
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment: When To Use Which
Learn the differences between continuous delivery vs continuous deployment and when to use each approach in your DevOps workflow for efficient software delivery.

Veethee Dixit
January 13, 2026
Continuous delivery and continuous deployment are fundamental concepts in DevOps, both aiming to achieve faster and more reliable software delivery. While they are part of a CI/CD pipeline, they serve different purposes within the DevOps strategy. Therefore, understanding the difference between continuous delivery vs continuous deployment in detail is crucial.
Understanding these concepts is essential for optimizing your software development process, reducing manual intervention, and ensuring consistent and efficient delivery of high-quality products.
What Is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Delivery (CD) ensures software is always ready for release, requiring manual approval before deployment to production. It’s ideal for organizations seeking control over the final release process, allowing thorough testing with automation testing tools followed by manual review by the Quality Assurance (QA) team. This approach enables businesses to maintain a regulated deployment environment while ensuring only validated changes reach end-users.
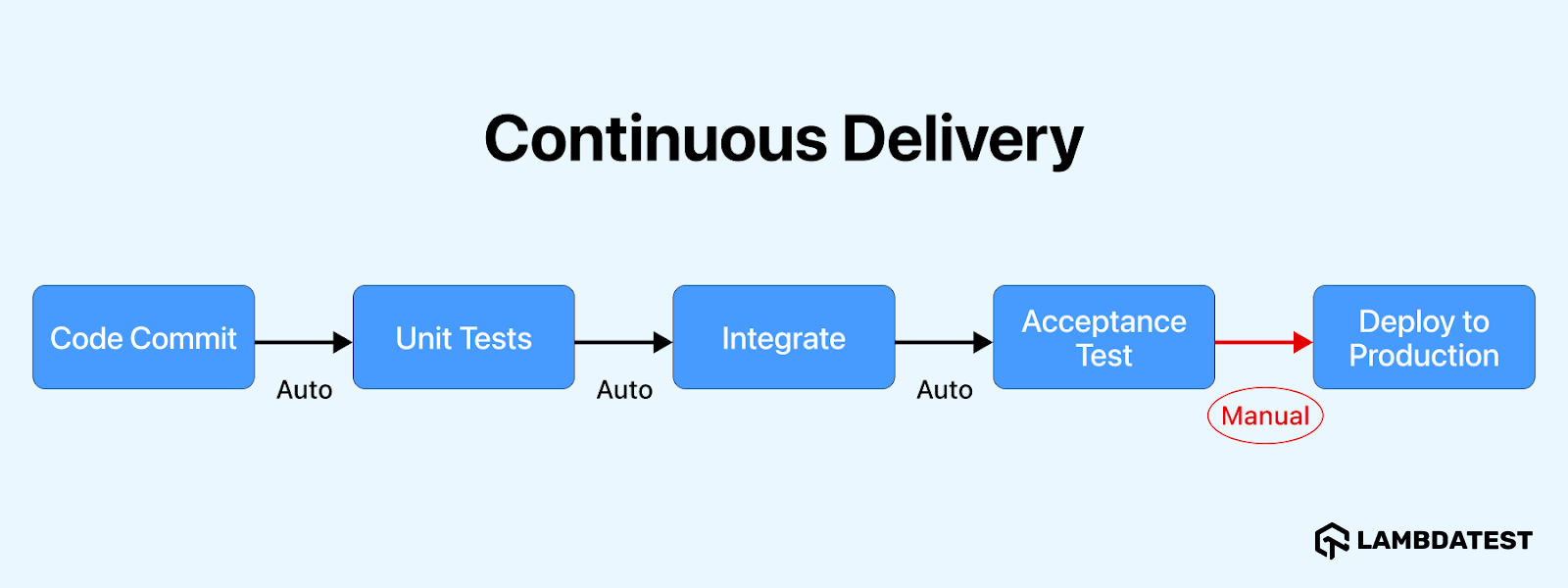
It ensures regular and timely releases through smaller, more frequent chunks, which are easier to manage and preferred by end-users. A robust CI/CD pipeline with quick feedback loops promptly addresses failures, ensuring stable and reliable software releases.
Some of the benefits of continuous delivery are mentioned below.
- Accelerating Feature Delivery: It enables faster time-to-market by enhancing collaboration between business teams and development. Marketing gains insights into release schedules; sales can focus on cross-selling and upselling opportunities, and customer service supports users with current and upcoming features.
- Avoiding Shipping Broken Code to Production: It ensures software deployment readiness in DevOps by integrating automated security, performance, and functional testing throughout the development lifecycle.
- Integration of CD in Your Teams: DevOps and continuous delivery represent cultural shifts rather than technological changes. Increasing awareness of their benefits among teams helps reduce deployment issues and fosters smoother adoption.
Note: Enhance efficiency, reduce tech debt, and ensure reliable releases with continuous delivery. Try TestMu AI Today!
What Is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment (CD) automatically deploys every code change to production without human intervention. Unlike continuous delivery, there is no manual approval process, and changes are pushed to production as soon as automated tests pass.
This approach ensures a highly streamlined workflow, minimizing bottlenecks and accelerating the delivery of new releases to customers. However, high trust in the CI/CD process is required to maintain the quality and reliability of deployed software.
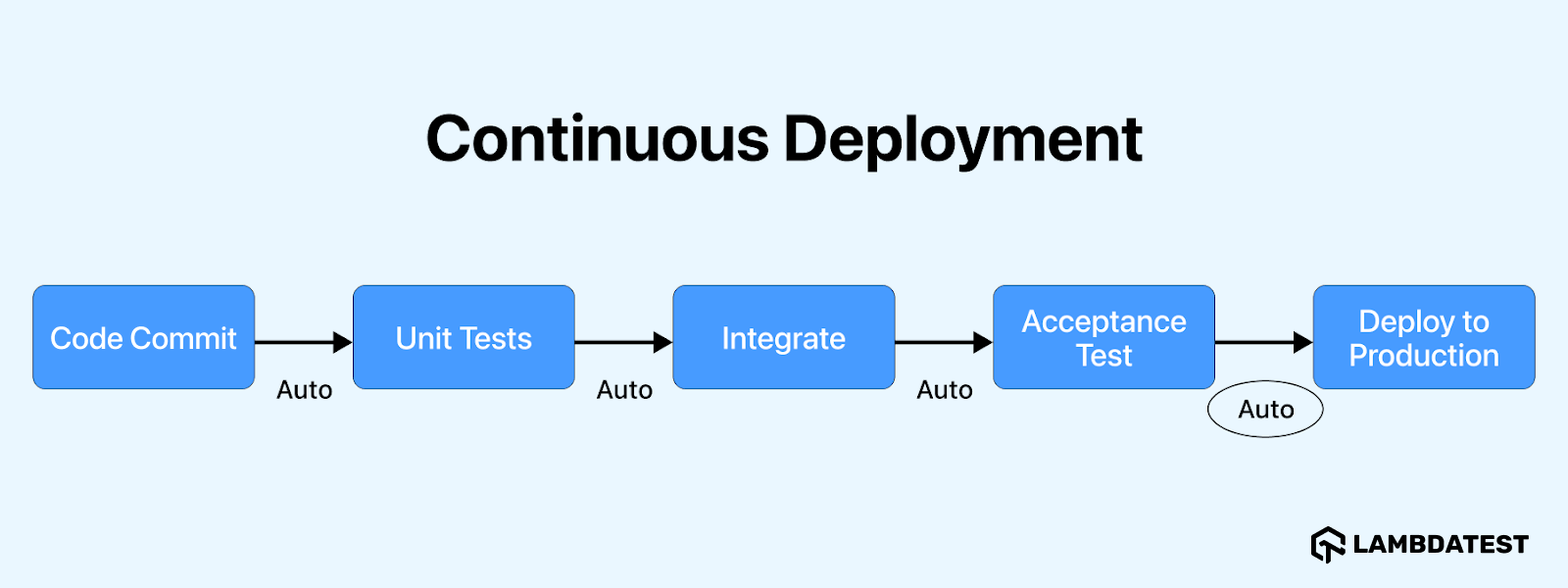
Continuous deployment succeeds when teams utilize automated infrastructure for rapid and reliable deployment of every aspect of their software. Unlike continuous delivery, continuous deployment minimizes manual testing to maintain efficiency and speed in the deployment process. Teams fully commit to automated pipelines, automatically pushing new releases to production and receiving immediate end-user feedback.
Some of the benefits of continuous deployment are mentioned below.
- Quicker Software Delivery: It allows end users to experience new features much sooner, avoiding long waits associated with traditional release cycles.
- Faster Feedback: With continuous deployment, developers receive feedback within minutes of merging code changes. This rapid feedback loop helps quickly identify and fix bugs, reducing the risk of issues reaching end users.
- Fewer Risks: It reduces the risk compared to traditional Big Bang releases, where all changes are bundled together. Deploying smaller, incremental updates makes tracing and promptly addressing issues easier.
- Improved Sense of Responsibility: It encourages developers to take ownership of their code quality. Knowing that changes can go live immediately after merging instills a sense of accountability and promotes higher standards in software development.
As we have learned what continuous delivery and continuous deployment are and their benefits, we will further understand the key differences between continuous delivery vs continuous deployment in detail.
Subscribe to the TestMu AI YouTube channel to learn more about other aspects of CI/CD, DevOps, and more.
Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment: Key Differences
In simple terms, continuous delivery emphasizes software release readiness, with manual approval playing a key role. In contrast, continuous deployment focuses on automating the entire release process through automatic deployment of changes to production upon passing of tests.
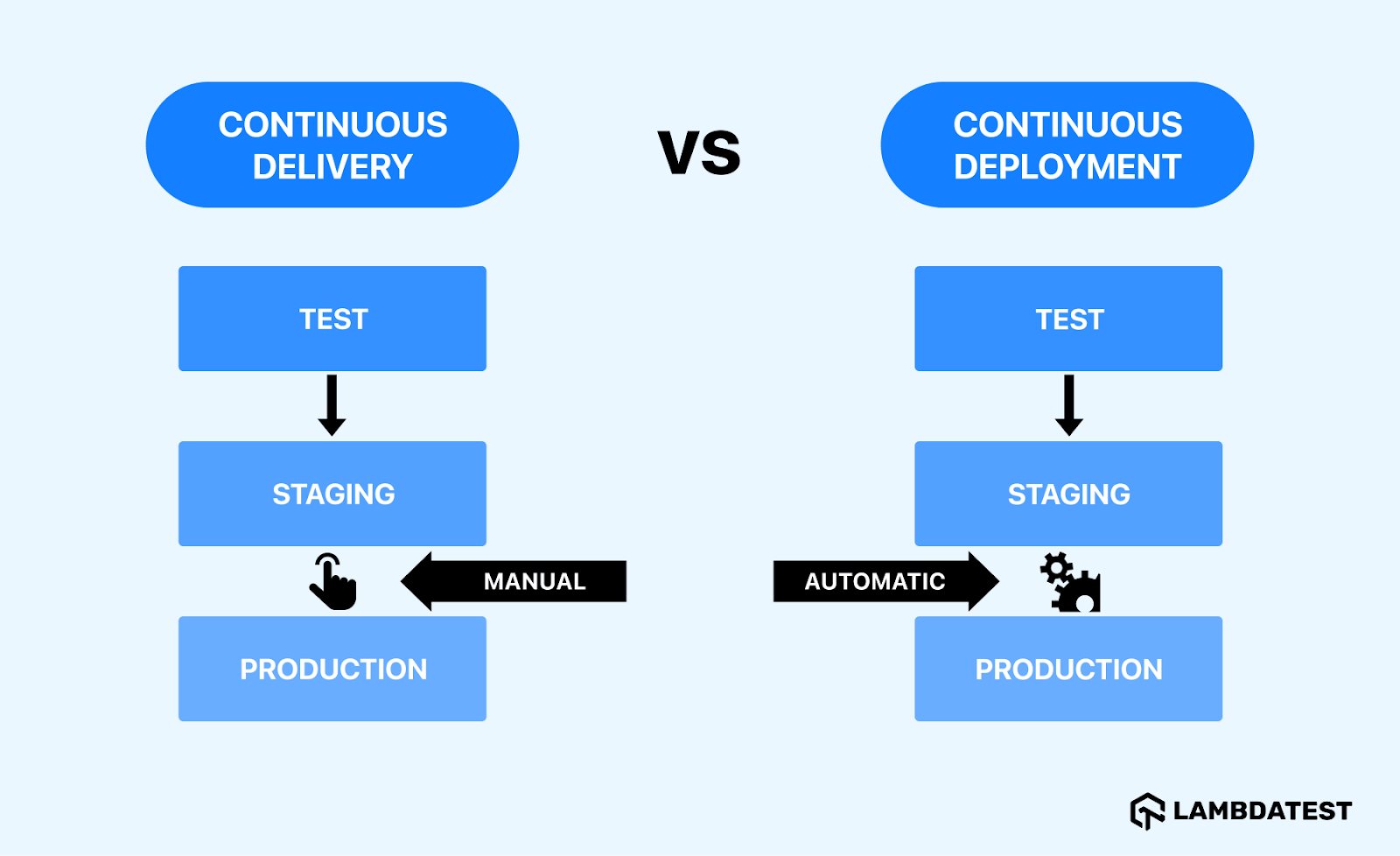
Here are some of the key differences between continuous delivery vs continuous deployment:
| Aspects | Continuous Delivery | Continuous Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures the software is always release-ready with a manual approval step before releasing it to production. | Automatically releases changes to production after passing automated tests without manual intervention. |
| Release Frequency | Regularly scheduled intervals (hourly, daily, weekly, etc.). | Very frequent, often multiple times daily. |
| Automation Effort | Automation with an option for manual approval/coordination. | Highly automated, minimal human intervention for deployments. |
| Scope of Deployment | Can deploy subsets or entire applications. | Deploys entire applications or systems. |
| Risk Management | Emphasizes rigorous testing and quality assurance. | Relies on robust automated testing to minimize risks. |
| Customer Feedback | Feedback loops may be slower due to controlled releases. | Enables rapid feedback due to frequent deployments. |
| Rollback Capability | It may require manual intervention for rollbacks. | Easily rolls back changes with automated processes. |
| Team Collaboration | Collaboration between development and operation teams is needed to validate the changes manually before they are released to production. | Closer collaboration between development and operation teams is needed to automate monitoring and deployment processes. |
| Adoption Complexity | Gradual adoption with a focus on automation and improvement. | Requires mature infrastructure for full automation. |
| Organizational Readiness | Focus on automation, continuous improvement, and Agile methodologies. | Requires a culture of trust and strong DevOps practices. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for organizations with regular release cycles, focusing on stability and reliability. | Ideal for organizations needing rapid innovation and frequent updates. |
To learn more about how continuous integration helps enhance the continuous delivery process, follow this blog on continuous integration and continuous delivery.
So far, we have learned what continuous delivery and deployment are and the difference between continuous delivery vs continuous deployment. Further we will learn which approach has to be used and when.
Continuous Delivery vs Deployment: Choosing the Right Approach
Before deciding whether to implement continuous delivery vs continuous deployment, ensuring that your organization operates within a DevOps culture and provides maximum support is crucial. Automating the entire software delivery process is a key aspect of DevOps.
Several factors influence the decision, such as the nature of the product under development, the maturity of the organization’s team, risk tolerance, and unique requirements.
Let’s take a detailed look at when different approaches can be suitable.
Continuous Delivery:
Some scenarios in which continuous delivery can be more beneficial include:
- Frequent Releases Are a Core Requirement: If your company has to frequently release changes to production but wants a certain level of human intervention for controlling the deployment of modifications, continuous delivery is a great fit.
- High Compliance or Regulatory Requirements: If you’re working in an industry with stringent compliance or regulatory standards, CD facilitates thorough review and testing before you release anything to production, giving stakeholders the required confidence amid the process.
- Manual Approval Holds Preference: If your organization strongly prefers manual approval before deployment, continuous delivery offers flexibility in regulating the release timelines.
- Limited Maturity of Automation: If a team is still transitioning to automation in the deployment process, they can start with continuous delivery, treating it as a stepping stone towards a complete continuous deployment.
Continuous Deployment:
Some scenarios in which continuous deployment can be more beneficial include:
- Need for Frequent or Rapid Releases: It is the most practical choice in fast-paced markets where consistent updates are crucial to maintain a competitive edge and address customer concerns quickly.
- High Confidence in Test Automation: Continuous deployment requires high trust in test automation to ensure that code changes won’t cause critical production issues.
- Streamlined Deployment Process: Continuous deployment automates the entire process for organizations, aiming to minimize manual intervention and human error during deployment.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: If a business seeks to gather continuous end-user feedback and iterate quickly based on that feedback, continuous deployment enables faster turnaround for bug fixes and feature updates.
- Mature DevOps and Agile Practices: Organizations with established agile development practices and a strong DevOps culture find continuous deployment a natural progression.
- Independent of Stakeholder Approval: Continuous deployment is ideal if your delivery process has been fully automated and does not rely on stakeholder approval.
- Fully Automated CI/CD Pipeline: Continuous deployment fits well if your CI/CD pipeline is completely automated from start to finish.
- Gradual Customer Adaptation: Continuous deployment is suitable if you are transitioning customers to accept minor but frequent updates or are already accustomed to them.
- Rapid Response to Production Issues: Teams that can quickly address production errors and continue rolling out releases to fix problems benefit from continuous deployment.
If you don’t meet these criteria, the best move forward is to fully automate your CI/CD process. The ultimate goal should be achieving continuous delivery, allowing you to deploy code changes to production with minimal manual steps, except for final human approval.
Over time, you can transition from continuous delivery to continuous deployment by further streamlining your release process.
Continuous Delivery vs Deployment: How Much to Automate?
CI/CD automation minimizes human intervention regardless of the process you’re dealing with. One of the most straightforward processes to consider for automation is the release, which is common to all DevOps practices. The extent to which you wish to automate depends on your business or organization and the associated infrastructural requirements.
According to the Future of Quality Assurance survey, around 88% of organizations claim to use CI/CD tools, and approximately 45% still trigger tests manually. By fully automating the testing process, organizations can achieve more consistent and efficient test execution.
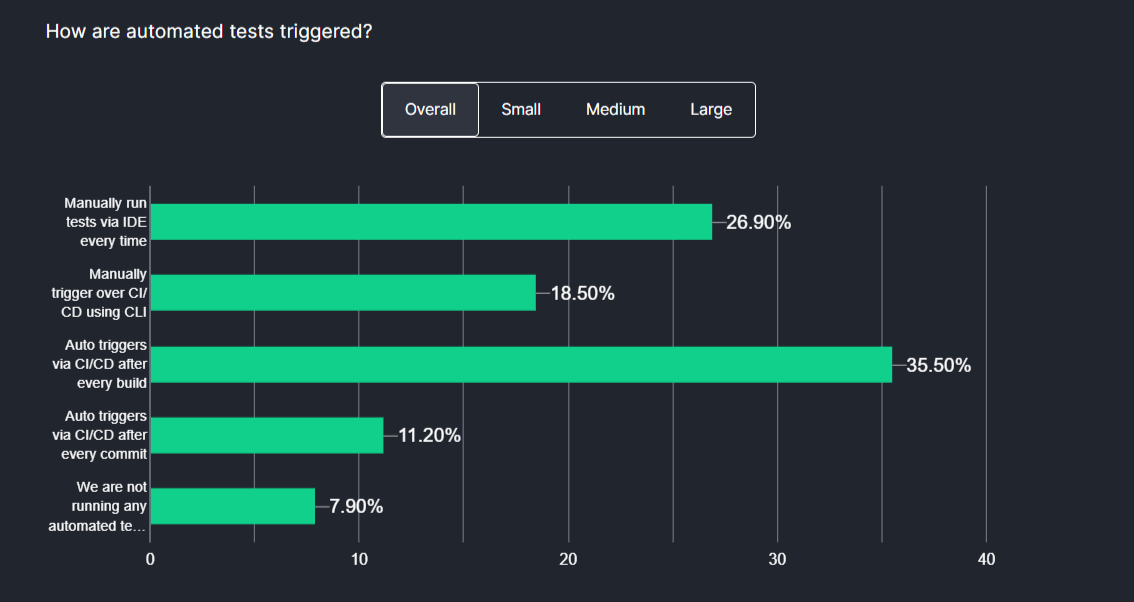
The level of automation depends on the organization’s infrastructure and ability to support automated processes. Insufficient infrastructure can damage the implementation of completed continuous delivery and continuous deployment processes, affecting efficiency and reliability.
There are many CI/CD tools available that can help organizations overcome specific challenges they face. However, organizations can use cloud-based platforms that offer robust and stable infrastructure to address infrastructure requirements. These platforms help manage the infrastructure required to automate continuous delivery and deployment processes.
To enhance your continuous delivery vs continuous deployment processes, you can use TestMu AI HyperExecute. This AI-Native testing platform is designed to accelerate automation testing speed and efficiency. TestMu AI is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
HyperExecute offers advanced features that streamline and optimize testing processes beyond traditional cloud-based test execution.
Integrating HyperExecute into your continuous delivery vs continuous deployment strategies enables faster test execution and quicker feedback on code changes. It supports parallel execution of large test suites, optimizes resource utilization to lower infrastructure costs, and ensures stable, reliable tests across diverse environments, enhancing overall software quality.
By incorporating HyperExecute into your continuous delivery vs continuous deployment pipeline, you can establish a robust, efficient, and scalable testing framework, facilitating the rapid and reliable delivery of high-quality software products.
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on TestMu AI
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
Best Practices for Continuous Delivery
A quick and reliable release process requires implementing CI/CD or DevOps monitoring solutions, logging practices, and quality checks.
Consider these best practices for effective automation of delivery:
- Start With Implementing CI: Continuous delivery is integral to a CI/CD pipeline. Therefore, it’s essential to establish the CI component well before moving on to continuous delivery.
- Catalog Your Artifacts and Containers: Ensure that all new features are deployment-ready for production by keeping the features under test throughout the pipeline, just as you would for deployment. Use self-sufficient application packages and containers to ensure consistency across various environments.
- Ensure a Sound Testing Suite: Functional, unit, and integration tests verify the integrity of new releases before deployment into production. Comprehensive testing should remove regressions on new features, with CI/CD platforms facilitating the complete automation and management of these tests.
- Increase Confidence in Your Tests: Quick test execution is crucial for an effective CI/CD pipeline. Tests should be quick to prevent delays in the delivery pipeline. Inefficient testing practices can lead to high wait times between tests, so it’s vital to refactor tests that take too long.
- Automate Database Deployments: Extend your CI/CD approach to databases, perform quality checks, and have a rollback strategy. Automate the conversion of production data to test data and maintain anonymized subsets for efficient handling. Plan database updates to facilitate rollbacks.
- Make Security Scanning Part of the Process: Include code and security scans in your development workflow. Static code analysis can uncover vulnerabilities and security issues, while runtime code analysis can detect errors. Incorporate these scans into the pull request process and prevent merges based on warnings.
- Implement Selective Release: Feature flags can help address concerns about releasing compromised features. Feature flags allow developers to control the visibility of elements, deciding what end-users can see and when.
- Increase the Frequency of Releases: Ensure your software is release-ready by pausing all tests in production-like environments and including a deployment stage with realistic testing environments.
- Automate Repeatable Processes: Focus on automating every repetitive task throughout the development, testing, and deployment phases. Identify tasks suitable for automation and those requiring manual intervention or approval.
Best Practices for Continuous Deployment
Depending on your organization’s dynamics and requirements, you can implement a precise CI and deployment process. However, some foundational practices are paramount to successful continuous integration and deployment.
Here are some best practices for continuous deployment:
- Start With Implementing Ongoing Delivery: Continuous deployment is the next part of continuous integration, where the final step of deploying to production is automated. Ensure the proper implementation of a standard CI/CD pipeline before moving on to continuous deployment.
- Control the Rollout Process: Even with a fully automated CI/CD pipeline, maintain control over your rollout processes. Techniques such as canary releases for testing new features with a limited user base and blue/green deployment for managing transitions to newer versions help minimize risks and control rollouts.
- Implement Progressive Delivery: Progressive delivery minimizes risks, continuously enhances user experience, and speeds up code shipping by extending CI/CD principles. The gradual rollout of new features limits the impact of bugs and allows for user engagement evaluation.
- Use Logs and Metrics: Automatically deploying applications requires a method for assessing real deployment results. Utilize metrics such as information traces, counters, feature monitoring metrics, and detailed event logs for comprehensive deployment assessments.
- Prepare for Faster Rollbacks: Verify deployment success with appropriate metrics to enable quick, automated rollbacks. Automate the review of these metrics to streamline rollbacks and ensure prompt response to deployment issues.
- Monitor the Production Environment: Be proactive in detecting bug indications and performance issues in the production environment.
- Streamline the Pipeline: Faster pipelines facilitate quicker changes and reduce feedback loop times, helping to address issues more efficiently and prevent problems that normal tests could catch.
By following these best practices, organizations can achieve successful continuous deployment, ensuring a smooth and efficient software delivery process.
Conclusion
Continuous delivery ensures software is always release-ready with manual approval before deployment. It’s ideal for organizations needing control over release processes, regulatory compliance, and thorough testing. Continuous delivery is best suited for organizations requiring control over release timelines, compliance with regulatory standards, and thorough manual testing before deployment.
On the other hand, Continuous Deployment automates every aspect of the deployment process, pushing changes to production as soon as automated tests pass. This approach accelerates delivery, enhances feedback loops, and requires high confidence in automation and quality checks.
Implementing either approach depends on factors like regulatory requirements, risk tolerance, and organizational maturity in automation. CI/CD fosters agility, efficiency, and reliability in software delivery, which is crucial for meeting modern business demands.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



