
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

A Comprehensive Guide To Blockchain Testing
Discover essential tips and techniques for effective blockchain testing. Ensure the security and reliability of your blockchain applications with expert insights.
Deeksha Agarwal
January 11, 2026
From 2009, when Satoshi Nakamoto implemented blockchain technology as a core component in Bitcoin, blockchain has been the buzzword in the industry. Bitcoin’s success proved the capabilities of blockchain based transactions and and now everyone is planning to implement blockchain technology in almost everything. According to World Economic Forum survey, by 2027, 10% of the global GDP may be stored using none other than blockchain based technology. Interesting, isn’t it?
As you can see, from digital transactions to voting process, from storing documents and transactions to making data transfer decentralized, blockchain tech is going to be everywhere. So for developers working this space, here’s the main question, how do you know that your blockchain app is working just the way you want it work? In simple terms, how can you test blockchain?
First, let’s dive a little deeper into what exactly is blockchain technology, how it can help us, and what all needs to be tested in a blockchain.
What is Blockchain Technology?
A blockchain is basically like a distributed ledger which stores the database of assets and transactions done across a peer to peer network. You can think of a blockchain as an open infrastructure that can store various types of assets.
Let me take this to a simpler level. Imagine you have to make a transaction of $10 from A to B. Now, in normal scenarios what happens is that transaction takes place through a third part app or payment processing system. First, A’s bank will identifying the details of B’s bank. Once that is done, then with the help of a payment processing service A’s bank will initiate a money transfer to B’s bank with a certain amount of deductions. Both banks will record transaction at their end. However a transaction fees is charged and B receives something like $9.95. This process is quite secure and have many redundancies in place to make sure that it stays secure and accurate, but even then there are some basic fundamental issues with the transaction process:
- Delay in process
- Dependency on a single intermediary whose effectiveness in never 100%
- In case of any gap in the transaction, no one takes the responsibility and people keep on blaming each other.
How Blockchain eliminates these problems?
Consider if there is a system where you no longer have to worry about these problems faced. You just need perform a transaction and there are people who are sitting and validating your transaction every second. The validation mechanism is called as Proof of block and this is done based on the public key provided for the encrypted data, and it is done by all listeners in the peer-to-peer network. And these are real people, not bots. Since there is not a single transaction validating authority, i.e. no centralized transaction service, the process is effectively decentralized.
Once more than a specified number of people validates the transaction the transaction details are stored in the form of a block, and that block is added to the existing ‘blockchain’. Hence the name, blockchain. Moreover, the blocks once validated and added are immutable. These blocks have a specific hash associated with every block. These hashes are like fingerprints, unique to every block. The persons validating the transaction process are called as miners. More the number of miners, better the efficiency of transaction.
A block in all contains of data, a hash and a hash of previous block. Since it contains a hash of a previous block hence in a blockchain all the blocks contain data for the previous blocks so it becomes almost impossible for a blockchain to be corrupt.
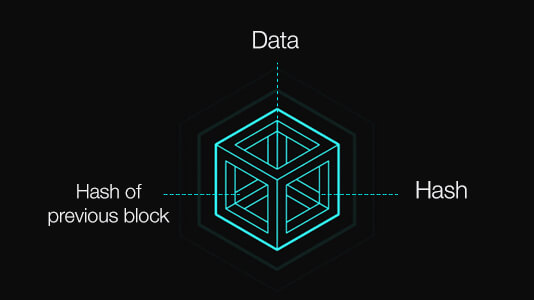
Components of a Block in a Blockchain
So you can think of this as a distributed ledger where a lot of people are actively updating and validating your transaction details based on the decryption key that are provided. And once more than specific number of people validates the transaction a new block is added to the blockchain.
Blocks connected back to back in a Blockchain
What is the need for testing in a Blockchain?
A block once added to the blockchain remains there forever and if you try to change the data in some block in between the chain, the following blocks become invalid. A single change in block of the blockchain will cause every subsequent blocks to change as well. This makes it important that whenever a new block is added, it’s being added the right way because it cannot be changed at a later date. It becomes complex to exploit a blockchain and the testing of blockchain becomes even more complex. Add to that, it’s contributes to large transactions which goes through validation, encryption, decryption, transmission, etc so it becomes necessary to make sure that these processes go smoothly.
What all do you need to test in a Blockchain?
- Block Size: The maximum fixed limit of a block is 1 megabyte. After the introduction of bitcoin, the average size of a block for the first 18 months came out to be under 30 KB. But in December 2017, it hovered around 1 MB. What if the size of a block exceeds beyond 1 MB? Well, this is yet to be decided how the blocks above 1 MB pan out.
- Chain Size: There is no limit on the size of the chain. So it is fun to test it for its function and performance. For example, the bitcoin chain’s size keeps on increasing day by day.
- Load: With so many people on the blockchain, load becomes a major parameter to test in a blockchain. Let’s take an example of bitcoin. It currently has a maximum throughput of 3-4 transactions per second but what if the transaction/second increases as in case of Visa(2000), Paypal(193), etc. Hence load remains the major problem with blockchain as its performance drops when load increases.
- Security: Since there are many miners involved with a transaction, ensuring security is a little complex. Well, there is a multi-layered security system in a blockchain. If one of the layers have been hacked, the instantaneous transactions cannot be stopped. It is therefore to be tested that one security layer doesn’t affect the other.
- Transmission of data: Encrypted and decrypted data is transferred from computer to computer so it is necessary to test if the transmission process is working flawlessly. Is the data being sent received on the other end or there is a loss in between. So it becomes necessary to make sure that the data is not lost.
- Addition of block: Every new block is added to the chain once the transaction’s validity is authenticated. So it must be tested that there should not be any leak in the block addition system and the block must be added after authentication.
- Cryptographical data: Cryptography is the backbone of blockchain technology. So, it is necessary to make sure that the data is properly encrypted and decrypted.
This is just the beginning of the emergence of Blockchain technology. It has a lot more to show and teach us. We are going to see more of blockchain in the coming years with the pace it is taking over the technology world.
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests




