
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

How To Setup And Install PhantomJS In Python: All You Need To Know
Learn how to set up and install PhantomJS in Python effortlessly. This guide provides the essentials you need to know for integrating PhantomJS in Python.

Jainish Patel
January 11, 2026
Running automation scripts on a normal browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge Browser takes too many resources and time as they run test scripts that include all the UI/UX of the website, such as animations and visual effects. So the concept of Headless browsers is introduced. Headless browsers are web browsers that can operate without a graphical user interface (GUI), allowing developers to automate tasks like web scraping and testing. They interact with websites programmatically, processing HTML and executing JavaScript instead of rendering web pages visually. PhantomJS was one of the earliest and simplest headless browsers, offering a JavaScript API for browser manipulation. However, alternatives like Puppeteer (for Node.js) and Selenium WebDriver have gained more traction in recent years.
In this article, we will cover various aspects of PhantomJS, starting from How to install PhantomJS, practical examples, advantages and disadvantages, and running test scripts with it. At last, we will see a test time execution comparison with PhantomJS and other browsers.
What is a Headless Browser?
A web browser that doesn’t use a Graphical User Interface (GUI) is known as a headless browser. An interface for a headless browser differs from that of a standard browser, such as Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, or Safari, in that it interacts with websites programmatically rather than rendering the content on a visible window. Testers and Developers can use scripts or code to control it, which enables them to automate a variety of web-related tasks like website monitoring, web scraping, and automated testing. PhantomJS, Headless Chrome, and Firefox are a few examples of popular headless browsers.
Several use cases in web development and testing necessitate headless browsers. Web scraping, the process of taking data from websites for analysis or commercial gain, is a major contributing factor. Large-scale scraping tasks can benefit from headless browsers since they offer a quicker and more effective method of retrieving data programmatically without requiring a visible browser window. Furthermore, automated testing is done with headless browsers to verify the functioning and speed of websites. Testers and Developers can save time and resources by conducting tests in a headless environment while guaranteeing the application operates successfully in various scenarios by executing scripts in headless mode.
Headless browsers are an invaluable tool for web developers and testers because they provide a solid and adaptable interface for programmatic interaction with web content.
Note: Automate your tests on a Selenium based cloud Grid of 3000+ real browsers. Try TestMu AI Today!
What is PhantomJS?
A headless browser called PhantomJS enables programmers to automate interactions with online pages and carry out operations like web scraping, automated testing, and website performance analysis. The WebKit rendering engine, also utilized by Safari browsers, serves as its foundation.
PhantomJS is suitable for server-side operations and automation activities since it runs in a headless mode or without a graphical user interface(GUI). It offers a JavaScript API that enables programmers to control the content of web pages and script browser behaviors.
The capability of PhantomJS to process and render web pages with JavaScript is one of its core capabilities. It has a JavaScript engine integrated within it that can run and parse JavaScript code, making it helpful for scraping dynamically created content or interacting with JavaScript-heavy websites.
It provides a range of features, such as network monitoring, screenshot taking, DOM modification, web page navigation, and form submission. It enables programmed data extraction from web pages and simulation of user interactions.
It’s crucial to remember that PhantomJS development has been halted since the 5th of August 2017; therefore, it might not be the option for a headless browser that is being maintained or updated the most. Because of that, Selenium 3.8.1 also deprecated PhantomJS from its support and recommends using Chrome and Firefox in headless mode.

Integration of PhantomJS in Python
The Selenium WebDriver enables smooth integration of PhantomJS in Python. A popular automation system called Selenium offers a Python API for managing web browsers. You can use PhantomJS’s capability for a variety of tasks by combining Selenium and PhantomJS.

The significance of utilizing PhantomJS in Python for activities like website testing, data extraction, and screenshot generation is due to its headless nature and features like network monitoring and JavaScript support:
- Website testing: Automated website testing is possible with PhantomJS without a visible browser window. It can mimic user interactions, evaluate UI components, test functionality, and record test results.
- Data extraction: Web scraping and data extraction are effective when Python, Selenium, and PhantomJS are used together. It can manage web pages with a lot of JavaScript, dynamically generated content, and intricate DOM structures. Web page navigation, element extraction, and data retrieval are all possible for developers.
- Creating screenshots: PhantomJS can display online pages and take screenshots, making it possible to conduct visual tests, create website thumbnails, or take pictures when web scraping. This can be helpful for visual documentation creation, preview creation, and website appearance monitoring.
You can automate web browser interactions, conduct effective testing, retrieve data from websites, and create screenshots headlessly by utilizing the combination of PhantomJS in Python through Selenium.
How to install PhantomJS in Python
In this section, we will see the installation process in detail, from setting up Python to PhantomJS WebDriver and Selenium. With that, we will verify it by running a simple script and scraping the website title on which the script runs.
Installation and Environment Setup
The process is quite simple if it follows the chronology. To install PhantomJS in Python, we will see it in a detailed manner, starting from installing Python -> PhantomJS -> Selenium.
Installation and Environment Setup
To install Python on your computer, you need to follow these steps:
- Visit the Python official website.
- Python provides installers for various platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. It will be selected according to your system automatically on which you are opening the above site.
- Download the latest version of Python, it can easily be downloaded by the Download Python 3.x.x button.
- Run the installer file once it has been downloaded to begin the installation procedure.
- Make sure you click the box on the installation wizard that states Add Python to PATH or Add Python to environment variables (the words vary depending on the version). This makes sure that Python is accessible from anywhere on your machine.
- You can change the directory according to your preferences.
- Click Install to begin the process of installation.
- Hold off until the installation is finished. The installer will configure Python on your machine and copy the required files.
- You should get a notification indicating a successful installation once the installation is complete.
- Open a command prompt or terminal and enter the following command:
python --version
Console Output:
If the above command runs fine, Python is installed successfully. Now that Python is installed successfully let’s install PhantomJS.
Installing PhantomJS and setup
- From the official website, get the PhantomJS binary that matches your operating system.
- Extract the downloaded archive into the desired location.
- You can find the phantomjs.exe file in the bin folder of the extracted folder.
- Add the location of the phantomjs.exe file to the Environment Variables.

You are just one step away before using it. To do that, Selenium WebDriver is needed, a part of the Selenium module. So let’s download Selenium.
Installing Selenium for Python
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Install the Selenium package for Python using the pip Python package manager.
Run the following command:
pip install selenium==3.8.0
Console Output:
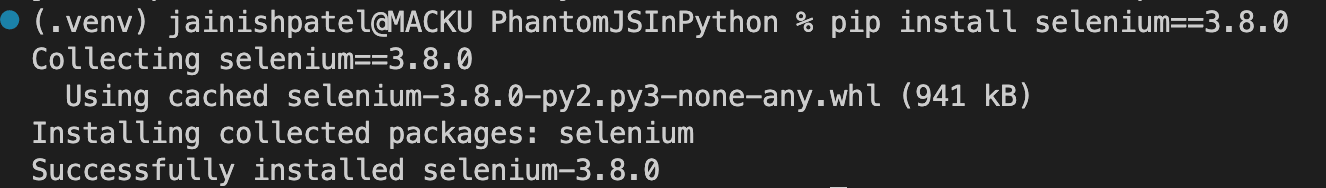
Note: From Selenium 3.8.1 PhantomJS is deprecated. So, to use the PhantomJS it is recommended to use Selenium 3.8.0 or lower version. You can also refer to the changelog for more information.
Verifying using a simple Python script with PhantomJS
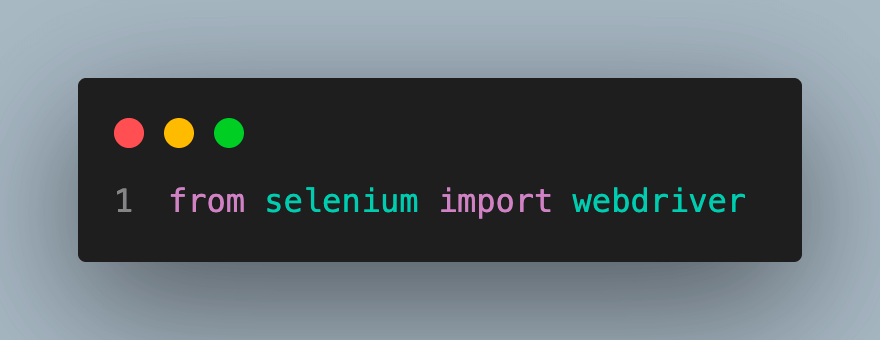
Here is a little piece of code that shows how to initialize the PhantomJS WebDriver and carry out fundamental operations:
from selenium import webdriver
# Initialize the PhantomJS WebDriver
driver = webdriver.PhantomJS()
driver.set_window_size(1120, 550)
# Navigate to a web page
driver.get('https://www.google.com')
# Get the page title
print("Page title:", driver.title)
# Take a screenshot of the page
driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')
# Close the WebDriver
driver.quit()

Let’s understand the code Step-by-Step:
- Import statement to get the webdriver from the selenium module.
- There are 2 ways to use PhantomJS. You can use it according to your requirements. But, we are using the first way as we already added the Driver to the system’s environment Variables.

As we are using a headless browser just to confirm that the website is opening this line, we will take the screenshot and store it in the same location where the Python file is.
Output Screenshot:
Practical Examples of PhantomJS
With the help of the headless web browser PhantomJS, you can automate testing and carry out numerous web scraping operations. It has a JavaScript API that enables you to manage websites, control the browser, and take screenshots. In this section, we are going to have a glance at both of them.
Automation Testing
In automation testing, there are various advantages to using a headless browser like PhantomJS. Without a visual interface, it mimics actual browser behavior, accelerating test performance. It makes it easier to test complicated applications across platforms because it can render and interact with web pages just like a regular browser. Because of its command-line interface and lightweight design to efficiently minimize resource usage and improve performance, testing frameworks may be quickly integrated, resulting in scalable and reliable automation.
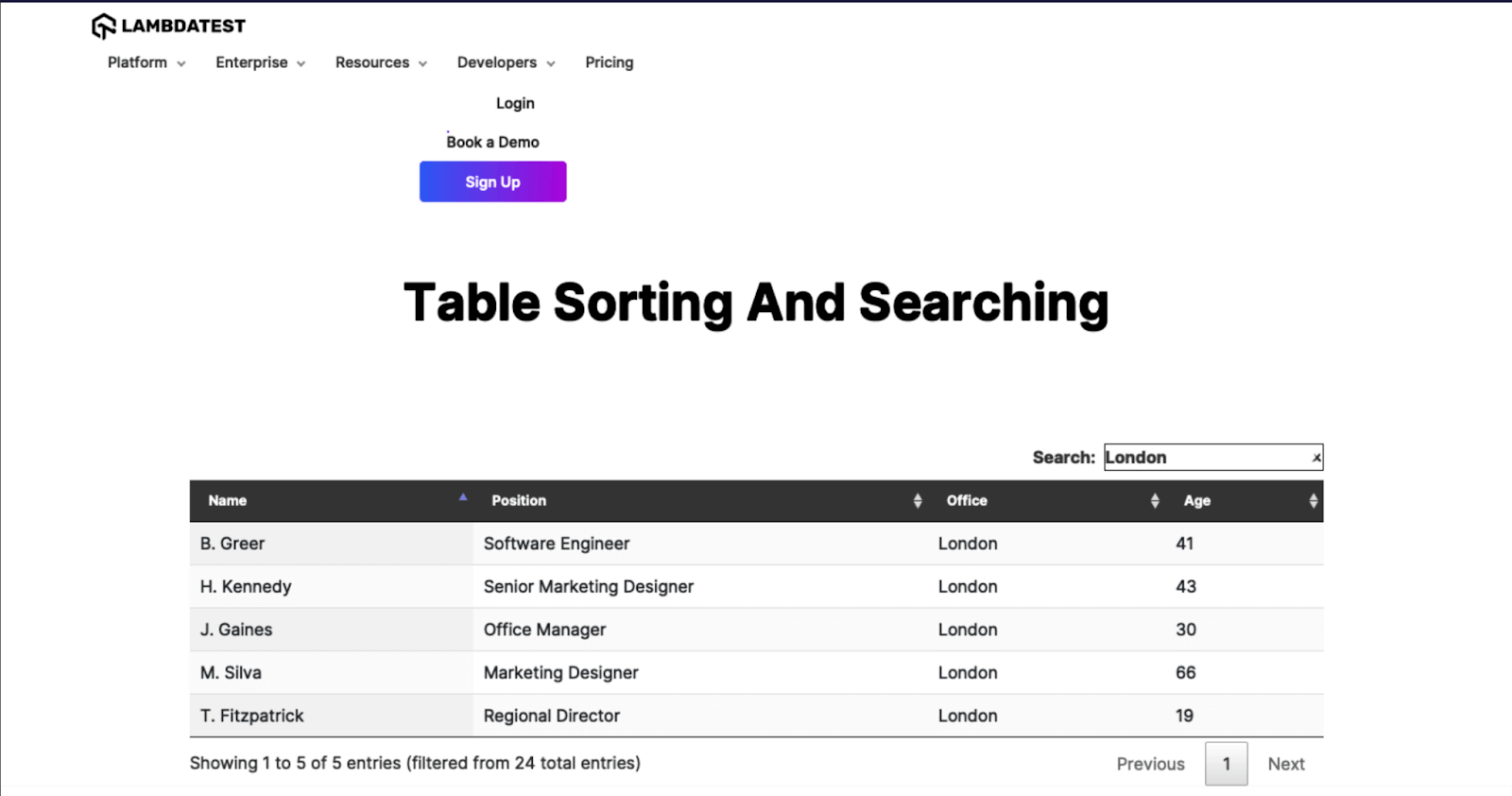
You can use frameworks like Selenium WebDriver to create Python and PhantomJS test cases. In the example, we will search for a query and get the resultant output by printing it in the terminal and taking a screenshot.
Here is an illustration of how to create a test case in Python and PhantomJS:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
# Configure the PhantomJS WebDriver
driver = webdriver.PhantomJS()
# Navigate to a web page
driver.get('https://www.lambdatest.com/selenium-playground/table-sort-search-demo')
driver.set_window_size(1440, 550)
# Getting the search bar
search_bar = driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//*[@id="example_filter"]/label/input')
search_bar.send_keys("London")
# Getting row of the table
rows = driver.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME,"tr")
# Capturing the screenshot of the window
driver.save_screenshot('table_data.png')
# Printing the rows
for row in rows:
data = row.text
print(data)
driver.quit()
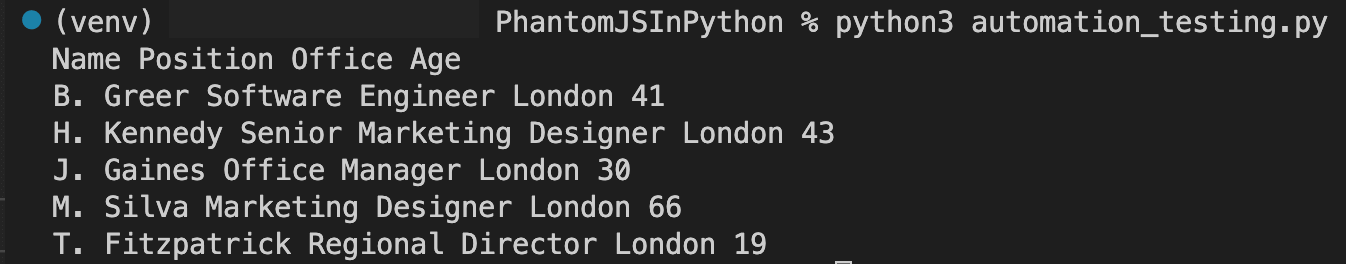
Screenshot of the result:
Web Scraping
PhantomJS in Python for web scraping has several advantages, including enhanced resource management and faster execution. It can extract data more quickly as it doesn’t need to visually render web pages because it runs in a headless context. Additionally, it enables better resource management because it uses fewer system resources than a full browser with a GUI.
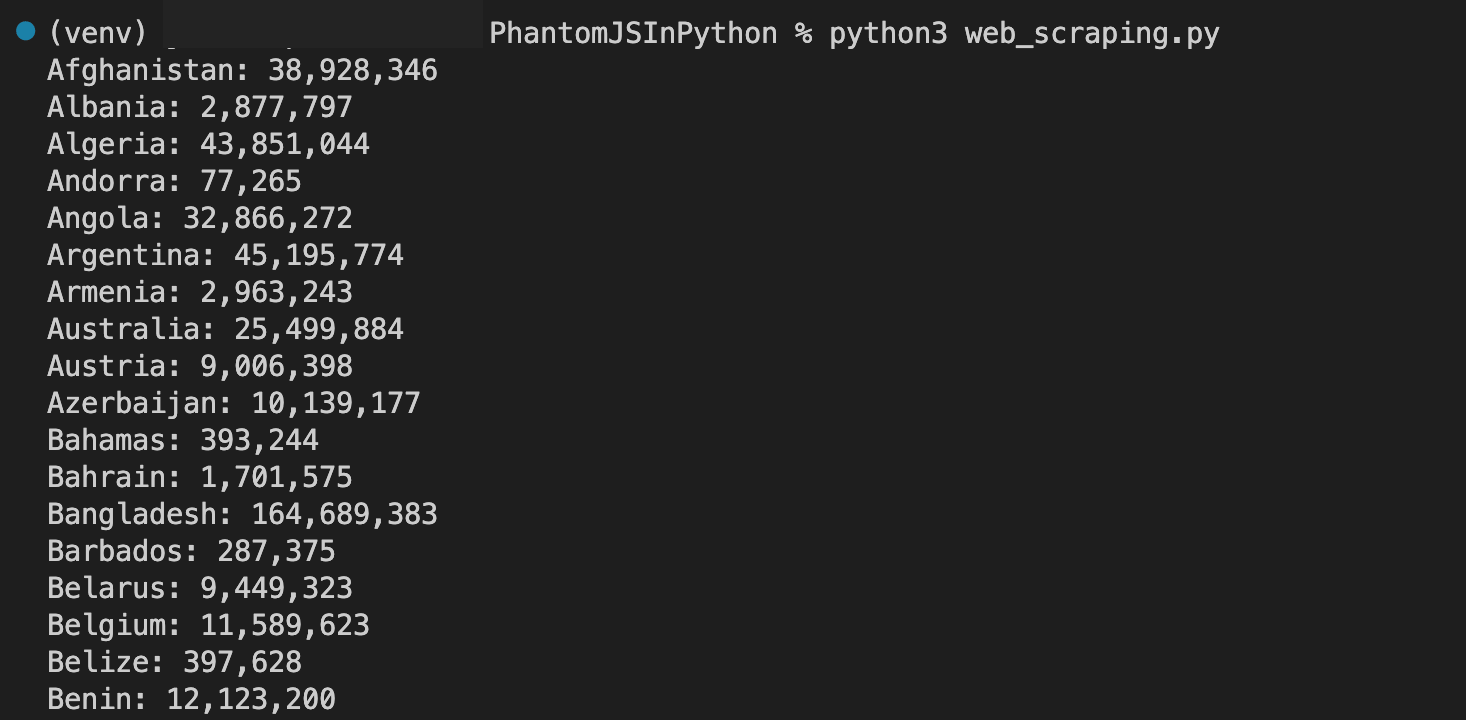
Python web scraping is effective when done using PhantomJS. You can programmatically control PhantomJS to browse websites, interact with components, and extract data with frameworks like Selenium or Puppeteer. Here is an illustration of how to scrape data of countries and their populations using Python and PhantomJS:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
# Configure the PhantomJS WebDriver
driver = webdriver.PhantomJS()
# Navigate to a web page
driver.get('https://www.worldometers.info/geography/alphabetical-list-of-countries/')
rows = driver.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME,"tr")
# Initialize a list to store the countries and populations
countries_populations = []
# Iterate over the rows of the table
for row in rows:
data = row.text.split(" ") # splitting the data
# Add the country and population to the list
countries_populations.append((data))
for countries_population in countries_populations:
if len(countries_population) == 5:
print(f"{countries_population[1]}: {countries_population[2]}")
# Close the WebDriver
driver.quit()
Advantages of PhantomJS
There are various benefits of using PhantomJS which are going to cover in this section like Headless nature, Cross-platform compatibility, and many more.
- Headless nature: PhantomJS is suitable for server-side automation and tasks where a visible browser window is not required due to its headless nature, which functions without a GUI.
- Cross-platform compatibility: PhantomJS supports Windows, macOS, Linux, and FreeBSD, making it cross-platform compatible and enabling developers to use it across numerous platforms.
- Support for JavaScript: PhantomJS comes with a JavaScript engine that allows it to handle and run JavaScript scripts on web pages. This makes it practical for scraping web pages that use a lot of JavaScript or dynamic information.
- Network monitoring: Network traffic analysis is possible with PhantomJS, which is useful for performance evaluation, troubleshooting, or recording HTTP requests and responses for site scraping.
- Screenshot capture: PhantomJS can render websites and take screenshots, making it handy for visual testing, creating thumbnails for websites, or storing screenshots of websites when scraping.
Disadvantages of PhantomJS
Some drawbacks related to Development discontinued, Performance, limited ecosystem support, and Data technology are going to cover in this section in detail.
Comparing Test Time Execution of Different Headless Browsers
There are various options available, like Chrome, Firefox, and Microsoft Edge, which provide a better performance, development tools, and many more. In this section, we will see how to use them and compare the execution speed of the script with the execution speed of PhantomJS.
For the execution speed comparison, we will run the below test on different browsers.
def scrape_table_data():
start = time.time()
driver.get('https://www.lambdatest.com/selenium-playground/table-sort-search-demo')
search_bar = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '//*[@id="example_filter"]/label/input')
search_bar.send_keys("London")
rows = driver.find_elements(By.TAG_NAME, "tr")
data_list = []
for row in rows:
data = row.text
data_list.append(data)
driver.quit()
end = time.time()
execution_time = (end - start) * 10 ** 3
return execution_time
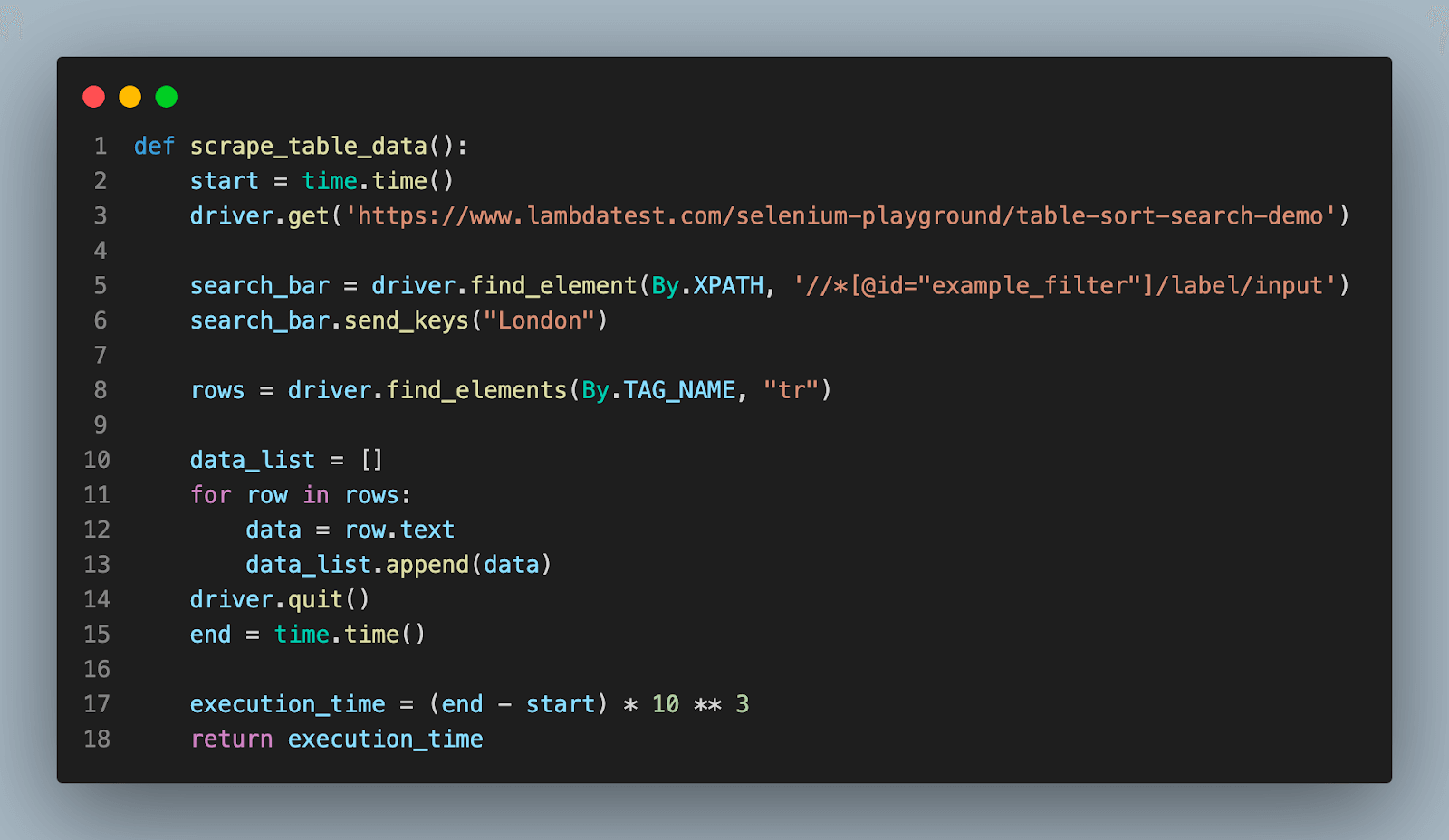
PhantomJS
The below code will run the test on PhantomJS and the functions return the execution time which will be printed in milliseconds.
from selenium import webdriver
driver = webdriver.PhantomJS()
execution_time = scrape_table_data()
print(f"Time taken PhantomJS Browser: {execution_time:.03f}ms")
Note: we are using Selenium 3.8.0 to use the PhantomJS browser.
Output:

Chrome
To run the test on the Chrome browser in the headless mode you are required to add –headless=new using the add_argument() method in the Options.
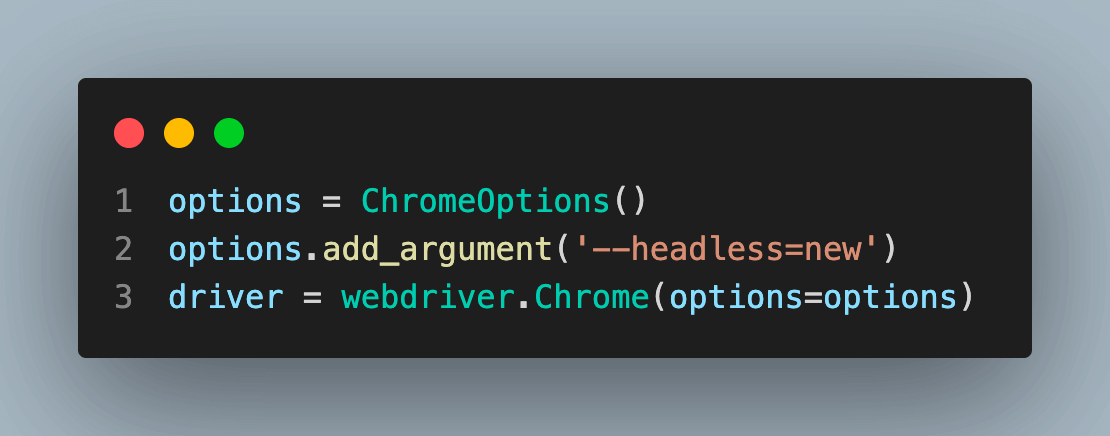
Note: It is recommended to use the latest version of the Selenium. While executing the code Selenium 3.11.2 is used.
The below code will run the test on the Chrome browser in headless mode.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options as ChromeOptions
options = ChromeOptions()
options.add_argument('--headless=new')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
execution_time = scrape_table_data()
print(f"Time taken Chrome Browser: {execution_time:.03f}ms")
Output:

Firefox
To run the test on the Firefox browser in the headless mode you are required to add –headless using the add_argument() method in the Options.

Note: It is recommended to use the latest version of the Selenium. While executing the code Selenium 3.11.2 is used.
The below code will run the test on the Firefox browser in headless mode.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.firefox.options import Options as FirefoxOptions
options = FirefoxOptions()
options.add_argument('--headless')
driver = webdriver.Firefox(options=options)
execution_time = scrape_table_data()
print(f"Time taken Firefox Browser: {execution_time:.03f}ms")
Output:

Microsoft Edge
To run the test on the Microsoft Edge browser in the headless mode you are required to add –headless using the add_argument() method in the Options.

Note: It is recommended to use the latest version of the Selenium. While executing the code Selenium 3.11.2 is used.
The below code will run the test on the Microsoft Edge browser in headless mode.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.edge.options import Options as EdgeOptions
options = EdgeOptions()
options.add_argument('--headless')
driver = webdriver.Edge(options=options)
execution_time = scrape_table_data()
print(f"Time taken Edge Browser: {execution_time:.03f}ms")

| Browser Name | PhantomJS | Chrome | Firefox | Microsoft Edge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed | 11038.025ms | 2842.276ms | 3452.816ms | 5360.607ms |
From the above table, it can be concluded that the Chrome browser executes the test script most efficiently. Though Firefox is not left behind in the race it equally performs well.
Clone the PhantomJSInPython GitHub repository to run the Python files mentioned in the blog.
Apart from headless browsers, several cloud grid options offer the functionality to run tests without utilizing the system’s resources. One prominent platform in this domain is TestMu AI, an AI-Powered Test Orchestration platform, set up as a cloud infrastructure. It provides a comprehensive suite of features, including Automation Testing, Smart UI Testing, and Screenshots, all delivered optimally.
Note: Automate your tests on a Selenium based cloud Grid of 3000+ real browsers. Try TestMu AI Today!
The main advantages of using Cloud Grid like TestMu AI are as follows:
- Ease of Use: TestMu AI is simple to use and has a user-friendly interface, making it simple to prepare and run tests without complicated settings or technical expertise.
- Cloud Grid architecture: TestMu AI offers a cloud-based grid architecture for executing tests across numerous operating systems, browsers, and versions, ensuring thorough test coverage.
- Scalability: TestMu AI makes it simple to scale testing efforts by giving users access to a huge variety of real browsers and devices, allowing for parallel testing, and shortening testing times in general.
- Optimized Testing: By utilizing cloud resources, TestMu AI does not require the installation or upkeep of local browsers, conserving system resources and guaranteeing consistent test findings in various circumstances.
- Smart UI Testing: A consistent user experience is ensured by TestMu AI’s Smart UI Testing features, which allow for the identification of visual regression problems and design inconsistencies by comparing screenshots of applications across browsers and devices.
- Hassle-free Integration: Through its API, CLI, and browser extensions, TestMu AI easily interfaces with well-known automation frameworks and CI/CD technologies, making it simple to include in current development and testing workflows.
Conclusion
PhantomJS is a powerful headless browser that offers a range of capabilities for automation testing and web scraping. Integrating PhantomJS with Python allows developers to harness its functionalities and leverage its potential in their projects.
We saw How to install PhantomJS in Python in a step-by-step process, including the installation of Python itself, the setup of PhantomJS, and the installation of Selenium for Python. Verifying the installation can be done through a simple Python script that utilizes PhantomJS.
PhantomJS provides numerous advantages, such as its ability to execute automated tests, scrape websites, and support various programming languages. However, it also has some disadvantages, including its declining support and limited compatibility with newer web technologies.
Moreover, PhantomJS can be employed in real-world scenarios, such as data extraction and mining, as well as web application testing. These applications showcase the practical use cases and examples of utilizing PhantomJS effectively.
In conclusion, PhantomJS, when integrated with Python, provides a robust solution for automation testing and web scraping. While it has its advantages and disadvantages, understanding its features and optimizing its performance can lead to successful implementation. By leveraging the capabilities of PhantomJS, developers can enhance their projects and achieve their desired outcomes.
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



