason autonomous tools are often expensive (exceptions are always there!) and if costs don’t balance out, customers may hesitate to opt for them.
Conclusion
The knowledge of autonomous testing put forward clearly illustrates that autonomous testing is not yet ready to be used as a plug-and-play software. We can divide the future of autonomous testing into three parts.
The first part is the current scenario. Most of the tools provide codeless testing, visual testing, and self-healing as part of their autonomous package. Along with it, some are translating the code with the help of AI. Since accomplishing testing using current technologies requires manual intervention, we can term it as semi-autonomous.
The second part is the near future, in which progress has already started to show up but it is still not refined to be used at the enterprise level. For the next three years, autonomous testing seems to focus more on integration into the third-party application, prediction beyond written reports and possibly during or before test execution, and understanding the context of the application through written means or any other form of input from the testing team.
The third part is a fully autonomous system, which could take at least five years to be brought to commercial use, handling the production of enterprise-level applications. This would be the stage where no manual intervention is required. While the timelines are yet not clear, one thing is for sure: the inventions and advancements in autonomous testing are happening each day bringing us closer to a completely autonomous system.
Citations
A New Approach Of Software Test Automation Using AI: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380459206
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



