Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What are Carousels?
- Components of Carousels
- Why Are Accessible Carousels Needed?
- Are Carousels Good for Accessibility?
- Role of WAI-ARIA in Creating Accessible Carousels
- Techniques to Build Accessible Carousels
- Demonstration: Building Accessible Carousels
- How to Test the Accessibility of Carousels?
- Best Practices for Accessible Carousels
Building Accessible Carousels: A Step-By-Step Guide
Learn how to build accessible carousels that work for everyone with keyboard controls, screen reader support, and clear visuals.

Alex Anie
January 30, 2026
Carousels are effective in conveying pieces of information in a concise format on the web page. Many organizations find value in using carousels to showcase their product offerings. This feature has proven to be a valuable asset for driving conversions and enhancing user engagement.
Despite being helpful and a great fit for everyday users, carousels come with a lot of accessibility issues, which prevent impaired users from interacting with them. Therefore, it becomes imperative to create accessible carousels that are truly beneficial and inclusive for all users. It’s an investment that pays off in terms of ethics, usability, and overall website performance.
In this article, we will dive deep into accessible carousels, why to use them, the components of carousels, and how to build accessible carousels.
What are Carousels?
A carousel is a group of individual elements, where each element is called a slide, and each slide is set to overflow horizontally across its containing element.
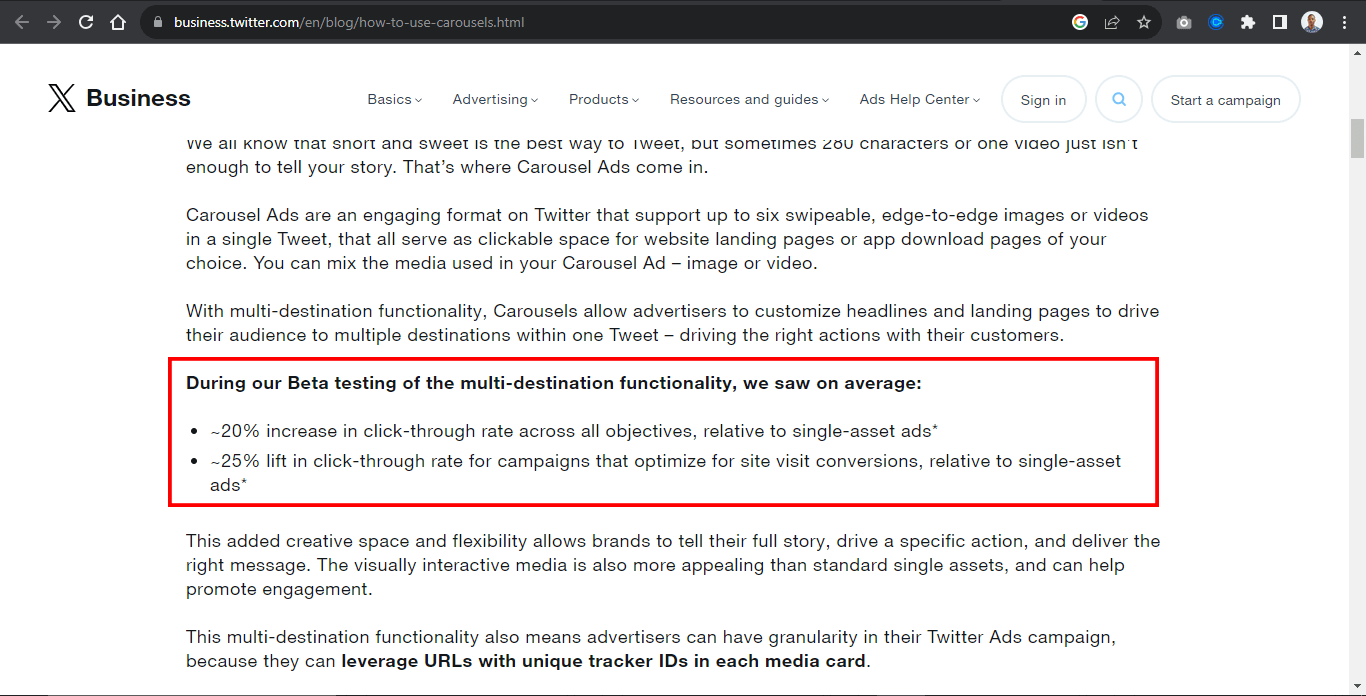
According to beta testing of the multi-destination function on the carousel by X Business, they saw a 20% increase in click-through rate across single posts of carousel assets and a 25% lift in click-through rate for campaigns that optimize for site visit conversion.
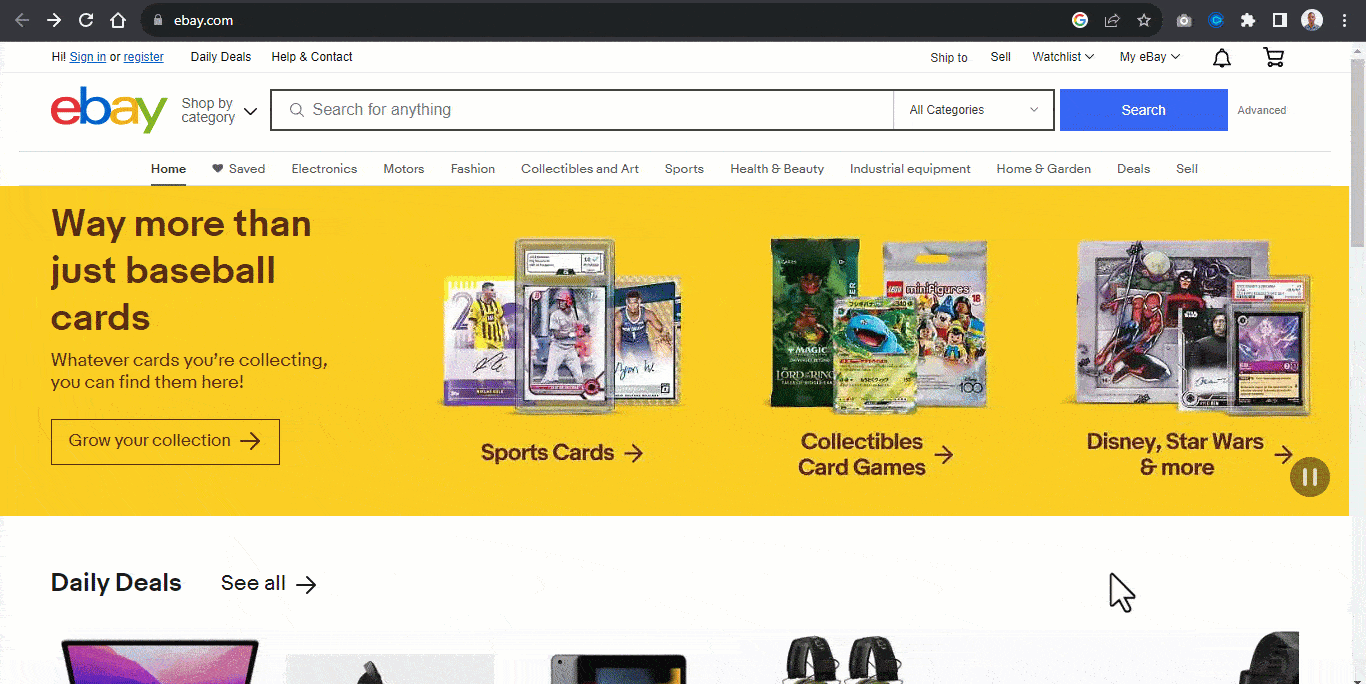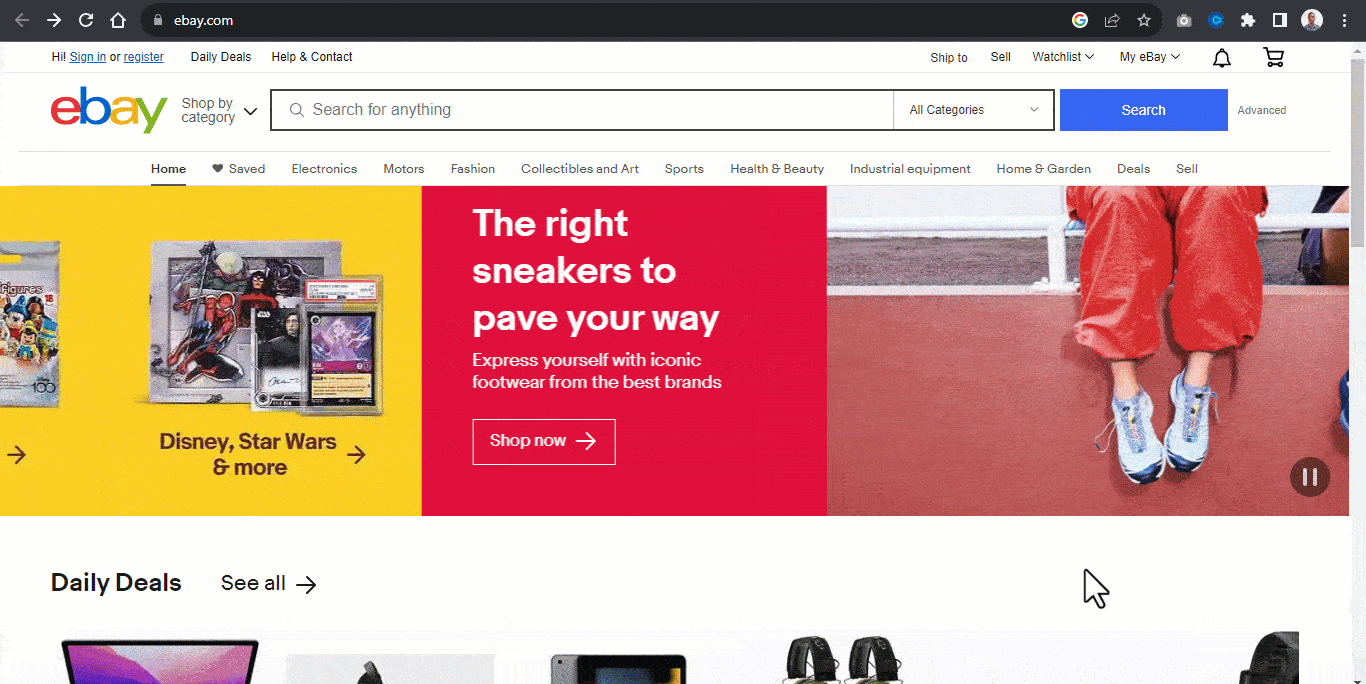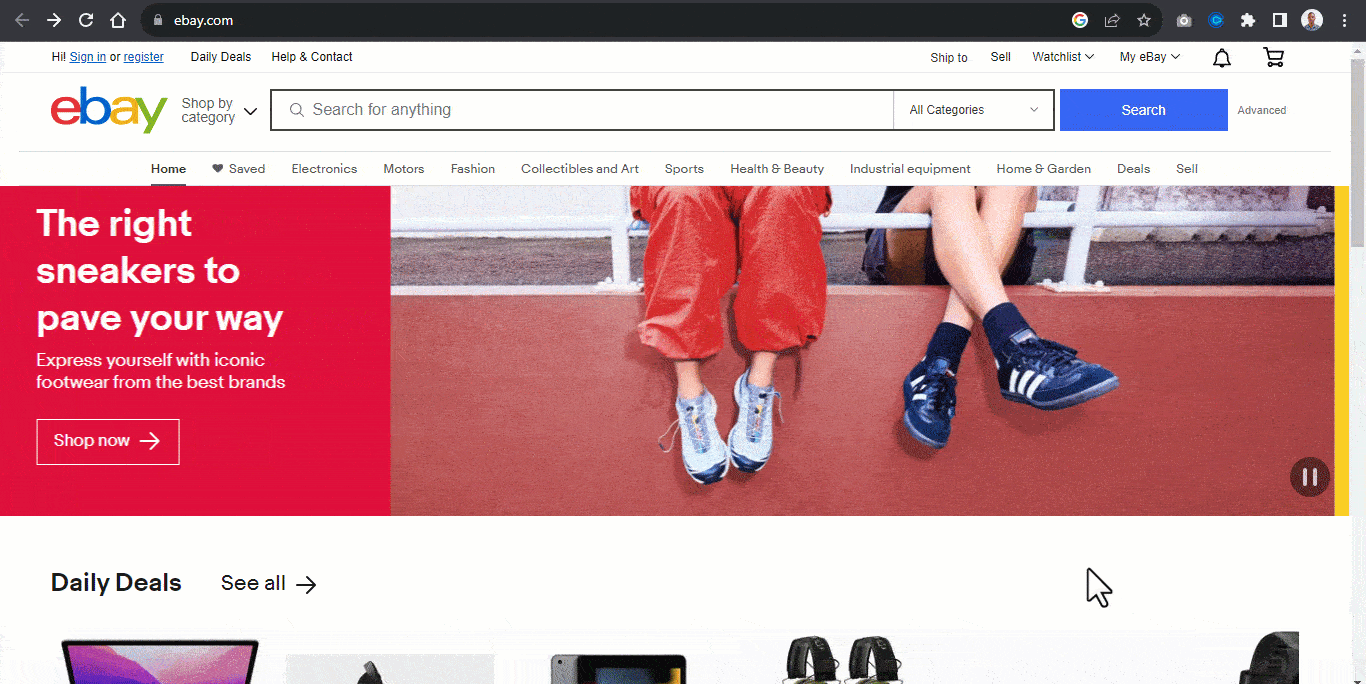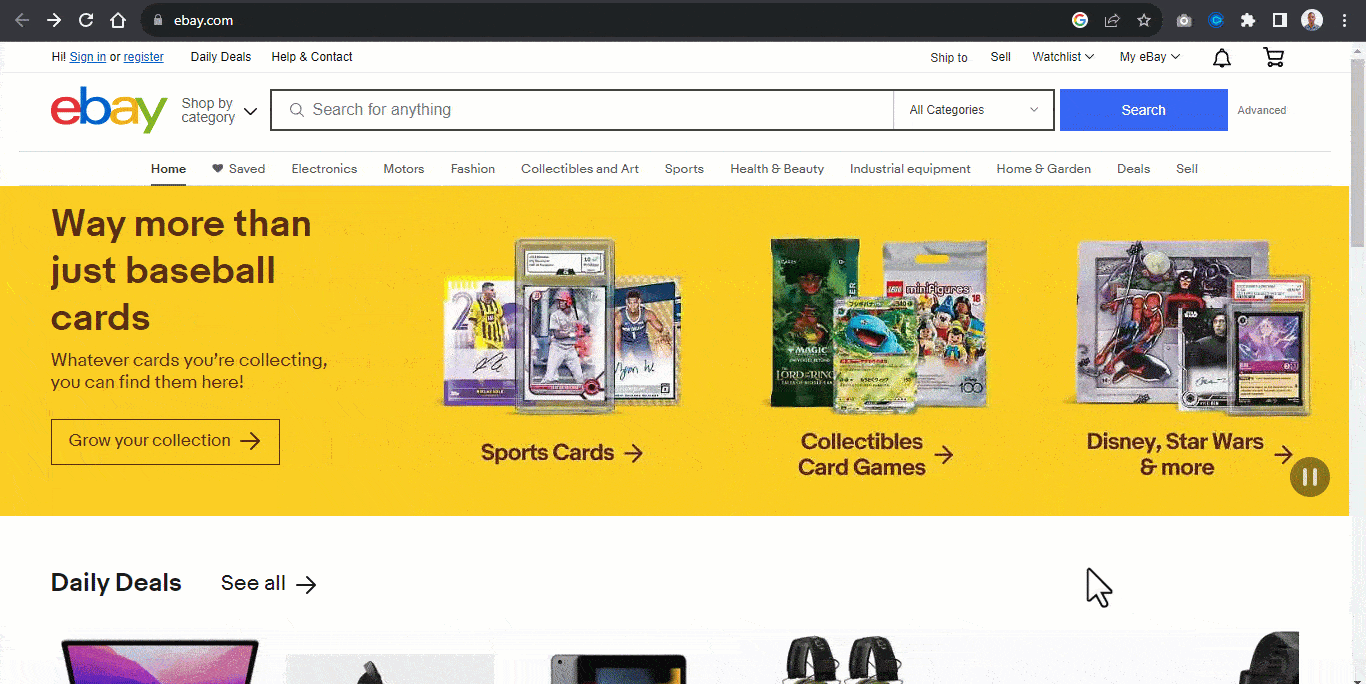
For example, the Airbnb website below contains four elements with header images. Each image within the header serves as a slide.
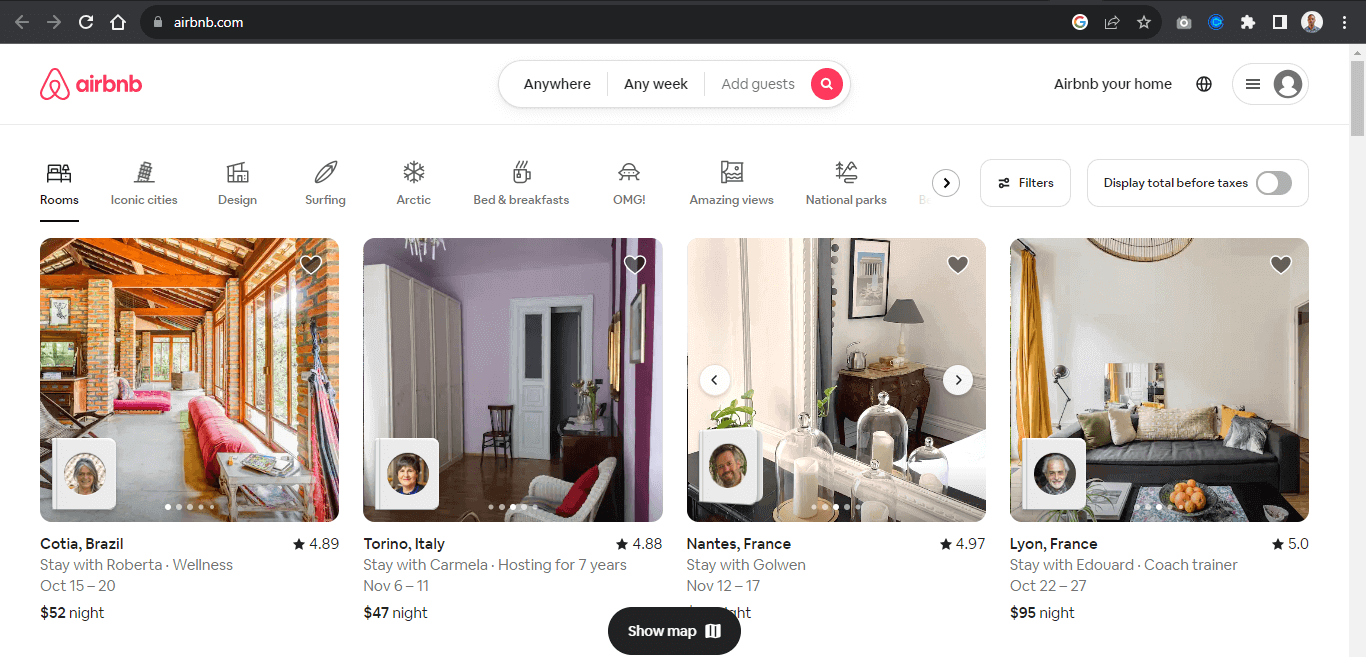
A slide in a carousel moves horizontally in sequential order; each slide rotates one at a time and hides to provide space for the next slide.
Once again, from the Airbnb website, each slide moves horizontally when the slider control is clicked on, revealing the next slide.
Users can directly interact with each slide by using the carousel controls. These controls enable the user to move the slides back and forth. Some carousels enable the keyboard or drag to scroll to move each slide within its slide container.
The carousel typically displays once the page loads, while the “slide picker controls” indicate which slide is displayed.
We can also see the same method replicated on the Motorola website, where each slide showcases the organization’s products as an ad. These types of carousels are banner carousels.
Components of Carousels
Before discussing the importance of accessible carousels, let’s explore different carousel components. Carousel slides are content in the form of a slide. Each slide displays different content and loops one after the other.
To ensure a good user experience, carousels typically have controls that enable users to navigate around the carousel content, known as slides. The controls also indicate which side (content) is currently on display.
The following examples are controls or slide controls that can be implemented when creating a carousel element.
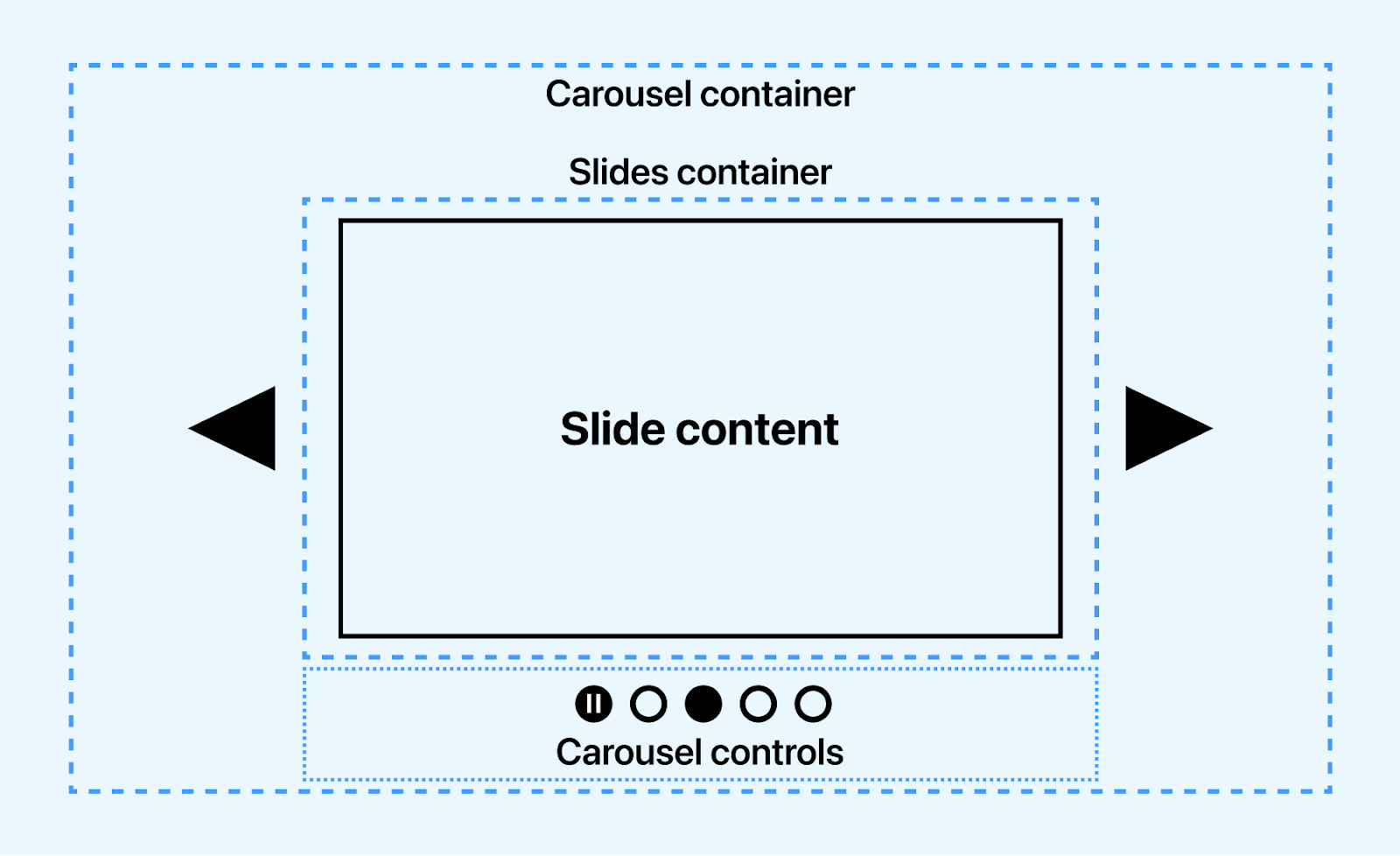
- Previous slide controls: This is a button element with a left arrow icon for navigating the slides back in sequence.
- Next slide controls: This is a button element with a right arrow icon for navigating the slides forward in sequence.
- Slide picker controls: These are small groups of button elements, usually at the base of the carousel. These buttons mainly do two things, one of which is to indicate which slides are currently on display and to navigate to a specific slide without using the slide controls.
- Pause/play controls: This control button controls the play and pause state of the carousel slides. This is mainly seen in the carousel displayed when the page loads.
- Slide: A slide is the individual items that displays in sequence. However, a slide is not a control but can be implemented as a control for drag events, where users can drag a slide to review the next slide.
The Toyota landing page shows how to trigger the animation play state using the play and pause button.
To improve user interaction, keyboards such as spacebars, taps, and arrow keys can be a good control source.
Note: Tests carousels for accessibility across 3000+ real environments. Try TestMu AI Now!
Why are Accessible Carousels Needed?
Accessible carousels are very much needed to provide instructions to visually impaired users to enable them to navigate carousel elements on the web page. According to WHO, almost 2.2 billion have a visual impairment in some way, making it difficult for people with visual impairment to access the web.
Accessible carousels are needed for multiple reasons:
- They enable visually impaired users to identify components/controls that make up the carousel.
- Assistive technology tools such as screen readers, text-to-speech, and refreshable braille display software reads aria Roles, States, and Properties as audible text to visually impaired users. This helps visually impaired users understand how the carousel works and how to use it.
- Accessible carousels are also necessary for compliance with accessibility standards such as WCAG 2.0 and Section 508.
- With accessible carousels, visually impaired users can navigate carousel components using voice input software and keyboard navigation with the help of accessibility.
- Carousel content can be paused with carousel control by users distracted by frequent movement of the content to enable them to listen to carousel content.
- Visual-impaired users can determine the state of the carousel if it’s pressed, disabled, checked, or hidden.
Accessible carousels generally provide good semantics in the form of audio/speech for visually impaired users. This helps to determine the landmark area the carousel occupies and its role, its content, and how to navigate it on the web page.
Are Carousels Good for Accessibility?
Despite being implemented across multiple sites by web developers, Carousels have numerous associated issues, which we will split into two parts.
Interactivity
Carousels have unpleasant user experiences, as users rarely interact with them. This might be due to a lack of understanding of interacting with carousels.
A study based on Google Analytics Event recorded the number of interactivity. The report states the percentage of visitors who clicked on a carousel feature is 1%, with the first feature getting the highest clicks or interactivity. In contrast, other features have to share the same or no interaction.
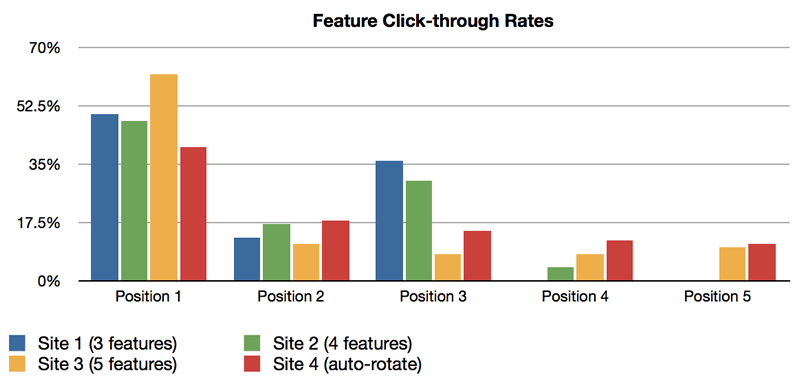
The image above shows click distribution by position. Position 1 is shown to take the highest number, while other positions share the same proposition evenly. This is not good for sites with multiple carousels, as the chances of them being interacted with are low or there is no interaction.
However, to increase the chance of interactivity,
- Consider reducing the number of slides to a maximum of four.
- Captivating headline titles and images can significantly impact click-through rates.
- Content should contain a single idea as it helps users understand what each slide presents.
Since the first slide gets the most attention, the most important slide should be implemented first to encourage user click-through.
Accessibility
Accessible carousels involve ensuring all users can access the content on each slide and navigate each slide via the slider controls.
However, for visually impaired users, screen-readers, and text-to-speech software (assistive technology tools) are relied upon to report the right content or information to the users. For instance, animated slides with pause/play control can display multiple shows within a slide without proper use of WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties. The screen reader can report this as multiple slides instead of showing within a slide or as a plain HTML tag.
Let’s take the Toyota homepage as an example.
From the Toyota homepage, the first slide has two shows that display before the next slide is displayed. At the bottom left corner is a pause /play control for pausing or playing each show within the slide. Without proper WAI-ARIA for labeling, this might not get the right accessible result from screen readers.
Accessibility plays an excellent role for visually impaired users, and assistive technology tools help convey digital content on the web to visually impaired users by speech synthesis (Text-to-Speech) TTS. For example, when a user clicks or interacts with web elements, the screen readers extract the content and report it as an audible speech.
For assistive technology tools to be effective or detect content, several factors have to be implemented, such as the following.
- Alternative text: Mainly referred to as alt text, alternative text is HTML attributes used to write descriptive text to describe the image or content provided within the HTML tag. This attribute is used for content such as images, videos, audio, logos, and web icons. They are helpful for Google search engines and assistive technology tools like screen readers.
<img src="https://www.example.com/images/sky" alt="Blue Sky" />
<h1>This is a top level 1 heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph text</p>
<button>Click here </button>
- Captions: Unlike alternative text, captions are displayed directly on the web page. Caption provides a descriptive text that explains what the provided content is about, especially for images. < figcaptions > are used to provide captions in HTML documents. Captions can be very useful for hearing-impaired users.
<figure>
<img src="https://www.example.com/images/sky" alt="Blue Sky" />
<figcaption>A beautify picture of blue sky</figcaption>
</figure>
In the next section, we will see the role of WAI-ARIA in building accessible carousels.
Role of WAI-ARIA in Creating Accessible Carousels
The WAI-ARIA, which stands for Web Accessibility Initiative – Accessible Rich Internet Applications, is a specification developed by W3C to provide semantic meaning to assistive technology tools such as screen readers for ensuring content on the web are interpreted the way they function and appear on the web.
For example, visually impaired users cannot see the carousel on the web or interact with the carousel directly, so the WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties are used by developers to provide additional text based information on the HTML tags that describe what the carousel actually means or how the carousel controls functions.
This enables screen readers to read WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties as audible speech back to visually impaired users as it enables them to navigate and use the website the way it was intended by the developer.
When the HTML document is loaded on the DOM by the User Agent, it creates a parallel structure called an accessibility tree, which is made up of accessibility objects. The accessible objects provide information on the HTML markup based on the Roles, States, and Properties of WAI-ARIA.
Following are the WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties that can be implemented to create accessible carousels:
- Roles: The Role defines what the element is meant to do. For example, in a carousel slider, we can add a role=”main” on the carousel-container, indicating that the specified element should be read as the main content of the carousel by screen readers.
- States: The State defines the current condition of the element. For example, we can add a aria-disabled to a disabled button to inform the screen reader to read it as a disabled button.
- Properties: The Properties provide more descriptive information about the element or content on the web page for screen readers. For example, the aria-describedby can be used to describe the content of the carousel slides for screen readers.
Remember that the Roles, States, and Properties are meant to be read as audible speech and do not have or add any functionality to the carousel or web elements.
Techniques to Build Accessible Carousels
Several crucial steps are important when building an accessible carousel. This step ensures that all carousel components are accessible, making it easy for visually impaired users to navigate.
How a carousel is structured, or functions should not prevent it from being accessible. The following techniques illustrate how to create accessible carousels.
Auto-Rotation
Auto-rotation carousels are very common in websites today. This type of carousel can also be called a banner carousel, mainly used to display ads that run as soon as the page loads and continues to auto-rotate.
To improve and make the auto-rotating carousel accessible, a few important steps must be taken.
Auto-rotate may be distracting for people with cognitive impairments. A control button (pause/play button) can be implemented to pause the animation to enable the users to concentrate.
- WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties: These should be implemented to indicate to screen readers that the carousel has an auto-rotation state.
- Pause auto-rotation on hover: Users need time to read content. Implementing pause animation on hover helps visually cognitively impaired users focus on interacting or listening to the carousels.
Visibility
For visually impaired users, visibility means the carousel components are well labeled with the appropriate WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties. This helps to improve the accessibility nature of the carousels.
Here are other aspects that should be considered:
- Hidden elements should have a WAI-ARIA state to indicate the element is hidden or disabled.
- Carousel components should be labeled according to their functions. This makes it easily accessible.
- Buttons with SVGs as content should be labeled and assigned an accessible role to make it accessible to visually impaired users.
- Overflow content should be hidden to make it easy to navigate the carousels.
- All carousel components should be responsive and easy to navigate on mobile, tablet, and desktop.
- Buttons, slides, slider picker controls, play/pause state buttons, and other carousel components should be implemented and labeled accordingly to make them accessible.
Structure, Semantic, and Labeling
Websites require good structure and semantic tags to make websites responsive, SEO friendly, and easy to navigate. This is because browsers can quickly load and render well-structured and semantic websites on the screen.
However, visually impaired users rely heavily on the accessibility of the WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties to determine the structure and semantics of the websites.
In this case, good use of WAI-ARIA should be implemented on semantic tags to let the users know which element holds the main carousel and which element serves as the control.
<main role="main" aria-label="carousel container">
<button role="button" aria-label="backward"></button>
<section role="region" aria-label="carousel">
<!-- Slides -->
</section>
<button role="button" aria-label="forward"></button>
</main>
Landmarks should be implemented to make sections or groups of elements on the page accessible. For example, the main, aside, form, section, article, and div elements can be assigned relevant landmarks that explicitly state their role in the element.
The WAI-ARIA role attribute serves as a way to provide landmarks on the element for accessibility purposes.
Now, let’s see a hands-on demonstration of building accessible carousels.
Demonstration: Building Accessible Carousels
In this blog section on accessible carousels, we will look at various kinds of carousels and how to implement them in your software projects regarding accessibility as specified in the previous examples. To demonstrate the creation of accessible carousels, we will take three popular carousel examples.
Product Carousels
Product carousels are one of the most common carousels and can be seen on major e-commerce platforms such as Amazon, eBay, Walmart, Best Buy, and Apple Store. They are beneficial in cases where collections or groups of products are to be displayed on the website for easy navigation by the users.
Here is a simple use case from the Apple Store. Each product is grouped based on the product’s items.
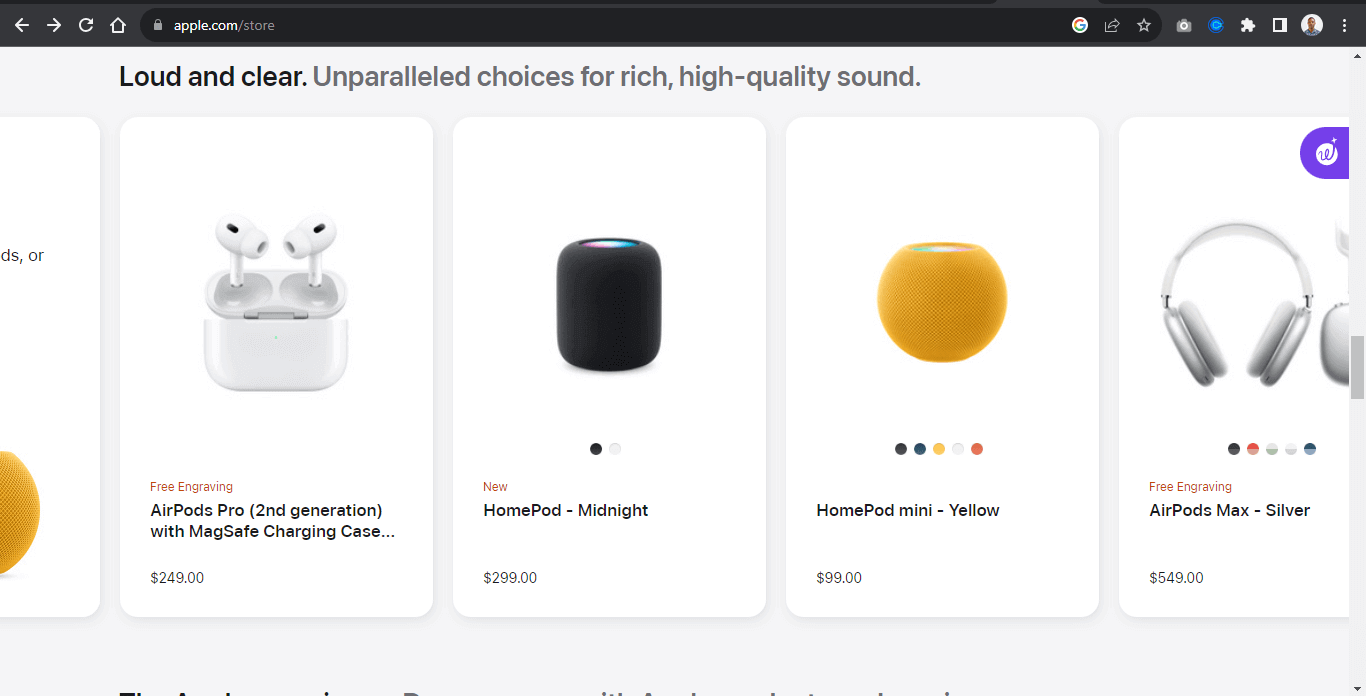
A simple example below shows how to implement a group of product items as carousels.
Example:
From the example above, the carousel contains nine images, each image split into three groups called view. Each view contains similar products.
For example, the first view is a display of Apple HomePod, the next is a display of Apple AirPods, and the last is the Apple 15 display.
This example is most useful when we want to display the same kinds of products or items simultaneously and enable users to navigate around different items from similar types in a roll.
HTML:
<div class="group">
<main class="carousel" role="main" aria-label="carousel">
<button type="button" id="backward" class="btn disabled" role="button" aria-label="backward">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24" width="30" height="30" class="main-grid-item-icon" fill="none" stroke="currentColor" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" stroke-width="2">
<polyline points="15 18 9 12 15 6" />
</svg>
</button>
<section class="carousel-sub">
<!-- View 1 -->
<section class="img-wrapper" id="view1">
<span role="img" aria-label="HomePod, AirPods, or select Beats product">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274978352-f0fc35e2-652b-428d-927f-09bf61805dbf.jpeg" alt="HomePod, AirPods, or select Beats product">
</span>
<span role="img" aria-label="HomePod - Midnight">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274980258-9f84204f-197f-4e0b-8c0e-5a9511f1db53.jpeg" alt="HomePod - Midnight">
</span>
<span role="img" aria-label="HomePod mini - Yellow">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274982370-6c49ff19-7f72-43f0-9592-1861a506fec2.jpeg" alt="HomePod mini - Yellow">
</span>
</section>
<!-- View 2 -->
<section class="img-wrapper" id="view2">
<span role="img" aria-label="AirPods Max - Silver">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274973852-afb2d3d0-2748-4612-a07a-b0f583c9d9b7.jpeg" alt="AirPods Max - Silver">
</span>
<span role="img" aria-label="AirPods (3rd generation) with Lightning Charging Case">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274973882-7cef7964-66fd-470f-8d5b-e8b3837ffcc9.jpeg" alt=" AirPods (3rd generation) with Lightning Charging Case">
</span>
<span role="img" aria-describedby="Beats Studio Buds + True Wireless Noise Cancelling Earphones in Transparent, with Beats logo, above convenient charging case.
TransparentBlack / GoldIvoryCosmic SilverCosmic Pink">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274973892-a5bdc3c6-ea67-46e2-b8cc-57f9a4f068a2.jpeg" alt="Beats Studio Buds + True Wireless Noise Cancelling Earphones in Transparent, with Beats logo, above convenient charging case.
TransparentBlack / GoldIvoryCosmic SilverCosmic Pink">
</span>
</section>
<!-- view 3 -->
<section class="img-wrapper" id="view3">
<span role="img" aria-label="iPhone 15 Pro FineWoven Case with MagSafe - Taupe">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274990709-1e3c4882-778f-49bd-9814-b940648ea4eb.jpeg" alt="iPhone 15 Pro FineWoven Case with MagSafe - Taupe">
</span>
<span role="img" aria-label="iPhone FineWoven Wallet with MagSafe - Black">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274990706-ecafd3a0-4a95-4c50-a6f5-69386c548be2.jpeg" alt="iPhone FineWoven Wallet with MagSafe - Black">
</span>
<span role="img" aria-label="iPhone 15 FineWoven Case with MagSafe - Pacific Blue">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/274990700-6d29a925-9e2a-487f-96c9-7decc3f4fb37.jpeg" alt="iPhone 15 FineWoven Case with MagSafe - Pacific Blue">
</span>
</section>
</section>
<button type="button" id="forward" class="btn" role="button" aria-label="forward">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24" width="30" height="30" class="main-grid-item-icon" fill="none" stroke="currentColor" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" stroke-width="2">
<polyline points="9 18 15 12 9 6" />
</svg>
</button>
</main>
<!-- Buttons -->
<div class="picker-wrapper">
<a href="#view1" class="picker-control active" role="link" aria-label="slide picker control"></a>
<a href="#view2" class="picker-control" role="link" aria-label="slide picker control"></a>
<a href="#view3" class="picker-control" role="link" aria-label="slide picker control"></a>
</div>
</div>
From the code above, the entire code is wrapped inside a single div tag of group.
The carousel is split between elements:
- Button: The < buttons > element is placed inside the carousel < main > element. This makes it easy to be positioned side by side with the carousel element
- Section: The < section > element is a wrapper for each “view” of the carousel items. This makes it easy to style and position each view one at a time
- < a >: The < a > element, which is implemented as picker-control , is placed at the bottom of the carousel for easy navigation of each carousel view within its container.
Here are the changes to make the carousel more accessible:
- Button: The < buttons > elements take a role and aria-label attributes. This is useful in cases where the content of the button element is an SVG icon and not an actual text. Providing a role=”button” of aria-label=”backward” makes the buttons more accessible for screen readers.
- Labeling: The < main > element takes a role=”main” and aria-label=”carousel”. The role=”main” indicates where the main content is, while the aria-label=”carousel” indicates that the main element is a carousel.
- Span: The < span > element wraps around each image slide and takes a role, aria-label, and aria-describedby (view 2 of the section element). The role indicates the role of the span as an image. The aria-label provides what type of image is included in the span while the aria-describedby describes what type of image is included in the span.
- < a >: The < a > element takes the role of link, and aria-label is set to slide picker control.
The role, aria-label, and aria-describedby attributes enable screen readers to read the value of these attributes as audible speech for visually impaired users.
CSS:
*, *::before, *::after {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
:root {
--bg-color: rgb(229 231 235);
--font: calibri;
--shadow: 0 4px 6px -1px rgb(0 0 0 / 0.1), 0 2px 4px -2px rgb(0 0 0 / 0.1);
}
body {
background-color: var(--bg-color);
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.carousel {
width: 100%;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.carousel-sub {
width: 70%;
display: flex;
overflow-x: scroll;
scroll-behavior: smooth;
}
.img-wrapper {
transition: all 0.5s ease;
}
.carousel .img-wrapper {
display: flex;
gap: 20px;
padding: 10px;
flex: 0 0 100%;
}
.carousel .img-wrapper img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
aspect-ratio: 1 /1;
filter: grayscale(100%);
transition:transform 0.5s;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: var(--shadow);
}
.carousel-sub::-webkit-scrollbar {
display: none;
}
.btn {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
border:none;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.23);
border-radius: 100%;
cursor: pointer;
transition: background 0.5s ease;
}
.btn:hover {
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.5);
}
svg{
display: block;
}
.btn svg {
stroke: #fff;
}
.carousel .img-wrapper img:hover {
filter: grayscale(0);
cursor: pointer;
transform: scale(1.1);
}
/* picker-wrapper */
.picker-wrapper {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
gap: 1em;
}
/* Slide Picker Control */
.picker-control {
display: inline-block;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.23);
border-radius: 100%;
transition: all 0.5s ease;
}
.picker-control:hover {
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.5);
}
.active {
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
}
.disabled {
transform: scale(0);
transition: transform 0.5s ease;
}
JavaScript:
const carousel = document.querySelector(".carousel-sub"),
backwardBtn = document.querySelector("#backward"),
forwardBtn = document.querySelector("#forward");
const carouselViews = document.querySelectorAll('.img-wrapper')
const pickerControls = document.querySelectorAll('.picker-control');
backwardBtn.addEventListener("click", function(e){
const size = document.querySelector('.carousel-sub').clientWidth;
carousel.scrollLeft -= `${size}`;
let i = 0;
let arr = [...pickerControls];
let lastIndex = arr.length -1;
if(carousel.scrollLeft === 0) {
backwardBtn.classList.add('disabled');
forwardBtn.classList.remove('disabled')
arr[i].classList.add('active')
arr[1].classList.remove('active')
}
else if(carousel.scrollLeft >= 0){
arr[1].classList.add('active')
arr[lastIndex].classList.remove('active')
forwardBtn.classList.remove('disabled')
backwardBtn.classList.remove('disabled')
}
})
// The forward button for navigating backward
forwardBtn.addEventListener("click", function(e){
const size = document.querySelector('.carousel-sub').clientWidth;
carousel.scrollLeft += `${size}`;
let i = 0;
let arr = [...pickerControls];
let lastIndex = arr.length -1;
if(carousel.scrollLeft === 0){
arr[i].classList.remove('active')
arr[1].classList.add('active')
backwardBtn.classList.remove('disabled')
}
else if(carousel.scrollLeft >= 0){
arr[1].classList.remove('active')
arr[lastIndex].classList.add('active')
forwardBtn.classList.add('disabled')
}
})
// Carousel Element
carousel.addEventListener("wheel", function(){
e.preventDefault();
carousel.scrollLeft += e.deltaY;
carousel.style.scrollBehavior = "auto";
})
// add active class to picker control
function eventHandler(index) {
carouselViews.forEach((view, i)=>{
pickerControls[i].classList.remove('active')
})
pickerControls[index].classList.add('active')
}
carouselViews.forEach((view, i)=>{
pickerControls[i].addEventListener('click', ()=>{
eventHandler(i)
})
})
From the code example above, the code snippet performs the following functions;
- The carousel variable is attached to an addEventListener method that listens for the mouse scroll wheel. This enables the carousel to scroll when a user scrolls the mouse wheel.
- The forwardBtn variable is attached to an addEventListener method that listens for a click and takes a callback function with a preventDefault() method and scrollLeft property that scrolls the carousel to 900px width when the user clicks the button.
- The backwardBtn variable behaves the same way as the forwardBtn variable, but the scrollLeft property is set to minus 900px. This moves the carousel slides backward.
- The eventHandler methods remove and add active classes.
- The carouselViews is attached to a forEach method that loops through each element (view) of the carouselViews. Then each element of the pickerControls takes an addEventListener of click that returns a callback function of eventHandler.
This enables the slider to add an active class to the pickerControl element to indicate the active element based on the user’s click.
Testimonial Carousels
Adding testimonials to your web page is a great way to instill confidence in a user about your product. This can quickly be done by creating a simple HTML mockup and CSS styling that displays the testimonials on the page.
However, there are cases where there are many testimonials to display. In this case, the testimonials can be implemented as a carousel that displays several testimonials from a single view. For example, Hashnode uses sample slide animation testimonials to display to the users on the home page.
Similar examples can also be seen on CodeSandbox.
Now, let’s see how to implement the above cases on a web page.
Example:
The example above shows how multiple elements can be implemented as a carousel that animates horizontally across the page.
The element animation-iteration-count is set to infinite to enable the animation sequence to keep repeating itself. In contrast, the animation-play-state is set to run to keep the animation going.
However, each animation is set to pause on hover to stop it from running. This is very useful as it lets users pause the animation and read the testimonials.
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Carousel Hover</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="main.css">
</head>
<body>
<main class="main">
<aside class="card-group g1" role="main" aria-label="carousel">
<!-- Card One -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">
Awesome job you did there <em>@testmuai</em> with the LT Browser. It's doing a fantastic job at responsive testing 🔥 see more >
</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654602-6b6c4303-587d-48ae-957a-3b88496f1fcc.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Mbaziira Ronald</h4>
<p class="at">@MbaziiraRonn</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Two -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Amazing Test software. I am very satisfied, I think it is excellent software and as the years go by it continues to offer the best service I have ever tried....see more ></p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654585-d0774fd3-5d90-42f0-bc53-7141f7735825.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Elias M.</h4>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Three -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Anyone who needs to test their code on different platforms try <em>@testmuai</em> Great service from this company!</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013776-40ac50f1-31f8-4250-acb2-05f16d683baa.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Stephan Smuts</h4>
<p class="at">spsmuts</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Four -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">See how <em>@testmuai</em> is #Futureready to enable blazing-fast test orchestration seamlessly integrated with organizations' existing CI/CD platforms, using #Microsoft Azure.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654608-d291d9df-439c-4a79-83b1-2f2d71cd25b5.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Microsoft India</h4>
<p class="at">@MicrosoftIndia</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Five -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Amazing Experience. That reduces a large amount of cost as well as manhours which can be used for other better things. In our team we have integrated lambdatest with our automation CI/CD pipeline, this shows how we trust <em>@testmuai</em>...see more >.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654585-d0774fd3-5d90-42f0-bc53-7141f7735825.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Padma kumar M.</h4>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Six -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial"><em>@testmuai</em> Efficient and User-Friendly Cross-Browser Testing with LambdaTest...see more ></p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013732-785b0223-9774-4918-964f-ce75f11138f2.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Ravi Kanth G.</h4>
</span>
</div>
</section>
</aside>
<!-- Group 2 -->
<aside class="card-group g2">
<!-- Card One -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Thank you <em>@testmuai</em> for providing free open source license to run the web and mobile tests of our open source projects for free on Lambdatest platform.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013783-757ea2d1-e396-4d56-ade8-8b641f78ce71.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Mohammad Faisal Khatri</h4>
<p class="at">@faisalkhatri</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Two -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Super top notch customer support from <em> @testmuai</em> - just throwing it out there if you're looking for a decent browser testing platform, they get my full double thumbs up. Thumbs upThumbs up :-) </p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013790-4d674d96-a311-47c3-9b7c-03feaa36c948.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Ben Pritchard</h4>
<p class="at">@yesiamben</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Three -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial"><em> @testmuai</em> is fantastic. Cross browser and device testingtesting frustration is minimized. You can't get rid of clients that need ie11 nor can you own every device but lambda test bridge that gap.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013776-40ac50f1-31f8-4250-acb2-05f16d683baa.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Mat Gargano</h4>
<p class="at"> @matgargano</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Four -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">second-day using <em> @testmuai</em> and it's already proven itself a lot faster than Cross Browser Testing and BrowserStack, at half the price! bargain</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013762-54201d6a-0923-4969-948c-790dec804253.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Matthew Bryson</h4>
<p class="at"> @mbrysonuk</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Five -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Really superb customer service from Arpit <em>@testmuai</em> tricky Automation problem using Selenium in Python and they talked me through it and got me up-and-running. Awesome.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013745-c09f21ff-cb29-49df-9110-d5e90810b5b9.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Michael (Mike) Horne</h4>
<p class="at">@recantha</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Six -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial"><em>@testmuai</em> can I just say, your support team are first class. I had the pleasure of talking with Prateek Singh. He went the extra mile and nothing was too much trouble. Clearly your support is also very technically adept, something which I really value. Thank you!</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013732-785b0223-9774-4918-964f-ce75f11138f2.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Timothy Wintle</h4>
<p class="at"> @timwintle1979</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
</aside>
<!-- Group 3 -->
<aside class="card-group g3">
<!-- Card One -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Also I recommend using <em> @testmuai</em> for testing out in all the devices. I am personally using it for my MERN project testing as well.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654599-4bc5d6e9-da64-47fd-83ae-4cbf109fed16.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Masroor Ejaz</h4>
<p class="at">@MasroorEjaz</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Two -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Checkout LambdaTest -<em>@testmuai</em> Perform manual or automated cross browser testing on 3000+ browsers online. Deploy and scale faster with the most powerful cross browser test... see more ></p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654591-2bc192b0-9c97-4fbf-a55c-e60791acc4c6.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Dev Tools</h4>
<p class="at">@finddevtools</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Three -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Browser for Designers & UI Developers Need to Test your App on Multiple Devices ? 🤔 Meet LT Browser by <em>@testmuai</em> See more ></p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654594-c037ce6e-6fdc-42f9-a4f6-07419089b689.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Satyam Anand</h4>
<p class="at">@IncodeSatx</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Four -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Quick way to test IE and MAC OS specific issues. Ability to spawn an instance within seconds and start working instantly....see more ></p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654625-985aaf83-2f72-4a57-9eb3-10fbe52d8413.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Syed Haroon P.</h4>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Five -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial">Really superb customer service from Arpit <em>@testmuai</em> </em> tricky Automation problem using Selenium in Python and they talked me through it and got me up-and-running. Awesome.</p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/266013745-c09f21ff-cb29-49df-9110-d5e90810b5b9.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">Michael (Mike) Horne</h4>
<p class="at">@recantha</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Card Six -->
<section class="card c1">
<p class="text" role="paragraph" aria-label="testimonial"><em>@testmuai</em> #TestMuConf 2023 has been interesting so far with lots of quality sessions with industry experts sharing from their wealth of knowledge and experience... Thank you LambdaTest for hosting this conference... see more ></p>
<div>
<span class="s1">
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/78242022/272654627-1536d3df-c0f2-414c-b631-0bd1159db223.png" alt="">
</span>
<span class="s2">
<h4 role="heading" aria-label="4">WALIU ANUOLUWAPO SANNI</h4>
<p class="at">@WALIUANUOLUWAPOSANNI</p>
</span>
</div>
</section>
</aside><!-- End of Group 3 -->
</main>
</body>
</html>
From the code sample above, the element is broken down into six cards, and each six cards is divided into three groups.
- Cards: Each card contains a paragraph with a role=’’paragraph” indicating that it should be read as a paragraph by screen readers, and aria-label=”testimonials” indicating that this paragraph should be read as a testimonial.
- Card numbers and group: The cards are numbered into six and grouped into three, making it possible for users to interact with each group individually rather than with each card.
CSS:
*, *::after, *::before {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: 0;
}
body{
background-color: #EEF5FF;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
.main {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
display: grid;
place-items: center;
}
.card-group{
display: flex;
gap: 1em;
}
.card {
width: 445px;
height: fit-content;
padding: 15px 30px;
box-shadow: 0 1px 3px 0 rgba(0,0,0,.1), 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0,0,0,.06);
-webkit-user-select: none;
user-select: none;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 1px solid #aaaaaa;
transform: translate(-1800px);
animation-name: moveforward;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
animation-timing-function: linear;
animation-duration: 10s;
animation-play-state: running;
}
.g1 .card, .g3 .card {
transform: translate(1800px);
animation-duration: 20s;
animation-name: movebackword;
}
.g1:hover .card {
animation-play-state: paused;
}
.g2:hover .card {
animation-play-state: paused;
}
.g3:hover .card {
animation-play-state: paused;
}
.card .text {
font: 14px Arial;
color: #4a4a4a;
line-height: 21px;
}
.card h4 {
font: 16px Arial;
font-weight: 600;
color: black;
}
.card .at {
font: 16px Arial;
font-weight: 400;
color: #007bff;
margin-top: 4px;
}
.card img {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: 50px;
}
.card div {
display: flex;
margin: 10px 0 0;
gap: 10px;
}
em {
font-style: normal;
color: #007bff;
}
@keyframes moveforward {
0%{
transform: translateX(0);
}
100%{
transform: translateX(-1800);
}
}
@keyframes movebackword {
0%{
transform: translateX(0);
}
100%{
transform: translateX(1800);
}
}
In the next section of this article, we will look at how to ensure accessible carousels by performing accessibility testing.
How to Test the Accessibility of Carousels?
Ensuring accessible carousels requires screen readers to test different page sections. This is very useful when a carousel element with WAI-ARIA is implemented on each component, such as buttons, slides, slider picker controls, containers, etc.
To test how screen readers read the specified WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties defined on the carousel elements, you can leverage cloud-based accessibility testing platforms to ensure accessible carousels on different combinations of browsers and operating systems.
AI-powered test orchestration and execution platforms like TestMu AI offer accessibility testing of websites and web apps on over 3000+ real browsers and OSes.
We use the TestMu AI screen reader feature on Real Time Browser Testing to run accessibility checks. This will read the WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties specified on the element as audible text, giving the same user experience as a visually impaired user.
Check out the tutorial below that explains how to test websites in Real Time on the TestMu AI platform.
Subscribe to the TestMu AI YouTube Channel to catch up with the latest videos on Selenium testing, automation testing, and more.
To make sure the carousels are accessible to all users, there are a few best practices that must be followed. Let’s look at some of the best practices to create accessible carousels.
Best Practices for Accessible Carousels
To ensure carousels are well implemented, we can consider the following best practices.
- Easy navigation: Ensure that the carousel slides are easily navigated by implementing navigation controls and control pickers.
- Image quality and bold text: Quality images with bold text should be implemented to encourage users to click through the slides.
- Reduce the number of slides: Avoid multiple carousel slides to maximize engagement.
- Design consistency: Ensure all elements, slides, and navigation controls, maintain consistent style in appearance such as height, width, colors, fonts, etc.
- Avoid autoplay sounds: Ensure sounds are disabled to prevent unpleasant sounds. Users should be given the option to enable sounds for a better experience.
- Semantics: To ensure that carousels are compatible across multiple browsers, developers should write well-semantic mockups and use the appropriate WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties when implementing accessible features on mockups.
- Performance tracking and analytics: Track the performance of the carousel to understand how users interact with each carousel component.
- Fallback options via vendor prefixes: Vendor prefixes such as -webkit-, -moz-, and -ms- just to mention a few, should be used on properties that require vendor prefixes to work well. This will help create a good fallback for legacy browser versions.
Adequate testing should be implemented to ensure the carousel components, such as previous slide control, next slide control, slide picker controls, and pause/play control, are rendered correctly on different browsers for a better user experience.
Conclusion
Carousels help boost users’ engagement and prevent endless scrolling in search of related content or items on the page. However, to create accessible carousels, WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties that enable carousels to be accessible need to be specified within the semantic HTML mockups of the carousel components.
Accessible carousels enable assistive technology tools such as screen readers, text-to-speech, and refreshable braille display software to read WAI-ARIA, Roles, States, and Properties as audible speech for visually impaired users.
Ensure you test each WAI-ARIA Roles, States, and Properties specified on the carousel elements using accessibility testing tools. This will enable you to get real user feedback on how the carousel will be used for visually impaired users.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests