
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

How to Use Playwright Sharding to Improve Test Automation
Optimize Playwright sharding to run tests in parallel, cut execution time, boost CI/CD speed, and ensure reliable test results.
Vipul Gupta
January 11, 2026
Testers often face increasing execution times for automated tests, which slows feedback loops and reduces productivity. Playwright sharding helps address this by splitting the test suite into smaller shards and running them in parallel across multiple workers or machines.
Playwright sharding significantly reduces overall execution time without compromising test coverage or reliability. It is especially useful in CI pipelines, where faster feedback loops are critical, allowing teams to divide the load and complete testing much more quickly than running all tests on a single machine.
Overview
What Is Playwright Sharding?
Playwright sharding allows breaking down large test suites into smaller chunks that can run simultaneously across environments, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall test throughput. It’s particularly useful for distributed cloud testing and large-scale automation scenarios.
Advantages of Playwright Sharding
- Parallel Efficiency: Execute multiple shards at the same time without waiting for sequential runs.
- Consistent Environment: Each shard can run in a pre-configured isolated setup, avoiding interference.
- Flexible Scaling: Add or remove shards dynamically based on workload.
- Resource-Aware Execution: Automatically balances tests to use available CPU and memory effectively.
- Faster CI/CD Cycles: Shortens release times by delivering near real-time test feedback.
Step to Run Sharded Tests
- Define Shards: Use –shard=X/Y to partition your suite.
- Balance Test Load: Ensure even distribution of test-heavy files across shards.
- Assign Workers: Combine with –workers=N for maximum parallelism.
- Execute Shards: Run locally or on cloud grids for faster results.
- Aggregate Results: Merge outputs to get a unified report.
Example Snippet:
# Run Playwright tests in 2 shards with 3 workers each
npx playwright test --shard=1/2 --workers=3
npx playwright test --shard=2/2 --workers=3
Pro Tip
Use TestMu AI’s cloud grid to run Playwright tests in parallel shards, letting idle machines pick up tasks automatically for faster, more efficient execution.
What Is Playwright Sharding?
Playwright sharding is a built-in feature which is not available in custom runners. It is used to split the cases in a test suite into multiple smaller groups called shards that can be executed independently and, most importantly, in parallel. These shards may not be perfectly equal in size, as the distribution depends on how test files are organised inside your automation suite.
Test sharding works on a simple goal: reduce total test execution time by distributing the workload instead of running everything on a single worker.
In Playwright, sharding is supported natively through the –shard flag. This flag works at the test file level, which means it divides the files into shards and not the individual test cases inside each test file.
--shard=X/Y
Where:
- Y is the total number of shards into which the test files inside the suite are divided
- X is the specific shard to execute.
For example, –shard=2/4 tells Playwright to run tests in only the second out of four shards. This makes it easy to set up a distributed test execution environment.
Note: Run Playwright tests in parallel across 3000+ real browser and OS combinations. Try TestMu AI Now!
Advantages of Playwright Sharding
Having understood about test sharding, let us have a look at the benefits it offers. Understanding this is important as it will help you analyse and implement test sharding accordingly in your test automation framework.
- Faster Execution Times: By running shards in parallel across multiple machines, Playwright sharding significantly reduces overall test execution time, improving speed and productivity.
- Higher Reliability with Isolated Executions: Each shard runs in an isolated environment, reducing flakiness from shared resources. Isolation depends on the test runner or container setup and is not enforced by sharding.
- Scalable Test Pipelines: Sharding allows the framework to scale easily. As the test suite grows, more shards can be added without changing the framework design.
- Efficient Resource Usage: Tests are distributed across multiple machines, enabling the use of lower-cost setups while optimizing infrastructure and performance.
- Improved Feedback Loops: Faster pass/fail results help developers catch issues earlier and iterate quickly.
All these advantages of test sharding make it a clear winner when you are dealing with a large-scale Playwright testing project, where faster execution results can make or break things.
Setting Up Playwright Sharding Project
Before moving to the actual demonstration, let us first set up Playwright on the system.
Pre-requisites for Playwright
Before getting started with the Playwright project, you need to make sure that the following tools and technologies are present in the system:
- Node.js: Playwright is a Node.js library that needs Node.js to run the test automation scripts.
- Terminal or Shell Environment: Able to execute the commands for test execution.
- IDE and Project Directory: An IDE of your choice with a new project directory. For this blog, VS Code is used.
Playwright Project Setup
Once you have the pre-requisites in place follow the below steps to install Playwright project:
- Create a Project: Create a Playwright Project and name it playwright-node-sharding.
- Initialize Playwright: Launch terminal, move to the project directory, and run the following command:
npm init playwright@latest
This installs Playwright and its test runner, prompting you to choose options like language (JS/TS), browser support, and example tests.
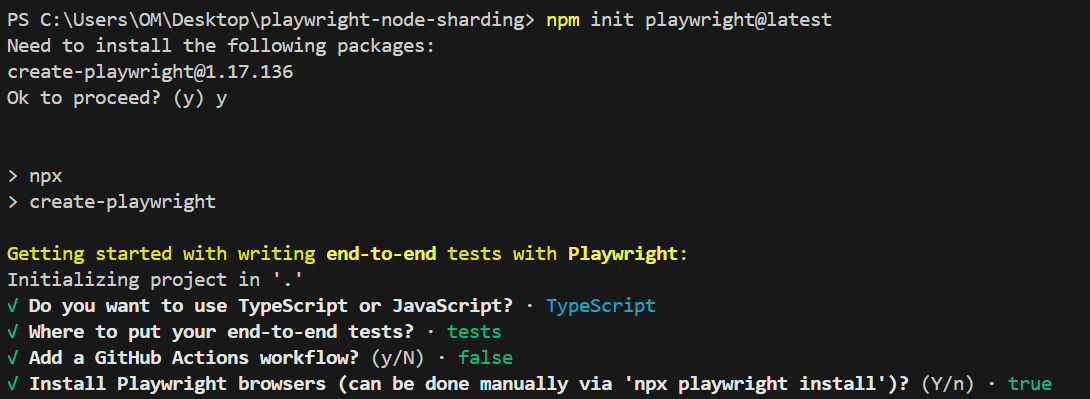
You will see logs like above in your terminal once Playwright installation is complete.
npm playwright test
npx playwright test --shard=1/2
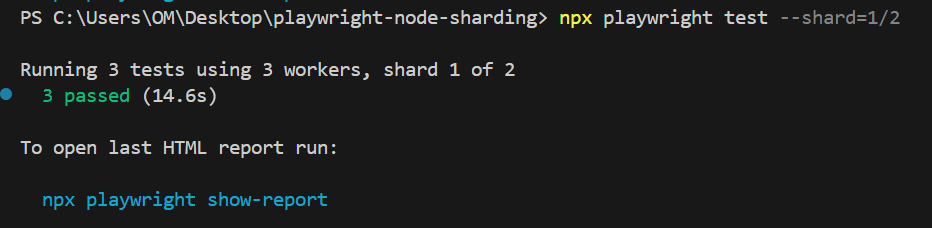
Executing shard 2
npx playwright test --shard=2/2
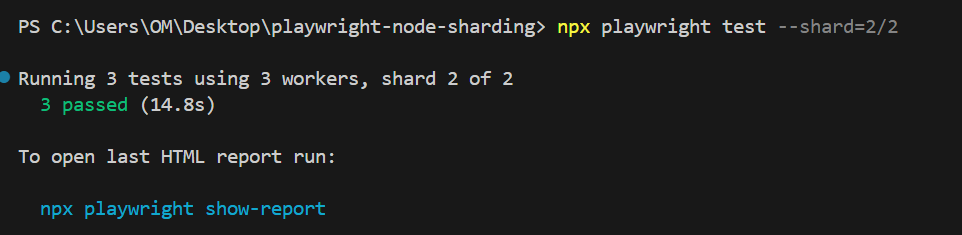
In the above sharded executions, each shard is by default executing using 3 workers, which means 3 parallel threads combining the power of sharding with parallel execution.
If you want to define the number of workers/threads for each shard, you can do so by adding the number of workers, like below, to the same command.
npx playwright test --shard=1/2 --workers=4
This completes the Playwright project setup and its verification on the system.
Now, you can run a demonstration by executing the test cases first using parallel execution and then with sharding, and observe how the execution becomes faster by comparing the execution times in both scenarios.
How to Use Playwright Sharding for Parallel Test Execution?
Having understood and done the basic Playwright setup by creating a project, now it is time to write your own small test cases and see how execution becomes faster using sharding.
In this demonstration, you will execute your Playwright cases on a cloud grid.
Running tests on the cloud gives you improved speed and scalability, making automation testing faster and more reliable with test sharding. It also lets you run multiple cases across different browsers and operating systems. One useful cloud testing platform is TestMu AI.
A GenAI-native test execution platform that allows you to perform Playwright automation for web applications on a wide range of over 3000+ real browsers and operating system combinations.
Let’s create a test file having 2 test cases for this demonstration.
Test Scenario
Test Case 1:
Test Case 2:
|
Before implementing the test files, take a look at the playwright.config.ts file, which will contain your TestMu AI configurations for cloud execution.
This config will help you run tests on the TestMu AI remote cloud and split them across 2 browser and OS combinations.
import { defineConfig } from '@playwright/test';
const buildName = 'Playwright Node Sharding';
const ltUsername = process.env.LT_USERNAME;
const ltAccessKey = process.env.LT_ACCESS_KEY;
export default defineConfig({
testDir: './tests',
reporter: 'html',
// ✅ Define two separate projects: Chrome on Windows and Firefox on macOS
projects: [
{
name: 'Chrome-Windows',
use: {
connectOptions: {
wsEndpoint: `wss://cdp.lambdatest.com/playwright?capabilities=${encodeURIComponent(
JSON.stringify({
browserName: 'Chrome',
browserVersion: 'latest',
'LT:Options': {
platform: 'Windows 10',
build: buildName,
name: 'Chrome on Windows',
user: ltUsername,
accessKey: ltAccessKey
}
})
)}`
}
}
},
{
name: 'Firefox-macOS',
use: {
connectOptions: {
wsEndpoint: `wss://cdp.lambdatest.com/playwright?capabilities=${encodeURIComponent(
JSON.stringify({
browserName: 'pw-firefox',
browserVersion: 'latest',
'LT:Options': {
platform: 'macOS Sonoma',
build: buildName,
name: 'Firefox on macOS',
user: ltUsername,
accessKey: ltAccessKey
}
})
)}`
}
}
}
]
});
Code Walkthrough:
- Import defineConfig: Import the defineConfig helper function of Playwright to define the test configurations for execution on various platforms and browsers.
- Set buildName: Create a constant buildName and assign a value to identify execution on the TestMu AI dashboard.
- Set Credentials: Set the Username and Access Key to connect with the TestMu AI cloud grid. Fetch these from the Account Settings> Password & Security section after creating your TestMu AI account and add them to environment variables.
- Add Configurations: Use the imported helper function to add configurations. The export and default keywords make it the default config that Playwright will use to execute test cases.
- Default Test Directory: Define the test directory where your test files are present. Update this if your test files are in a different location.
- Report Format: Specify the format of the execution report. In this case, an HTML report will be launched in the browser.
- Define Projects: Using projects, define multiple test execution environments with different browser and OS combinations. Each project represents a unique OS and browser combination and supports test sharding.
- Project Configurations: In this demonstration, two project configurations are used: Chrome on Windows and Firefox on macOS. Each can be identified using the name key.
- Dynamic Endpoint URL: Create a dynamic endpoint URL using the specified capabilities to connect to the TestMu AI cloud grid.
wsEndpoint: `wss://cdp.lambdatest.com/playwright?capabilities=${encodeURIComponent(JSON.stringify(capabilities))}`
const capabilities = [
{
browserName: "MicrosoftEdge",
browserVersion: "latest",
"LT:Options": {
platform: "Windows 11",
build: "Playwright Sample Build",
name: "Playwright Parallel & Sharding",
user: process.env.LT_USERNAME,
accessKey: process.env.LT_ACCESS_KEY,
network: true,
video: true,
console: true,
}
}
];
You can generate the above Playwright capabilities from the TestMu AI Automation Capabilities Generator.
Code Implementation:
Having understood the execution config, let’s understand the test file and the test cases before moving to execution.
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
test('Checkbox demo page loads', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('https://www.lambdatest.com/selenium-playground/');
await page.getByText('Checkbox Demo').click();
await expect(page.getByText('Single Checkbox Demo')).toBeVisible();
});
test('Checkbox checked on click', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('https://www.lambdatest.com/selenium-playground/');
await page.getByText('Checkbox Demo').click();
const checkbox = await page.locator("input[type='checkbox']");
await checkbox.nth(0).click();
await expect(page.getByText('Checked!')).toBeVisible();
});
Code Walkthrough:
- Add Test File: Add a new test file as checkbox.spec.ts and import required libraries.
- Add First Test Case: Add the first test case as the Checkbox demo page loads, and navigate to TestMu AI Selenium Playground.
- Click Checkbox Demo Link: Click on the Checkbox Demo link using the click() function.
- Assert Page Load: Assert that the new page is loaded by checking if the Single Checkbox Demo is visible on the page.
- Add Second Test Case: Add a new test case and perform similar actions to the previous one to reach the checkbox demo page.
- Locate Checkbox Element: Locate the checkbox element on the page using the type attribute and store the reference to a variable.
- Click Check the Box Using nth(): Using this element variable, click on the checkbox. Since the locator returns a list of all checkbox-type elements, use the nth() method to click on the first occurrence (0 index).
- Assert Checked Text: Once the click action is performed, assert that Checked! text is shown on the webpage using the toBeVisible() function.
Parallel Test Execution Result:First, execute the cases using Playwright’s default parallel execution, using the following command:
npx playwright test
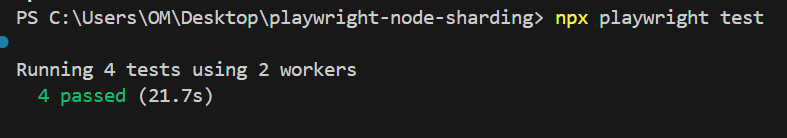
Total execution time without test sharding: 21.7 seconds.
Playwright Sharding Test Execution Result:Now, execute the same cases using 2 shards and notice the execution time using the following command:
npx playwright test --shard=1/2
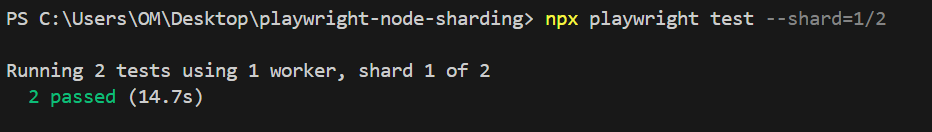
Total execution time with test sharding – shard 1: 14.7 seconds
npx playwright test --shard=2/2
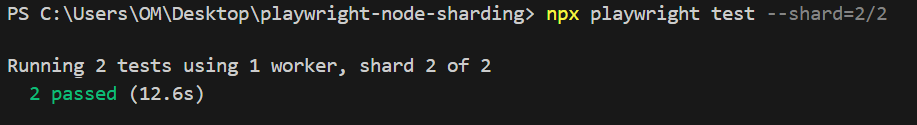
Total execution time with test sharding – shard 2: 12.6 seconds
Effective total execution time with test sharding: 14.7 seconds
(Since both shards run in parallel, we consider the longer of the two execution times as the total time.)
To get started, refer to the documentation on Playwright testing with TestMu AI.
This demonstration shows that when you execute the same test cases with identical configurations using test sharding, you save around 7 seconds. Even at this small scale, the improvement is noticeable.
You can also navigate to the TestMu AI dashboard and see the execution results. The results are available on Automation > Web Automation.
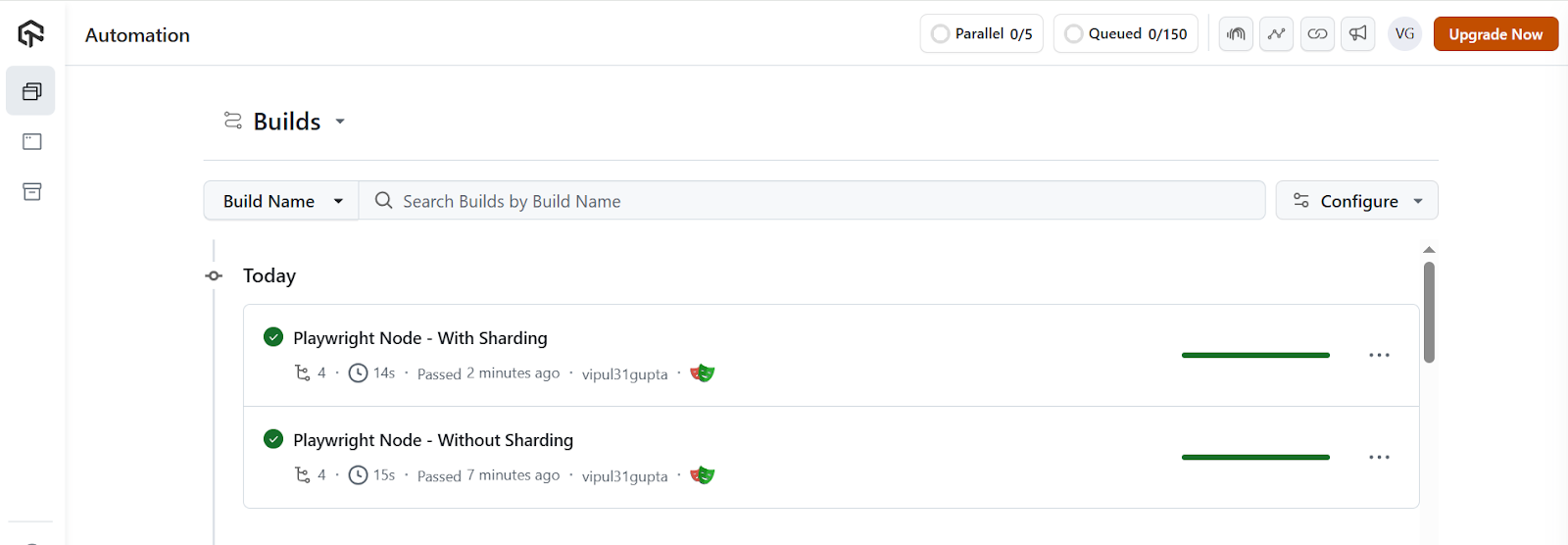
Difference Between Sharding and Parallel Execution in Playwright
It’s quite common to get confused about how sharding differs from parallel execution, because at a higher level, both help to speed up test execution by executing multiple tests in parallel.
In smaller automation suites with only a limited number of test cases, this difference is often not even visible, as the execution time looks almost the same regardless of whether sharding is used or not.
To understand the differences better, let’s examine the features and see how Playwright sharding and parallel execution differ from each other.
| Feature | Sharding | Parallel Execution |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Splits tests across multiple machines or workers, allowing distributed execution of the entire test suite. | Splits tests on a single machine, running multiple tests concurrently on available cores or threads. |
| Usage | Enabled using the –shard flag in Playwright Test. | Built into Playwright Test by default; controlled via the –workers flag. |
| Distribution Level | Operates at the entire test suite level, dividing test files into shards that can run on different machines or terminals. | Operates at the test file level within a single machine, running multiple files concurrently. |
| Implementation Strategy | Designed for scaling large test suites and CI pipelines by distributing tests across machines or environments. | Designed to optimize execution on a single machine by maximizing available CPU cores. |
| Resource Requirements | Requires multiple machines, terminals, or CI agents for full benefit. | Requires only a single machine with multiple cores. |
| Best Use Case | Large test suites, CI/CD pipelines, cloud execution, and scenarios where execution speed is critical. | Small to medium test suites, local development, or when only a single machine is available. |
| Fault Isolation | Each shard can run independently, which can help isolate failures. | Parallel tests share the same environment; failures can sometimes affect other tests if resources are shared. |
| Setup Complexity | Slightly more setup required (shards, CI configuration, environment variables). | Minimal setup, mostly automatic with Playwright Test. |
Sharding and parallel execution can be used together to improve performance. Multiple shards run concurrently, and within each shard, parallel execution uses multiple workers or threads. This combination speeds up execution and increases system productivity.
Troubleshooting Playwright Sharding
While working with Playwright sharding, you might encounter a few of the common problems that most of us face as first-time users.
Let us see what these top concerns could be and how we can address them.
- Challenge: One of the most common challenges with sharding is uneven execution times across shards. Here, sharding didn’t really speed things up, but some shards finished quickly while others took almost twice as long.
The root cause here is understanding how sharding actually works. Shards are divided at the test file level, not by individual test cases. So, if one file contains a heavy and more tests and another has a few, the shards will always be imbalanced.
How to fix: By keeping test cases distributed as evenly as possible across files. This way, when Playwright splits them into shards, each shard runs a similar number/type of test cases, and the overall execution time stays uniform across shards.
- Challenge: Another issue you might face is that every shard ends up running the full test suite instead of splitting the tests. This usually happens due to a misconfigured shard flag in the execution command.
If the shard values aren’t set correctly, Playwright has no way of knowing which shard should handle which portion of the suite.
npx playwright test --shard=1/2
npx playwright test --shard=2/2
How to fix: Double-check that the syntax is correct and that each shard index is unique, and that the index values fall within the total shard count (e.g., 1/2, 2/2 for two shards). A small typo here can easily cause all shards to execute the same set of tests.
In most cases, this happens because the required credentials are incorrect or you don’t have access to that particular utility.
How to fix: Always confirm that your cloud credentials (e.g., LT_USERNAME and LT_ACCESS_KEY for TestMu AI) are set correctly in your environment variables or config file. Also, verify that you have the necessary permissions for the utility that is being configured for this execution.
If the underlying machine doesn’t have enough resources, tests start failing inconsistently, making the results flaky.
How to fix: Be aware of the limits and configurations of your execution infrastructure and try to limit the number of workers per shard or the total number of shards accordingly. Alternatively, you can upgrade the machine or switch to a larger machine that can handle the additional parallel load as required.
Remember, more shards and workers do not necessarily mean faster execution and results. Stable execution setu,p even with fewer shards/worker,s is more reliable as it saves flakiness and retires.
Best Practices for Playwright Test Sharding
Implementing Playwright sharding is very easy, but one must follow a few best practices while working with sharding. This helps to ensure that the test automation execution always remains fast, consistent, and reliable, irrespective of how many new tests get added as the project scales.
- Smart Testcase Grouping in Test Files: Playwright implements sharding at the test file level. So, for the best results, avoid having too many test cases in a single test file. Instead, group related test cases smartly in test files, keeping the number and execution time balanced for efficient sharding.
- Avoid Dependent Tests: As sharding runs test files in isolation, make sure all the tests are independent and idempotent. This helps to reduce flaky tests. To achieve this, make sure no tests share state and all mocks and databases are reset before test execution as needed.
- No Test Ordering or Sequence: In sharding, each shard picks its set of cases and starts execution without any ordering. So, don’t implement any kind of test dependencies that need a test or cases to be executed in a particular order/sequence. Having such tests also impacts execution time as it limits parallel execution.
- Balanced Execution Time per Shard: The number of Shards is based on the test file count and not the test duration. So, we should constantly analyse the execution reports to determine which shard execution takes more time. Any such shard having files with longer execution duration should have the files split for better results and parallelism.
- Clear Logging of Shard: When working with many shards, it becomes important to have clear logs in reports about which shard is executing. This makes debugging easier and also helps to review failures or execution trends across shards.
Conclusion
Playwright sharding can dramatically reduce execution time and improve feedback loops by splitting test files into parallel shards. You’ve seen how it differs from parallel execution, how to set it up locally or on a cloud grid, and how effective it is through a practical demonstration.
By following best practices, balancing test files, avoiding dependencies, and monitoring shard execution, you can ensure faster, reliable, and scalable test automation. Implement Playwright sharding in your projects to optimize execution and accelerate your CI/CD pipelines.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests


