
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What Is Gherkin?
- What Are Gherkin Test Cases?
- Writing Effective Gherkin Test Cases
- Integrating Gherkin with Test Automation Frameworks
- Implementing Gherkin for Selenium Automated Testing
- How to Run Your First Gherkin Test Case?
- Run Gherkin Test Case on TestMu AI KaneAI
- Advanced Techniques in Gherkin Testing
- Overcoming Common Challenges in Gherkin Testing
- Future Trends in Gherkin and BDD
- Best Practices for Writing Effective Gherkin Test Cases
Gherkin Test Cases: A Strategic Guide for Enterprise QA
Learn how to write effective Gherkin test cases with clear structure, tags, and scenario outlines to improve collaboration and automation.

Saniya Gazala
January 11, 2026
Gherkin test cases provide a structured way to define how software should behave. Using plain English, they bridge the gap between business teams, developers, testers, and other stakeholders.
Writing Gherkin test cases effectively promotes shared understanding, with precise wording, logical organization, and consistent structure, ensuring scenarios stay clear, maintainable, and easy to automate.
Overview
Gherkin test cases translate complex software requirements into simple, readable steps that anyone on the team can understand. They help align development and testing efforts by making expected behaviors explicit and easy to validate.
Writing Effective Gherkin Test Cases
Write clear, behavior-focused test cases that are easy to understand, maintain, and execute:
- Structuring Scenarios Clearly: Make each scenario’s purpose obvious.
- Using Tags for Organization: Group scenarios with meaningful tags.
- Write declarative steps: Prefer “what” over “how” using Given-When-Then.
- Define actors: Use third-person (e.g., “the user”).
- Avoid pitfalls: Keep scenarios short, specific, and independent; collaborate with stakeholders.
Example:
Feature: User login
As a user
I want to log in to the system
So that I can access my account
Background:
Given the user navigates to the login page
Scenario Outline: Successful login with multiple credentials
When the user enters username "<Username>" and password "<Password>"
Then the user should see the welcome message "<Message>"
Examples:
| Username | Password | Message |
| [email protected] | pass123 | Welcome, User1! |
| [email protected] | abc456 | Welcome, User2! |
| [email protected] | qwe789 | Welcome, User3! |
Run Your First Gherkin Test Case
- Define Scenario: Login to TestMu AI eCommerce Playground.
- Add Dependencies: Include Selenium, Cucumber, JUnit, and WebDriverManager in pom.xml.
- Create Feature File: src/test/resources/features/Login.feature with Given-When-Then steps.
- Create Step Definitions: Map Gherkin steps to Selenium code in src/test/java/stepDefinitions/LoginSteps.java.
- Create Test Runner: Connect feature files to step definitions in runners/TestRunner.java.
- Run Tests: Execute Test Runner and generate HTML/JSON reports.
What Is Gherkin?
Gherkin is a structured, domain-specific language designed to express software behavior in plain, human-readable text. It provides a formalized syntax that bridges communication between technical teams and business stakeholders, ensuring requirements are precise and unambiguous.
Beyond simply describing behavior, Gherkin forms the backbone of Gherkin testing in Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), where these specifications can be executed as automated tests. This approach allows teams to validate functionality continuously, maintain consistency across environments, and keep documentation synchronized with actual software behavior.
What Are Gherkin Test Cases?
Gherkin test cases are human-readable scenarios that describe software behavior using Given-When-Then steps. Each test case represents a single scenario capturing expected system behavior, making requirements clear for both technical and non-technical team members.
They are widely used in BDD frameworks like Cucumber or Behave, enabling automated testing while keeping tests readable, consistent, and reusable.
Writing Effective Gherkin Test Cases
Writing effective Gherkin test cases is about clarity, simplicity, and maintainability. Well-written test cases make it easier for teams to collaborate, understand system behavior, and automate testing efficiently, especially when leveraging frameworks like Cucumber for seamless execution in Gherkin testing.
Following structured guidelines ensures scenarios remain readable, focused, and reusable.
Structuring Scenarios Clearly
Organize each scenario so its purpose is immediately obvious, guiding readers step by step through expected behavior. Focused, well-structured scenarios make it easier to spot gaps and maintain tests over time.
- Clear titles and descriptions: Each scenario should have a concise title describing the behavior being tested. A clear description helps anyone reading the test understand its purpose without needing background knowledge.
- Focus on a single behavior: Limit each scenario to testing one specific action or outcome. Avoid combining multiple behaviors in a single scenario, as this makes tests harder to read, maintain, and troubleshoot when failures occur.
Implementing Scenario Outlines
Scenario Outlines allow you to define a single scenario template that can run with different input values, streamlining repetitive tests. This makes it easy to expand coverage without creating separate scenarios for each data set.
- Data-driven testing with Scenario Outlines: Scenario Outlines let you run the same scenario with multiple sets of data, reducing duplication and ensuring comprehensive coverage across combinations, a strategy often applied in Cucumber testing.
- Example of a Scenario Outline with Examples table:
Scenario Outline: Successful login with multiple credentials
Given the user navigates to the login page
When the user enters username "<Username>" and password "<Password>"
Then the user should see the welcome message "<Message>"
Examples:
| Username | Password | Message |
| [email protected] | pass123 | Welcome, User1! |
| [email protected] | abc456 | Welcome, User2! |
| [email protected] | qwe789 | Welcome, User3! |
Using Scenario Outlines ensures tests remain concise, readable, and maintainable while covering multiple data variations efficiently, making them ideal for Cucumber testing workflows.
Integrating Gherkin with Test Automation Frameworks
Integrating Gherkin test cases with test automation frameworks allows teams to turn human-readable specifications into executable tests, bridging the gap between business requirements and automated testing.
This integration ensures that scenarios written in Given-When-Then format are directly mapped to automation scripts, making tests both readable and actionable.
- Select a suitable framework: Choose a framework that supports Gherkin syntax and matches your tech stack. Examples: Cucumber for Java/Ruby, SpecFlow for .NET, or Behave for Python. Consider CI/CD compatibility and team familiarity.
- Define Feature Files: Write clear, human-readable feature files using the Given-When-Then format. Focus on one behavior per scenario to keep tests understandable and maintainable.
- Map steps to automation code: For each Gherkin step, create a corresponding function or method in your automation framework. For instance, a “Given the user is on the login page” step triggers a navigation command in Selenium or another tool.
- Modularize Step Definitions: Organize reusable steps into modules or libraries so multiple scenarios can share them. This reduces duplication and simplifies maintenance when requirements change.
- Organize Features and Scenarios: Group related scenarios under features and maintain a logical folder structure. Use meaningful names to make navigation and reporting easier.
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines: Configure automated execution of Gherkin scenarios as part of your build process. Use reporting tools to capture pass/fail results and link them back to the original feature files.
- Review and maintain regularly: Regularly update scenarios and step definitions to reflect application changes. Keep scenarios concise, readable, and aligned with evolving requirements.
Note: Write and run Gherkin BDD scenarios faster with KaneAI. Try KaneAI today!
Implementing Gherkin for Selenium Automated Testing
For demonstration purposes, you will use IntelliJ IDEA as it makes it easy to create and manage Java projects. You will use Selenium as your test automation framework.
To get started, follow the steps below:
Installation
The installation process consists of the following steps:
- Install JDK: You can download JDK from any of the following options:
- Install IntelliJ IDEA: You can download the latest version from the IntelliJ IDEA Alternatively, you can also use any other popular IDE like JetBrains WebStorm, Eclipse, etc.
- Install a BDD Framework (Cucumber): Download Cucumber Java dependencies or add them via Maven in your pom.xml.
Gherkin Project Setup
Below are the steps to create gherkin project:
- Open IntelliJ IDEA: Launch IntelliJ and select your workspace directory.
- Create a New Java Project: Go to File > New > Project > Java and enter project name (e.g., GherkinSeleniumDemo) > Click Finish.
- Create Packages:
- Create src/test/java/stepDefinitions for your step definition classes.
- Create src/test/resources/features for your Gherkin feature files.
How to Run Your First Gherkin Test Cases?
You will define a real-world scenario for automated testing using Gherkin. This section guides you to structure your feature file logically, ensuring each scenario clearly represents a single user action and its expected outcome.
Let’s write Gherkin test cases for the scenario: Login to an E-commerce Website. You will perform your tests on the sample website: the TestMu AI eCommerce Playground platform.
Test Scenario:
- Launch the Chrome browser.
- Open TestMu AI eCommerce Playground.
- Click on My Accounts.
- Select from the Dropdown the Login option.
- Enter the credentials.
- Click on the Login button.
Before code implementation, make sure you have the dependencies in place in the pom.xml file as shown below:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-java</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.cucumber</groupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junit</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.bonigarcia</groupId>
<artifactId>webdrivermanager</artifactId>
<version>5.0.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Now, in your project, create a folder: src/test/resources/features and inside it, create a new feature file named Login.feature. Write your Gherkin scenario using Given-When-Then syntax, as shown below:
Feature: User Login
As a registered user
I want to log into the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground
So that I can access my account
Scenario: Successful login via My Account dropdown
Given the user launches the Chrome browser and opens the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground
When the user clicks on "My Account" and selects "Login" from the dropdown
And enters username "[email protected]" and password "pass123"
And clicks the "Login" button
Then the user should see the dashboard page
To write the Step Definition code, you need to now create a Java class in src/test/java/stepDefinitions and map each Gherkin step to the main file:
package stepDefinitions;
import io.cucumber.java.en.*;
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
public class LoginSteps {
WebDriver driver;
@Given("the user launches the Chrome browser and opens the LambdaTest eCommerce Playground")
public void launchBrowserAndOpenWebsite() {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.get("https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/");
}
@When("the user clicks on {string} and selects {string} from the dropdown")
public void selectLoginFromDropdown(String menu, String option) {
WebElement myAccount = driver.findElement(By.linkText(menu));
myAccount.click();
WebElement loginOption = driver.findElement(By.linkText(option));
loginOption.click();
}
@When("enters username {string} and password {string}")
public void enterCredentials(String username, String password) {
driver.findElement(By.id("username")).sendKeys(username);
driver.findElement(By.id("password")).sendKeys(password);
}
@When("clicks the {string} button")
public void clickLoginButton(String buttonName) {
driver.findElement(By.id("loginButton")).click();
}
@Then("the user should see the dashboard page")
public void verifyDashboard() {
boolean dashboardVisible = driver.findElement(By.id("dashboard")).isDisplayed();
assertTrue(dashboardVisible);
driver.quit();
}
}
Code Walkthrough:
Below is the code walkthrough for the above code:
- Class LoginSteps: Contains all step definitions for login functionality.
- WebDriver driver: Declares the browser driver instance for automation.
- @Given: Defines preconditions for the scenario, like opening a browser.
- WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup(): Sets up ChromeDriver automatically.
- driver = new ChromeDriver(): Launches a new Chrome browser instance.
- driver.manage().window().maximize(): Maximizes the browser window for visibility.
- driver.get(url): Navigates to the specified web page.
- @When: Defines actions taken by the user during the scenario.
- driver.findElement(By.linkText(menu)): Finds a web element using its visible link text.
- element.click(): Performs a click action on the specified element.
- driver.findElement(By.id(“username/password”)): Finds input fields by ID for typing.
- element.sendKeys(text): Enters text into input fields.
- driver.findElement(By.id(“loginButton”)): Locates the login button by ID.
- @Then: Defines the expected outcome or verification step.
- element.isDisplayed(): Checks if an element is visible on the page.
- assertTrue(condition): Asserts that the expected condition is true.
- driver.quit(): Closes the browser and ends the session.
Once you have created your step definition file then you need to create the test runner file that connects your Gherkin feature files with the step definitions and executes them.
It ensures that your scenarios are run in an organized manner and generates readable test reports.
Test Runner
By running the Test Runner, you can execute all scenarios in your feature files at once. You can also customize it to generate HTML or JSON reports for better visibility of test results.
package runners;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import io.cucumber.junit.Cucumber;
import io.cucumber.junit.CucumberOptions;
@RunWith(Cucumber.class)
@CucumberOptions(
features = "src/test/resources/features",
glue = "stepDefinitions",
plugin = {"pretty", "html:target/cucumber-reports.html"}
)
public class TestRunner {}
Execute Test
To execute your code right-click TestRunner.java > Run.
Gherkin works best when scenarios are written in clear, plain English, making them easy for both technical and non-technical teams to follow. This approach became even more powerful with the introduction of the Cucumber framework, which allowed teams to connect plain-language scenarios directly to automated tests.
By leveraging Selenium automation testing with Cucumber, teams can implement Gherkin scenarios in a fully automated workflow, ensuring test cases are readable, maintainable, and executed seamlessly across multiple browsers and environments.
Now, AI is extending this capability, making it simpler to draft consistent, BDD-style Gherkin test cases in plain English. Solutions like TestMu AI KaneAI help teams plan, author, and refine tests using natural language.
Designed for high-speed quality engineering teams, TestMu AI KaneAI integrates seamlessly with TestMu AI’s suite for test planning, execution, orchestration, and analysis.
TestMu AI KaneAI helps in:
- Write Gherkin Scenarios: Create BDD-style tests in plain English.
- Generate Steps Automatically: Convert high-level objectives into executable steps.
- Multi-Language Code Export: Export tests to major languages and frameworks.
- Cross-Platform Testing: Run scenarios on web and mobile devices.
- API Testing: Include backend and integration checks in BDD scenarios.
- Reusable Test Data: Use variables for flexible and maintainable scenarios.
- Organize & Sync Tests: Manage scenarios and keep instructions in sync with code.
- Smart Versioning: Track and evolve test scenarios safely over time.
- AI-Assisted Debugging: Identify and fix issues faster with GenAI support.
- HyperExecute Integration: Execute tests faster across 3000+ environments.
- Automated Test Planning: Plan and prioritize tests using AI insights.
- Scenario Evolution: Update and refine tests easily as requirements change.
- Execution Insights: Get detailed reports, analytics, and performance metrics.
- Collaboration-Friendly: Share and collaborate on BDD scenarios across teams.
Run Gherkin Test Cases on TestMu AI KaneAI
Execute your Gherkin test cases seamlessly on TestMu AI KaneAI. Leverage cloud infrastructure to run tests across multiple browsers and devices. Accelerate automation while ensuring accuracy and consistency in your test results.
Follow the steps below to get started:
- Go to KaneAI: Click the KaneAI option from the TestMu AI dashboard.
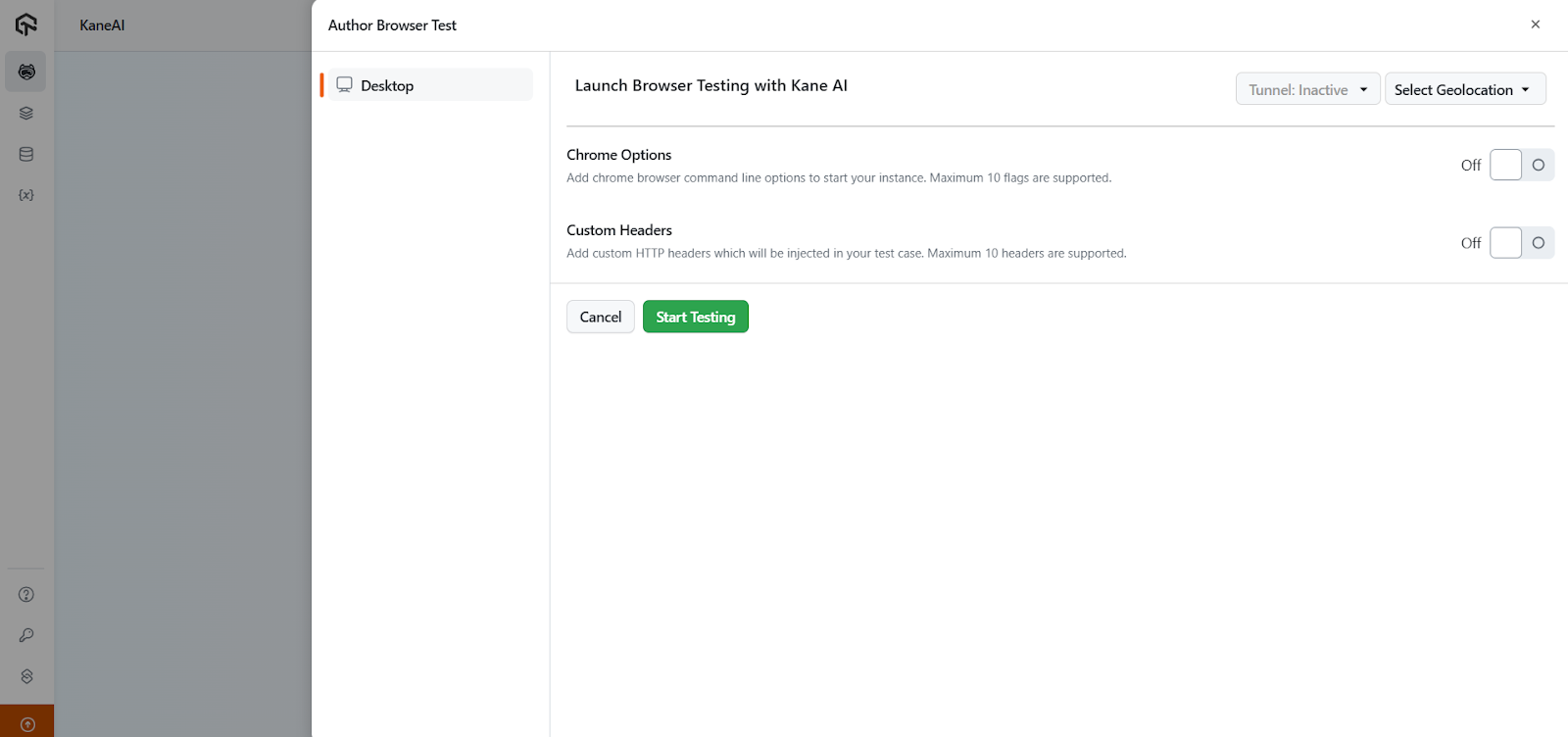
- Author Browser Test: Click on the Author Browser Test button to open the browser with a side panel.
- Start Testing: Click the Start Testing button to proceed with the default settings.
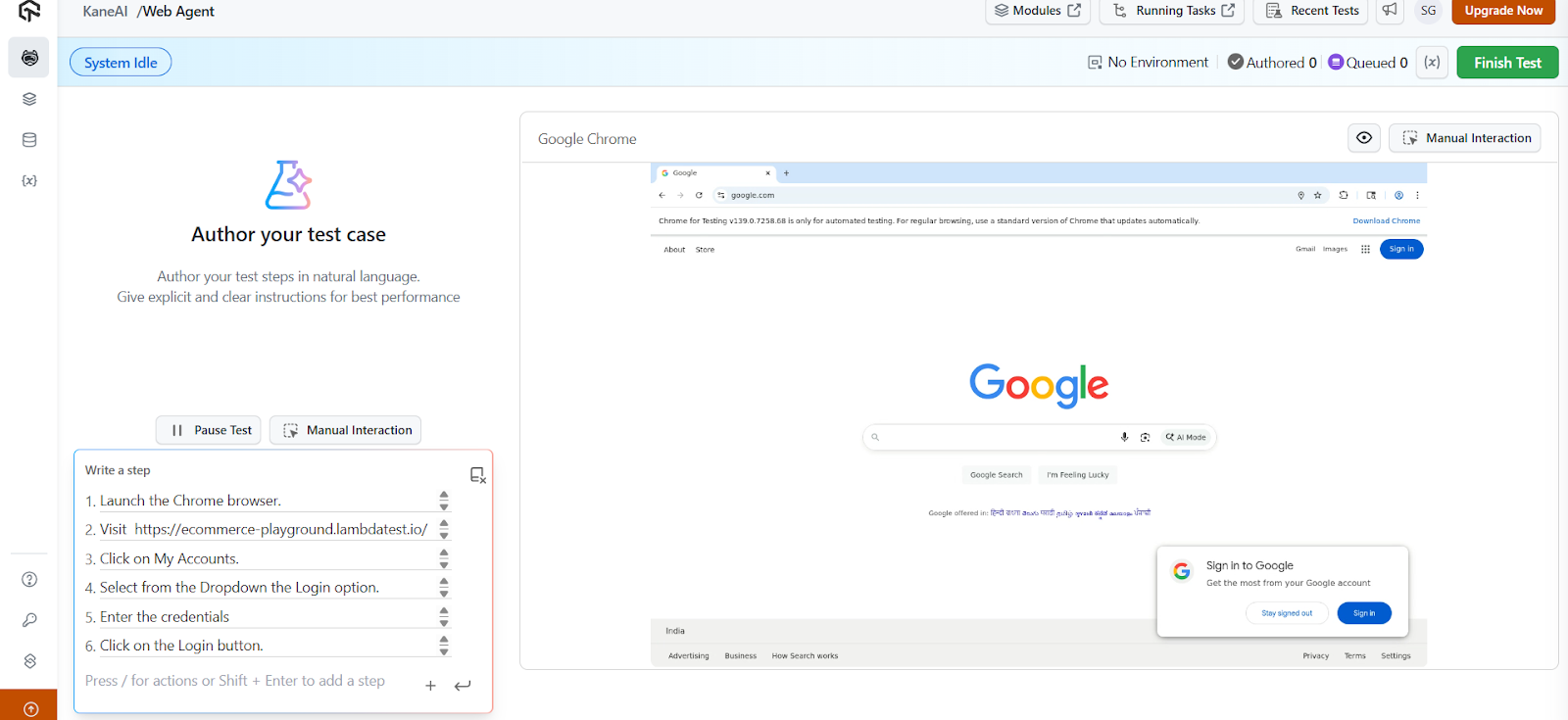
- Enter Test Scenario: Once redirected, enter your plain English test scenario.
- Launch the Chrome browser.
- Visit https://ecommerce-playground.lambdatest.io/
- Click on My Accounts.
- Select from the Dropdown the Login option.
- Enter the credentials:
- E-Mail Address: [email protected]
- Password: Example@123
- Click on the Login button.
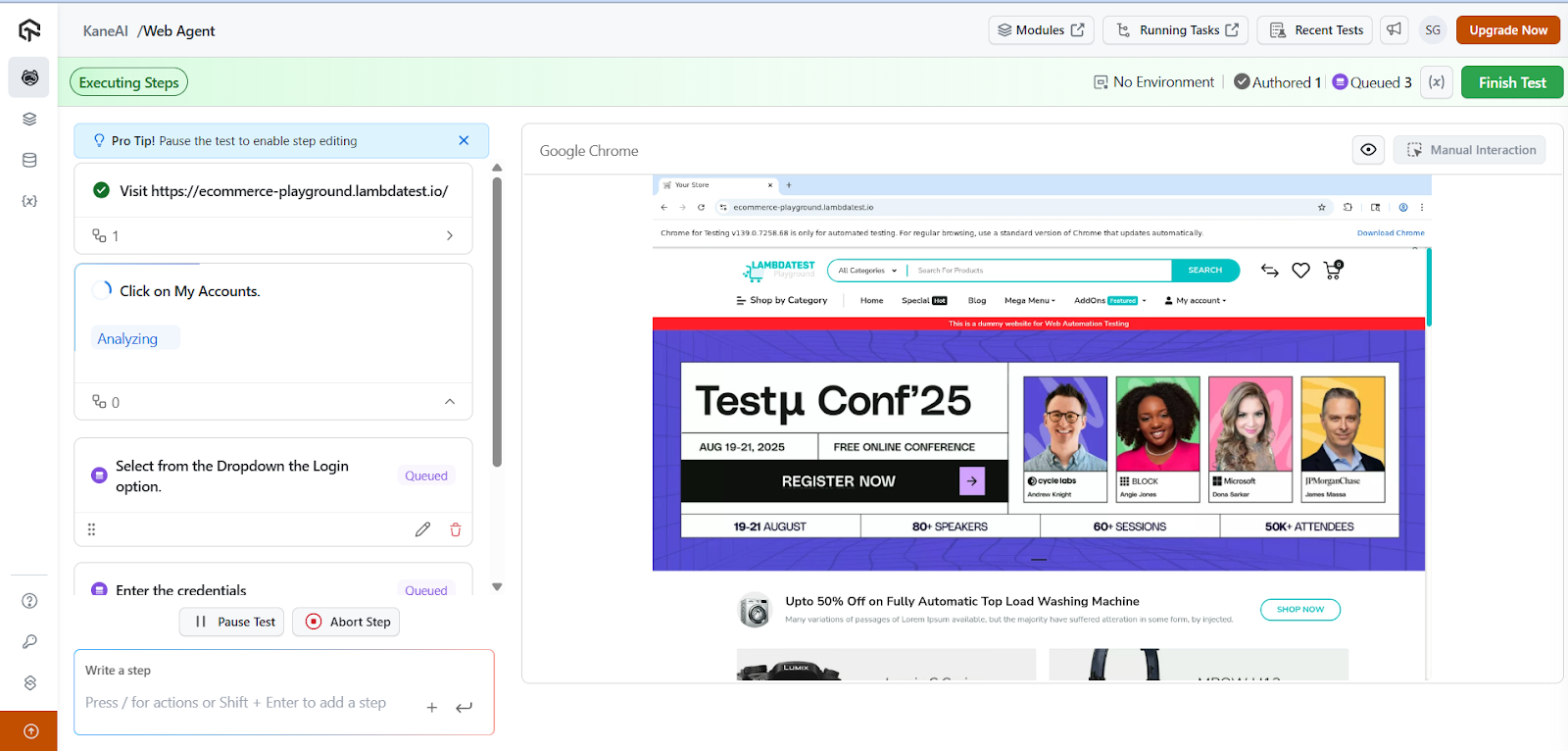
- Test Case Conversion : All the above test steps (or actions) are automatically converted into test cases.
- Auto-fill Fields: AI automatically fills in all required fields to save tester time. Click on the Finish Test button.
- Save Test Case : Select the folder, choose type and status, modify details if needed, then click on the Save Test Case button.
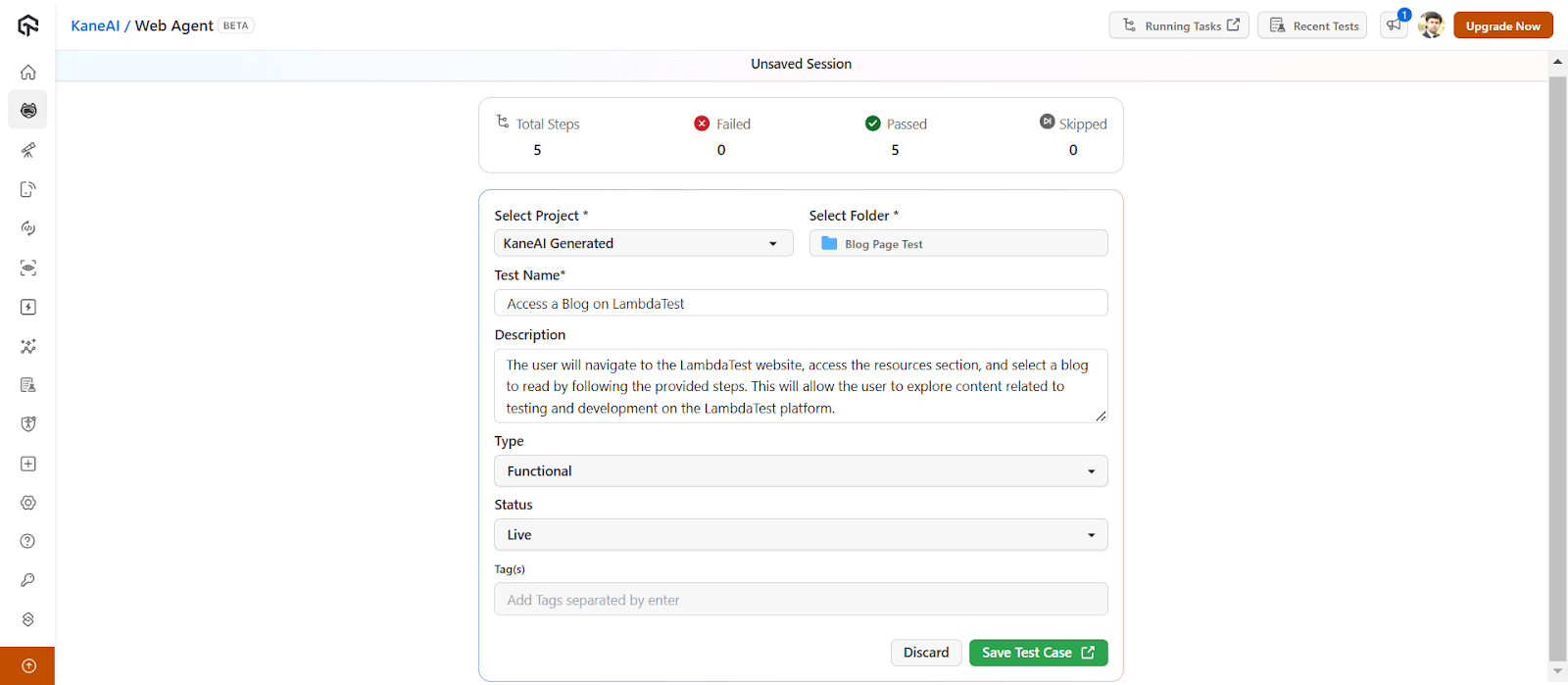
- Redirect to Test Manager : You will be redirected to the TestMu AI Test Manager to manage your test cases.
- View Details: Access additional information such as Summary, Code, Runs, Issues, and Version History.
- Generate Tests : Click on the Code tab to generate your tests for the above test cases.
For this demo, follow these steps:
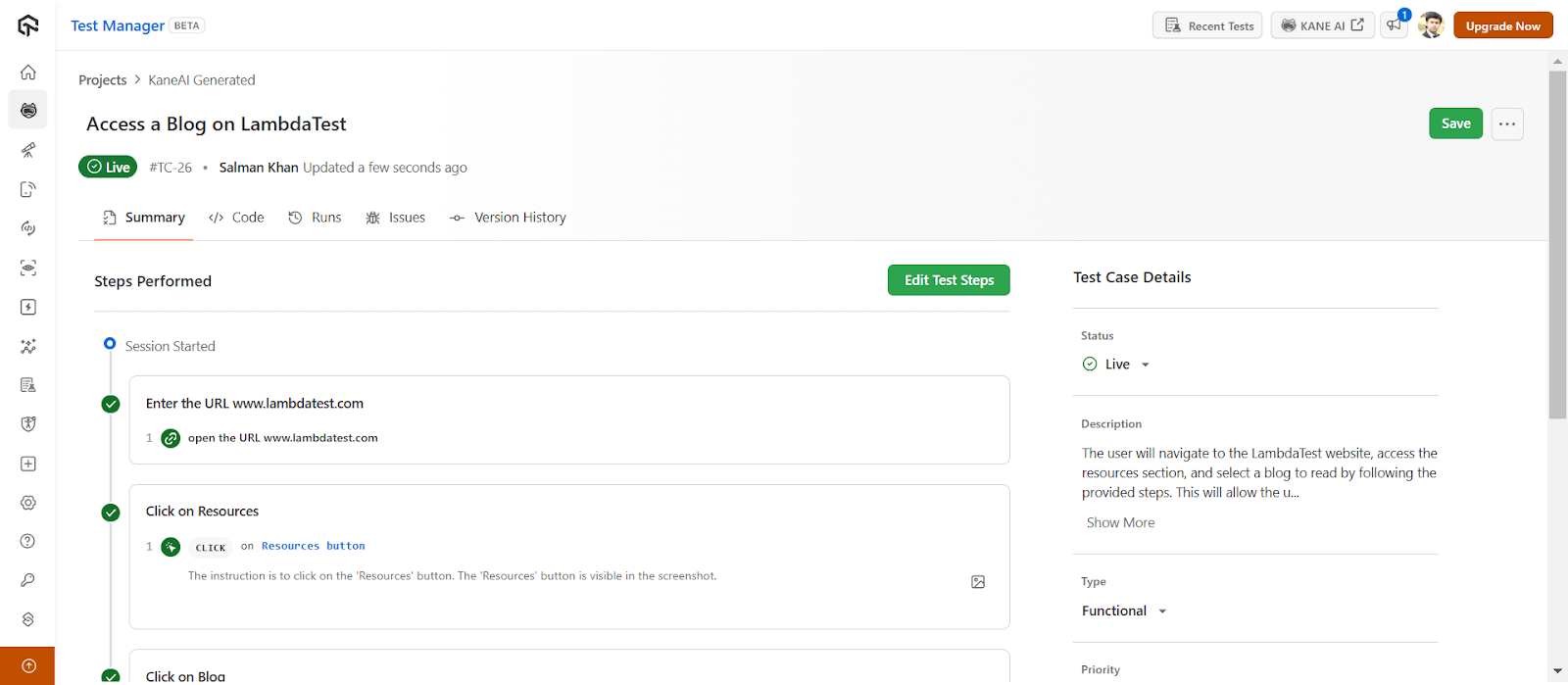
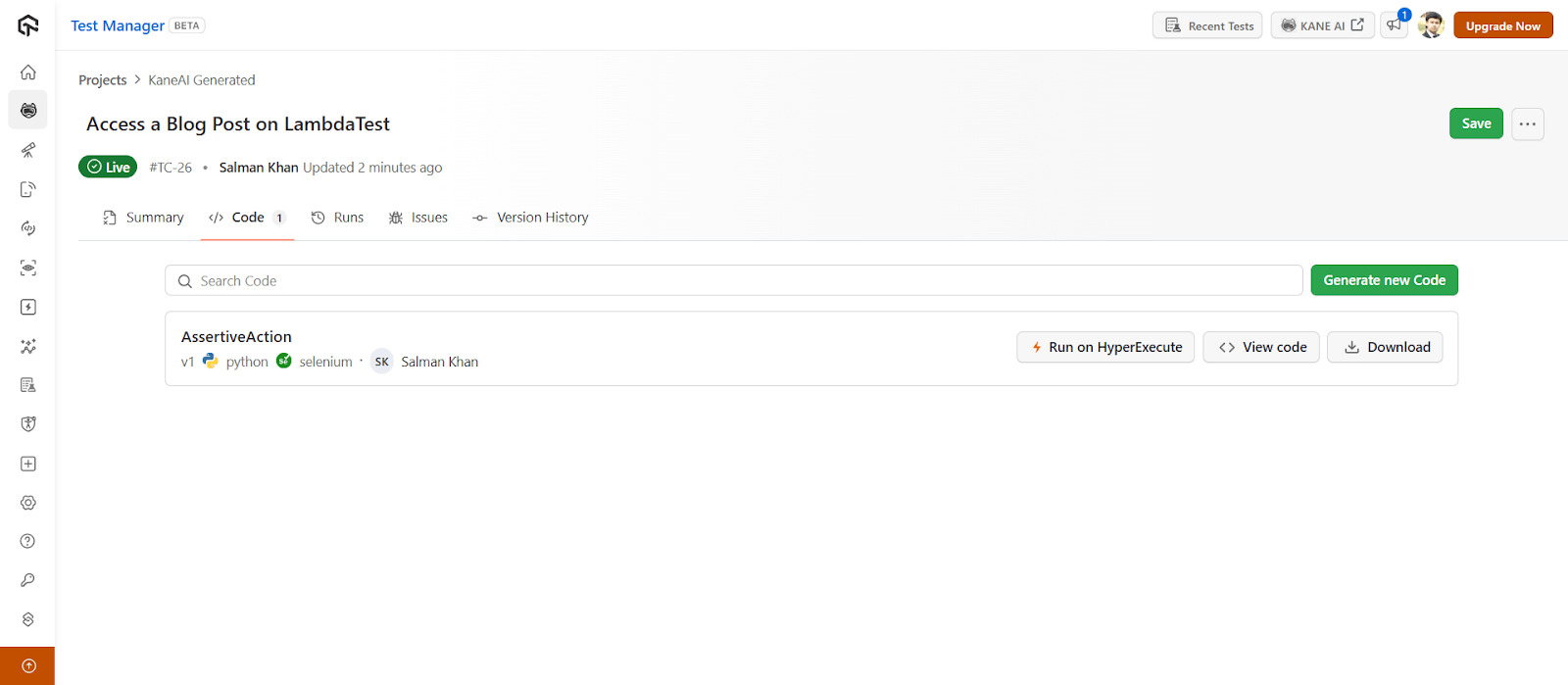
You will notice the following options and go ahead with the one that you need:
- Generate new Code: Generates new code in a different language or framework for the same test case.
- HyperExecute: Triggers tests on the TestMu AI HyperExecute platform.
- View code: Opens the code in a built-in editor to edit code files and download them.
- Download: Lets you download the entire generated tests (with code files).
To get started, refer to this getting started guide on KaneAI.
Advanced Techniques in Gherkin Testing
Once you’re comfortable with basic Gherkin scenarios, you can adopt advanced techniques to make your test suite more robust, maintainable, and adaptable to complex applications.
These strategies help you write reusable, scalable, and high-quality scenarios that go beyond simple “happy path” testing.
- Parameterization with Scenario Outlines: Use Scenario Outlines with example tables to run the same steps with multiple data sets. This improves coverage and keeps feature files concise.
- Using Backgrounds for Common Setup: Define common starting conditions in a Background section. It removes duplication and ensures all scenarios start consistently.
- Tagging and Selective Execution: Use tags to categorize scenarios by priority, functionality, or environment. This lets you run specific sets like smoke or regression tests in CI/CD.
- Step Reuse with Modular Definitions: Create modular, reusable step definitions instead of hardcoding values. Parameterized methods reduce duplication and make maintenance easier.
- Handling Conditional Flows: Add conditional logic in step definitions for dynamic or optional steps. This keeps Gherkin scenarios readable while adapting to app changes.
- Integrating External Data Sources: Pull test data from CSV, Excel, or databases for advanced scenarios. It allows dynamic execution and covers more edge cases.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Gherkin Testing
Even with a structured language like Gherkin, teams often face challenges when writing and maintaining test scenarios. Understanding these challenges and how to address them ensures your tests remain reliable, readable, and effective.
- Problem 1: Ambiguous steps
Sometimes Gherkin steps are vague, making it hard for team members or automation scripts to understand the intended behavior.
Solution: Write clear, precise steps describing exact actions and expected outcomes that everyone can understand.
- Problem 2: Scenario duplicationSimilar scenarios are often repeated with minor variations, creating maintenance overhead.Solution: Use Scenario Outlines with example tables or reusable step definitions to reduce repetition and simplify updates.
- Problem 3: Flaky testsSome tests pass or fail intermittently due to dynamic content or timing issues.Solution: Handle waits, dynamic elements, and asynchronous behavior properly to stabilize test execution.
- Problem 4: Overly technical stepsSteps that include implementation details are hard for non-technical stakeholders to read.Solution: Focus on what the user does and expects, keeping Gherkin scenarios human-readable.
- Problem 5: Large feature filesFeature files can grow too big, making them difficult to navigate and maintain.Solution: Break them into smaller, logically grouped files and use tags for selective execution.
- Problem 6: Evolving requirementsFrequent changes in requirements can quickly make scenarios outdated.Solution: Regularly review and refactor Gherkin files and step definitions to stay aligned with current behavior.
Future Trends in Gherkin and BDD
Future trends in Gherkin and BDD point toward tighter integration with AI testing, real-time collaboration tools, and seamless CI/CD pipelines. These advancements will make test creation faster, more accurate, and easier for both technical and non-technical teams.
- AI-Assisted Scenario Generation: As AI advances, AI testing tools for developers will emerge that can draft Gherkin scenarios directly from user stories, design mockups, or stakeholder conversations. These systems will highlight gaps, suggest edge cases, and prioritize tests based on historical defect data, helping teams focus on critical paths faster.
- Real-Time Collaboration in Cloud-Based Editors: Future Gherkin editors will enable real-time, multi-user editing, much like Google Docs, where product owners, testers, and developers can refine scenarios together. Instant feedback loops will ensure that ambiguity is caught early, and updates are reflected across test automation suites automatically.
- Integration with Visual Requirement Mapping: Expect tools that map Gherkin steps to interactive flow diagrams. Stakeholders will be able to click on a visual journey and see corresponding Given–When–Then steps. This will bridge the gap between business language and technical implementation, making BDD more accessible to non-technical participants.
- Self-Healing Test Steps: Self-healing automation frameworks will identify and fix broken Gherkin steps when application changes occur. Instead of test failures piling up due to minor UI or API changes, the framework will adjust step definitions on the fly, keeping test suites stable and reducing maintenance overhead.
Best Practices for Writing Effective Gherkin Test Cases
Writing effective Gherkin test cases in alignment with Cucumber best practices ensures scenarios are clear, concise, and business-readable, using consistent step definitions while avoiding technical jargon.
Each scenario should focus on a single behavior to ensure clarity, improve readability, and make maintenance easier.
- Use clear, business-friendly language: Make scenarios understandable for non-technical stakeholders.
- Stick to one behavior per scenario: Prevent confusion and make debugging straightforward.
- Follow a consistent Given–When–Then flow: Keeps test steps predictable and uniform.
- Avoid technical jargon: Describe actions in business terms, not implementation details.
- Name features and scenarios meaningfully: Clearly describe the purpose without being vague.
- Re-use existing step definitions: Reduces redundancy and improves maintainability.
- Keep scenarios short: Aim for 3–7 steps to ensure focus and readability.
- Organize with features, tags, and background steps: Streamlines execution and improves navigation.
- Use examples for data-driven testing: Apply Scenario Outlines with Examples tables where needed.
- Write independent scenarios: Ensure each can run in isolation without dependencies.
Conclusion
Gherkin test cases are more than just a format for writing tests, they are a communication tool that unites teams around a clear understanding of software behavior. By using plain English and following best practices such as precision in wording, logical organization, and consistent structure, teams can create scenarios that are easy to read, maintain, and automate.
Investing time in writing effective Gherkin test cases not only improves collaboration but also strengthens the quality and reliability of the entire development process.
Citations
- Gherkin Features in Open-Source Projects: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362181847
- Cucumber Gherkin : https://cucumber.io/docs/gherkin/
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



