
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

AI and Accessibility: Examples, Insights and Future
Explore the intersection of AI and accessibility, featuring key insights, practical examples, and future trends for a more inclusive digital landscape.
Harish Rajora
January 13, 2026
Access to information is essential for everyone, yet individuals with impairments often face significant challenges when navigating digital content such as websites, articles, and videos. This is where AI can play a transformative role in identifying and overcoming these accessibility challenges.
When AI and accessibility are combined, it can help identify issues related to screen readers, keyboard navigation, and color contrast more efficiently, ensuring compliance with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). This approach not only enhances the overall user experience but also drives inclusivity by making digital platforms more accessible to everyone.
Overview
Why Use AI in Accessibility?
AI is transforming accessibility by helping individuals with disabilities navigate digital content more efficiently. It aids in overcoming challenges like screen reader compatibility, color contrast, and keyboard navigation, ensuring compliance with accessibility standards such as WCAG.
- Enhanced User Experience: AI improves accessibility by offering solutions like automated captioning, image recognition, and personalized navigation.
- Detects Accessibility Issues: Identifies issues like missing alt text, poor contrast, and broken screen reader support.
- Seamless Integration: Combines with front-end development to ensure accessibility features are embedded directly into the digital experience.
- Faster Accessibility Checks: Provides real-time insights, speeding up testing and debugging.
- Inclusive Development: AI helps integrate accessibility elements automatically in the development process.
Key Examples of AI in Accessibility
AI plays a crucial role in various accessibility enhancements:
- Language Captioning & Translation: AI speech recognition and NLP provide automatic captions for videos, helping those with hearing impairments.
- Image Recognition: AI tools describe images, scenes, and objects, assisting individuals with visual impairments.
- Facial Recognition: AI algorithms provide real-time descriptions of people’s identities, emotions, and expressions.
- User Navigation: AI offers navigation support for individuals with mobility impairments, suggesting accessible routes and nearby facilities.
- Lip Reading: AI converts lip movements into text or audio, aiding those with hearing impairments.
- Summarizing Information: AI helps people with cognitive disabilities by summarizing long texts into digestible content.
How AI Enhances Accessibility Testing
AI-native testing platforms, like TestMu AI, assist in accessibility testing across browsers and devices. These tools help detect accessibility issues early in the development cycle and streamline the testing process:
- Manual Testing: Leverage tools like Chrome extensions and screen readers.
- Automated Testing: Use frameworks like Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress for automated accessibility checks.
Key Insights on AI and Accessibility
AI’s impact on accessibility has been mostly positive, but challenges remain:
- Positive Impact: Around 67% of people report AI advancements improving their lives, making them more independent.
- Trust Issues: Only 19% find existing AI solutions fully reliable, especially in image and speech recognition.
- Barriers to Use: Many users struggle with incompatible features, especially in screen readers.
- Community Engagement: 87% of users are willing to provide feedback to improve AI accessibility tools.
Current and Future Scenario
The current scenario shows a positive shift with AI’s involvement in accessibility testing, particularly through solutions like TestMu AI’s Accessibility Test Suite. The suite has evolved from supporting Android TalkBack to incorporating iOS VoiceOver and in-browser issue inspections. However, more work is needed for full integration.
- Enhancements: AI improves traditional accessibility solutions, such as screen readers, by enabling text extraction from images.
- Innovations: AI-driven solutions like the TestMu AI Accessibility MCP Server integrate real-time accessibility checks directly into the development process.
What Are AI and Accessibility?
AI and accessibility mean how compatible artificial intelligence-based solutions are when people with disabilities use them. Today, 16% of the population suffers from some kind of disability – WHO. With 1 out of every 6 people having difficulty using a software application, accessibility becomes an integral part of building the software using artificial intelligence (or even without it).
A simple example of this is developing a web page through Generative AI, either partially or completely. In such solutions, we can demand the code and expect AI to generate a code that contains accessibility elements in it as well.
For instance, consider the following example where a developer wants to insert an image in a web page and ask for help from ChatGPT.
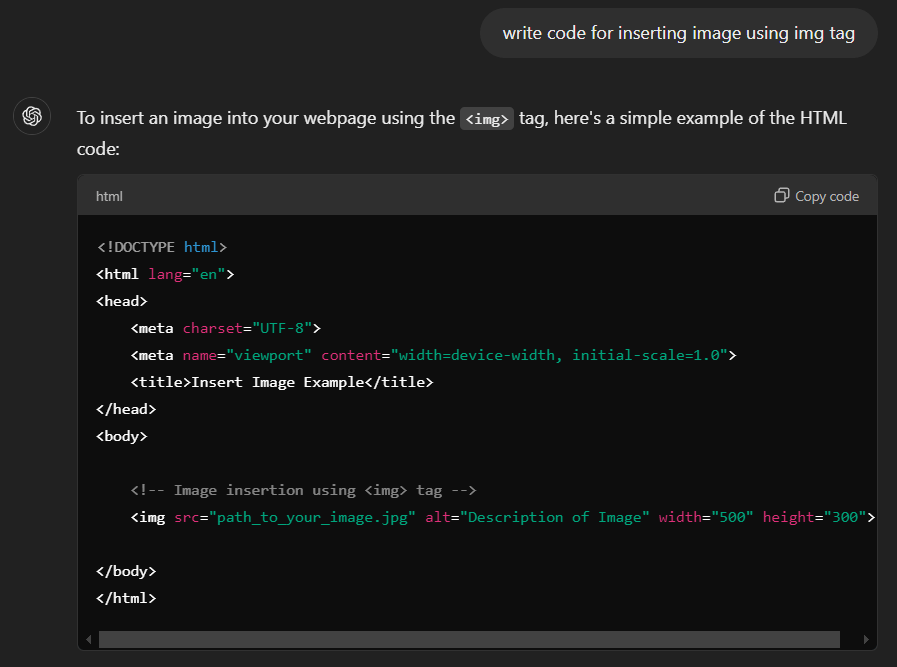
The code generated is correct, and can insert an image on the web page, too. However, notice that < img > tag comes with an alt attribute. This is an important attribute for visually challenged people as it helps describe the image context. It is one of the many examples of how AI and accessibility should go hand in hand.
Looking to make your website more accessible? Check out this blog on ways to ensure easier accessibility.
Examples of AI and Accessibility
The following are examples where AI is used to improve accessibility for impaired individuals:
- Language Captioning and Translation: AI speech recognition and natural language processing make captions for videos and transcriptions for audio. It helps people with hearing impairments access multimedia. AI translation tools also help people speak different languages, translating between spoken languages and Sign Languages. For example, the Hand Talk Plugin translates written text on websites from English to American Sign Language (ASL).
- Image Recognition: AI image recognition helps individuals with visual impairments understand their surroundings. These technologies describe objects, scenes, and text in images, allowing users to navigate more independently.
- Facial Recognition: AI facial recognition helps individuals with visual impairments recognize faces. It uses algorithms to give real-time audio descriptions of people’s identities, emotions, and expressions.
- User Navigation: AI improves navigation for individuals with mobility impairments by providing real-time guidance and suggesting accessible routes. AI navigation systems also offer information about nearby accessible facilities, helping individuals with disabilities navigate unfamiliar places more easily.
- Lip Reading: AI lip-reading technology converts visual input from lip movements into text or audio. It greatly assists individuals with hearing impairments, especially when Sign Language interpretation isn’t available.
- Summarizing Information: AI algorithms analyze and summarize large amounts of text. It makes it easier for individuals with cognitive disabilities or reading difficulties to understand complex information. It also helps those with limited time or attention spans quickly grasp key points from long documents.
In addition, performing accessibility testing of software applications ensures that digital content is usable by all people, including those with impairments. For this, developers and testers can leverage AI-native testing platforms like TestMu AI to perform accessibility testing across various browsers, devices, and OSes.
TestMu AI provides both manual and automated accessibility testing. For manual testing, you can leverage the Accessibility DevTools Chrome extension and screen readers. Next comes automated accessibility testing, which you can automate with frameworks such as Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress. To get started, refer to this guide on Accessibility Automation.
Also, our Accessibility Testing Suite was launched in April 2025 and recognized as Product of the Day, securing the top spot on Product Hunt.
Key Insights on AI and Accessibility
AI has the potential to enhance accessibility that can enhance the lives of individuals with disabilities. Here are some of the key insights by Fable that indicate promise and challenges with AI in this context:
- Positive Impact: Roughly 67% of respondents indicate recent AI advancements have positively affected lives, suggesting AI’s potential for greater independence and information access.
- Trust Issues: Merely 19% find existing AI solutions trustworthy. There raised issues regarding image and speech recognition accuracy hindering broader reliance on AI tools.
- Barriers to Use: Many face challenges with AI technologies. For instance, screen reader compatibility and customizable features are often lacking, making it hard for individuals to fully use advanced capabilities.
- Community Engagement: A notable 87% express willingness to provide feedback to AI developers, reflecting a desire for tools that genuinely address needs and enhance accessibility.
- Assistive Technologies: Existing tools like Seeing AI and Be My Eyes showcase how AI can assist individuals with visual impairments by interpreting visual information. Further investment in such technologies can expand capabilities and reach.
- Enhancing Communication: AI has the potential to improve communication for those who are deaf or hard of hearing. Innovations like real-time transcription and automatic captioning significantly enhance engagement and access to information.
Current Scenario of AI Compliance With Accessibility
The current scenario of AI compliance with accessibility can be measured broadly by observing two scenarios:
- Enhancement of Existing Solutions
- Innovations for Accessibility Using AI
Enhancement of Existing Solutions
Existing solutions that supported people with disabilities or were built with inclusive code in mind have seen meaningful improvements with the rise of artificial intelligence. One of the most impactful examples of this shift is seen in screen readers.
These tools have evolved over time, but their core functionality reading on-screen text aloud still depends heavily on how well the content is structured. For example, if text is embedded in an image without alt attributes, traditional screen readers can’t interpret it. Today, AI bridges that gap by enabling screen readers to extract text from images, recognize visual elements, and describe what’s on-screen even without predefined tags.
For instance at TestMu AI, this evolution is reflected in a fully enhanced Accessibility Test Suite. It began with support for Android TalkBack and has now expanded to include iOS VoiceOver, allowing teams to test across a broader range of native screen readers on real devices. But that’s just the start.
The suite now includes the Accessibility DevTools for in-browser issue inspection, automated accessibility testing, scheduled test runs, and comprehensive reports to help teams detect, track, and resolve issues faster. These enhancements bring AI and accessibility together in a powerful way making it easier than ever to build inclusive digital experiences right from development to deployment.
Innovations for Accessibility Using AI
If accessibility has seen good days in any area, it is the newer innovation and research taking place across wide domains. These researches bring new ideas into reality that use AI and accessibility blended and make the lives of people with disabilities much easier.
One such advancement is the TestMu AI Accessibility MCP Server, an AI-native solution designed to enhance accessibility testing across development environments. It brings AI and accessibility together by embedding real-time validations into the developer workflow. Whether it’s testing local React apps or apps routed through the TestMu AI tunnel, the server automatically detects and flags accessibility issues such as missing alt attributes, incorrect ARIA roles, or poor contrast ratios.
Using advanced AI models, it analyzes content structure and visual elements, offering intelligent remediation suggestions to ensure better compatibility and a more inclusive user experience and all this within your IDE.
Future of AI and Accessibility
The current situation of AI with a focus on accessibility is promising, especially with the entry of big tech giants into the picture. They have the capital to spend on solutions that might not even provide returns and maybe just serve society. This will not only encourage smaller businesses to innovate and develop but also provide researched technical help and modern tools developed by big techs to facilitate the development process.
Other than the development process, it’s also important to incorporate AI in the testing process to complement your accessibility efforts. This is where AI test agents such as KaneAI by TestMu AI can help you.
Lambdatest KaneAI is a GenAI native QA Agent-as-a-Service platform featuring industry-first capabilities, including test authoring, management, and debugging. Designed specifically for high-speed quality engineering teams, KaneAI enables developers and testers to effortlessly create and evolve complex test cases using natural language, significantly reducing the time and expertise required to start software testing.
As AI continues to shape the future of accessibility and testing, it’s vital for professionals to keep their skills current. The KaneAI Certification validates your hands-on expertise in AI testing, helping you stay ahead of the curve and contribute meaningfully to more inclusive digital experiences.
In addition, the future of AI and accessibility may also seem bright by looking at the steps taken by various agencies that work as regulators and provide compliance rules to be followed. For instance, the European Accessibility Act is the European standard requirements to be followed while working on accessibility solutions. This ensures that the solutions are compliant and also provides an estimation that things are progressing in a positive direction.
The last pillar on which the future depends is the people working towards developing these solutions. They are the individuals with their ideas that notice people with disabilities and the problems they are facing. For instance, people with speech problems are not able to communicate on the phone. Solutions such as RogerVoice help transcribe the call so that people can read and use AI to communicate further.
All three pillars of AI and accessibility are moving in a positive direction that gives us a good estimate about better days and technologies to come.
Conclusion
In this digital landscape, it is important to understand the current picture of AI and accessibility as a single unit blended to provide innovative solutions. The examples and current scenario described in this blog all point to the fact that the existing solutions are acceptable as a good foundational start. However, we still have a long way to go where accessibility and AI will not be defined as two terms but as a single unit altogether.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



