
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What Is Selenium Stealth Mode?
- Key Benefits of Using Selenium Stealth Mode
- Running Selenium Stealth Mode for Anti-Bot Bypass
- Running Selenium Stealth Mode on Cloud Selenium Infrastructure
- Stealth Mode Techniques to Avoid Detection
- Ethics and Legal Aspects of Selenium Stealth Mode
- Limitations of Selenium Stealth and Alternatives
- Undetected ChromeDriver vs. Selenium Stealth
How to Use Selenium Stealth Mode to Bypass Bot Detection
Learn how to use Selenium Stealth Mode to bypass bot detection in web scraping with step-by-step setup, examples, and cloud testing on TestMu AI.

Jacob Muganda
January 11, 2026
Web scraping is a crucial technique for extracting data from websites, but many sites deploy anti-bot measures that can block standard automation tools like Selenium. Selenium Stealth Mode helps make automated browsers appear more like real users by adjusting browser behavior, reducing the chances of detection and enabling more reliable data extraction.
Overview
What is Selenium Stealth Mode?
Selenium Stealth Mode simulates real user behavior to help automation avoid bot detection. It also adapts easily to different website security checks.
Key features of Selenium Stealth Mode
- Mask Automation: Hides navigator.webdriver and other detectable properties.
- Realistic Browsing: Spoofs headers, user-agent, and platform info.
- Human-Like Behavior: Adds delays, scrolling, and click patterns.
- Cloud & Local Ready: Works seamlessly across environments and Selenium grids.
Steps to Run Selenium Stealth Mode for Anti-Bot Bypass
- Set up environment: Initialize a Python virtual environment for isolated testing.
- Install dependencies: Add Selenium, Selenium Stealth, WebDriver Manager, and dotenv.
- Configure ChromeDriver: Apply Chrome options to handle sandboxing and system resources.
- Enable stealth Mode: Mask automation flags, headers, WebGL, and platform info.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium_stealth import stealth
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
stealth(driver, webdriver=False)
driver.get("https://example.com")
print(driver.title)
driver.quit()
- Navigate and interact: Open the target site, wait for elements, and simulate user actions.
- Verify stealth: Check page title, user agent, and WebDriver detection status.
- Handle exceptions: Catch and log errors for debugging.
- Close browser: End session and free system resources.
Steps to Run Selenium Stealth Mode on Cloud
- Set up credentials: Create a .env file and add your TestMu AI username and access key.
LT_USERNAME="<your_username>"
LT_ACCESS_KEY="<your_access_key>"
- Configure capabilities: Define browser, OS, and other automation settings for your test.
- Connect to TestMu AI Selenium Grid: Link your local script to the cloud infrastructure.
# Connect local Selenium script to LambdaTest Selenium Grid
driver = webdriver.Remote(
command_executor=f"https://{os.getenv('LT_USERNAME')}:{os.getenv('LT_ACCESS_KEY')}@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub",
options=Options()
)
- Run your tests: Execute Selenium Stealth Mode scripts, verify stealth functionality, and interact with elements as usual.
What Is Selenium Stealth Mode?
Selenium Stealth Mode is a Python library that modifies browser properties to prevent detection by anti-bot systems when using Selenium WebDriver. It tweaks automation indicators, like the navigator.webdriver flag and certain browser fingerprints, by adjusting JavaScript properties, headers, and interaction patterns.
The library is lightweight and integrates easily into existing Selenium scripts, helping you scrape or automate protected websites with a lower risk of detection. For a broader understanding of Selenium’s features and usage, you can also follow this Selenium tutorial.
Key Benefits of Using Selenium Stealth Mode
Using Selenium Stealth Mode provides significant advantages for web scraping operations, particularly when dealing with protected websites and sophisticated anti-bot systems.
- Modify browser behavior: Adjusts browser properties and JavaScript variables to mimic human-like interactions.
- Conceal automation signatures: Tweaks indicators like navigator.webdriver and other detectable patterns.
- Easy integration: Works seamlessly with existing Selenium scripts with minimal code changes.
Note: Run Selenium tests in stealth Mode across 3000+ browser and OS combinations Try TestMu AI Now!
Running Selenium Stealth Mode for Anti-Bot Bypass
Let’s implement Selenium Stealth Mode through practical examples, starting with environment setup and progressing through local to cloud-based implementations.
Environment Setup:First, create a virtual environment and install the required packages, using the following commands below:
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv Stealth
# Activate virtual environment (Windows)
StealthScriptsactivate
# Activate virtual environment (macOS/Linux)
source Stealth/bin/activate
# Install required packages
pip install selenium
pip install selenium-stealth
pip install webdriver-manager
pip install python-dotenv
Now that all the required packages are installed, let’s consider a simple test scenario to understand how Selenium Stealth Mode works.
Test Scenario
- Launch the Chrome browser with Stealth Mode enabled.
- Open the TestMu AI Selenium Playground page.
- Verify that stealth Mode is applied by checking the page title, WebDriver detection, and User Agent.
- Wait for the input field to be present on the page.
- Print success messages for verification.
- Close the web browser.
Code Implementation:
Now let’s implement the given test scenario:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from selenium_stealth import stealth
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
# Setup WebDriver with Chrome options
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument("--no-sandbox")
options.add_argument("--disable-dev-shm-usage")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(service=Service(ChromeDriverManager().install()), options=options)
# Apply stealth mode
stealth(driver,
languages=["en-US", "en"],
vendor="Google Inc.",
platform="Win32",
webgl_vendor="Intel Inc.",
renderer="Intel Iris OpenGL Engine",
fix_hairline=True,
webdriver=False)
try:
# Navigate to LambdaTest Playground
driver.get("https://www.lambdatest.com/selenium-playground/")
# Verify stealth mode is working
print("Page Title:", driver.title)
print("WebDriver detected:", driver.execute_script("return navigator.webdriver"))
print("User Agent:", driver.execute_script("return navigator.userAgent"))
# Interact with form elements
wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10)
form_element = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.TAG_NAME, "input")))
print("Stealth mode test completed successfully")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error encountered: {e}")
finally:
driver.quit()
Code Walkthrough:
- Calling webdriver.Chrome(): Main thread pushes the Chrome WebDriver creation onto the stack; the browser starts with the given Chrome options (–no-sandbox, –disable-dev-shm-usage).
- Nested Function stealth(driver, …): The WebDriver instance calls stealth(), which is pushed onto the stack; it modifies browser properties such as navigator.webdriver, user agent, platform, vendor, and WebGL renderer to appear human-like. The main thread waits while these changes apply.
- Calling driver.get(URL): The main thread pushes the get() call onto the stack to navigate to the TestMu AI Playground page; execution pauses until the page fully loads.
- Nested Function driver.title: The WebDriver retrieves the page title; this call is pushed onto the stack, executed, and popped once the title is returned.
- Nested Functions driver.execute_script(…):
- navigator.webdriver check is pushed to the stack and executed to verify Stealth Mode.
- navigator.userAgent retrieval is pushed to the stack and executed to confirm the modified User Agent.
- Nested Function WebDriverWait(driver, 10): Main thread pushes the wait setup onto the stack to monitor the page for elements.
- Nested Function wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.TAG_NAME, “input”))): The wait object calls until(), pushed onto the stack; execution pauses until the input element is found.
- Calling print() statements: Each print command is pushed onto the stack sequentially to display the page title, WebDriver detection status, user agent, and test completion message, then popped after execution.
- Nested Function except Exception as e: If any error occurs, the exception block is pushed onto the stack; the error message is printed, and the block is popped.
- Calling driver.quit(): The main thread pushes quit() onto the stack; the browser closes and resources are freed, then the call is popped.
- navigator.webdriver check is pushed to the stack and executed to verify Stealth Mode.
- navigator.userAgent retrieval is pushed to the stack and executed to confirm the modified User Agent.
Test Execution:
To Execute the code run the following command:
Python StealthLocalTest.py
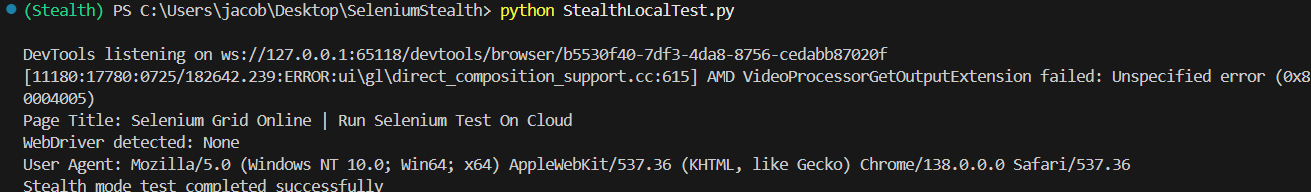
Running Selenium Stealth Mode locally can often be challenging for testers and developers. Differences in browser versions, limited system resources, IP-based restrictions, and inconsistent environments can make stealth automation unreliable and difficult to scale. These issues may sometimes result in detection or script failures.
In such situations, cloud-based Selenium automation offers a more reliable approach. Platforms like TestMu AI provide consistent browser and OS environments, enable parallel test execution, and give access to geographically distributed IPs for enhanced stability and scalability.
This setup can make Selenium Stealth properties more stable across different configurations, while also providing real browser instances with monitoring and debugging tools, supporting smoother and more manageable automation workflows.
Key takeaway: Local stealth setups work but are fragile across environments. Cloud Selenium grids provide more consistent results.
Running Selenium Stealth Mode on Cloud Selenium Infrastructure
Executing Selenium Stealth Mode on cloud-based platform like TestMu AI allows you to perform Selenium automation testing without worrying about local system limitations or environment inconsistencies.
With TestMu AI, you can scale your tests across multiple browsers and OS combinations effortlessly, while also gaining access to detailed logs and real-time debugging tools for improved test reliability.
TestMu AI is a GenAI-native test execution platform that allows you to perform manual and automated tests on a Selenium Grid online at scale across 3000+ browser and OS combinations. It helps you maintain consistency while minimizing detection risks and environment issues, even in Stealth Mode.
To get started with Selenium Stealth Mode on TestMu AI, all you need to do is follow the instructions below.
- Create .env file: Securely store your TestMu AI credentials, create a .env file in the root of your project and add the following values:
LT_USERNAME="<your_username>"
LT_ACCESS_KEY="<your_access_key>"
gridURL = "@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub"
ChromeOptions browserOptions = new ChromeOptions(); browserOptions.setPlatformName("Windows 10");
browserOptions.setBrowserVersion("121.0");
HashMap<String, Object> ltOptions = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ltOptions.put("username", "YOUR_LT_USERNAME");
ltOptions.put("accessKey", "YOUR_LT_ACCESS_KEY");
ltOptions.put("project", "Selenium Stealth Mode");
ltOptions.put("w3c", true);
ltOptions.put("plugin", "java-testNG");
browserOptions.setCapability("LT:Options", ltOptions);
You can generate the necessary Selenium Stealth Mode capabilities using TestMu AI Automation Capabilities Generator.
Running your Stealth Mode tests on TestMu AI’s cloud infrastructure removes the need to manage local environments, while support for parallel execution allows you to scale efficiently, reduce test times, and run reliable anti-bot automation with minimal setup.
For more details, check out the documentation on running Selenium Automation Testing Using TestMu AI.
Finally, combine cloud execution with Selenium Stealth Mode capabilities.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
import os
import dotenv
import time
dotenv.load_dotenv()
def test_lambdatest_stealth():
username, access_key = os.getenv("LT_USERNAME"), os.getenv("LT_ACCESS_KEY")
if not username or not access_key:
print("Error: Set LT_USERNAME and LT_ACCESS_KEY in .env file")
return
remote_url = f"https://{username}:{access_key}@hub.lambdatest.com/wd/hub"
options = Options()
# LambdaTest capabilities with stealth Chrome options
options.set_capability("LT:options", {
"build": "Stealth-Test", "name": "LambdaTest Stealth", "browserName": "Chrome",
"browserVersion": "latest", "platformName": "Windows 10", "network": True, "visual": True,
"chrome.options": {
"args": ["--no-sandbox", "--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled", "--disable-extensions",
"--user-agent=Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"],
"excludeSwitches": ["enable-automation"], "useAutomationExtension": False
}
})
try:
print("Initializing LambdaTest stealth driver...")
driver = webdriver.Remote(command_executor=remote_url, options=options)
# Comprehensive stealth JavaScript injection
driver.execute_script("""
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'webdriver', {get: () => undefined});
delete navigator.__proto__.webdriver;
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'plugins', {get: () => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]});
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'languages', {get: () => ['en-US', 'en']});
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'userAgent', {get: () => 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'});
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'platform', {get: () => 'Win32'});
Object.defineProperty(navigator, 'hardwareConcurrency', {get: () => 4});
const getParameter = WebGLRenderingContext.getParameter;
WebGLRenderingContext.prototype.getParameter = function(parameter) {
if (parameter === 37445) return 'Intel Inc.';
if (parameter === 37446) return 'Intel Iris OpenGL Engine';
return getParameter(parameter);
};
['webdriver', 'callPhantom', '_phantom', 'phantom'].forEach(prop => delete window[prop]);
""")
print("Navigating to test site...")
driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/")
# Quick stealth verification
print("Page Title:", driver.title)
detection_tests = {
"webdriver": "return navigator.webdriver",
"window.webdriver": "return window.webdriver",
"webdriver in window": "return 'webdriver' in window"
}
print("
--- Detection Tests ---")
for test, script in detection_tests.items():
result = driver.execute_script(script)
status = "✅ HIDDEN" if result is None or result is False else f"❌ DETECTED: {result}"
print(f"{test}: {status}")
# Browser properties check
print(f"
User Agent: {driver.execute_script('return navigator.userAgent')}")
print(f"Platform: {driver.execute_script('return navigator.platform')}")
print(f"Languages: {driver.execute_script('return navigator.languages')}")
# Test page interaction
wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 15)
try:
products = wait.until(EC.presence_of_all_elements_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, ".product-item, .product-thumb, .item, .product")))
print(f"Found {len(products)} products")
except:
elements = driver.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME, "a")
print(f"Found {len(elements)} links")
# Simulate human behavior
print("Simulating human behavior...")
for i in range(3):
driver.execute_script(f"window.scrollTo(0, {(i+1)*300});")
time.sleep(1)
print("✅ Stealth test completed successfully!")
time.sleep(5) # Keep session alive briefly
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
if 'driver' in locals():
driver.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("LambdaTest Stealth Test (Optimized)")
test_lambdatest_stealth()
This code highlights the shift from basic Selenium setups to a cloud-based stealth Mode implementation, showing how each step overcomes different scraping challenges.
Test Execution:
You can review the session details directly in the TestMu AI Automate dashboard, as shown in the screenshot below.
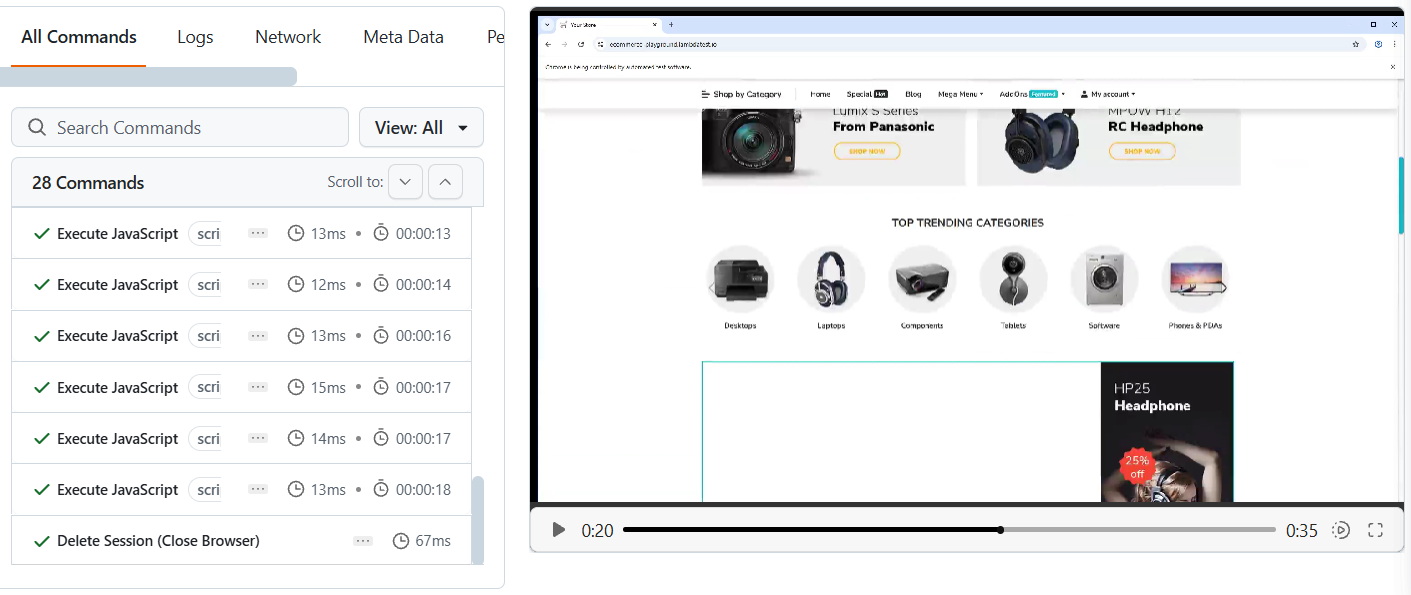
Stealth Mode Techniques to Avoid Detection
Selenium Stealth Mode employs multiple sophisticated techniques to mask automation signatures and avoid detection by anti-bot systems. Understanding these techniques helps optimize your scraping implementation.
- WebDriver Property Masking: The most fundamental detection method involves checking the navigator.webdriver property. Stealth Mode disables this flag:
stealth(driver, webdriver=False)
stealth(driver,
languages=["en-US", "en"], # Sets Accept-Language header
vendor="Google Inc.", # Browser vendor information
platform="Win32") # Operating system platform
stealth(driver,
webgl_vendor="Intel Inc.", # GPU vendor masking
renderer="Intel Iris OpenGL Engine", # Graphics renderer info
fix_hairline=True) # Canvas fingerprint protection
import time
import random
# Add human-like delays
time.sleep(random.uniform(1, 3))
# Use JavaScript for natural interactions
driver.execute_script("arguments[0].scrollIntoView(true);", element)
time.sleep(0.5)
driver.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", element)
These patterns make automation less distinguishable from genuine user behavior. Instead of executing commands instantly (which no human does), small delays and simulated scrolling/clicking mimic normal browsing.
According to Cloudflare’s bot management documentation, modern detection often relies on behavioral analysis beyond browser fingerprints. Independent research from Distil Networks highlights how bots are identified through request velocity and anomaly detection. This setup helps you avoid most common detection methods while still working smoothly on most websites.
Ethics and Legal Aspects of Selenium Stealth Mode
Web scraping with stealth capabilities requires careful attention to ethical and legal considerations. Responsible scraping practices protect both your projects and the websites you’re accessing.
- Respect Website Terms of Service: Always review and comply with website terms of service before implementing any scraping solution. Many sites explicitly prohibit automated access, and violating these terms can result in legal consequences regardless of your technical approach.
- Follow robots.txt Guidelines: Check the website’s robots.txt file to understand which areas are off-limits to automated tools:
import requests
def check_robots_txt(base_url):
robots_url = f"{base_url}/robots.txt"
try:
response = requests.get(robots_url)
print(f"Robots.txt content for {base_url}:")
print(response.text)
except requests.RequestException:
print("No robots.txt found or accessible")
# Example usage
check_robots_txt("https://example.com")
import time
import random
# Add delays between requests
time.sleep(random.uniform(2, 5))
# Limit concurrent connections
# Use session pooling when making multiple requests
session = requests.Session()
session.mount('http://', requests.adapters.HTTPAdapter(pool_maxsize=1))
Remember that stealth capabilities should enhance legitimate scraping operations, not enable malicious or unauthorized data collection.
Beyond legality, scraping responsibly helps preserve site performance. Industry standards, such as the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) guidelines for automated web agents, emphasize respecting robots.txt, limiting request rates, and ensuring fairness in resource usage.
Limitations of Selenium Stealth and Alternatives
Selenium Stealth Mode offers powerful advantages in bypassing common anti-bot mechanisms, but it comes with trade-offs that developers must consider.
Limitations of Selenium Stealth Mode:
- Relies on Chrome only, limiting other browser compatibility.
- Performance overhead slows large‑scale scraping jobs.
- Requires frequent updates, increasing maintenance effort.
- Fails against machine‑learning detection analyzing behavior.
Alternative and Complementary Solutions:
- Undetected ChromeDriver and Puppeteer stealth plugins.
- Managed services handle proxies, CAPTCHA, and fingerprint evasion.
- Official APIs provide reliable, compliant, rate‑limited data access.
- Layered strategies combine proxies, timing, and varied tools.
Ultimately, the best approach depends on factors like target site complexity, data volume, team expertise, and budget, often requiring a layered solution that combines stealth with proxy rotation, smart timing, or browser automation alternatives.
Undetected ChromeDriver vs. Selenium Stealth
The table contrasts two approaches for stealthy browser automation:
| Aspect | Undetected ChromeDriver | Selenium Stealth |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | pip install undetected-chromedriver | pip install selenium-stealth |
| Driver Initialization | uc.Chrome() | webdriver.Chrome() + stealth() call |
| Evasion Method | Uses a patched ChromeDriver binary to bypass checks | Modifies session parameters (user agent, WebRTC, etc.) |
| Code Changes Required | Swap webdriver.Chrome() → uc.Chrome() only | Keep webdriver.Chrome() and add explicit stealth calls |
| Configuration Effort | Minimal, handled internally | Manual, must set each stealth parameter yourself |
| Browser Support | Chrome only | Any browser supported by Selenium |
| Out-of-the-Box Evasion | High, many flags pre-configured | Moderate, depends on how many parameters you tweak |
| Portability | Limited to Chrome | Easily portable across browsers |
| Ease of Use | Very easy to get started | Requires more setup and understanding of options |
Playwright also offers a stealth plugin via community packages, which applies similar browser property masking. While not as lightweight as Selenium Stealth, it integrates well with modern async scraping workflows, making it worth evaluating for Node.js-based teams.
Conclusion
Selenium Stealth Mode provides a powerful solution for bypassing anti-bot detection systems in web scraping applications. By modifying browser properties and masking automation signatures, it enables access to protected websites while maintaining the familiar Selenium WebDriver interface.
The implementation progresses from local environments to cloud-based solutions, offering scalability for enterprise-level data extraction operations. However, success with stealth Mode requires understanding its limitations, implementing ethical scraping practices, and choosing appropriate alternatives when necessary. As anti-bot systems continue evolving, staying informed about detection methods and countermeasures remains essential for effective web scraping strategies.
Citations
- Selenium Official Documentation: https://www.selenium.dev/documentation/
- Selenium-Stealth PyPI Package: https://pypi.org/project/selenium-stealth/
- Python Virtual Environment Guide: https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/venv.html
- WebDriver Manager Documentation: https://pypi.org/project/webdriver-manager/
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



