
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What Is Verification Testing?
- What Is Validation Testing?
- Digging Deep Into Differences Between The Two
- Test Verification vs Validation – What is the Aim?
- Test Verification vs Validation – What it Involves?
- Test Verification vs Validation – Difference in Methods
- Test Verification vs Validation – Who Does What?
- Test Verification vs Validation – When Does the Process Get Executed?
- Test Verification vs Validation – What do They Target?
- Test Verification vs Validation – Cost of the Process
- How Test Verification & Validation Balance the SDLC?
- Let Us Evaluate Some Examples
- Conclusion
What is Verification and Validation in Software Testing?
This article will present a detailed difference between verification vs validation in software testing with examples around cross browser testing.
Arnab Roy Chowdhury
January 11, 2026
Verification and Validation, both are important testing activities that collectively define all the mandatory testing activities a tester along with the entire team needs to perform when you are developing a website for either your organization or for the client. For testers, especially those who are new in the industry, understanding the difference between test verification vs validation in website testing may seem to be a bit complex. Because both involve checking whether the website is being developed in the right manner. This is also why I have observed a lot of ambiguity among the teams working on a project.
This article is my attempt to help you clarify the difference between test verification vs validation in website testing. Now, let’s take a deep dive in the following article where we shall get a detailed understanding of what is verification and validation testing. I will be explaining the difference using a cross browser testing scenarios.
Before we get started I would want to highlight the key distinguishment between test verification vs validation. Verification testing involves checking whether the team is following the right approach, it could be related to design, SRS document etc., while Validation testing involves checking whether the finished product satisfies all the needs of the customer. So, like whether it supports all the required browsers and devices.
What Is Verification Testing?
Verification Testing, also known as static testing, checks if a software meets specified requirements at a development stage through inspections, reviews, and code walkthroughs. It’s vital in the engineering process, ensuring the product design aligns with requirements and is commercially viable.
Before the commencement of any website or application development, the stakeholders or client sends a detailed document that consists of the specifications of the desired application. However, often we tend to ignore reviewing the documents and miss out some critical functionality during development. This may include specs like the website should support a specific browser or device.
The steps required to start verification testing can be understood by taking a look at the following document.
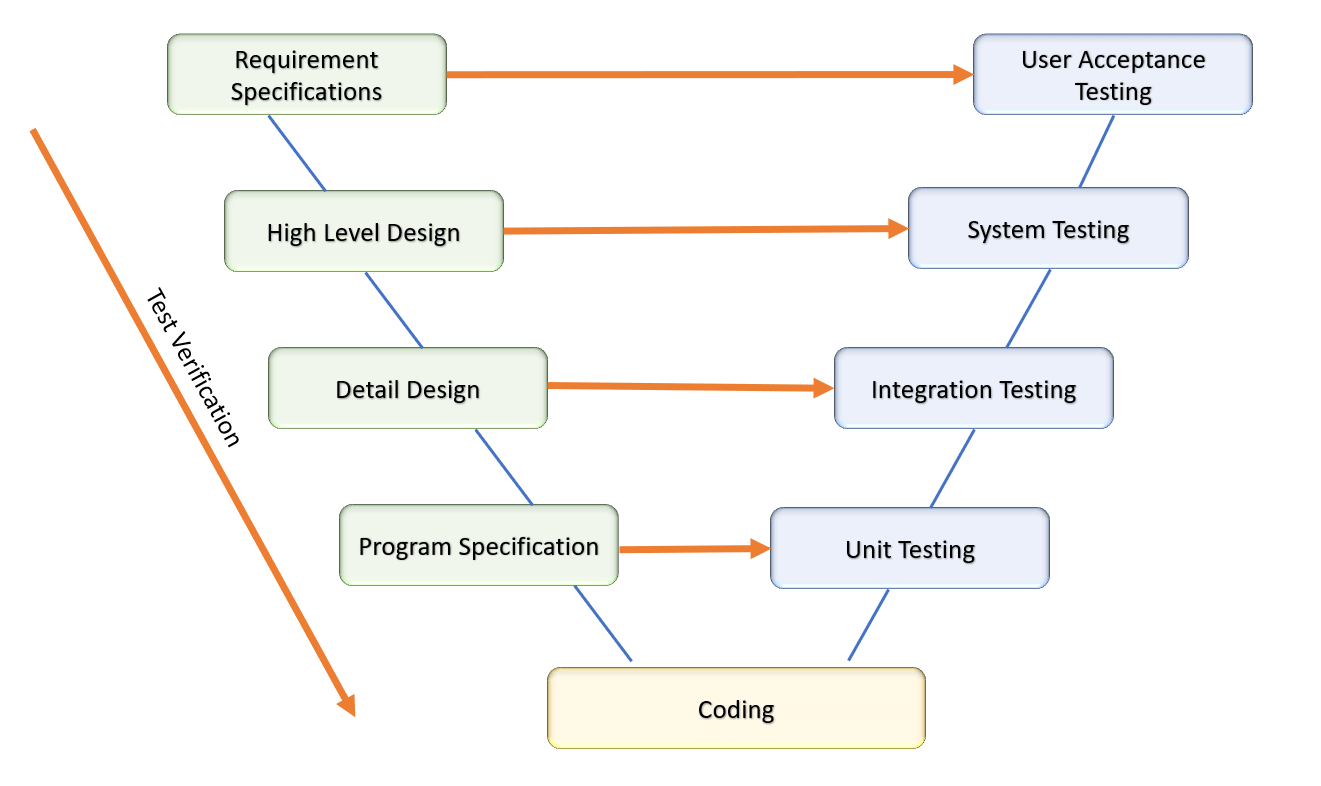
Importance Of Test Verification
Verification testing is a must to perform process when it comes to testing a website for cross-browser compatibility.
- Suppose you are building a single page web application. Verification testing is all about checking whether the webpage has all the components or supports all the browsers mentioned in the SRS. If any anomaly is found in the web application during verification testing it will create a critical bug in the next phases of testing. Hence, test verification is carried out to ensure that the number of bugs is reduced in the later phases.
- Test verification is the only answer to the very basic question of “Are you developing the website correctly?”
- In each phase of the development life cycle, verification testing demonstrates completeness, correctness, and consistency of the web application.
- Verifying the product in the very beginning makes you understand it better. It even reduces the chance of bug occurrence during development as well as validation testing.
- Reduces the chance of failure and helps in creating a product as per the requirements of the customer.
What Is Validation Testing?
Validation testing is the evaluation of software during or after development to ensure it meets specified business requirements and user needs. It focuses on testing the functionality and performance to validate the software’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios. Unlike verification, validation confirms the product’s actual utility and relevance to end-users, ensuring it fulfills its intended purpose.
During web application testing, the primary aim is to check for quality. Whenever any new bug is found, the developers fix the bug. After that, testing is executed once again to check if any bug persists. The aim of test validation is to find out whether the website performs all the functions which were intended and thereby meet the needs of the end users or stakeholders.
Validation testing takes place after the development as well as verification testing is completed. All the popular and mandatory testing procedures like unit testing, system testing, acceptance and integration testing, etc fall under the category of validation testing. The following diagram can be referred to in order to understand how it works.
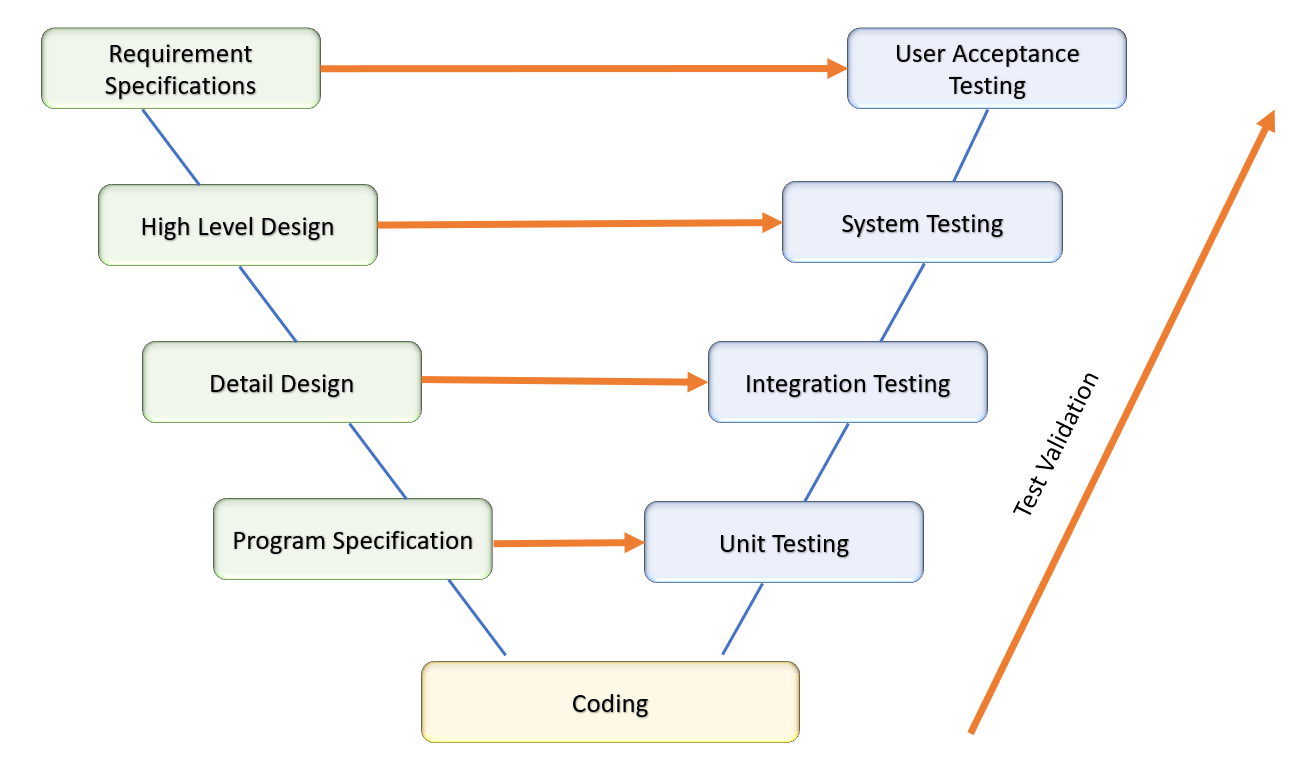
Importance of Test Validation
A product can pass verification testing since it involves only a pen and paper and not the developed application. However, some points which passed verification testing may fail when it is implemented in the actual product. Validation testing is important because
- Defects which are missed during verification testing can be caught as bugs during validation testing. For example, supporting a minor CSS feature in multiple browsers. This can only be tested once validation testing is carried out.
- Validation testing is done in multiple phases like load testing, acceptance testing, unit testing, etc. Thus the web application goes through all the mandatory testing phase.
- Validation testing ensures that after development, the finished product satisfies all the requirements of the customer.
- Let’s suppose your website is supposed to run perfectly on a specific browser in a specific operating system. However, the concept got misunderstood during verification testing. When the feature is implemented and validation testing is carried out, the tester will be able to understand the functional difference between the actual and expected result.
Digging Deep Into Differences Between The Two
Now, that we have a good understanding of what the two terms i.e. test verification & test validation stand for! It is time we dig deeper into the differences among the two.
Test Verification vs Validation – What is the Aim?
One of the key points, when we compare verification and validation, is the aim. The aim of verification testing is to confirm whether the planned web application will meet the customer’s specification before the development begins. While validation testing is aimed at checking whether the finished product meets the requirement after development has been completed. Here is an example of cross browser testing, suppose you are about to develop a cross browser compatible web application. The client wants it to run properly in 4-5 different operating system – browser combinations. Verification testing ensures that the site is developed in a way which makes it run properly in all the combinations. Validation testing is aimed at ensuring that the developed site actually runs properly in all the combinations.
src:(https://www.sitepoint.com/usability-testing-goals-knowing/)
Test Verification vs Validation – What it Involves?
Verification testing is mostly a pen and paper job. It involves assessing the SRS, workflow of the site design, program and documents. However, it involves multiple members from different teams and the process is quite lengthy.
Validation, on the other hand, is completely dynamic and checks the quality of the product in multiple environments, both manual and automated testing after development is completed.
Test Verification vs Validation – Difference in Methods
Since verification is a static process it does not involve code execution. It mostly involves evaluation of specifications, page workflow, design, and test cases. Sometimes it involves code review as well. It can only be done manually since it involves mostly analysis. There is no scope of automation in verification testing.
Validation, however, involves the execution of the code along with unit testing and also the execution of the test cases to find out if the code works perfectly in satisfying the requirements of the end user. Since most of the common testing phases like the unit, functional or regression testing can be done with the use of automated scripts, there is plenty of scope for automation in validation testing.
Test Verification vs Validation – Who Does What?
Verification testing, since it involves analysis is carried out by multiple teams.
- The client, as well as the dev team, reviews the business requirement.
- Design review is done by the dev team.
- Code reviewing is performed, primarily by the developers.
- The QA team reviews the test plan.
- The test plan is again reviewed externally by the QA manager as well as business analyst.
- Peer reviewing of the test documentation is performed by the QA team.
- Finally, the business analysts along with the dev team reviews the test documentation.
Validation testing is performed entirely by the QA team which involves both manual as well as automation testers from the organization as well as sometimes from the client side.
Test Verification vs Validation – When Does the Process Get Executed?
Let’s take a detailed look at the process. During verification testing:
- The team makes sure that the requirements have been correctly gathered. Once they have been finalized, the next step begins – design review.
- The dev team reviews the design and ensures all the suggested functional requirements can be actually implemented.
- Coding starts and it is thoroughly reviewed to ensure that it is free from any syntax errors. This is a casual activity and can be performed by the developer.
- A formal code review is carried out by the developer as well as the architect to check whether it satisfies the best practices and requirements specified.
- Now the job shifts to the QA team. They create a test plan and reviews it internally to check the accuracy and completeness.
- The test plan is reviewed by the QA manager as well as the project manager and BA to make sure that testing is in sync with other project activities.
- After the test documentation is signed off, the team members review each other’s activity internally to ensure that the documentation does not have any mistakes.
- Once everything is done, the test documentation again goes through a final review by the dev team after which it is shared to all the team members and ready for the next phase, i.e. validation testing.
Now, let us look into what Validation testing involves?
- Unit testing – Done by the developer once the coding is completed as well as by the tester. Many common defects are caught during unit testing itself.
- Integration testing – This is the phase where all the individual pieces of code or units are combined and tested as a whole. This evaluates whether the code complies to the required criteria.
- System testing – This testing phase is carried out on the complete system once the integration is complete. It has multiple sub-categories like functional, load testing, regression testing and other forms of testing which ensures that the application does not have any bugs once it is live. Browser compatibility testing or cross browser testing is an integral part of system testing. It ensures that the website runs perfectly on all the device-operating system-browser combination specified by the client.
- User acceptance testing – This is the last phase of validation testing. Here, actual users test the application to make sure that all the real world scenarios intended by the user can be handled smoothly by the application. This activity is carried out either by the organization or by the client.
Test Verification vs Validation – What do They Target?
Verification testing usually targets architecture of the website, database design, specifications, design of the product, etc.
Validation testing targets each component of the website, the modules, security, integrated components as well as the final website once it is ready for Golive.
Test Verification vs Validation – Cost of the Process
Verification testing does not cost much since it involves internal team members, manual labor cost and analysis only. If carried out properly, it reduces the overall project cost as well, since the cost of detecting errors during verification testing is much less than doing the same thing during validation testing.
Validation testing, on the other hand, cost a lot because it involves manual labor, automation tools, cost of licenses of the testing as well as reviewing tools and in case of a cross browser compatible website, the cost increases since the organization has to purchase multiple devices and operating systems on which testing should be carried out. However, the device and OS cost can be reduced a lot if you are using a cloud-based testing platform like TestMu AI, where you can test your application seamlessly across hundreds of different device-browser-OS combinations simultaneously.
How Test Verification & Validation Balance the SDLC?
Test verification and Test Validation are both mandatory activities and one cannot be completed without the other. It is a completely possible scenario that a website passes verification testing but fails when validation testing is carried out. Sometimes, your requirements itself may not be aligned with what user needs and that may lead to a scenario where test verification may pass with flying colors but the development may sink in test validation phase.
For example, the customer may ask for a certain feature like a hovering effect on a certain image or button for his cross-browser compatible website. This requirement may pass verification testing but will fail validation testing since certain hover effects of CSS3 are not supported in Internet Explorer 11 or below.
Let Us Evaluate Some Examples
Let’s suppose your client wants to you add a CTA on your page has a box shadow of a certain dimension. Both verification and validation testing takes place in the following sequence.

Verification testing
- The team analyzes and checks whether the feature suggested by the client is feasible.
- Test cases are written to test the feature in multiple browsers, especially the browsers suggested by the client.
- What if it is found out that while documenting the requirements, there was some mistake in the color code. We don’t want the button to look something like this

In that case, the necessary corrections are made in the document and it is again sent for review.
- The documents are sent to the respective team members for a final review.
- Once that is done, the development team starts coding.
Validation testing
Once development is done, validation testing starts in the following sequence.
- Unit testing – The developer checks if the box-shadow works properly in his system.

- Integration testing – The tester checks if the box-shadow works properly when used with other components in the page
- System Testing – The tester checks if the box-shadow works perfectly when integrated with the entire page or the site. Manual or comes into play here, where it is checked whether the button and the shadow are displayed perfectly across all the required browsers.
- User Acceptance Testing – Finally, in UAT, real users or testers representing end users test the feature from their perspective and report if any anomaly is found.
Conclusion
Based on the difference mentioned above, we can state that involving the product is not necessary during test verification. But, it is mandatory during test validation. They both have different filters for finding out the errors and both of them check for bugs In their own way. Hence, it can be concluded that both verification, as well as validation testing, are mandatory activities when you are developing a cross-browser compatible website and should be executed before the website goes live.
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on TestMu AI
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




