
Next-Gen App & Browser Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

What Is Cyclomatic Complexity: A Complete Guide
Learn how cyclomatic complexity works, its definition, calculation, testing, and analysis techniques to improve code quality, readability, and maintainability.

Nazneen Ahmad
January 11, 2026
Cyclomatic complexity is a software metric used to measure the complexity of a program’s control flow. It helps teams identify the minimum number of test cases needed to cover all paths through a program’s source code. By using this metric, teams can ensure thorough testing, improve code quality, and make the codebase easier to maintain and manage.
What Is Cyclomatic Complexity?
Cyclomatic complexity is a software quality metric that quantifies the complexity of the program by calculating the number of independent paths in the code. A higher score indicates more execution paths and complexity, whereas a low score indicates low complexity with fewer paths and simple code.
Programs with higher complexity are more open to errors and are difficult to test and maintain. On the other side, programs with lower complexity are very easy to understand, test, and modify.
Basically cyclomatic complexity helps in identifying which areas of the code need more testing or a redesign to make the code easier to manage. This metric helps measure how complicated the code is by counting the different paths.
Note: Boost your software quality with AI and cloud. Try TestMu AI Today!
Formula to Calculate Cyclomatic Complexity
The method to calculate complexity is straightforward as it involves the evaluation of the structure and flow of the code as it relies on the program’s Control Flow Diagram (CFG), which shows all possible paths the code can take during execution. The calculation considers different decision points in the code, including the loops, conditions, and branching statements.
Cyclomatic Complexity Formula
The primary formula to calculate complexity is:
Formula 1:
| V(G) = E – N + 2P |
|---|
Here is the formula breakdown:
- V(G): The cyclomatic complexity of the code.
- E: Number of edges or control paths in the CFG
- N: Number of decision points in the code, like if-statements, loops, or switch cases.
- P: Number of connected components, usually 1 for a single program.
Key Definitions
- Control Paths (E): These are the transitions between nodes in the CFG.
- Decision Points (N): These are the parts of the code where decisions are made, such as if-statements, loops, or case conditions.
- Connected Components (P): This represents a single block of code (value 1). If the code is divided into multiple functions or classes, this number might increase.
Steps to Calculate Cyclomatic Complexity:
- Identify all the decision points in the code, like if-statements, loops, or switch cases.
- Count the total decision points you found.
- Add 1 to the count to calculate the complexity.
The final number you get is the complexity. If you get a higher number, it indicates more complexity and has more paths.
Additional Formulas for Cyclomatic Complexity
There are additional formulas as well for the calculation of complexity.
Some of them are mentioned below:
Formula 2:
| V(G) = P + 1 |
|---|
Here, P is the total number of decision points (like if statements or loops). Each decision point creates two branches in the control flow.
Formula 3:
| V(G) = R + 1 |
|---|
Here, R is the total number of closed regions in the CFG. These regions represent areas where the flow is enclosed by loops or conditions.
Example of Cyclomatic Complexity
Here’s an example of a simple code where you will be using all three formulas to calculate cyclomatic complexity:
IF A > B
THEN
C = A + B
ELSE
C = A - B
END IF
PRINT C
Control Flow Graph (CFG):
CFG is a visual representation of all possible execution paths in a program; this approach consists of nodes and edges, helping testers analyze the flow of the program code and help calculate cyclomatic complexity.
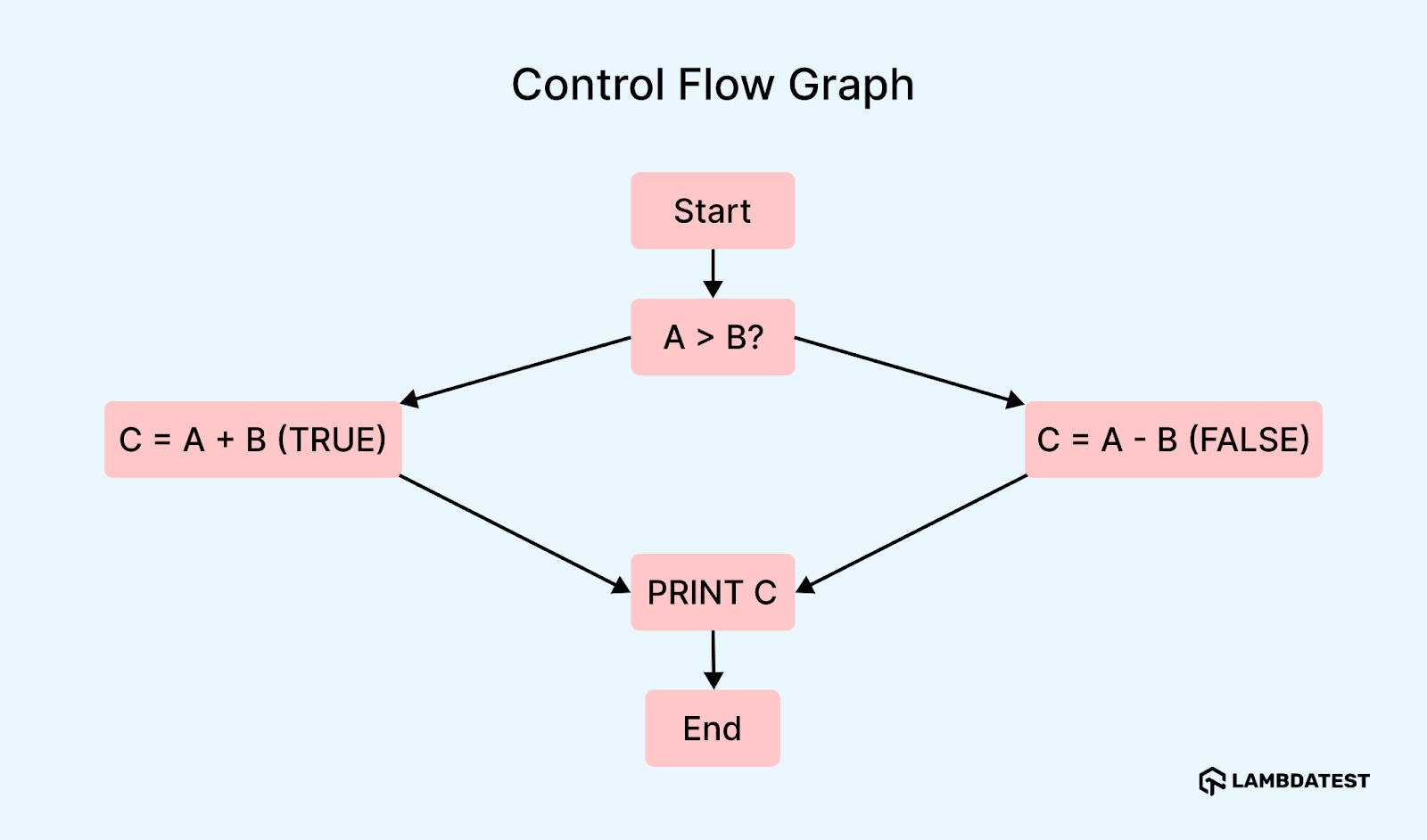
To understand this better, let’s take the visual representation of the control flow graph of the previous example, where decision three uses the if-else statement.
CFG breakdown:
- Nodes (N): 5 nodes represent the different decision points and actions in the code:
- Start node
- Decision node IF A > B
- Action node C = A + B (if condition true)
- Action node C = A – B (if condition false)
- End node (after PRINT C)
- Edges (E): 6 edges represent the transitions between nodes:
- Start → Decision (IF A > B)
- Decision → Action (True path: C = A + B)
- Decision → Action (False path: C = A – B)
- Action (True path) → End node
- Action (False path) → End node
- Start → End node (skip to print)
- Connected components (P): 1 connected component (since this is one method/block of code).
- Closed regions (R): There is 1 closed region formed by the conditional node (IF A > B).
Applying the Formulas:
Here, you can see different methods to calculate cyclomatic complexity based on the program’s control flow. Each of the formulas provides a unique approach that will help calculate the complexity by evaluating nodes, edges, and regions in the graph.
- Formula 1: V(G) = E – N + 2 * P
- E (Edges) = 6
- N (Nodes) = 5
- P (Connected components) = 1
Calculation:
| V(G)=E−N+2∗P=6−5+2∗1=3V(G) = E – N + 2 * P = 6 – 5 + 2 * 1 = 3V(G)=E−N+2∗P=6−5+2∗1=3 |
|---|
- Formula 2: V(G) = P + 1
- P (Conditional nodes) = 1
Calculation:
| V(G)=P+1=1+1=3V(G) = P + 1 = 1 + 1 = 3V(G)=P+1=1+1=3 |
|---|
- Formula 3: V(G) = R + 1
- R (Closed regions) = 1
Calculation:
| V(G)=R+1=1+1=3V(G) = R + 1 = 1 + 1 = 3V(G)=R+1=1+1=3 |
|---|
The graph for the given code shows 5 nodes and 6 edges. Hence, the cyclomatic complexity is:
| V(G)=E−N+2P=6−5+2(1)=3V(G) = E – N + 2P = 6 – 5 + 2(1) = 3V(G)=E−N+2P=6−5+2(1)=3 |
|---|
So, the cyclomatic complexity for this code is 3.
Hope you now have a clear understanding of how to calculate cyclomatic complexity using the control flow graph (CFG). Next, you will learn where cyclomatic complexity can be applied and its significance in software development.
Where Is Cyclomatic Complexity Used?
Cyclomatic complexity plays a crucial role in improving code quality and guiding better development practices.
Here’s how it’s used:
- Improving Code Quality: It helps identify overly complex or messy code. Simplifying such code makes it more readable and maintainable, reducing the chances of errors and making future changes safer.
- Finding Error-Prone Code: It helps identify these sections, allowing developers to prioritize testing and debugging, ultimately reducing the number of bugs in the software.
- Checking Maintainability and Readability: High complexity often indicates code that is difficult to understand and maintain. By measuring complexity, developers can pinpoint sections for improvement, whether by rewriting confusing logic or adding helpful comments.
- Guiding Code Refactoring: It highlights functions or methods that are overly complicated. Developers can break these into simpler units, improving the code’s structure and reducing the likelihood of future errors.
- Estimating Testing Effort: It helps estimate the amount of testing needed to cover all possible paths.
- Evaluating Risks: It helps identify risky areas that need extra attention, ensuring that critical sections are tested thoroughly to minimize defects.
Now that you are familiar with various topics related to cyclomatic complexity, its formula, and its uses, let’s understand how it relates to the software testing process.
How to Test Cyclomatic Complexity?
In software testing, cyclomatic complexity directly impacts the testing process by helping testers decide how many test cases are needed to cover all the possible paths of the code. Higher complexity helps testers focus on the areas that may have more errors.
By analyzing complexity, testers can plan more effectively, ensuring better test coverage and reducing the risk of undetected bugs. It highlights complex code sections, allowing testers to prioritize and improve software quality while minimizing the chances of bugs reaching users.
Testing complexity is important for improving code quality as it helps to identify the areas of code that are more likely to be error-prone and need thorough testing. When testing cyclomatic complexity, you measure and validate all the possible paths in a program. It means checking every possible path your code can take. This ensures your code is reliable and of good quality.
Let us learn how to test complexity in step by step process:
- Calculate Cyclomatic Complexity: Start by calculating the complexity of your code. This highlights the total number of paths or decision points, such as if statements, loops, or switch cases. For instance, if the complexity value is 3, you will need at least 3 test cases to cover all paths.
- Identify All Paths: Break your code into all the possible paths. Each decision point adds a new path, such as:
- An if-else creates two paths.
- A loop adds another path.
- Create Test Cases: Write test cases to cover every path. The goal is to run your code in all possible ways to confirm each part functions correctly. This helps catch errors in the code’s logic.
- Run Tests Using Tools: Use automation testing tools to execute your test cases. Once the test is executed, you can review the results to check for failed tests or unexpected behavior. A failed test usually points to a specific issue in your code.
- Refactor Complex Code (If Needed): If your code is too complex, simplify it to make testing and maintenance easier.
- Splitting large functions into smaller ones.
- Removing unnecessary conditions.
- Test Regularly: Calculate and test the complexity regularly to keep your code simple, easy to maintain, and less prone to errors.
You can do this by:
After refactoring, test the code again to make sure it still works as intended.
Cyclomatic complexity is also a key part of Basis Path Testing, a white-box testing method. This ensures that all independent paths are tested, giving complete code coverage. By using this metric, testers can maintain reliable and manageable code.
Well-structured code usually has a complexity value between 1 and 10. Higher values may indicate areas that need improvement. Tools like OCLint, Reflector Add-In, and GMetrics can help automate complexity calculations, especially for larger projects.
To summarize, testing complexity helps you understand your code’s structure and improve its quality and reliability. By identifying and fixing overly complex areas, you can create cleaner code that is easier to test and manage and less likely to have errors. This approach keeps your code strong, easy to work with, and ready to grow as needed.
How to Perform Cyclomatic Complexity Analysis?
Performing analysis is essential for maintaining code that is easy to understand, update, and expand. High complexity can make bug fixes, feature additions, and adapting to new requirements more difficult. By analyzing complexity, you can identify problem areas and improve the overall health of your code.
- Gather Source Code: Collect the code you want to analyze. This can be a single function, a specific module, or the entire application, depending on your objective.
- Use Static Code Analysis Tools: Utilize static code analysis tools to calculate the cyclomatic complexity of each module. These tools provide insights into the complexity of your code.
- Identify High-Complexity Areas: Examine the code for sections with high complexity scores. These areas are typically harder to understand, test, and maintain. Focus on critical modules or functions.
- Prioritize and Refactor: Identify which high-complexity areas to refactor first. Simplify the code by reducing decision points, breaking down large functions, or removing unnecessary conditions, making it easier to maintain and more reliable.
- Update Tests and Rerun: After refactoring, update your test cases to reflect the changes. Run the tests to ensure the refactored code behaves as expected.
- Recalculate Complexity: Reassess the complexity to confirm the changes have reduced it. Lower complexity scores indicate the code is now easier to maintain and test.
- Regularly Analyze Your Code: Conduct complexity analysis regularly to keep your codebase clean and manageable. This proactive approach helps maintain reliable, testable, and adaptable code.
Conclusion
This cyclomatic complexity is a practical approach to improving your code. It helps you identify issues, create better test cases, and write software that is easier to manage and grow. By using it, you can ensure all code paths are covered, simplify complex logic, and make use of automation tools to handle coding challenges effectively.
It acts as a checkpoint in your development process. It evaluates every decision point and branch in your code for quality. Making it a regular part of your coding and testing process helps identify bugs and gives you confidence in delivering software that performs well and is easy to maintain.
Begin with small steps, apply the methods discussed earlier, and see how they enhance your approach to software development.
Citations
- Cyclomatic Complexity – 40 Years Later: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309568444_Cyclomatic_Complexity
- A Critique of Cyclomatic Complexity as a Software Metric: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3407068_A_Critique_of_Cyclomatic_Complexity_as_a_Software_Metric
- Use and Analysis on Cyclomatic Complexity in Software Development: https://ijcat.com/archieve/volume8/issue5/ijcatr08051002.pdf
Frequently asked questions
Did you find this page helpful?
More Related Hubs
TestMu AI forEnterprise
Get access to solutions built on Enterprise
grade security, privacy, & compliance
- Advanced access controls
- Advanced data retention rules
- Advanced Local Testing
- Premium Support options
- Early access to beta features
- Private Slack Channel
- Unlimited Manual Accessibility DevTools Tests



