
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

On This Page
- What is Equivalence Partitioning?
- Types of Equivalence Classes
- Step-by-Step Process of Equivalence Partitioning
- Equivalence Partitioning vs. Boundary Value Analysis
- Advantages of Equivalence Partitioning
- Limitations of Equivalence Partitioning
- Best Practices for Implementing EP
- Real-World Examples of EP
- Tools and Resources for EP
- Conclusion
Equivalence Partitioning in Software Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the power of Equivalence Partitioning and learn how this technique simplifies test case design, reduces redundancies, and enhances test coverage.

Poornima Pandey
January 11, 2026
Equivalence Partitioning (EP) can help in optimizing testing efforts and secureing software reliability. It allows testers to reduce test cases because it groups input data into equivalence classes that behave in a similar manner, ensuring full coverage with a lesser redundant software.
We’ll cover the basics of Equivalence Partitioning, its types, benefits, and best practices for implementation.
Overview
Equivalence Partitioning (EP) is a black-box testing technique that divides input data into equivalence classes, reducing the number of test cases while ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Key Features of Equivalence Partitioning
- Simplifies Test Case Design: Reduces redundancy by selecting representative values from each equivalence class.
- Improves Test Coverage: Ensures all relevant input scenarios are tested, even with fewer test cases.
- Enhances Defect Detection: Helps find potential issues faster by focusing on varied input conditions.
- Combines with Other Techniques: Works well with methods like Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) to enhance testing accuracy.
- Best Practices for Implementation: Involves clear steps like defining equivalence classes and leveraging automation for better efficiency.
Steps to Implement Equivalence Partitioning
- Identify input variables and understand their impact on the system.
- Define valid and invalid equivalence classes based on the input.
- Select representative test cases from each class to reduce test load.
- Execute tests and analyze the results to identify defects.
What Is Equivalence Partitioning?
A black-box testing technique, Equivalence Partitioning, divides input data into different groups or separate sets where similar behavior is expected.
Testers do not test each and every single possible input value, but instead select representative values. This is done from each equivalence class in order to verify the system’s behavior.
Key Points to Understand:
- Equivalence classes are divided into valid and invalid sets.
- Test cases are chosen from each class to reduce redundancy while maintaining effective coverage.
Types of Equivalence Classes
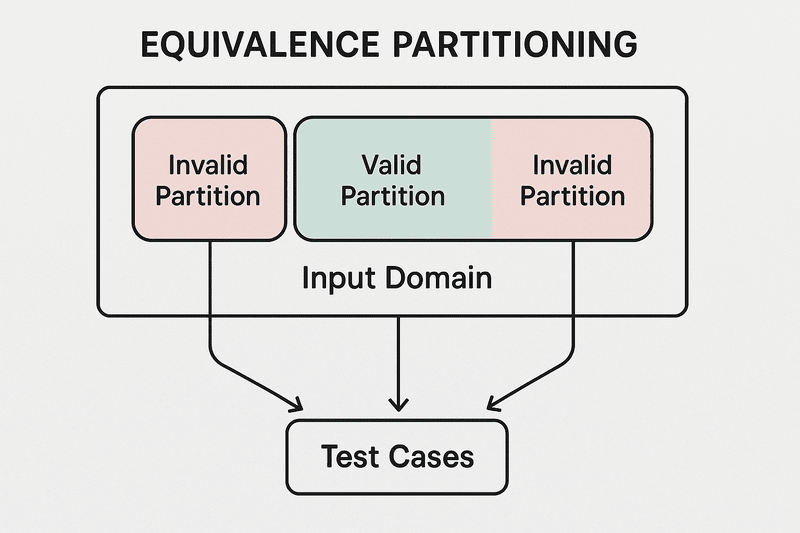
There are two primary types of equivalence classes:
Valid Equivalence Classes
- These are input sets for the system to process correctly and accept. For example, valid equivalence classes could be any integer from 18 to 60, as a form asks for an age. It should be an inclusive range.
Invalid Equivalence Classes
- The system will handle or reject all of these sets of inputs without any errors. Like 17 or even 61, examples do include ages greater than 60 or less than 18.
Example:
- For a login form requiring a username and password, valid classes might include correct usernames and passwords, while invalid classes might include empty fields or incorrect combinations.
Note: Capture automated Firefox screenshots across 3000+ real browsers and OS. Try TestMu AI Today!
Step-by-Step Process of Equivalence Partitioning
Implementing Equivalence Partitioning effectively involves the following steps:
- Identify Input Variables: Acknowledge that the system’s output surely will be affected by input variables, as well as input fields, so identify them first.
- Define Equivalence Classes: Then data must be categorized into valid and invalid classes, based on the input variables.
- Select Representative Test Cases: Pick typical values from each equivalence class to cut test case load.
- Create Test Cases: Develop test cases using the selected representative values from the equivalence classes.
- Execute and Analyze: Run the tests and analyze the results to identify defects.
Equivalence Partitioning vs. Boundary Value Analysis
Equivalence Partitioning focuses upon dividing input data into meaningful groups, whereas BVA targets the edges of these groups, as the defects often arise near the boundaries of input ranges, where BVA helps in revealing them.
Equivalence Partitioning
- Concentrates on the inputs that are anticipated to behave in a similar manner.
- Representative values from each class are selected, which facilitates the reduction of the number of test cases.
Boundary Value Analysis
- The focus here is on testing input data extremes that include upper, lower boundary values in the equivalence classes.
- Usually, this process is used along with Equivalence Partitioning to provide more thorough and in-depth testing while reducing the number of test cases altogether.
Let’s take at look at the following tabular comparison of Equivalence Partitioning & Boundary Value Analysis to understand them better:
Advantages of Equivalence Partitioning
The advantages of Equivalence Partitioning include:
- Reduced Test Cases: Testers are able to reduce the number of tests greatly just by selecting representative values out from each equivalence class while maintaining strong test coverage.
- Efficient Test Case Design: It simplifies the process of creating test cases via its focus on the classes needing testing. It does not focus on all possible values.
- Improved Defect Detection: EP finds possible defects faster because it focuses on many input situations.
- Enhanced Test Coverage: All relevant scenarios are tested, despite the fewer test cases than usual.
Limitations of Equivalence Partitioning
While Equivalence Partitioning is highly effective, it does have certain limitations:
- Assumption of Homogeneous Behavior: EP assumes that all inputs in a class will behave similarly, which may not always be true.
- Complex Input Scenarios: EP may not be as effective when inputs have interdependencies or when testing complex system behavior.
- Limited Focus: EP primarily focuses on input validation, which means output or system behavior might not be thoroughly tested.
Best Practices for Implementing Equivalence Partitioning
To get the most out of Equivalence Partitioning, follow these best practices:
- Thorough Requirement Analysis: Ensure you have a solid understanding of the system’s requirements to define accurate equivalence classes.
- Regular Review and Update: Equivalence classes should be updated as the system evolves, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Combine with Other Techniques: Combine Equivalence Partitioning with Boundary Value Analysis for broader test coverage.
- Leverage Automation: Use test automation tools to efficiently create and execute tests based on equivalence classes, reducing manual effort.
Real-World Examples of Equivalence Partitioning
Example 1 – Age ValidationFor an application that validates users’ ages:
- Valid Class: Ages between 18 and 60.
- Invalid Classes: Ages below 18 and above 60.
Test cases could include ages like 18, 30, 45, and 60 for valid input, and 17, 61 for invalid input.Example 2 – Login Form ValidationFor a login form:
- Valid Classes: Correct username and password.
- Invalid Classes: Empty fields, incorrect password, incorrect username.
Tools and Resources for Equivalence Partitioning
Many tools can assist in automating test case creation based on Equivalence Partitioning:
- Test Automation Tools: Tools like Selenium and Playwright can automate the process of creating and running tests.
- Training Resources: TestMu AI offers various resources to help testers better understand and implement Equivalence Partitioning.
- Community Forums: Platforms like Reddit are valuable for discussing challenges and best practices.
Conclusion
Equivalence Partitioning is a powerful technique that simplifies software testing, reduces test cases, and improves coverage. It is particularly valuable for black-box testing, where internal system logic is not available. By focusing on representative test cases, this method ensures that you are testing the most relevant scenarios with minimal effort. Whether you’re an experienced SDET or a beginner, incorporating Equivalence Partitioning into your testing strategy can help you optimize your test coverage and improve software quality.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



