
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Enhancing Backend Microservices Ecosystem with Contract Testing [Spartans Summit 2024]
Learn how contract testing improves backend microservices reliability, agility, and integration, revolutionizing development approaches.

TestMu AI
January 30, 2026
Backend systems often include many small services, and ensuring they all work smoothly can be challenging. Regular testing methods only sometimes catch problems with how services communicate with each other, causing many issues and downtime. Contract testing has proven to be a better approach when testing these services and overcoming such challenges.
In this session at Spartan Summit 2024, Subhash Kotra, a QA Automation Lead at Tide, bringing nearly two decades of experience in Software Testing & Engineering, highlights how contract testing can mitigate these challenges using a structured approach to testing inter-service communication. He elaborates on the benefits of contract testing for backend microservices, which include improved reliability, agility, and overall system stability. Subhash illustrates how teams can enhance their design, development, and deployment processes within the microservices domain by focusing on understanding lower-level tests and implementing contract tests.
If you couldn’t catch all the sessions live, don’t worry! You can access the recordings conveniently by visiting the TestMu AI YouTube Channel.
Subhash starts with a kickoff guide, helping viewers gain insight into the session and learning points.
Agenda
- What is Contract Testing
- Testing Pyramid
- Components of Contract Testing
- Defining Contracts – Key Aspects
- How to implement Contract Testing using pact.io
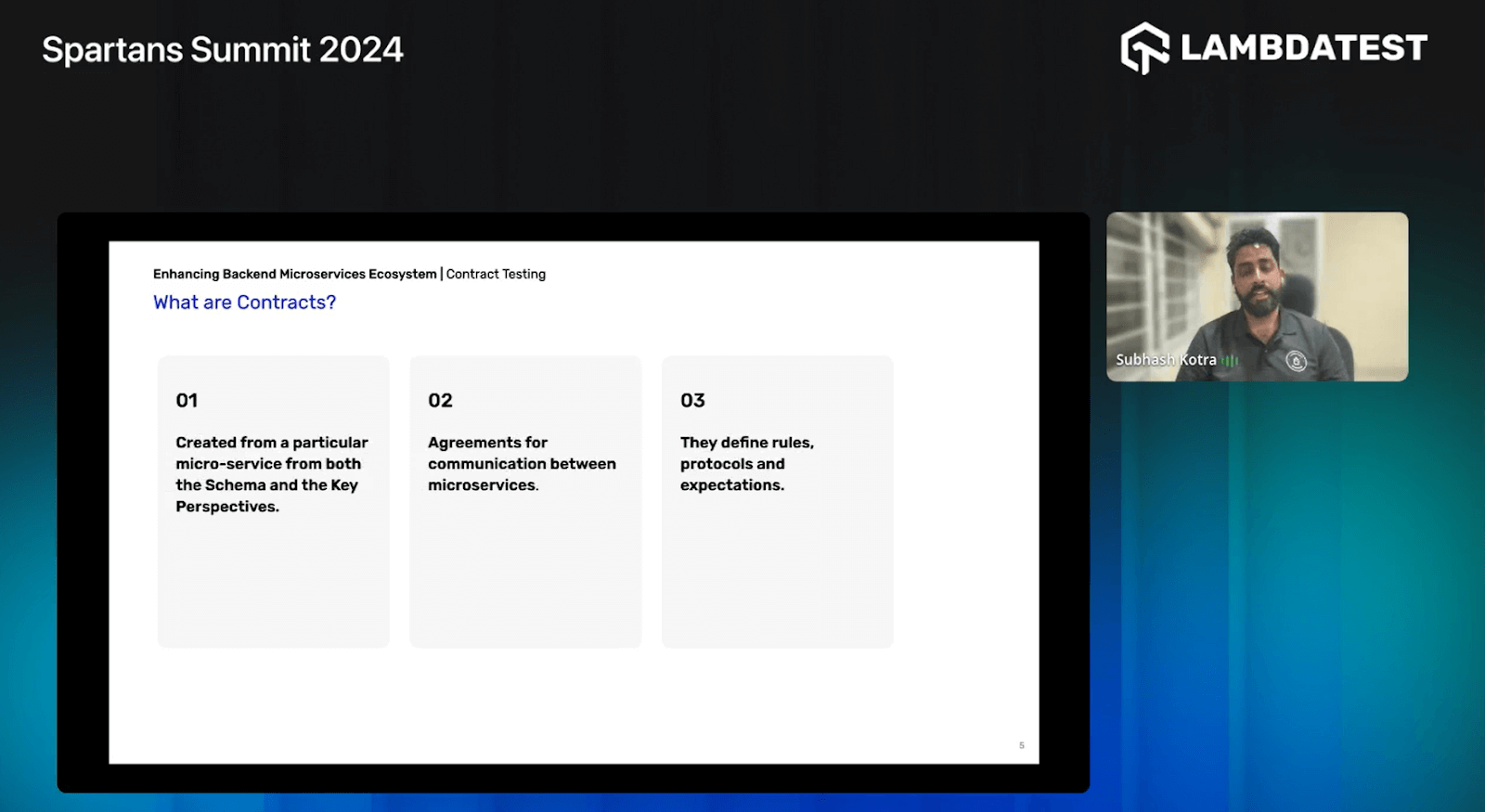
What are Contracts?
Contracts are carefully created agreements from a specific microservice, capturing both the Schema and the critical perspectives. They serve as the cornerstone for communication between microservices within a distributed system. By outlining rules, protocols, and expectations, contracts establish a clear understanding of how different services should interact with each other.
To understand the concept better, Subhash explains the contract testing with an example below.
Subhash highlights that service dependencies refer to the relationships and interactions between different microservices within a distributed system. Let’s consider the scenario where Service A is connected to Service B, and then Service C and Service D are also involved.
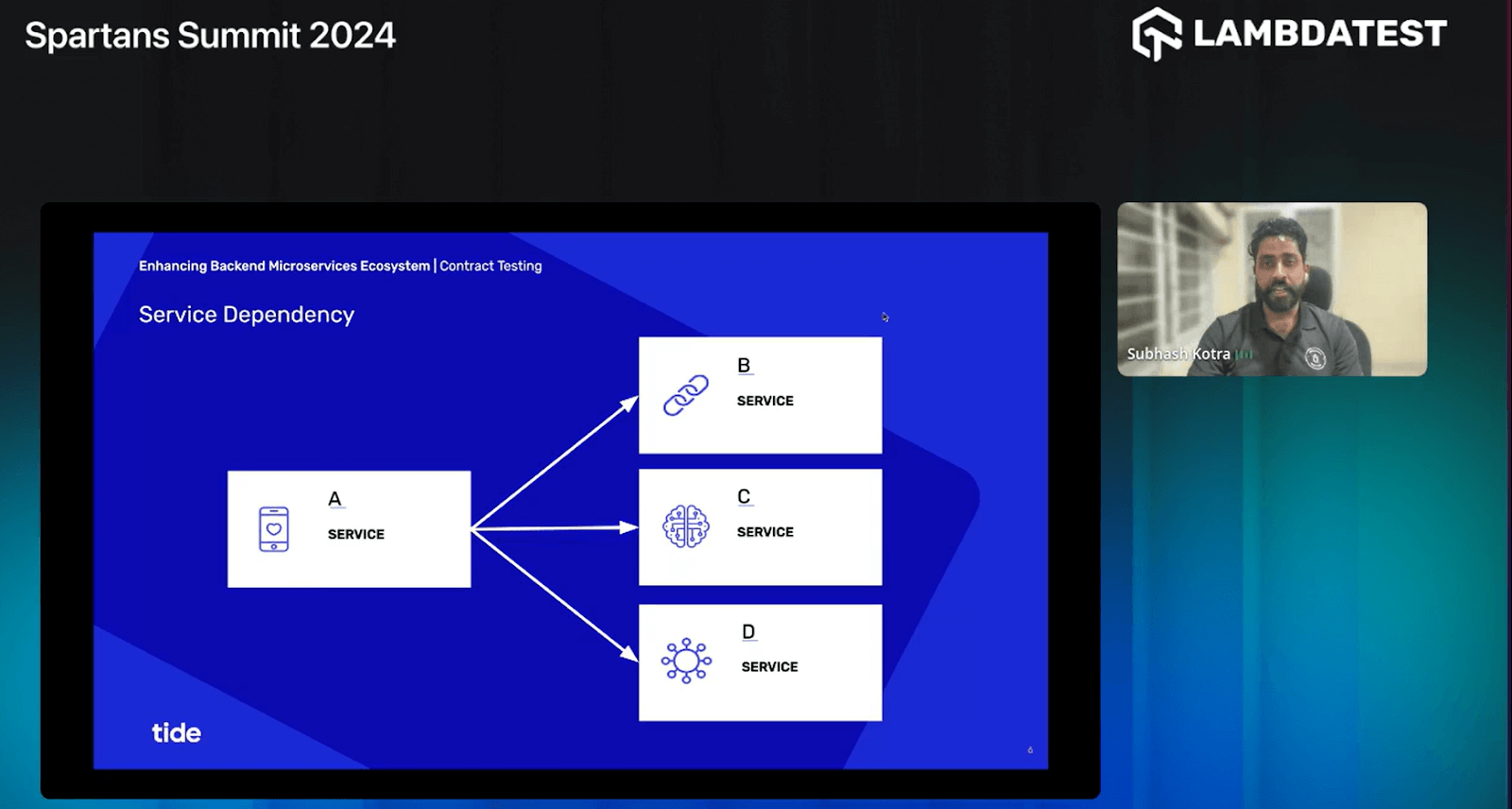
- Service A: This represents one of the microservices involved in the system. Service A might handle specific functionalities or process certain data types. It serves as a client to Service B, meaning it sends requests and expects responses in return.
- Service B: This is another microservice in the system, likely providing complementary functionalities or data processing capabilities to Service A. Service B acts as a server to Service A, receiving requests from Service A and sending back responses based on the requested actions or data.
- Service C and Service D: These additional services may be part of the broader ecosystem, serving as downstream dependencies for Service B. In other words, Service B might rely on Services C and D to fulfill specific tasks or provide supplementary data needed to complete its operations successfully.
After the basic explanation of the relationship between Services A, B, C, and D of contract testing, Subhash highlights how contract testing relates to these service dependencies:
- Service A and Service B Interaction: Subhash states that contract testing ensures that the interaction between Service A and Service B adheres to the agreed-upon contracts. This involves verifying that Service A sends requests to Service B in the expected format and that Service B responds appropriately according to the defined contract.
- Service B, Service C, and Service D Interaction: He also highlights that it can also extend to validate the interactions between Service B and its dependencies, such as Services C and D. This ensures that Service B correctly communicates with these downstream services and handles their responses according to the specified contracts.
At the end of explaining the workflow, Subhash emphasizes the importance of comprehensively testing microservice dependencies for organizational benefit. This proactive approach maintains system integrity, promotes smoother integration, and enhances service collaboration. Embracing this mindset ensures the reliability and cohesion of our system, facilitating seamless integration and cooperation.
Subhash continues by proposing his concept of incorporating contract testing between layers of the testing pyramid. He emphasizes the significance of integrating contract testing within the testing pyramid and elaborates on why and how this approach enhances testing strategies.
Testing Pyramid
Here, Subhash provides insights into each type of testing represented in the testing pyramid, emphasizing the importance of unit testing, followed by an exploration of integration and end-to-end (E2E) testing.
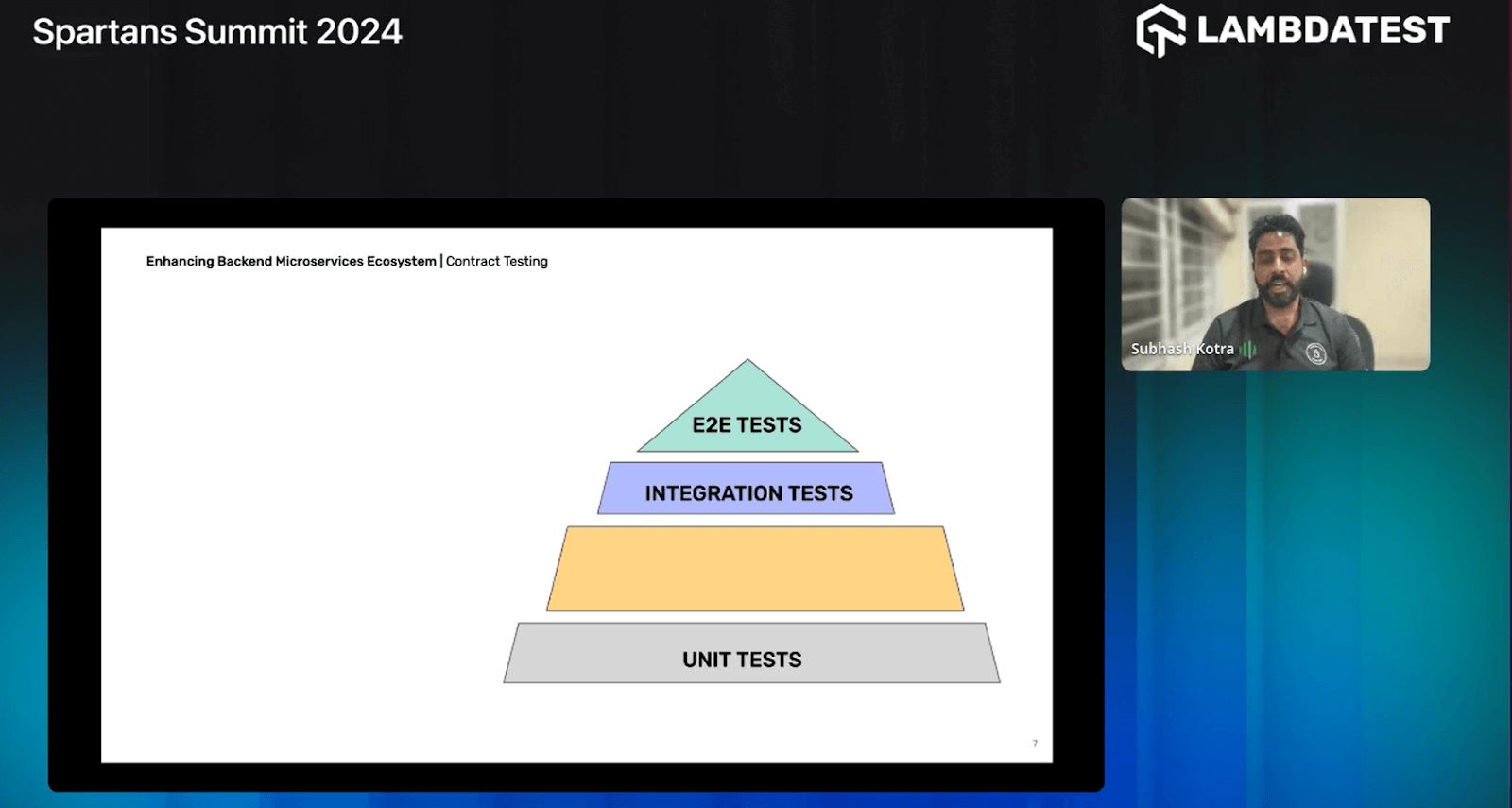
Subhash highlights the significance of unit testing as the foundational layer of the testing pyramid. He elaborates on how unit tests focus on individual components or functions, ensuring each unit behaves as expected in isolation. This careful examination at the unit level lays a solid foundation for building reliable and robust software systems.
He further delves into integration testing, which occupies the middle tier of the testing pyramid. He describes how integration tests verify the interaction and compatibility between various components or modules within the system. By simulating the integration of these components, integration testing ensures seamless collaboration and functionality across the interconnected parts of the application.
Subhash addresses end-to-end (E2E) testing, positioned at the testing pyramid’s apex. He explains how E2E tests validate the entire workflow or user journey from start to finish, mimicking real-world scenarios. By testing the application, including its interfaces with external systems, E2E testing provides comprehensive validation of the system’s behavior and performance, ensuring a smooth and satisfactory user experience.
After explaining the fundamental concepts of the testing pyramid, Subhash suggests integrating contract testing into the pyramid structure, as shown below.
Where does Contract Testing fit in the microservices testing ecosystem? As per Subhash, it is an imperative piece in the testing pyramid and ideally sits between the “Integration Tests” and “Unit Tests”. pic.twitter.com/4d42P1TODl
— LambdaTest (@testmuai) February 6, 2024
He elaborates on how this addition could enhance the testing process and strategies. Subhash emphasizes the potential to detect and address integration issues early by incorporating contract testing, ensuring excellent reliability and cohesion across microservices. This approach strengthens the testing strategy and fosters a more proactive and resilient development process.
Later, Subhash asserts that contract testing is critical in the testing pyramid. He emphasizes that contract testing is imperative to ensure the integrity and reliability of the entire testing process. Contract testing is pivotal in maintaining system cohesion and facilitating seamless service integration by validating microservice interactions based on established contracts.
With Subhash’s insightful suggestion in mind, he proceeds to delve into the components of contract testing. He outlines vital elements such as the Consumer, Provider, and Pact Broker, emphasizing their roles in establishing and maintaining agreements between microservices. Subhash underscores the importance of understanding these components for implementing effective contract testing strategies and ensuring the reliability and cohesion of the microservices ecosystem.
Let us understand the components of contract testing in detail below.
Components of Contract Tests
Subhash highlights the critical components for validating microservice interactions. He emphasizes the Consumer, Provider, and Pact Broker as crucial elements in this process.
Subhash delves into the essential elements of contract testing: Consumer, Provider, and Pact broker. pic.twitter.com/PahA4zNZCX
— LambdaTest (@testmuai) February 6, 2024
- Consumer: A consumer generates and stores their expectations in a Contract file. This file ties its contents to the Consumer code.
- Provider: Providers are the services that use the Consumer and validate its service against the Contract file generated by the Consumer.
- Pact Broker: A Pact broker is a centrally located storage to maintain all an organization’s contracts.
Subhash discusses the pivotal components facilitating the validation of microservices interactions:
- Consumer: He emphasizes that Consumers play a critical role by generating and storing their expectations in a Contract file. This file, intricately tied to the Consumer code, serves as a blueprint for the expected behavior of the service.
- Provider: He highlights Providers as essential services that utilize Consumers and validate their service against the Contract file generated by the Consumer. This ensures that Providers adhere to the agreed-upon contracts, fostering interoperability and reliability.
- Pact Broker: He underscores the significance of a Pact Broker, describing it as a centrally located storage hub for maintaining all of an organization’s contracts. This centralized repository streamlines team collaboration and communication, facilitating seamless contract management and verification.
Together, these components form the foundation of contract testing, enabling organizations to uphold the reliability and integrity of their microservices interactions.
Defining Contracts – Key Aspects
Subhash emphasizes defining contracts within microservices, highlighting critical aspects for ensuring seamless communication and system reliability.
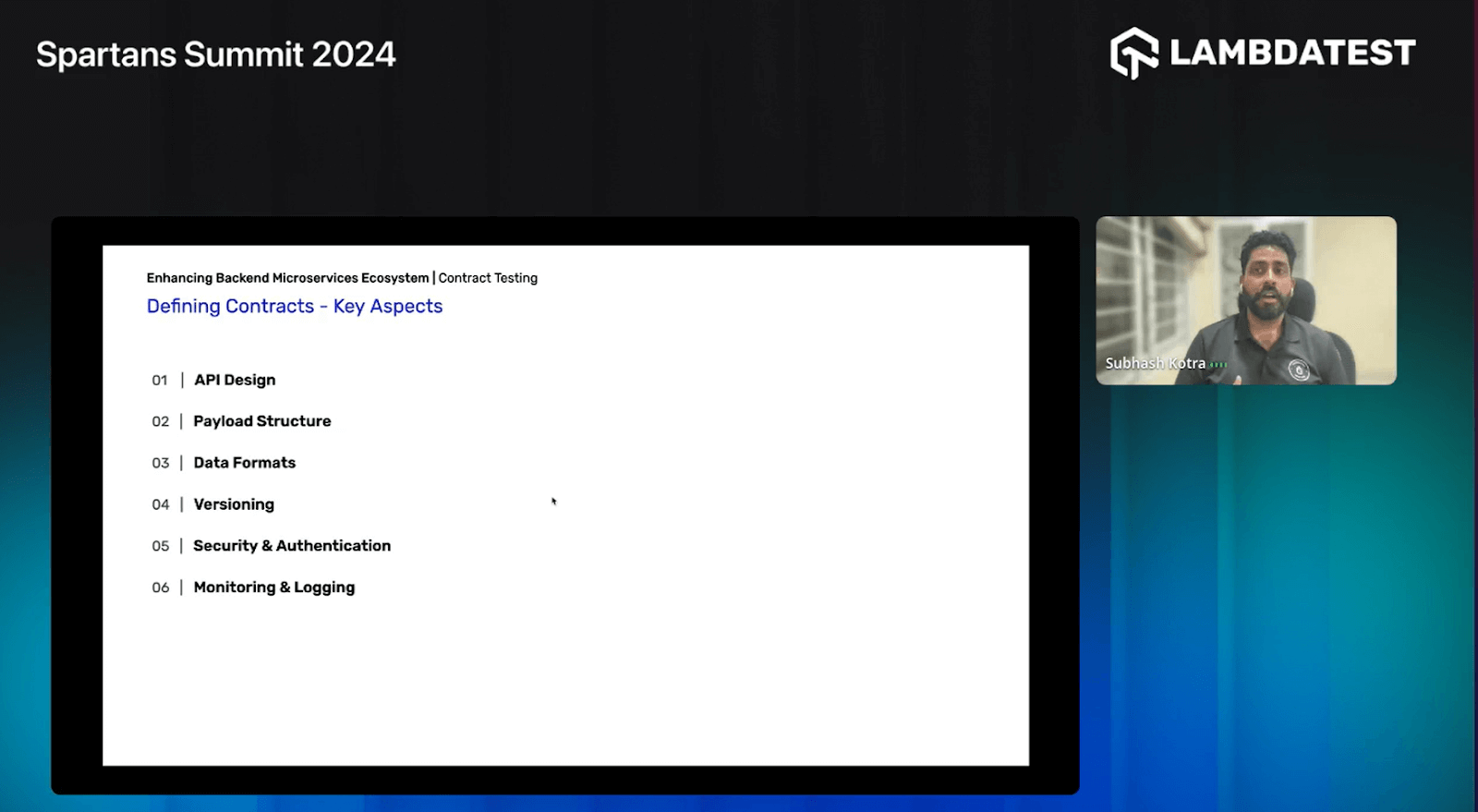
- API Design: Designing clear and intuitive APIs ensures seamless communication between microservices and enhances system interoperability.
- Payload Structure: Defining the structure of data payloads exchanged between microservices, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of errors.
- Data Formats: Specifying data formats, such as JSON or XML, to ensure compatibility and consistency across different services.
- Versioning: Versioning contracts to accommodate changes over time while maintaining backward compatibility, enabling the smooth evolution of contracts.
- Security & Authentication: Incorporating security measures and authentication mechanisms into contracts to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitoring & Logging: Defining monitoring parameters and logging standards to enable efficient tracking of service interactions, facilitating troubleshooting and performance optimization.
To explore the key aspects and best practices for enhancing contract testing, watch the video below.
With all the theoretical knowledge shared, Subhash demonstrates how to implement contract testing using pact.io.
How to Implement Contract Testing Using pact.io?
Subhash introduces pact.io, emphasizing its role in facilitating contract testing for microservices, and then directs attendees to the GitHub repository to access comprehensive documentation and resources for implementing pact.io in their projects.
First, he shows the official pact.io websites. Then, he clicks on the “View on Github” button by selecting Node JS and Javascript from the list of options.
Secondly, Subhash encourages attendees to explore the documentation in the Git repository, emphasizing its importance as a valuable resource for further understanding and implementing contract testing effectively in their projects.
With the enlightening discussion on enhancing the backend microservices ecosystem with contract testing drawing to a close, Subhash graciously answers a few questions from the engaged attendees, providing further clarity and insights to enrich their understanding.
Question and Answer Session
- Can you recommend essential tools or frameworks for implementing contract testing in microservices?
Subhash: I recommend Pact for its comprehensive support across languages and Spring Cloud Contract for Spring ecosystem users. These tools are robust for implementing contract testing in microservices.
- As a beginner, what initial steps or resources do you recommend for starting with contract testing?
Subhash: Start with online tutorials and Pact or Spring Cloud Contract documentation, depending on your tech stack. Experimenting with simple example projects can also be very insightful.
- How do you handle cases where the API call to the provider is made via a standard library used in multiple services/consumers? Are there ways to avoid repeating the same test in all the consumers?
Subhash: In such cases, it’s efficient to centralize your contract tests within the standard library itself. This approach avoids repetition and ensures consistency across all consuming services.
- As a quality team member, how can we implement this in our organization if you give some process steps that help us? How can we start from the root?
Subhash: Establish a clear understanding of contract testing within your team. Then, select a small, manageable project to implement as a pilot and gradually expand as your team gains confidence and expertise.
Feel free to add questions or clear your doubts on the TestMu AI Community.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests


