
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

Streamline Your Development Process With Google Cloud CI/CD Pipeline
Learn how to use Google Cloud CI/CD to build and deploy your applications efficiently. This article covers all details from pipeline setup to testing automation.

Chandrika Deb
January 11, 2026
In the present disruptive IT landscape, the latest version deployments get pushed every minute. At the same time, developers must ensure that they align themselves with agile methodologies and practices. Here comes the role of continuous integration and continuous deployment that enables to tackle integration issues as quickly as possible and helps in packaging and delivering risk-free releases to the customer.
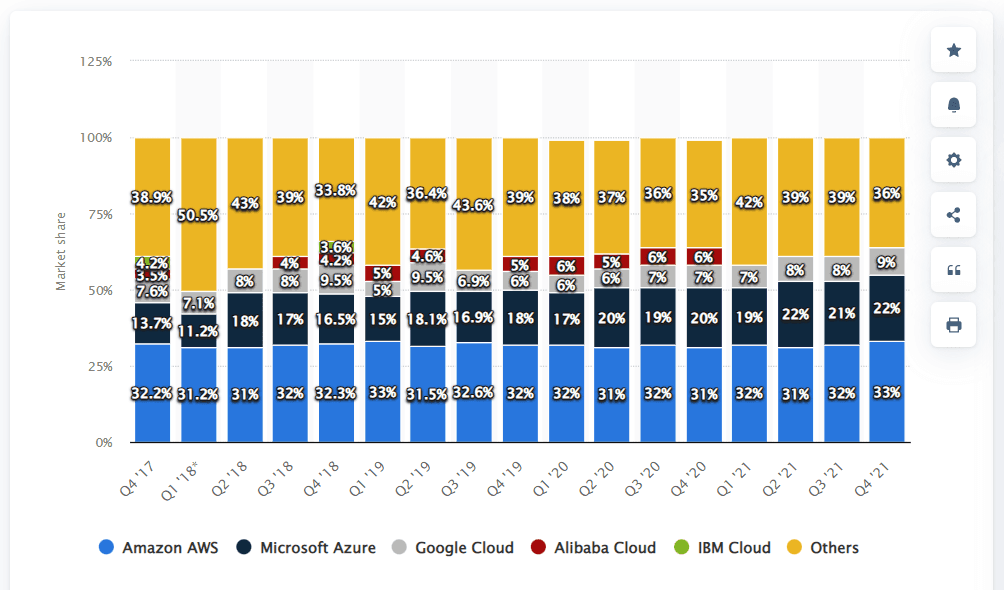
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is one of the leading cloud services providers in the public cloud market. GCP has a market share of 9% as of Q4 in 2021, according to Statista. Google Cloud CI/CD provides various tools for continuous integration and deployment and integrates seamlessly with third-party solutions.
Google Cloud Build and Google Cloud Run are two Google Cloud services that use pipelines to automate builds and deployments. Cloud Build, Google Cloud’s continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) platform, was named a Leader in a report by The Forrester Wave.
Online Selenium Grid helps to speed up testing. By providing an environment that allows tests to be run on multiple browsers and operating systems simultaneously, you can address cross browser testing issues all at once, saving time over doing so sequentially. A cloud based Selenium Grid helps you focus on writing Selenium test scripts better rather than worrying about infrastructure maintenance.
Google Cloud CI CD pipelines can integrate with the cloud-based automation testing platform TestMu AI, which allows you to perform of web applications on an online browser farm of 3000+ browsers, operating systems, and devices.
With TestMu AI + Google Cloud CI/CD integration, you can also perform local testing of locally or privately hosted projects and parallel testing to cut short test execution cycles and achieve faster go-to-market delivery.
Note: Wondering How To Accelerate Test & Release Velocity? Try TestMu AI Now!
In this article on the Google Cloud CI CD pipeline, we will explore the Google Cloud Platform CI/CD pipeline, its architecture, features, and how its integration with TestMu AI can make CI pipelines more efficient.
So, let’s get started!

Google Cloud Platform CI/CD
Efficient CI/CD strategies enable companies to deliver better value by reaching out to the market with shorter turn-around times, increasing revenues and gaining market share. CI/CD practices help us proactively resolve bugs, issues, and other problems at a much earlier stage. This practice results in a significant reduction in the overall software development cost.
Now let’s explore the prerequisites for building a Google Cloud CI CD pipeline using its tools, like Google Cloud Build, Google Container Registry, and Source Repository.
Note: Integrate Google Cloud CI with TestMu AI and bring all Testing on Cloud! Try TestMu AI Now!
Cloud Source Repository
You can design, develop, and securely manage your code with Cloud Source Repository. You can collaborate smoothly on a fully featured, scalable, and private Git repository. You also have options to extend your Git workflow by connecting to other Google Cloud tools.
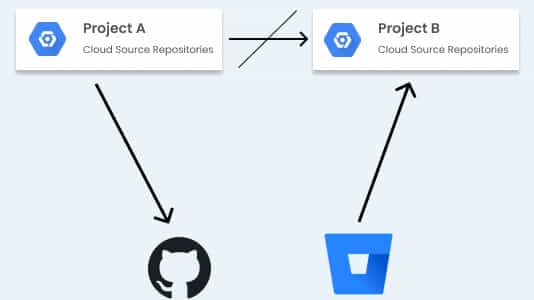
- Cloud Source Repositories are fully-featured, private Git repositories hosted on Google Cloud.
- Cloud Source Repositories can be used for collaborative, version-controlled development of any app or service, including those that run on App Engine and Compute Engine.
- Cloud Source Repositories can connect to an existing GitHub or Bitbucket repository. Connected repositories are synchronized with Cloud Source Repositories automatically.
- Cloud Source Repositories automatically send logs on repository activity to Cloud Logging to help track and troubleshoot data access.
- Cloud Source Repositories offer security key detection to block git push transactions that contain sensitive information, which helps improve the security of the source code.
- They provide built-in integrations with other GCP tools like Cloud Build, Cloud Debugger, Cloud Operations, Cloud Logging, Cloud Functions, and others that let you automatically build, test, deploy, and debug code within minutes.
Note: Want to make your life of testing easy and fuss-free while debugging? Try LT Debug Chrome extension!
Cloud Build
Cloud Build is a service that executes your build on Google Cloud Platform’s infrastructure. Cloud Build can import source code from a variety of repositories or cloud storage spaces, execute build according to your specified specifications, and produce artifacts such as Docker containers or Java archives.
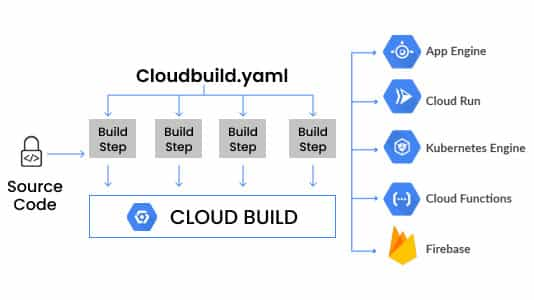
- A fully managed, server-less service that executes builds on Google Cloud Platform’s infrastructure.
- Can pull/import source code from a variety of repositories or cloud storage spaces, execute a build to produce containers or artifacts, and push them to the artifact registry.
- Executes the build as a series of build steps, where each build step specifies an action to be performed and is run in a Docker container.
- Build steps can be provided by Cloud Build and the Cloud Build community or can be custom as well.
- Build config file contains instructions for Cloud Build to perform tasks based on your specifications, e.g. the build config file can contain instructions to build, package, and push Docker images.
- Builds can be started either manually or using build triggers.
- Uses build triggers to enable CI/CD automation.
Container Registry
We often use the short name GCR for Google Container Registry. Google Container Registry, or GCR, is a service provider on the Google cloud platform that lets us store the Docker images and share them with the team. Now let’s look at some of the features of the GCR:
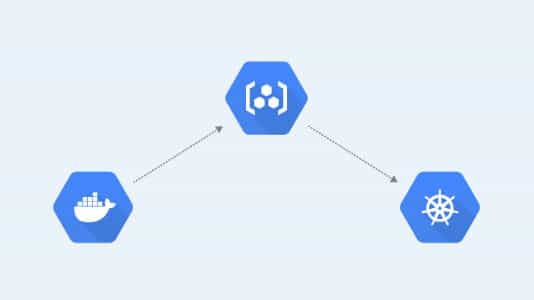
- Container Registry is a private container image registry that supports Docker Image Manifest V2 and OCI image formats.
- Container Registry provides a subset of Artifact Registry features.
- It stores its tags and layer files for container images in a Cloud Storage bucket in the same project as the registry.
- Access to the bucket is configured using Cloud Storage’s identity and access management (IAM) settings.
- Integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud services.
- Works with popular continuous integration and continuous delivery systems, including Cloud Build and best CI/CD tools such as Jenkins. If you want to create your first Jenkins pipeline, please refer to the Jenkins Pipeline Tutorial and get started.
Artifact Registry
Artifact Registry is a single place for your organization to manage container images and language packages (such as Maven and npm). It is fully integrated with Google Cloud’s tooling and runtimes and comes with support for naive artifact protocols.
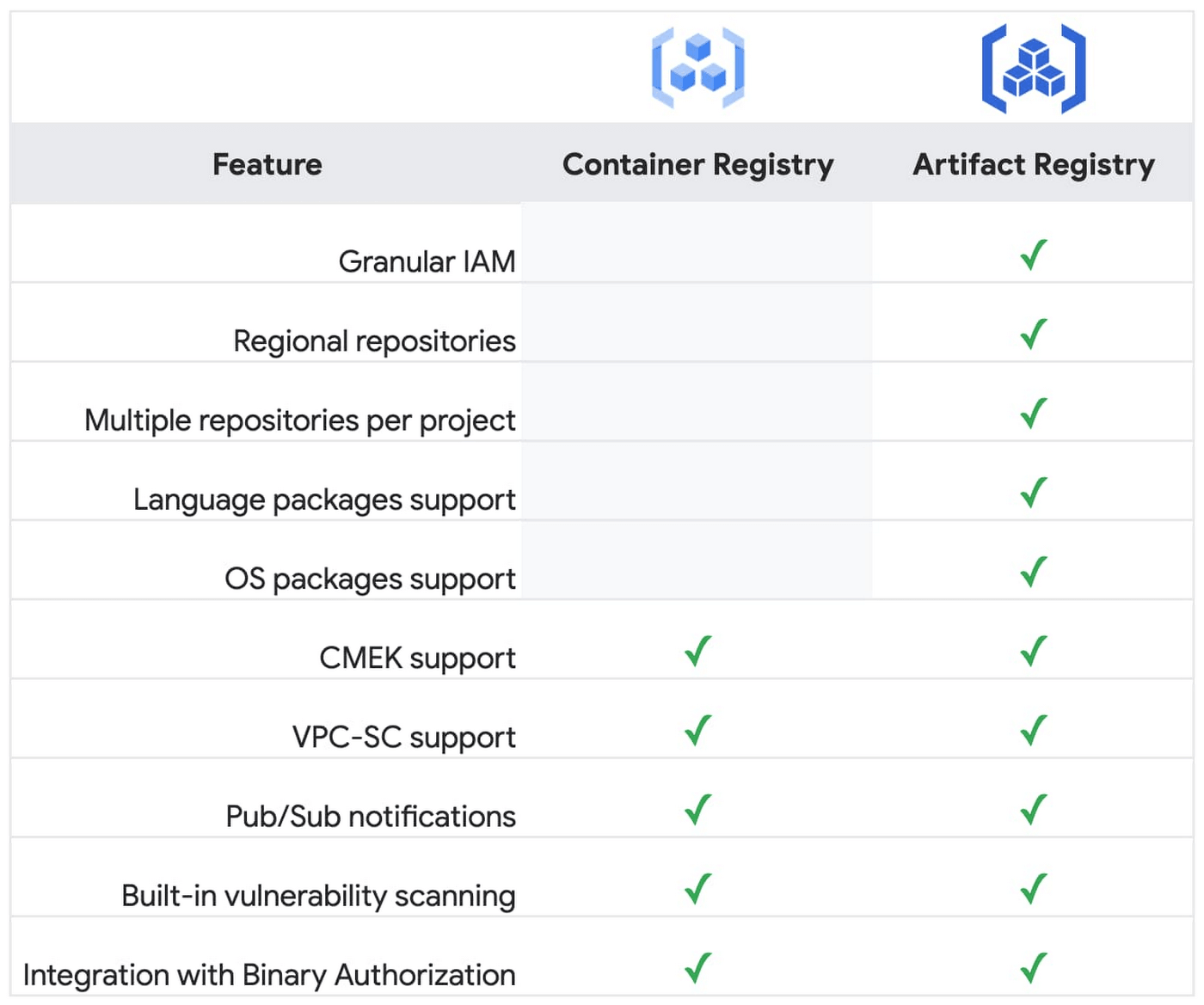
- Artifact Registry is a fully-managed service with support for both container images and non-container artifacts, Artifact Registry extends the capabilities of Container Registry.
- Artifact Registry is the recommended service for container image storage and management on Google Cloud.
- Artifact Registry comes with fine-grained access control via Cloud IAM. This enables scoping permissions as granularly as possible, for example, to specific regions or environments as necessary.
- Artifact Registry supports the creation of regional repositories.
Cloud Deploy
Google Cloud Deploy is a managed service that automates the delivery of your applications to a series of target environments in a defined promotion sequence. Google Cloud Deploy uses Scaffold to separate rendering tools from the delivery pipeline.

It makes manifest rendering more flexible without affecting how you define your delivery pipeline.
Google Cloud Platform CI/CD Architecture
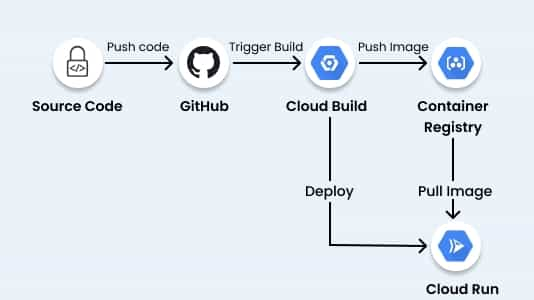
A general Google Cloud CI CD pipeline may involve the following steps:
- Developer checks the source code to a Version Control system such as GitHub.
- GitHub triggers a post-commit hook to Cloud Build.
- Cloud Build builds the container image and pushes it to the Container Registry.
- Cloud Build then notifies Cloud Run to redeploy.
- Cloud Run pulls the latest image from the Container Registry and runs it.
How to build Continuous Quality with Google Cloud CI CD Pipeline?
Using TestMu AI, you can perform both manual and automated cross browser testing at scale over an online device farm of 3000+ real devices and operating systems. Automation testing tools like TestMu AI allow you to harness the power of cloud-based online Selenium Grids in conjunction with our local grid setups.
While the local Selenium Grid is a good start, it is difficult to scale the test efforts exponentially. This is where cloud Selenium Grid can be helpful in reaping the benefits offered by Cloud and Selenium. A cloud Selenium Grid like TestMu AI lets you scale your automation efforts by performing Selenium automation testing at scale on a secure, reliable, and scalable grid on the cloud.
Here’s a quick glimpse of performing Selenium automation testing on the TestMu AI platform.
You can also Subscribe to the TestMu AI YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around automated browser testing, Cypress E2E testing, CI/CD, and more.
If you are a Selenium fanatic, you must have used Selenium 4. Selenium 4 is the latest version of the Selenium WebDriver with a host of new features that makes Selenium automation testing more stable and less flaky than previous versions. However, if you are intrigued to know more about what’s new in Selenium 4, you can go through the Selenium 4 tutorial to learn about the features and improvements in Selenium 4.
And that’s not all! Users can also perform mobile app testing (Android or iOS) on TestMu AI emulators & simulators and real device cloud for a multitude of configurations.
TestMu AI can be used as part of your Google Cloud CI CD pipeline to test your applications. Let us explore more about the prerequisites and the step-by-step guide to integrating TestMu AI with Google Cloud CI.

Some Prerequisites!
Make sure you are ready with the following steps mentioned before integrating Google Cloud CI with TestMu AI:
- Your TestMu AI account.
- Your code repository, on GitHub/Bitbucket etc.
- TestMu AI username and token, found in the top right ‘Access Key’ option on Automation Dashboard.
- Lastly, login into your Google Cloud CI CD platform and go to Cloud Build API.
- Click on ENABLE and add a billing account to your Google Cloud Platform for the CI/CD tool to function.

Integrate your code repository with Google Cloud CI
In order to run tests on TestMu AI via Google Cloud CI, we first need to connect our code repository. For this article, let us fork this TestMu AI Repository on GitHub to begin with.
Now let us open our GCP console and follow the below-mentioned steps:
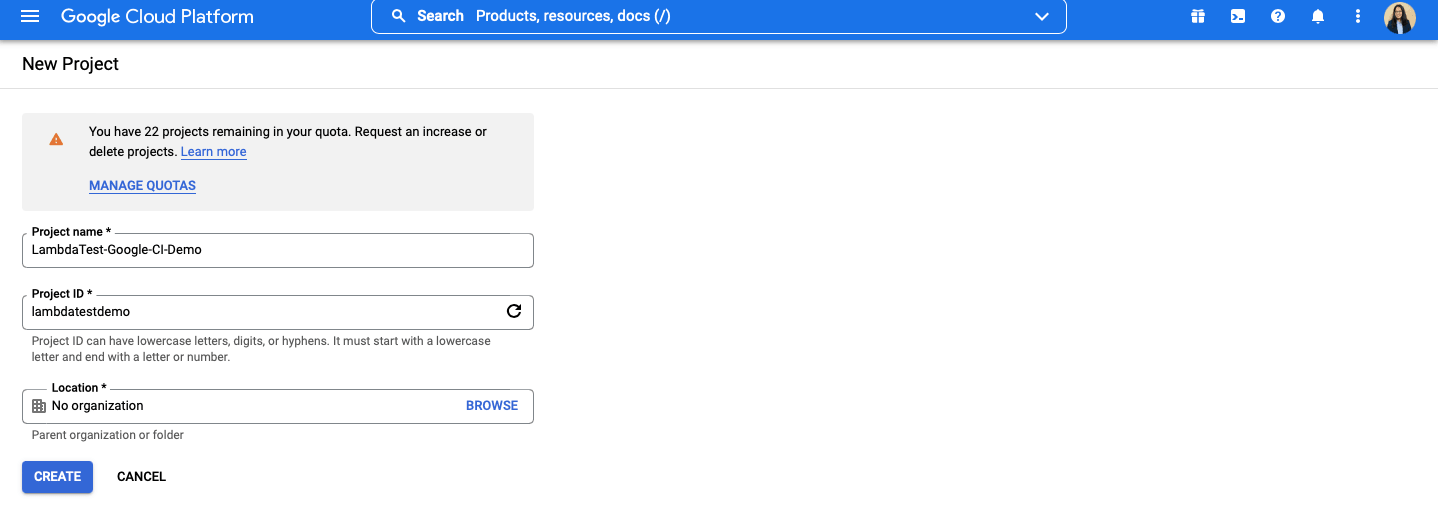
- Click on the Console option in the top right corner.
- Create a New Project and name it ‘TestMu AI-Google-Cloud-CI-Demo’.
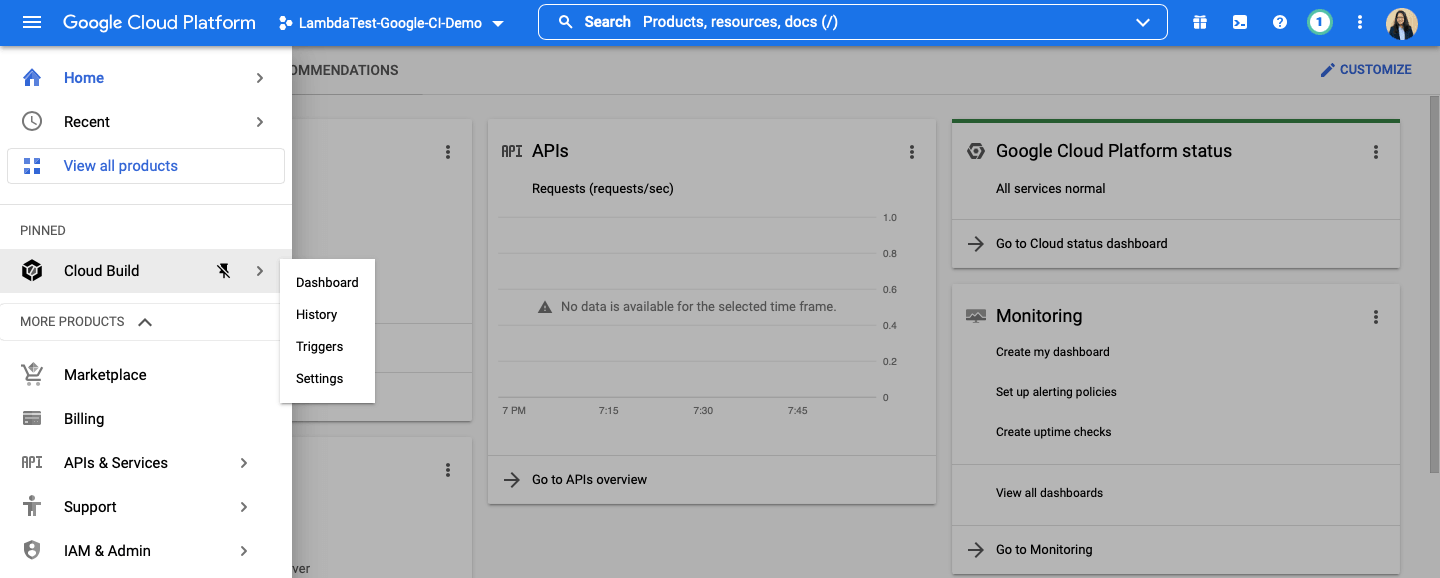
- Open the left pane of the dashboard and pin the ‘Cloud Build’ tool found under CI/CD category.
- Click on ‘Triggers’ from the drop-down options.
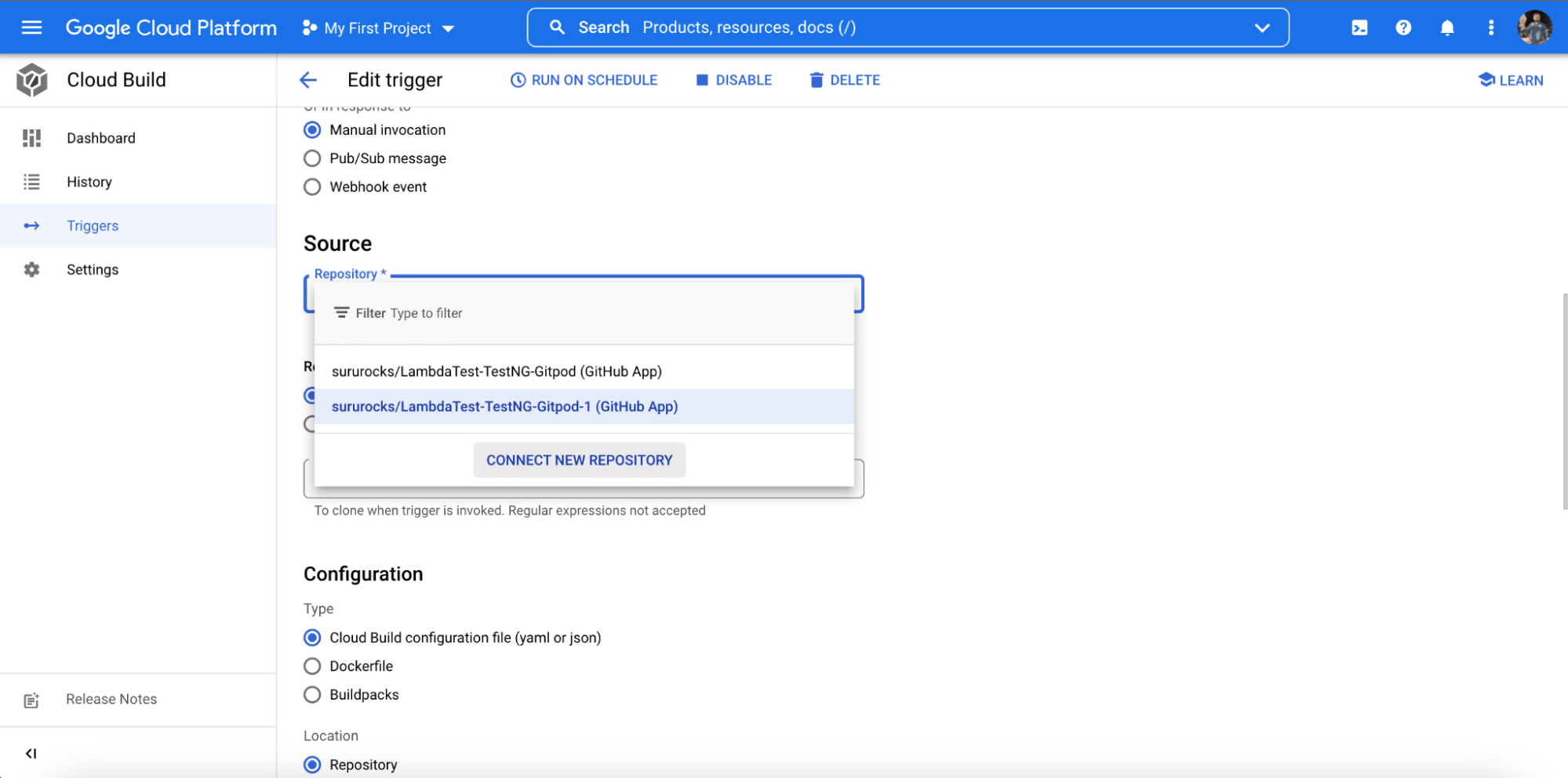
- Now we will connect our code repository using the ‘CONNECT NEW REPOSITORY’ option.
- After that, follow the remaining steps, which are pretty straightforward to complete the integration process.
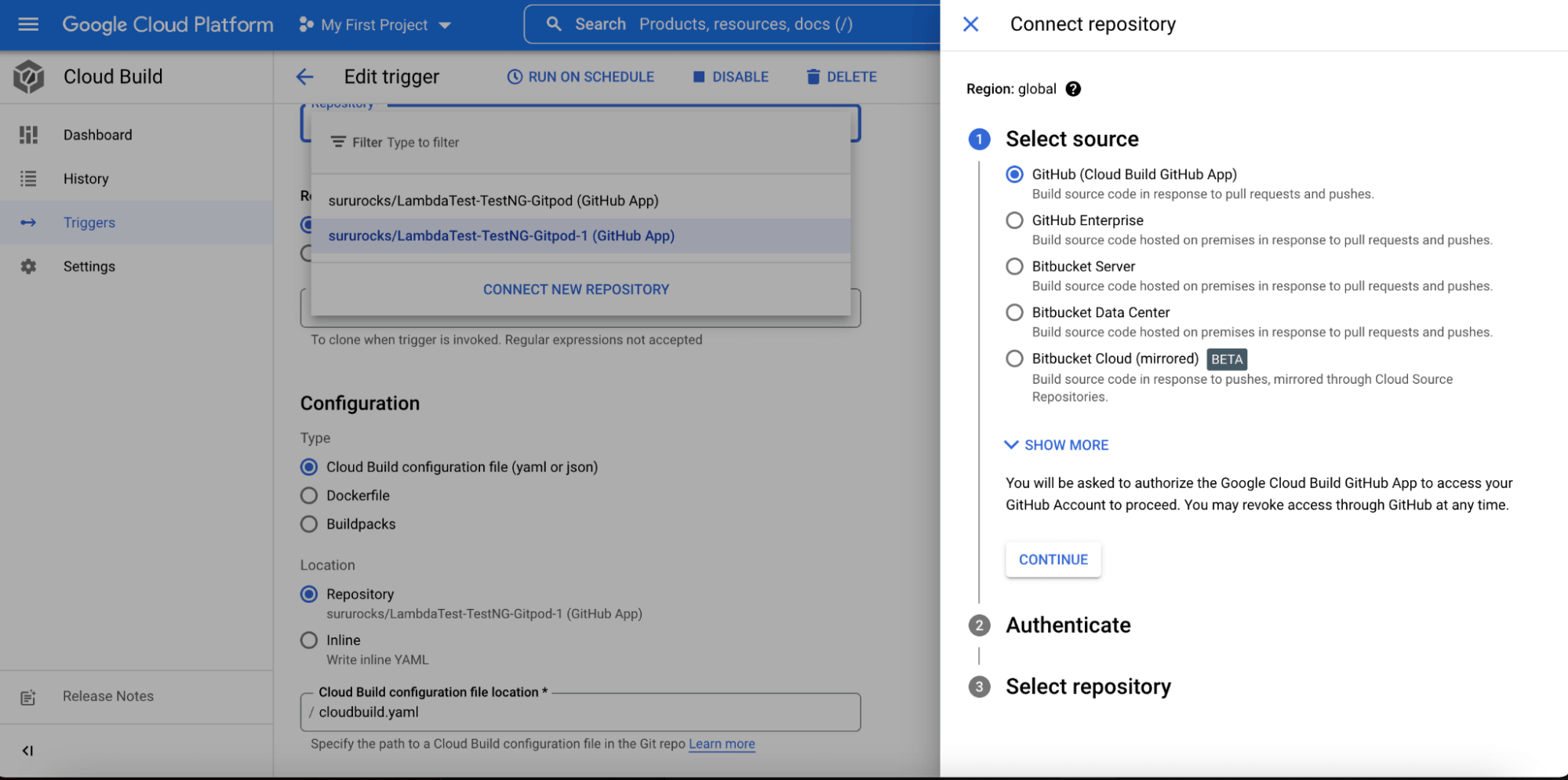
Running Single Selenium Test Via Google Cloud CI
Selenium is a very popular test framework using which you can create scalable test cases for automated UI testing or cross browser testing. Building and executing Selenium projects with automation platforms is a powerful way to test websites (or web apps) at a faster pace. By using Selenium testing tools, you can test faster, more often, and more accurately.
In this section of this article on the Google Cloud CI CD pipeline, we will try to run our Selenium tests without any cluster or Docker configuration via Google Cloud CI. We just need the correct Cloud Build config file to proceed with this case. Since we have already connected to the repository, which contains some sample TestNG-Selenium tests, now we will run them via Google Cloud Build.
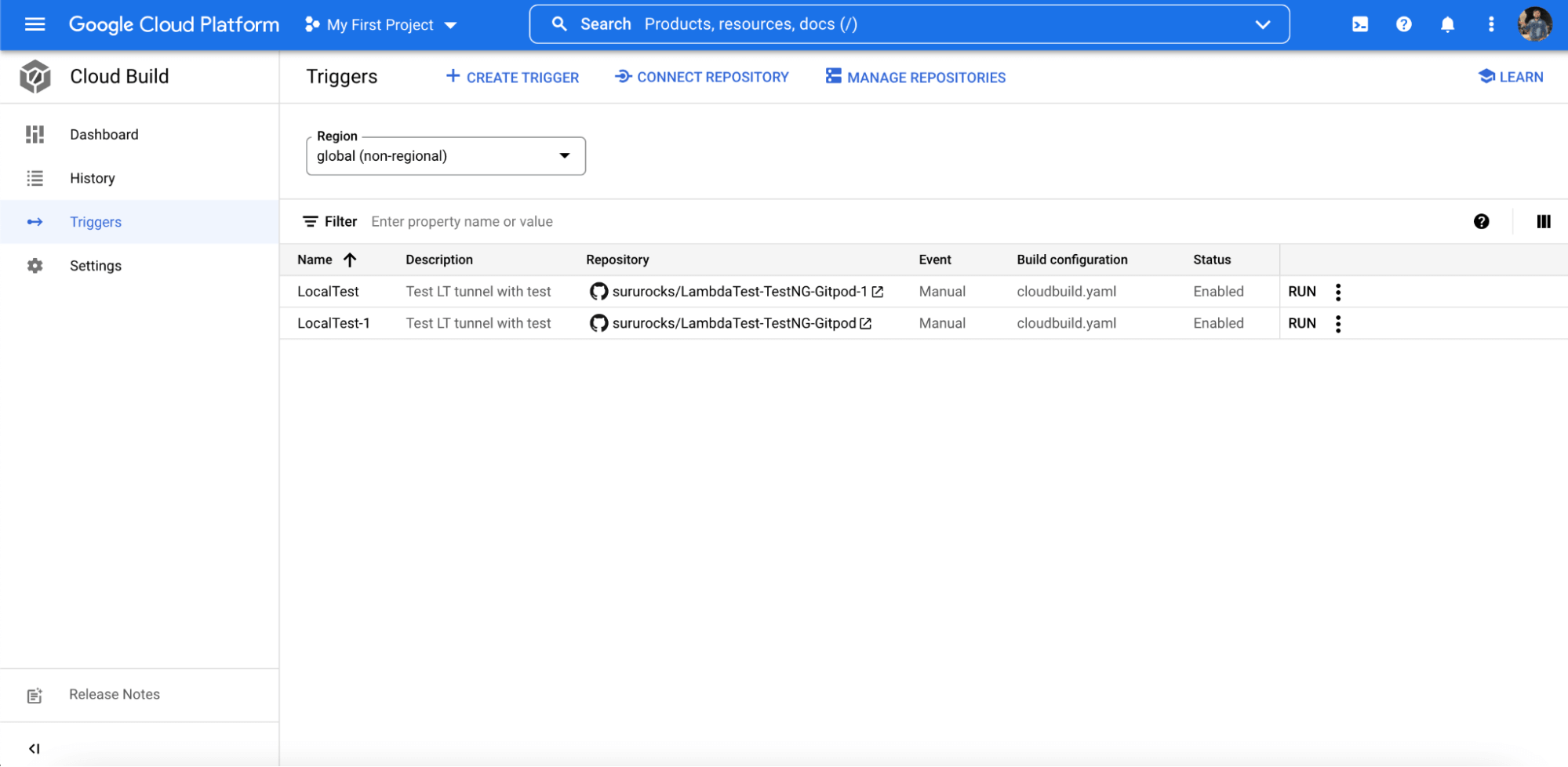
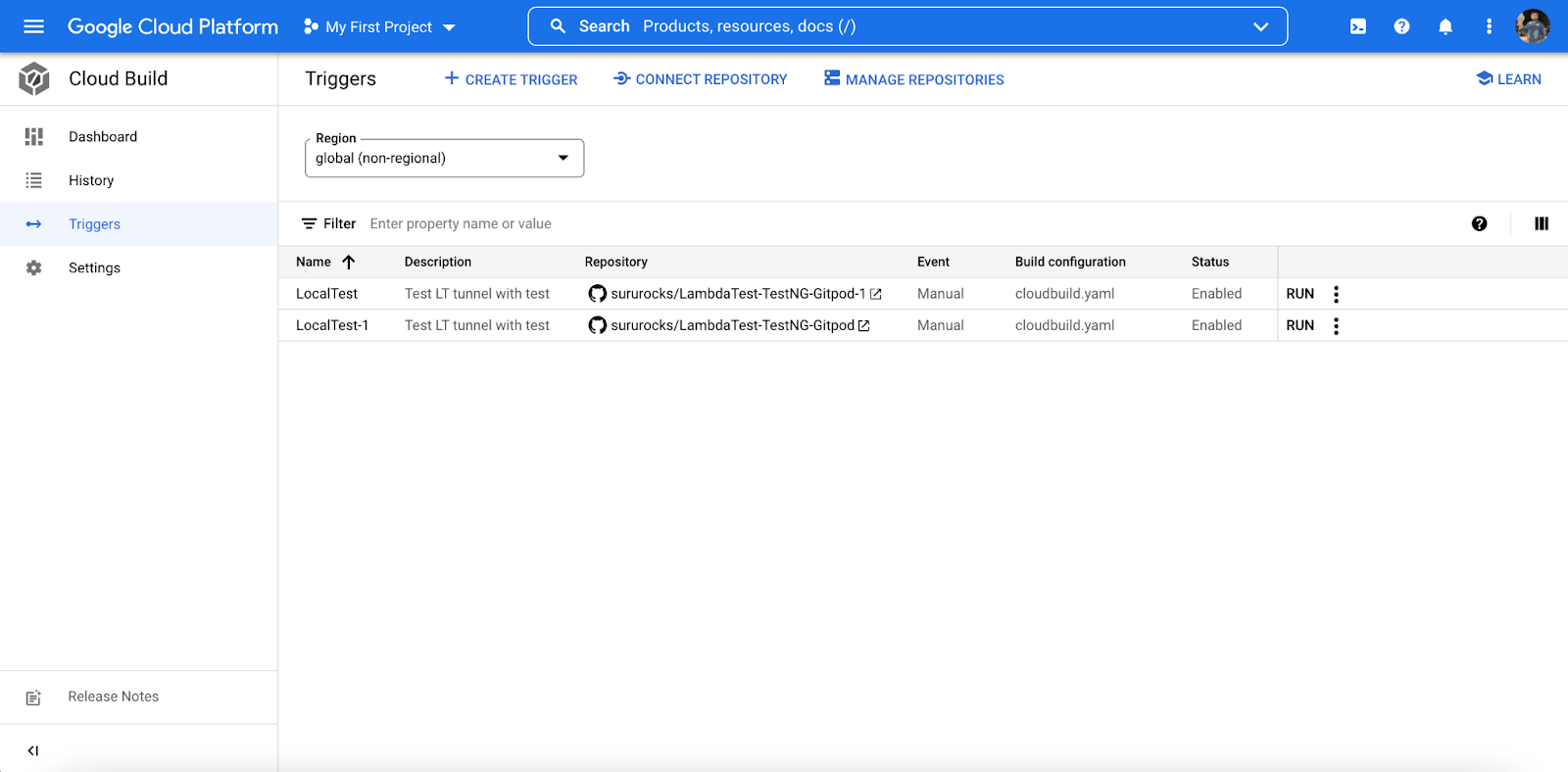
- Click on the ‘Create Trigger’ option and provide a name for it.
- Select the testing code repository and its branch.
- Under the ‘Configuration‘ option, select Cloud Build configuration file (yaml or json).
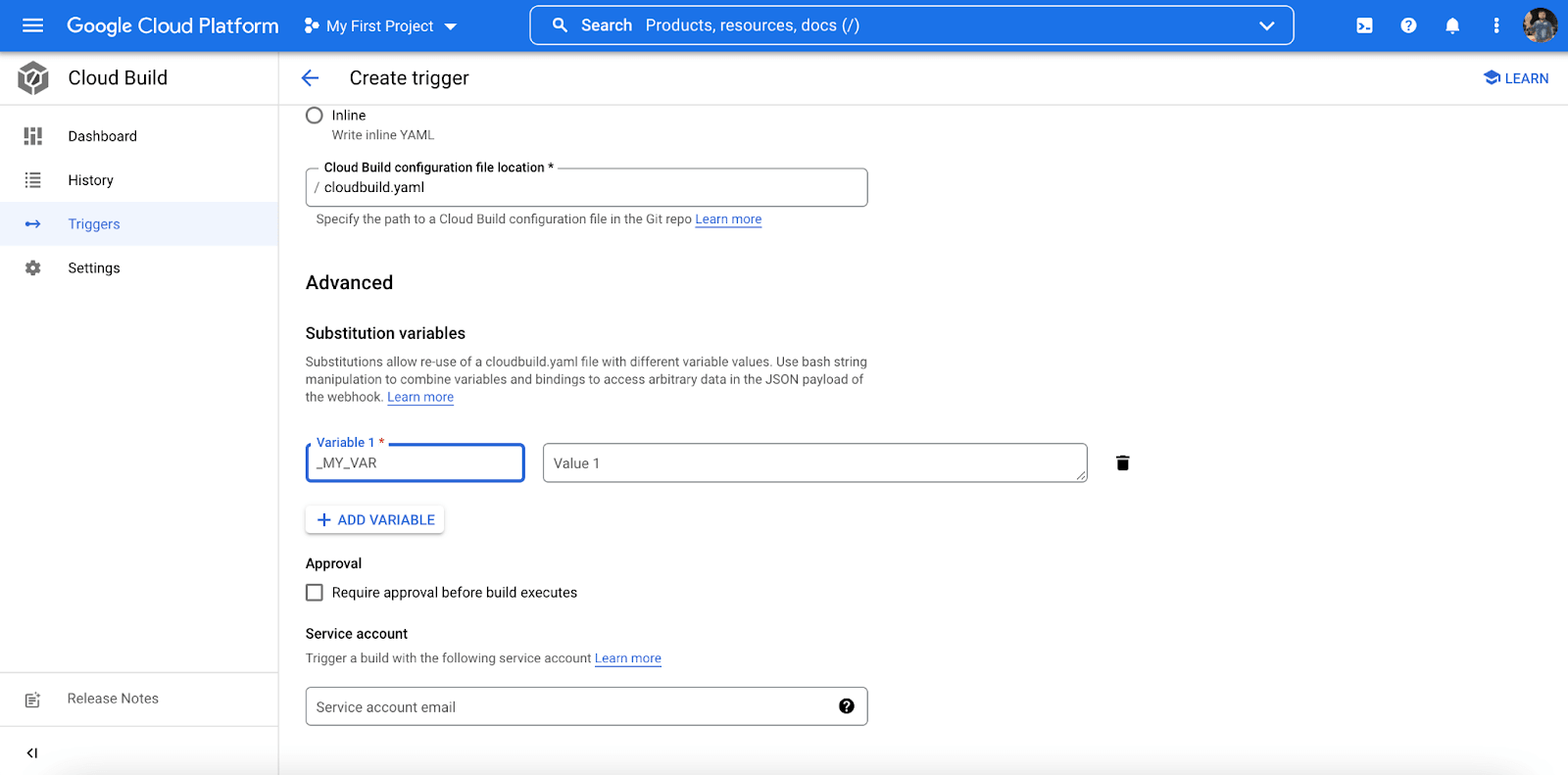
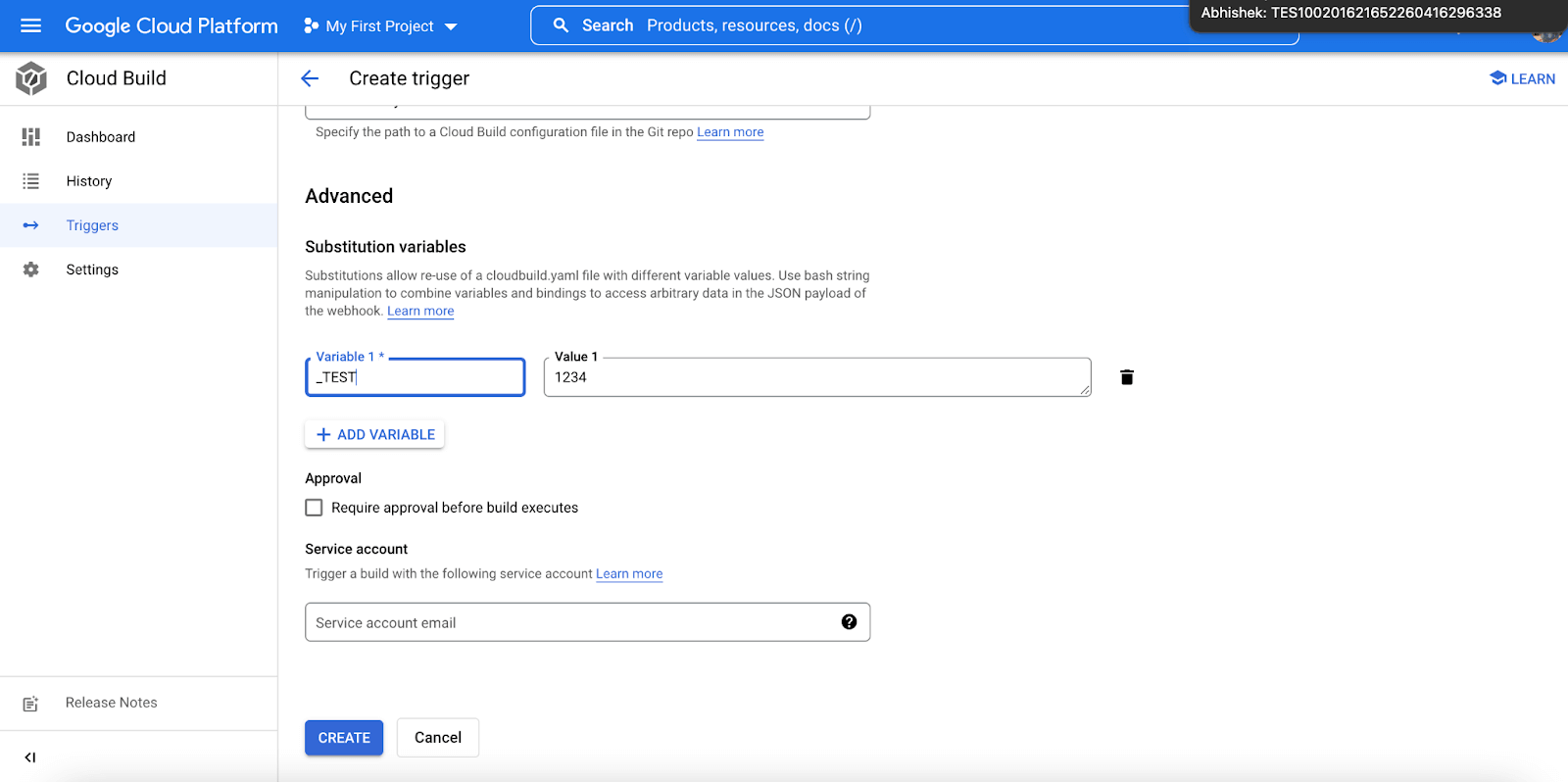
- In the ‘Advanced’ category, select ADD VARIABLE option. Enter your TestMu AI Access Token details as shown below.
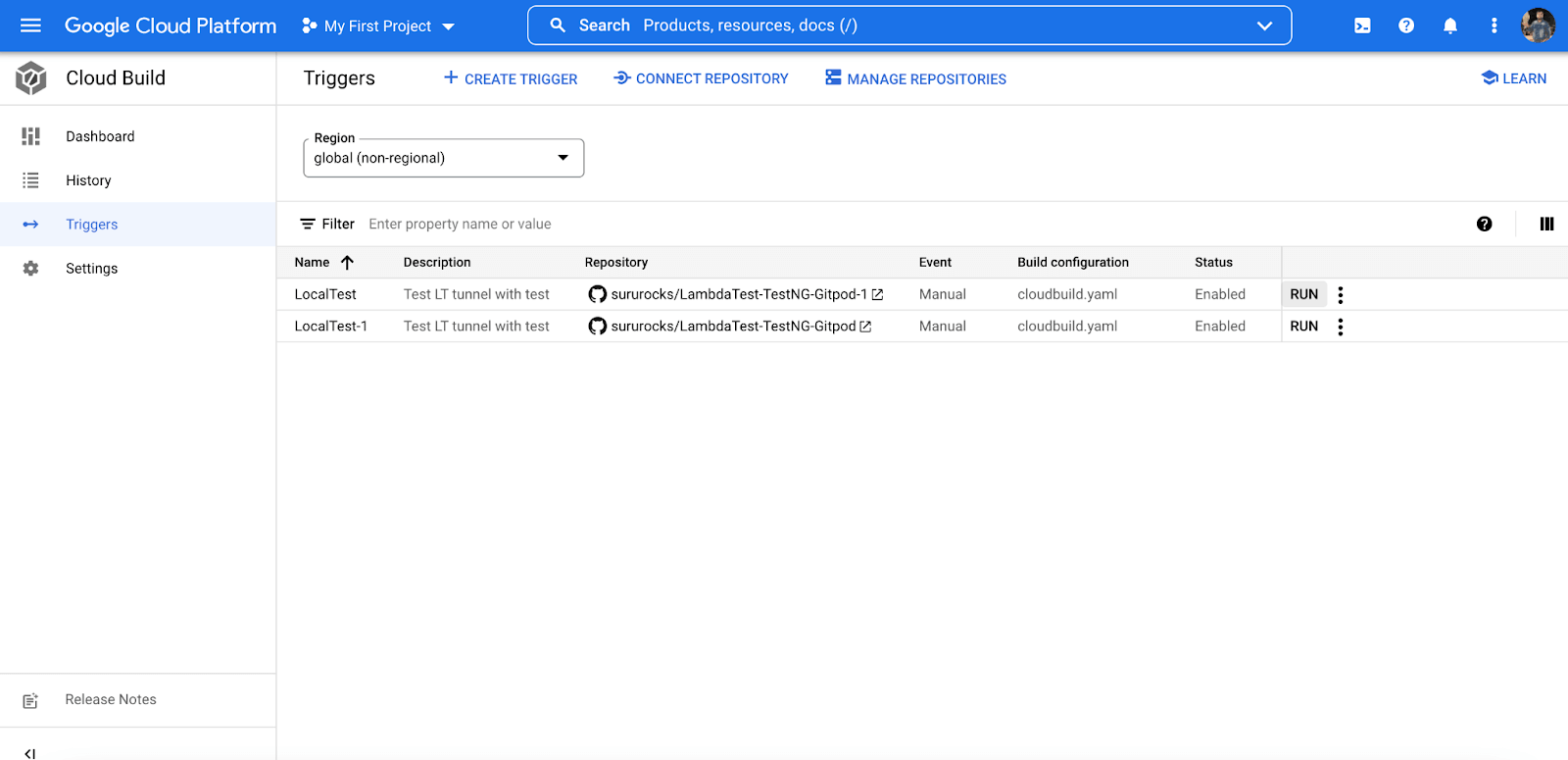
- Click on ‘CREATE’ option, and our trigger project will be created on the selected Google Cloud CI GitHub repository.
- To run a single test from the sample TestNG Selenium GitHub repository through Google Cloud CI, click on ‘RUN‘ as shown below.
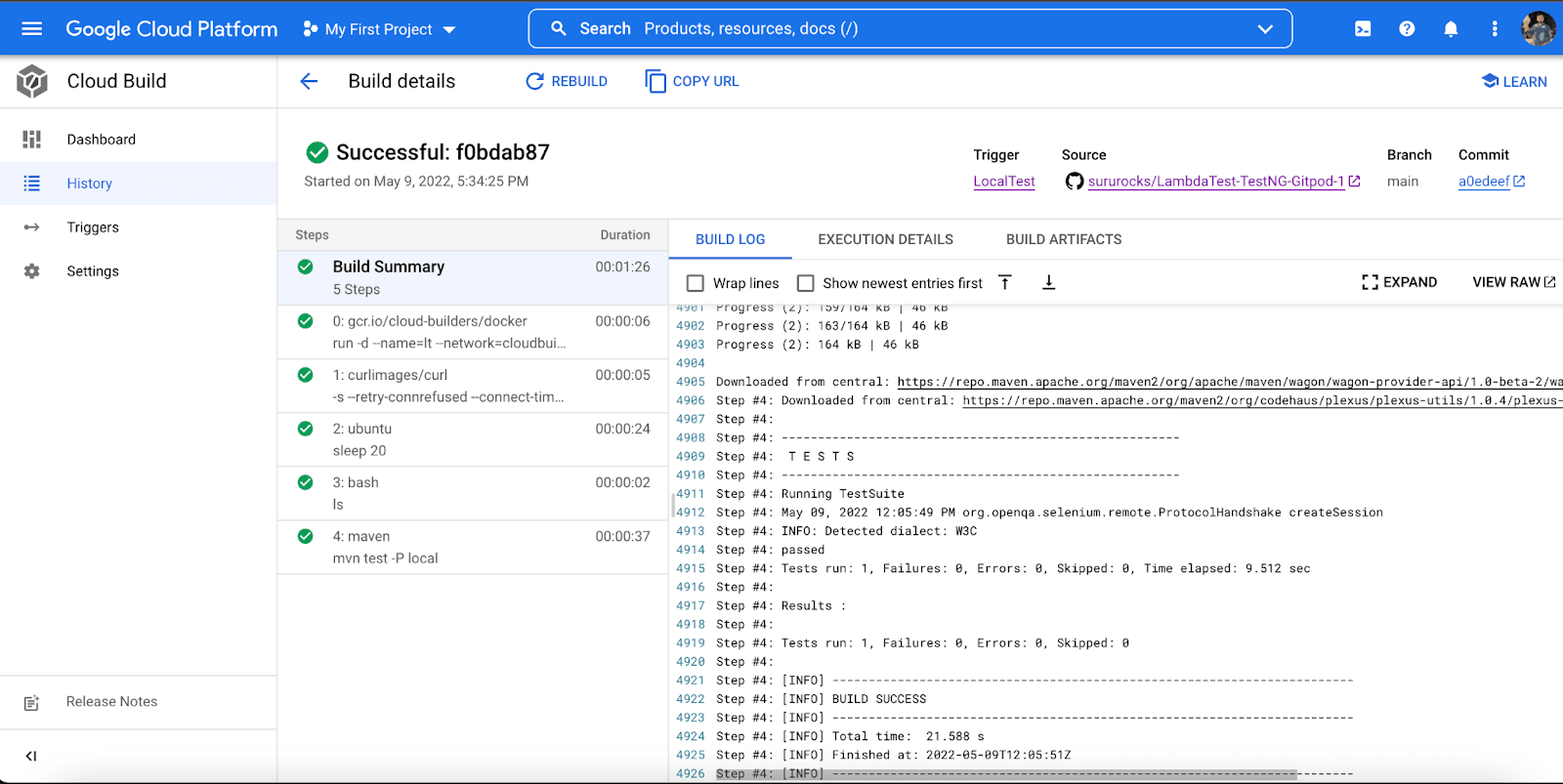
- The Google Cloud CI console shows the new build which has been triggered. The current status of this build will be ‘Running’ or ‘Successful’.
- The detailed insights of the test execution can also be found on TestMu AI Automation Dashboard.
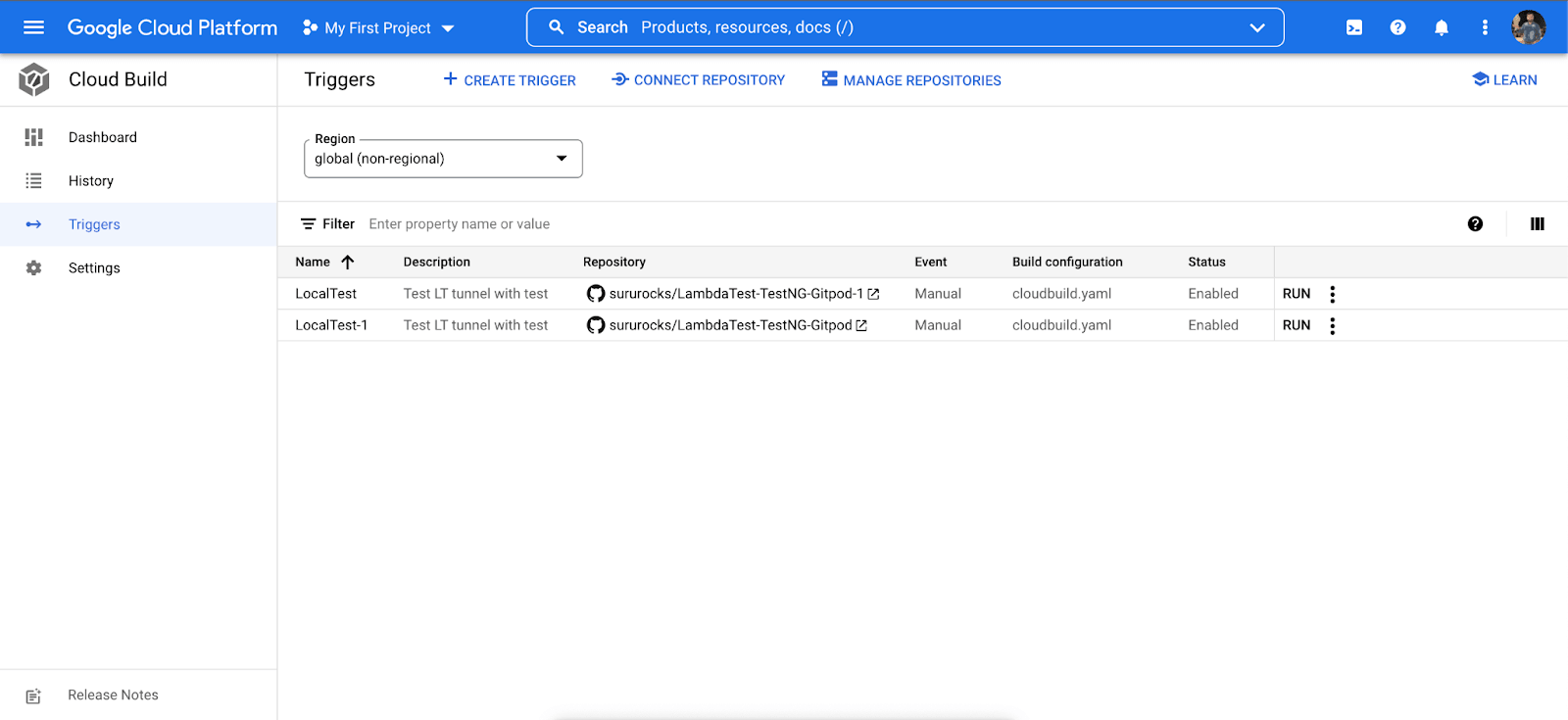
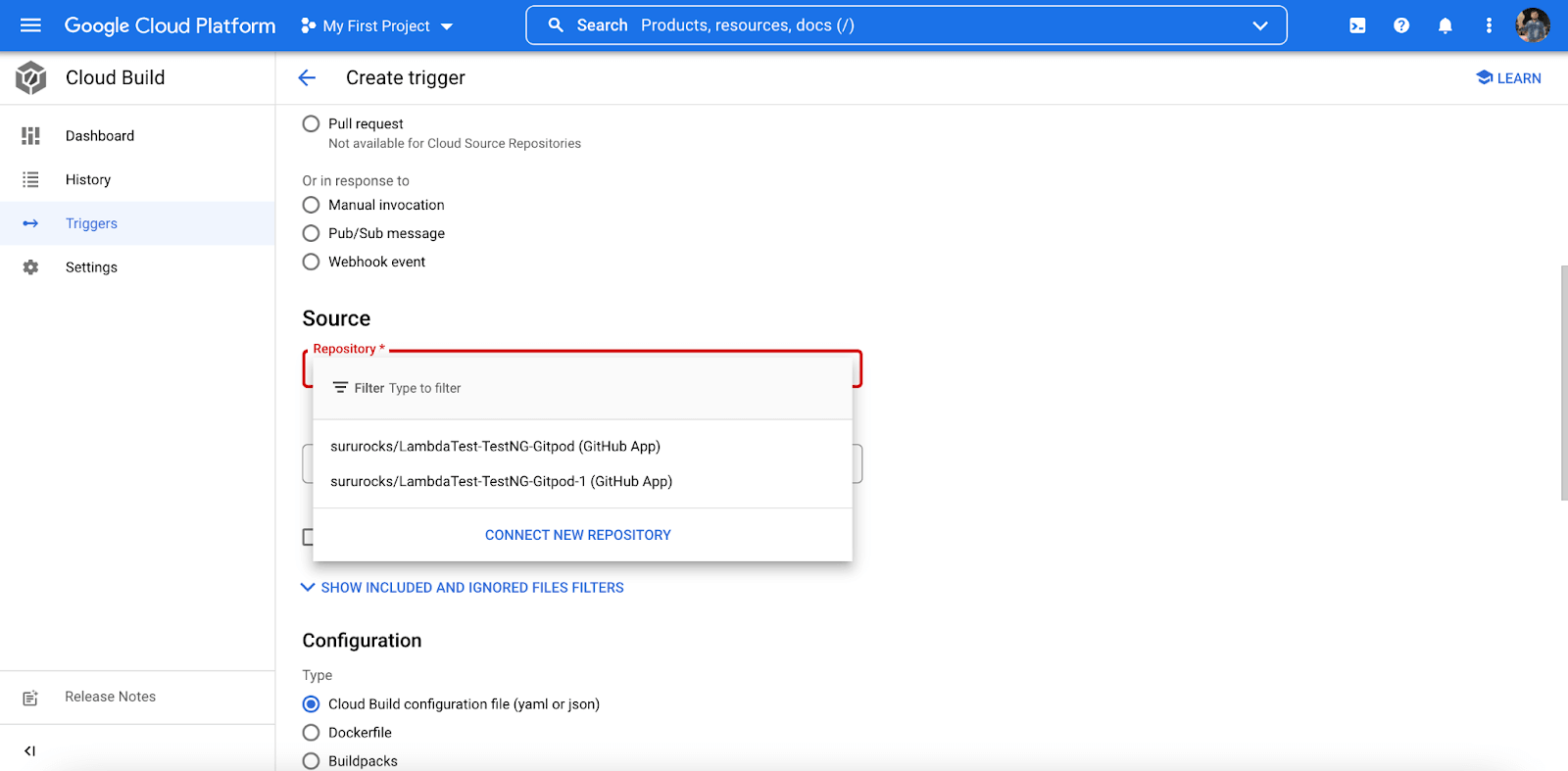
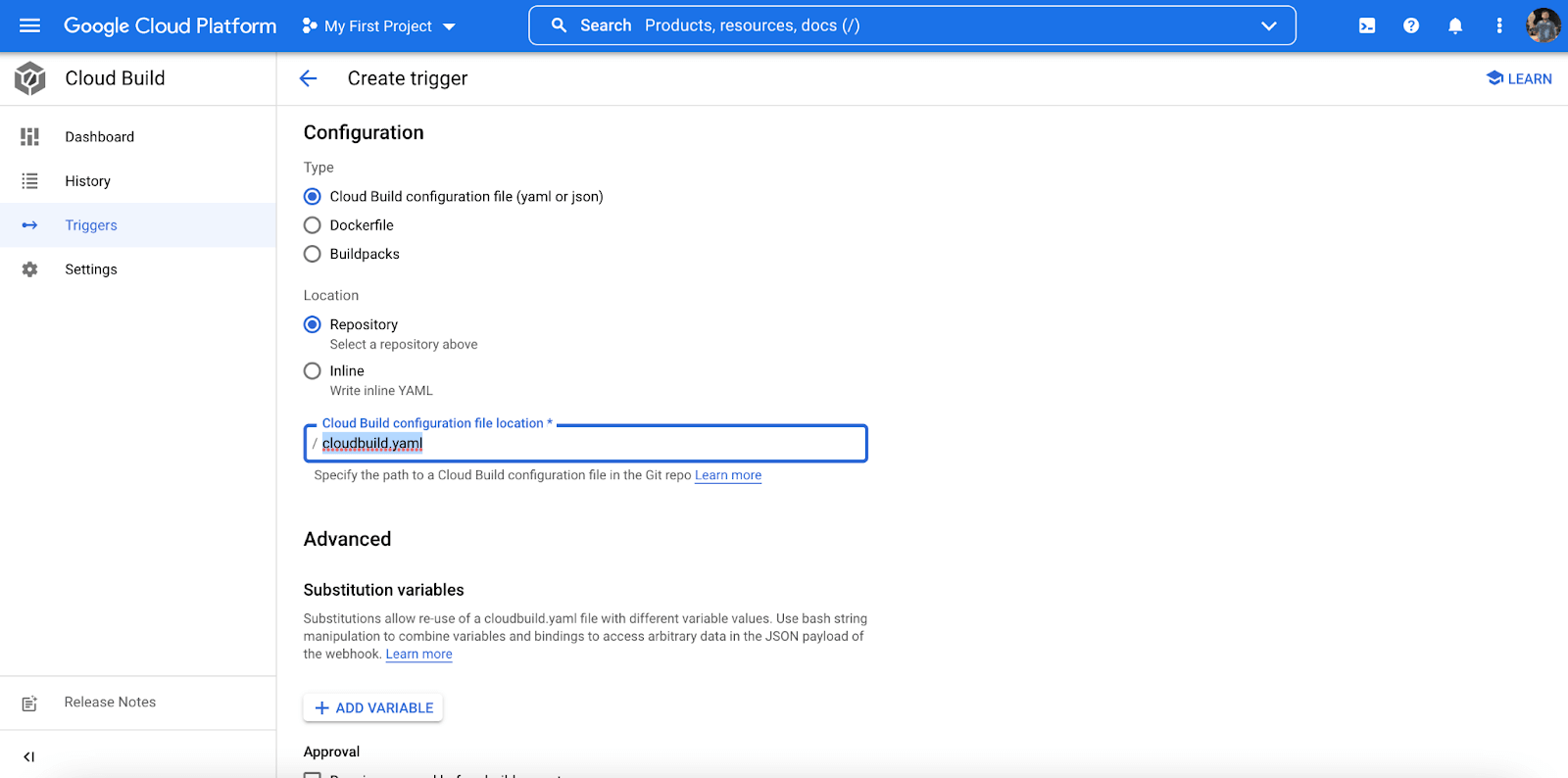
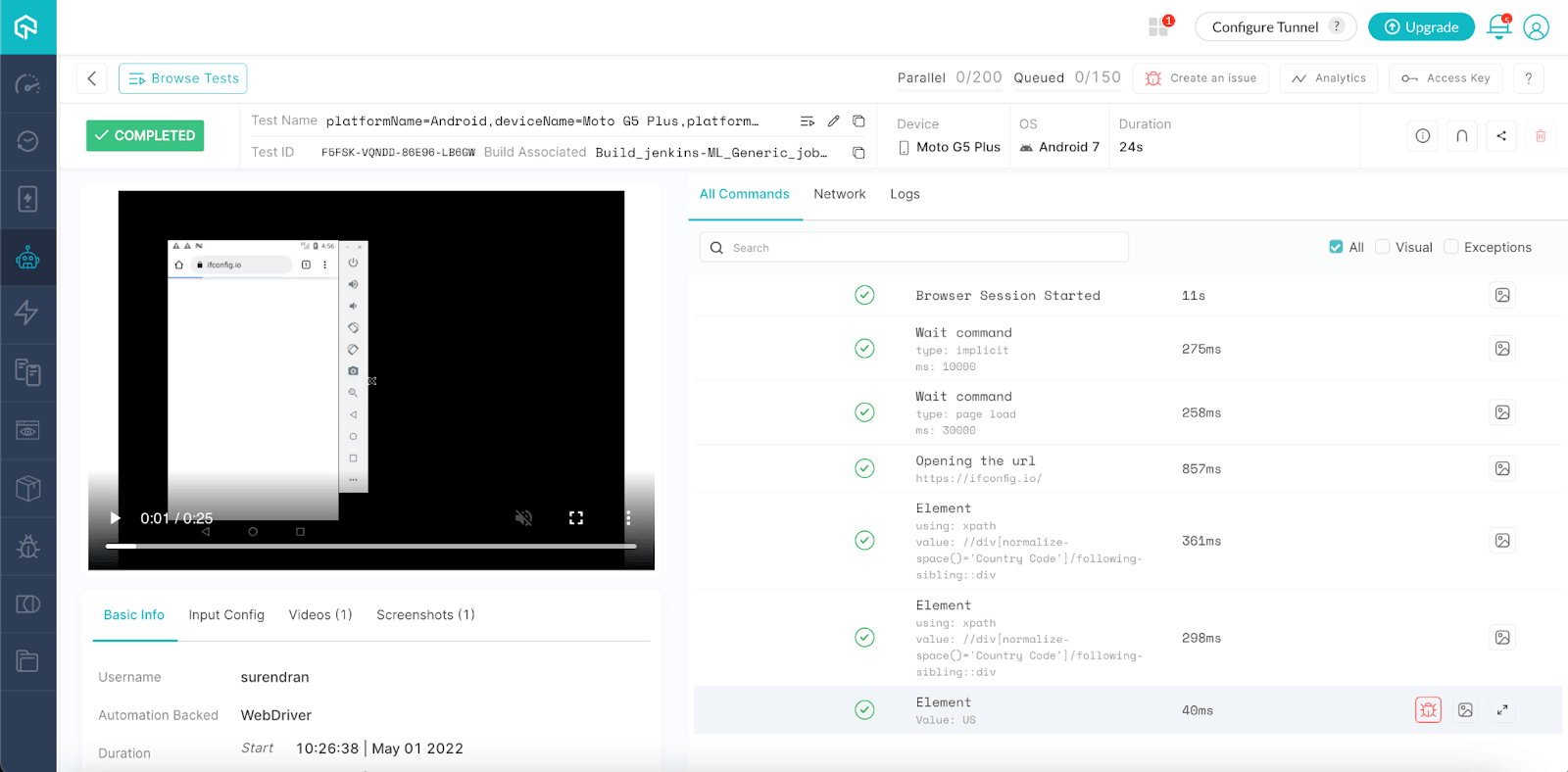
Running Parallel Test Via Google Cloud CI
Parallel testing is a process where you run the same tests simultaneously in different environments. The goal of this process is to resolve the limitations of time and budget while still assuring quality.
To run parallel tests on TestMu AI cloud via Google Cloud CI, we need to perform minor tweaks in the cloudbuild.yml file.
Add the following command mvn test -P parallel in the args of the YAML file to allow parallel testing.
Filename: cloudbuild.yaml
steps:
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
args: ['run' , '-d', '--name=lt', '--network=cloudbuild', 'lambdatest/tunnel', '--user', '${_LT_USERNAME}', '--key', '${_LT_ACCESS_KEY}', '--tunnelName', 'GCloud', '--infoAPIPort', '15000','--load-balanced']
- name: curlimages/curl
args: ['-s', '--retry-connrefused', '--connect-timeout', '5', '--max-time', '5', '--retry', '30', '--retry-delay', '2', '--retry-max-time', '60', 'http://lt:15000/api/v1.0/info']
- name: 'ubuntu'
args: ['sleep', '20']
- name: 'bash'
args: ['ls']
- name: 'maven'
entrypoint: 'mvn'
args: ['test', '-P', 'local', 'mvn test -P parallel']
env:
- 'LT_USERNAME=${_LT_USERNAME}'
- 'LT_ACCESS_KEY=${_LT_ACCESS_KEY}'
Rebuild and trigger the project again from the Google Cloud Build dashboard to execute the tests in parallel.
Running Local Test Via Google Cloud CI
Local testing is a perfect time saver when you are building and testing on the go. During development, you can run and test your container image locally before deploying. You can use Cloud Code or Docker installed locally to run and test locally, including running locally with access to Google Cloud services.
However, TestMu AI allows you to run your local tests via Google Cloud CI just with the help of a configuration file!
You can test your locally hosted pages and privately hosted pages at the TestMu AI Selenium test automation platform using the TestMu AI tunnel app. Interestingly, you can also run such parallel tests via Google Cloud CI.
To run your local tests on TestMu AI cloud via Google Cloud CI, we need to perform minor tweaks in the cloudbuild.yml file.
Add the following command mvn test -P local in the args of the YAML file to allow local testing.
Filename: cloudbuild.yaml
steps:
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
args: ['run' , '-d', '--name=lt', '--network=cloudbuild', 'lambdatest/tunnel', '--user', '${_LT_USERNAME}', '--key', '${_LT_ACCESS_KEY}', '--tunnelName', 'GCloud', '--infoAPIPort', '15000','--load-balanced']
- name: curlimages/curl
args: ['-s', '--retry-connrefused', '--connect-timeout', '5', '--max-time', '5', '--retry', '30', '--retry-delay', '2', '--retry-max-time', '60', 'http://lt:15000/api/v1.0/info']
- name: 'ubuntu'
args: ['sleep', '20']
- name: 'bash'
args: ['ls']
- name: 'maven'
entrypoint: 'mvn'
args: ['test', '-P', 'local', 'mvn test -P local']
env:
- 'LT_USERNAME=${_LT_USERNAME}'
- 'LT_ACCESS_KEY=${_LT_ACCESS_KEY}'
The below snapshot shows the local tests being executed.
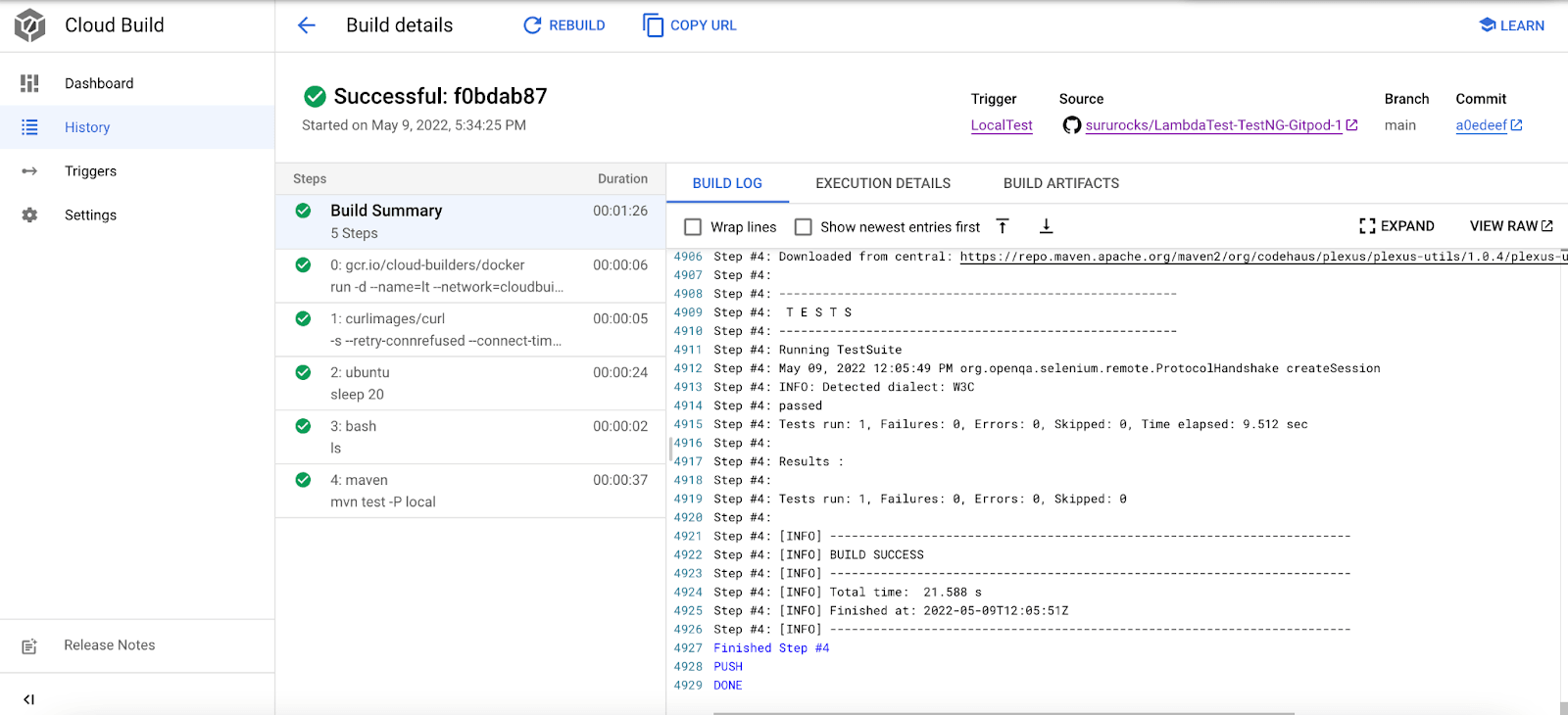
Conclusion
In this article on building a Google Cloud CI CD pipeline, we have learnt about the Google Cloud CI CD platform, its tools, and architecture in detail. We also learnt about a hands-on, step-by-step guide to running your Selenium tests on the TestMu AI platform via Google Cloud CI. Be it parallel testing or running your local tests, TestMu AI makes it super easy to run your flows via Google Cloud!
I hope you found this article useful. Please do share your feedback in the comments section.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



