
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

What Is Mobile Web: Definition and Checklist
Learn about mobile web, web apps, and mobile apps, their differences, and how to optimize mobile web performance for a seamless user experience.

Zikra Mohammadi
February 15, 2026
The mobile web refers to websites and applications designed specifically for smartphones and tablets. Unlike traditional websites built for desktops, mobile web content is optimized for smaller screens, touch interfaces, and slower network speeds. This ensures a responsive and seamless browsing experience for users, regardless of their device.
With mobile usage surpassing desktop traffic globally, understanding the mobile web is essential for businesses, developers, and users alike. This includes grasping its functionality and the tools and practices needed to optimize it for better performance and user experience.
Overview
What Is Meant by Mobile Web
The mobile web enables browsing on smartphones and tablets through optimized browsers, responsive layouts, and faster designs tailored for smaller screens.
How Does the Mobile Web Actually Work
Mobile browsers handle requests render content and optimize performance using design techniques frameworks and network efficiency strategies.
- Request and Response Cycle: Browsers send requests to servers receive HTML CSS and JavaScript then render optimized pages for smaller touch screens.
- Responsive and Adaptive Design: Layouts adjust to screen sizes while loading device appropriate resources to improve speed navigation and overall usability.
- Caching and Compression: Stored data and reduced file sizes decrease loading times conserve bandwidth and improve reliability on slower mobile networks.
- JavaScript and Frameworks: Interactive features are powered by technologies like React Angular and Vue enabling dynamic updates gestures and responsive interfaces.
What Is Mobile Web?
The mobile web refers to the use of Internet-based services and websites on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Users access the web through mobile browsers designed to adapt to smaller screens, touch interfaces, and varying network conditions. Mobile web content is often optimized for responsive design, ensuring layouts automatically adjust to different screen sizes and lighter designs for faster loading speeds.
Mobile web design involves creating responsive layouts specifically designed for smaller screens and touch inputs. Websites optimized for the mobile web prioritize performance, ease of navigation, and efficient content delivery to ensure a seamless user experience. Businesses leverage the mobile web to effectively engage users and provide services customized to the unique constraints of mobile platforms, including screen size, connectivity, and processing power.
Note: Test your mobile web apps across 5000+ real devices. Try TestMu AI Today!
How Does Mobile Web Work?
Mobile browsers power the mobile web, allowing users to access websites on smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices. These browsers are optimized to handle the limitations and unique features of mobile devices, such as small screens, touch navigation, and varying network speeds.
The process behind how mobile web works involves several steps and techniques to ensure a seamless experience for users:
- Request and Response Cycle: When a user types in a website URL or clicks a link, the mobile browser sends an HTTP request to the server hosting the requested content. The server responds by sending back a combination of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and other multimedia files that make up the webpage. The mobile browser then processes this data and displays it appropriately on the screen, optimizing it for smaller, touch-enabled displays.
- Responsive Design and Adaptive Content: A key element of the mobile web is Responsive Web Design (RWD). Websites using RWD adjust their layout based on the device’s screen size. For instance, a website may display a full navigation bar on a large desktop screen but use a hamburger menu on a smaller mobile screen, ensuring easy navigation.
- Caching and Compression: To improve performance, particularly in environments with less reliable network connectivity, mobile websites use caching and compression techniques:
- Caching stores temporary website data on the mobile device after the first visit, allowing faster access to frequently visited pages. This avoids re-downloading resources like images or CSS files each time the user revisits the site.
- Compression reduces the size of content, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, before they are sent over the network. Smaller file sizes mean faster loading times, which is crucial for users with slower data connections or mobile networks.
- JavaScript and Mobile Frameworks
JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, and Vue.js are commonly used on mobile websites to provide dynamic functionality. These frameworks allow developers to build interactive user interfaces, such as live updates, real-time data fetching, and more. JavaScript is essential for making web pages interactive.
It enables the page to respond to user actions like clicks, swipes, and gestures. JavaScript can update the page’s content without reloading, create animations, validate forms, and more. On mobile devices, JavaScript is optimized for touch events, gestures, and other tasks that ensure a smooth user experience.
The mobile browser may resize images or adjust text sizes to fit the screen, ensuring the content is readable and usable. Optimizing this process is crucial for performance, especially since many mobile users are on the go or using cellular data.
Another characteristic of mobile-friendly sites is adaptive content delivery. This ensures that appropriate images, videos, and other resources are loaded according to the user’s device. This helps speed up page loading and prevents excessive data consumption, especially when mobile users have slower connectivity or data limitations.
These practices ensure that mobile websites are responsive and quick to load, improving user satisfaction, especially on mobile networks with lower bandwidth.
Some websites also use device detection to serve mobile-specific content. For example, if the website detects it is being accessed from a smartphone or tablet, it may automatically adjust the content or layout for optimal viewing. This adaptability is necessary to provide an efficient mobile web experience.
Mobile Web vs Web App vs Mobile App
Understanding the distinctions between the mobile web, web apps, and mobile apps is crucial for making informed decisions about development and user experience. The mobile web delivers content through mobile-optimized browsers, ensuring accessibility across devices. Web apps, on the other hand, provide enhanced interactivity, resembling native apps but running in browsers. Finally, mobile apps offer a rich, tailored experience, leveraging device-specific features and offline capabilities.
This section breaks down the major differences between these platforms to help you choose the right approach for your needs, whether it’s accessibility, performance, or advanced functionality. When considering the types of mobile apps, it’s essential to evaluate factors like installation, device features, performance, and user experience to select the best platform for your business.
| Feature | Mobile Web | Web App | Mobile App |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Websites optimized for mobile devices accessible via browsers | Applications built for the web that run on a browser and can be accessed on any device. | Software applications designed for specific mobile platforms (e.g., iOS, Android). |
| Internet Dependency | Requires constant Internet connectivity | Typically requires Internet | Can function offline (for static content) |
| Platform Dependency | Platform-independent | Platform-independent | Platform-specific (iOS, Android) |
| Development Cost | Low | Moderate | High (due to platform-specific builds) |
| Performance | Limited by browser and Internet speed | Dependent on browser and connection speed | Superior use device hardware efficiently |
| Installation | No installation required | No installation required | Requires download and installation |
| Access to Device Features | Limited (via APIs like geolocation) | Limited (browser-based APIs) | Extensive (camera, GPS, sensors) |
| User Experience | Standardized and responsive design | Similar to websites but with dynamic features | Optimized for specific platforms |
| Push Notifications | Not supported | Limited (via browser notifications) | Fully supported |
| Update Process | Immediate, server-side | Immediate, server-side | Requires user updates via app stores |
| Market Reach | Accessible on all devices with a browser | Wide, browser-based | Limited to users who install the app |
To learn more in detail about the differences between web apps, mobile apps, and mobile web, and how each slightly differs from the others, check out the following blogs: web app vs mobile app and mobile app vs mobile web. This will help you make more informed decisions based on your project’s goals and target audience.
Now that you have an understanding of what the mobile web is, how it works, and the differences between the mobile web, web apps, and mobile apps, let’s explore the various tools and frameworks that can help you build a mobile-friendly web app.
Frameworks to Build Mobile Web Apps
Developers have several options to choose the right framework that meets the requirements for creating mobile websites and web applications.
Below are some well-known mobile web frameworks designed to optimize mobile websites and web application development.
Bootstrap
Bootstrap is an open-source front-end framework for designing and developing responsive, mobile-first websites and web applications. It was originally developed by Twitter and is the most widely used framework. Bootstrap streamlines the process of creating visually appealing and functional designs that adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices.
Key features of Bootstrap:
- Responsive Grid System: Bootstrap provides a 12-column grid system that allows developers to build responsive layouts easily. The grid is customizable for different screen sizes (small, medium, and large devices).
- Pre-Built Components: It offers a library of pre-designed UI components, such as navigation bars, buttons, forms, modals, and carousels, which can be customized for mobile interfaces.
- Mobile-First Approach: Bootstrap prioritizes mobile responsiveness by default, optimizing websites for smaller screens first and scaling up for larger devices, improving usability and performance.
- Customizable Themes: Developers can modify the default Bootstrap themes using built-in Sass variables or by overriding CSS styles, ensuring design alignment with branding.
Flutter
Flutter is an open-source software development kit (SDK) developed by Google for creating cross-platform applications with a single codebase. It’s great for building natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop, offering creative and flexible user interfaces. Developers can quickly see changes in real time with a hot reload.
Key features of Flutter:
- Single Codebase: Flutter allows developers to write one codebase that works across mobile devices, web browsers, and desktop platforms, reducing development time and effort.
- Rich Widget Library: The framework provides a comprehensive library of pre-designed and customizable widgets to ensure consistent design and functionality across platforms.
- Hot Reload: Developers can instantly see code changes reflected in the application without restarting, making debugging and UI iteration faster and more efficient.
- High Performance: Flutter’s rendering engine, Skia, compiles code to native ARM or Intel machine code, ensuring smooth animations and a seamless user experience.
- Web Support: Flutter extends its capabilities to build web applications with the same performance and functionality as its mobile counterparts.
React Native
React Native, developed by Facebook, allows developers to build mobile applications using JavaScript and React. By employing native components, React Native delivers an authentic user experience while enabling cross-platform development, widely adopted for its robust performance and extensive community support.
Key features of React Native:
- Cross-Platform Development: React Native enables developers to write one codebase that works across Android and iOS, reducing development time and effort. Native components are used for rendering, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Native-Like Performance: React Native bridges the gap between native code and JavaScript, allowing near-native performance and direct communication with native APIs for efficient performance.
- Hot Reloading: The hot reloading feature allows developers to instantly see the effects of code changes without recompiling the entire app, speeding up development and testing.
- Rich Ecosystem of Libraries and Components: React Native offers a wide range of third-party libraries, components, and pre-built modules for additional functionalities like navigation, animations, and camera access.
- Native Modules Support: React Native allows integration of native code (Java, Swift, Objective-C) for more complex or platform-specific functionality, enhancing the app’s capabilities.
Ionic
Ionic is an open-source, comprehensive SDK for hybrid mobile app development using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It helps build high-quality, consistent experiences across platforms from a single codebase. Ionic integrates with popular frameworks such as Angular, React, and Vue.
Key features of Ionic:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Ionic enables the development of a single application that works seamlessly across Android, iOS, and the web.
- Web-Based Development: As a hybrid framework, Ionic leverages web technologies, allowing developers to use familiar tools and skills.
- Pre-Built UI Components: Ionic provides a library of pre-styled UI components like buttons, cards, and modals, optimized for mobile devices.
- Capacitor Integration: Ionic uses Capacitor to access native device features like camera, geolocation, and push notifications.
- Progressive Web App (PWA) Support: Ionic apps can be deployed as PWAs, offering flexibility and broader reach without requiring app store distribution.
Xamarin
Xamarin, owned by Microsoft, uses C# and .NET to develop cross-platform mobile applications for iOS, Android, and Windows. It offers direct access to native APIs, enabling code sharing across platforms to enhance development efficiency. Integration with Visual Studio simplifies the development process for .NET developers.
Key features of Xamarin:
- Native UI and Performance: Xamarin provides access to native APIs and libraries, ensuring a true native-like experience for mobile apps.
- Shared Codebase: Developers can write shared business logic in C# while maintaining platform-specific UI for Android and iOS.
- Access to Native Features: Xamarin gives direct access to platform-specific functionalities like GPS, camera, and biometrics.
- Integration with Visual Studio: Integration with Visual Studio IDE provides robust debugging and development tools.
- Cloud Integration: Xamarin Test Cloud allows developers to test apps on multiple devices for compatibility and performance.
NativeScript
NativeScript allows developers to create native mobile applications using JavaScript, TypeScript, or Angular. It provides direct access to native APIs, ensuring native performance and user experience while eliminating additional abstraction layers for performance-critical applications.
Key features of NativeScript:
- True Native Performance: NativeScript ensures that apps interact directly with native platform APIs, offering the same performance and experience as native apps.
- Cross-Platform Development: Using a single codebase, developers can create applications for both Android and iOS devices, with full access to native device features.
- Framework Flexibility: NativeScript supports multiple frameworks, including Angular, Vue.js, and plain JavaScript/TypeScript, allowing developers to choose the best fit for their expertise and project.
- Native UI Components: NativeScript renders truly native UI components for both Android and iOS, providing a smooth and authentic native feel.
Checklist to Improve Mobile Web Performance
Making your mobile website seamless and fast requires the best practice techniques and performance optimization methods. An optimized mobile website improves customer satisfaction, engagement, and conversion rates.
This checklist highlights key areas in page speed, responsive design, and content optimization to help make your site faster, more responsive, and user-friendly.
- Optimize Images and Videos: Ensure all images and videos are resized and compressed to decrease load times. Use newer formats such as WebP and tools like ImageOptim to compress file sizes without sacrificing quality.
- Responsive Design: Make sure your site is mobile-friendly and responsive, ensuring it looks and functions well on any device. This involves flexible grids, layouts, responsive images, and CSS media queries.
- Minify and Compress Code: Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to reduce file sizes and improve load times. Tools like UglifyJS and CSSNano can help streamline your code for faster processing.
- Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Use a CDN to minimize TTFB and enhance content delivery speeds. A CDN caches content in multiple locations worldwide, bringing it closer to users.
- Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content: Serve the most important content first to improve perceived performance, ensuring that critical content loads instantly, even if the rest of the page takes longer.
- Enable Browser Caching: Use browser caching to make frequently accessed resources available on users’ devices, preventing repeated downloads of the same files.
- Minimize Server Response Time: Optimize server settings to use the most efficient web server. Regularly check server performance and reduce bottlenecks to keep response times as low as possible.
- Lazy Load Images and Videos: Implement lazy loading, where images and videos load only when they come into view. This minimizes first-load times and saves bandwidth.
- Optimize Web Fonts: Use strategies to prevent font render-blocking, such as font-display, and reduce font variants to minimize the negative impact on performance.
- Reduce HTTP Requests: Minimize the number of HTTP requests by merging files and using sprites. Fewer requests lead to faster load times.
- Implement Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): Use AMP to create lightweight pages that load faster on mobile, delivering a smooth user experience.
- Mobile-friendliness Test: Test your website using tools or platforms like TestMu AI and Google Mobile Friendly Test. To monitor its performance, use PageSpeed Insights to diagnose and improve its mobile-friendliness.
How to Test the Responsiveness of Mobile Web Apps?
Testing the responsiveness of your mobile website and mobile web applications is essential for delivering an optimal user experience across different devices and screen sizes. Responsive design ensures that your content is displayed correctly, whether it’s viewed on a smartphone, tablet, or desktop, offering users a consistent and engaging experience.
To conduct responsive testing, you can manually check how your website or app looks on various screen sizes by adjusting the browser window or using real devices. However, manually testing across multiple devices can be time-consuming and impractical, especially when considering the wide variety of screen sizes and resolutions available today.
To enhance the responsive testing process, you can make use of responsive checker tools like the LT Browser offered by TestMu AI. This enables users to test the responsiveness of their website across more than 53+ device viewports, including mobiles, tablets, desktops, and laptops.
Here’s how LT Browser can assist you in running comprehensive responsiveness tests:
- Simultaneously interact with and test up to six devices, accelerating the responsive development process.
- Dedicated DevTools and hot reloading support simplify debugging with real-time updates. The built-in network simulation feature enables testing under diverse conditions for accurate performance analysis.
- Leverage the Chromium engine for improved performance, along with Chrome settings, APIs, and extension support.
- Track and analyze website behavior with multiple test recording options for comprehensive insights.
- Generate performance reports powered by Google Lighthouse to get web performance metrics.
Subscribe to the TestMu AI YouTube Channel for more videos on mobile website testing and other related topics.
For example, following the different versions of the LinkedIn website on tablet, mobile, and laptop.
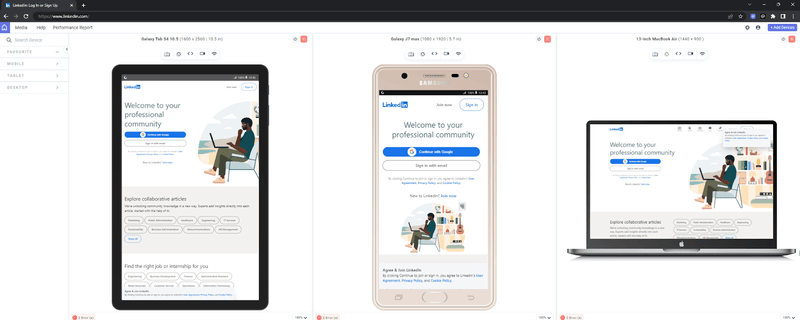
To begin testing your responsive design with LT Browser, check out the support documentation: Getting Started with LT Browser.

Conclusion
Optimizing your mobile website or web app for performance and responsiveness is crucial in delivering a seamless user experience across all devices. By using the right frameworks and testing tools and following best practices, you can ensure that your site loads quickly, adapts to different screen sizes, and functions flawlessly.
Regular testing and optimization will be necessary to maintain a competitive advantage and keep users engaged. Follow the strategies discussed in the blog to build a mobile web experience that satisfies users’ expectations and delivers more robust performance.
Citations
- Mobile Web: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333568368_Mobile_Web
- The next generation mobile web: https://developers.google.com/web/shows/google-io/2015/mobile-web
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests


