Database Connection in KaneAI
Managing test data in isolation or manually updating it across different test cases can lead to inconsistencies, increased maintenance efforts, and slower test execution. Integrating database connections within KaneAI allows teams to access and manipulate real-time data directly during test creation and execution. This capability ensures that tests are always aligned with the latest data, reducing manual data management, improving test accuracy, and enabling more efficient and scalable test automation workflows.
This document provides a step-by-step process to connect databases within the KaneAI platform. It covers the creation of a new connection, selecting database types, entering necessary details, and performing operations like queries and assertions. The guide ensures a smooth setup and usage experience for users looking to integrate their databases seamlessly with KaneAI.
Creating a database connection
To begin, you need to access the database connections page within KaneAI and initiate the creation of a new connection by clicking on Create New Connection.
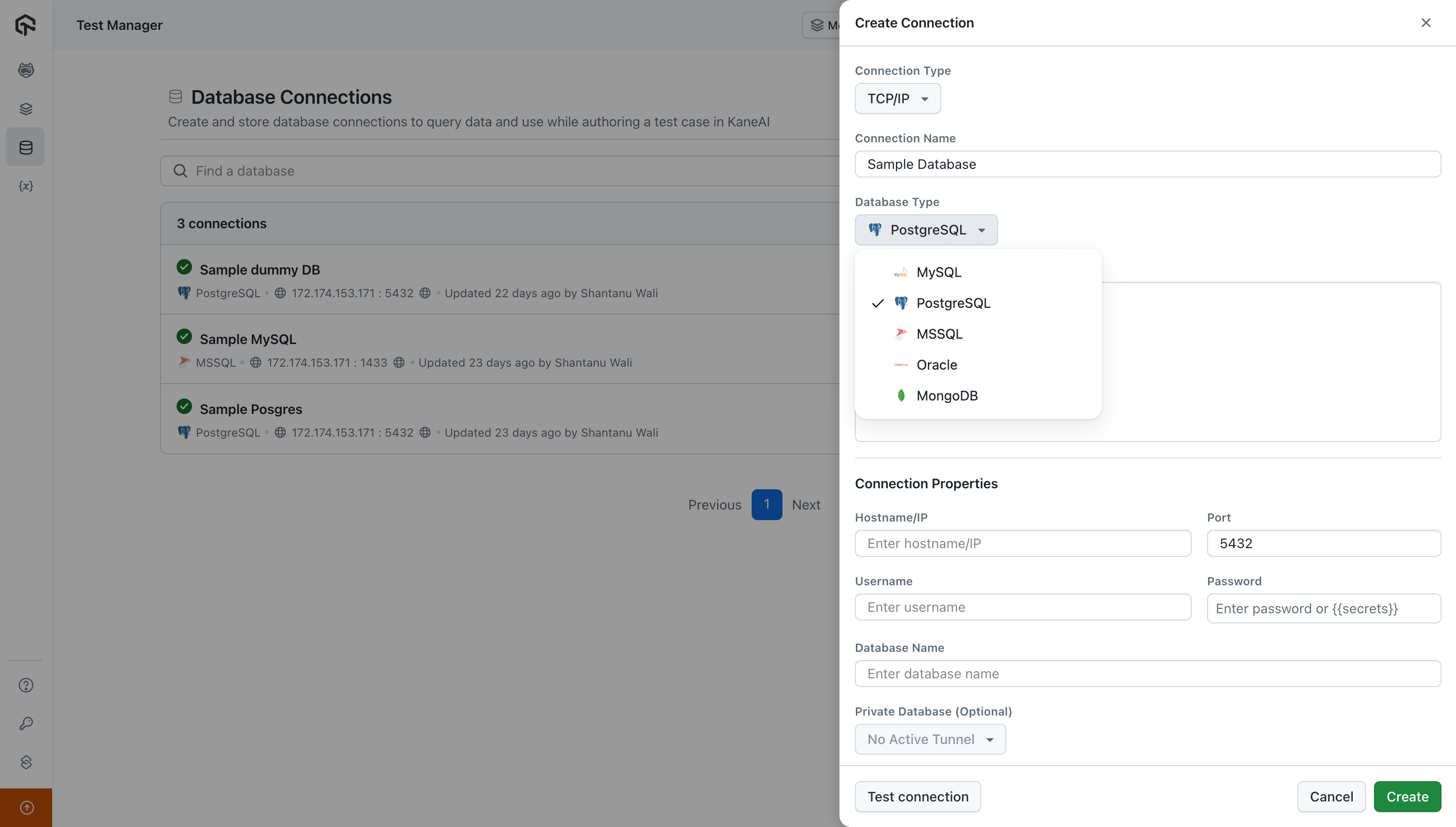
Add connection details
Select the connection type as either TCP/IP or over SSH. Enter the database name and choose from available database types, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL, Oracle, Mongo DB, and GCP Spanner.
Provide a description and input your host name, port, username, and other relevant details. You can enter the password using an organisation-level secret or directly entering the password. For PostgreSQL, ensure you select the database name.
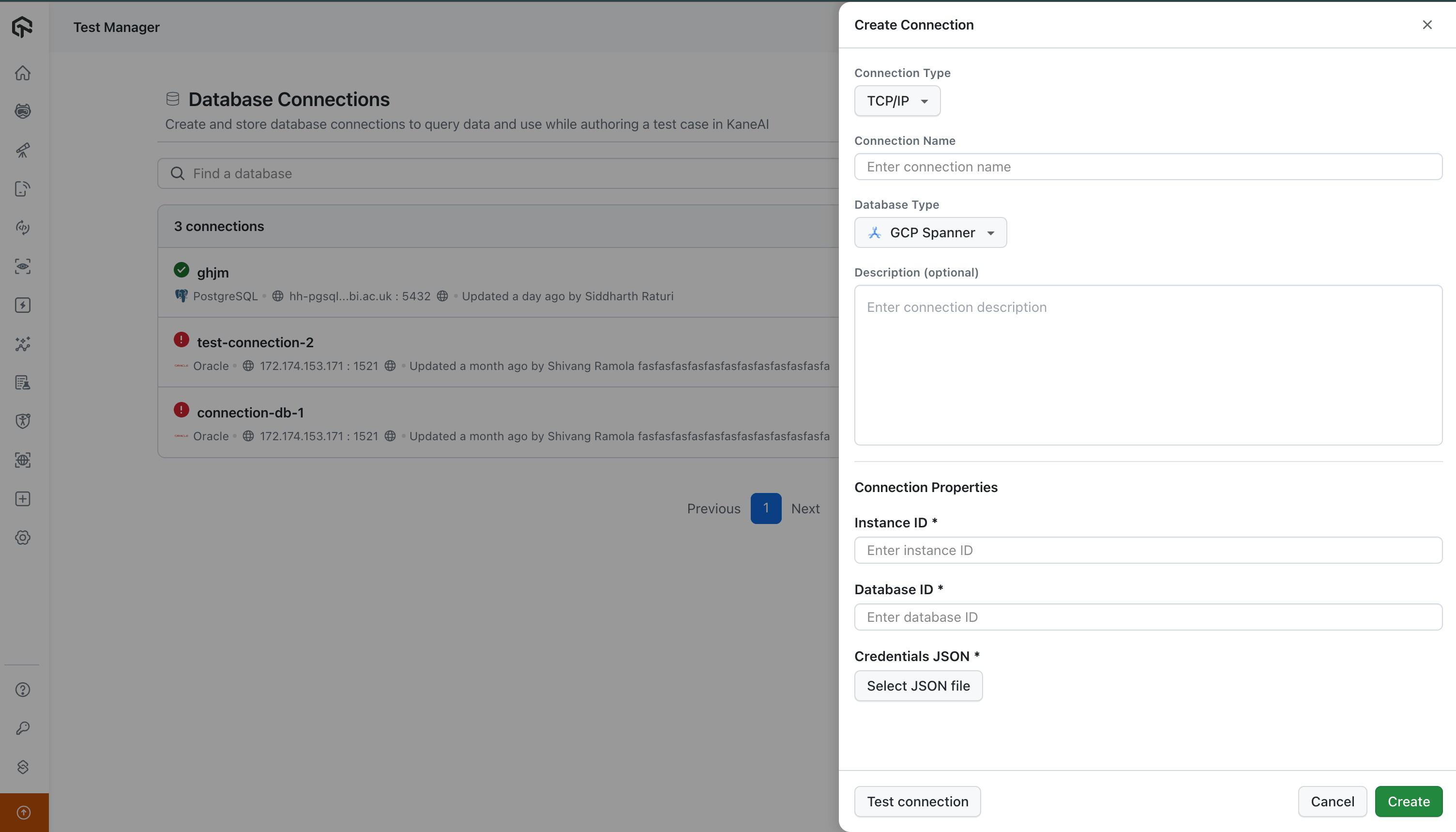
Special Connection Types (GCP Spanner): Unlike traditional databases, GCP Spanner does not use standard hostnames, ports, usernames, or passwords. To connect to a Spanner instance, you will instead need to provide:
- Instance ID (The Spanner instance name)
- Database ID (The database name within the instance)
- Credentials JSON (The service account credentials file used for authentication)
KaneAI supports SQL, NoSQL, and Cloud-native (GCP Spanner) database connections.
Connecting local databases
For local or private databases, select a tunnel if your tunnel is active. The tunnel can be activated easily by following the details available here. Test the connection and create it to see the sample database added.
Note: GCP Spanner does not support SSH tunneling since it utilizes Google Cloud's native built-in security and networking.
Following flag will be additionally required for database connections: --expose database_type:host:port.
So, your command will look like:
./LT --user undefined --key undefined --expose mysql:0.0.0.0:3306 --verbose --env ht-prod
Using Database queries within KaneAI session
Navigate within your KaneAI session. Use the slash command to add a database query. All connected databases will be visible, allowing you to view the schema or directly enter a query. For instances like GCP Spanner, the schema discovery will automatically show all user-created tables and column data types for the configured database.
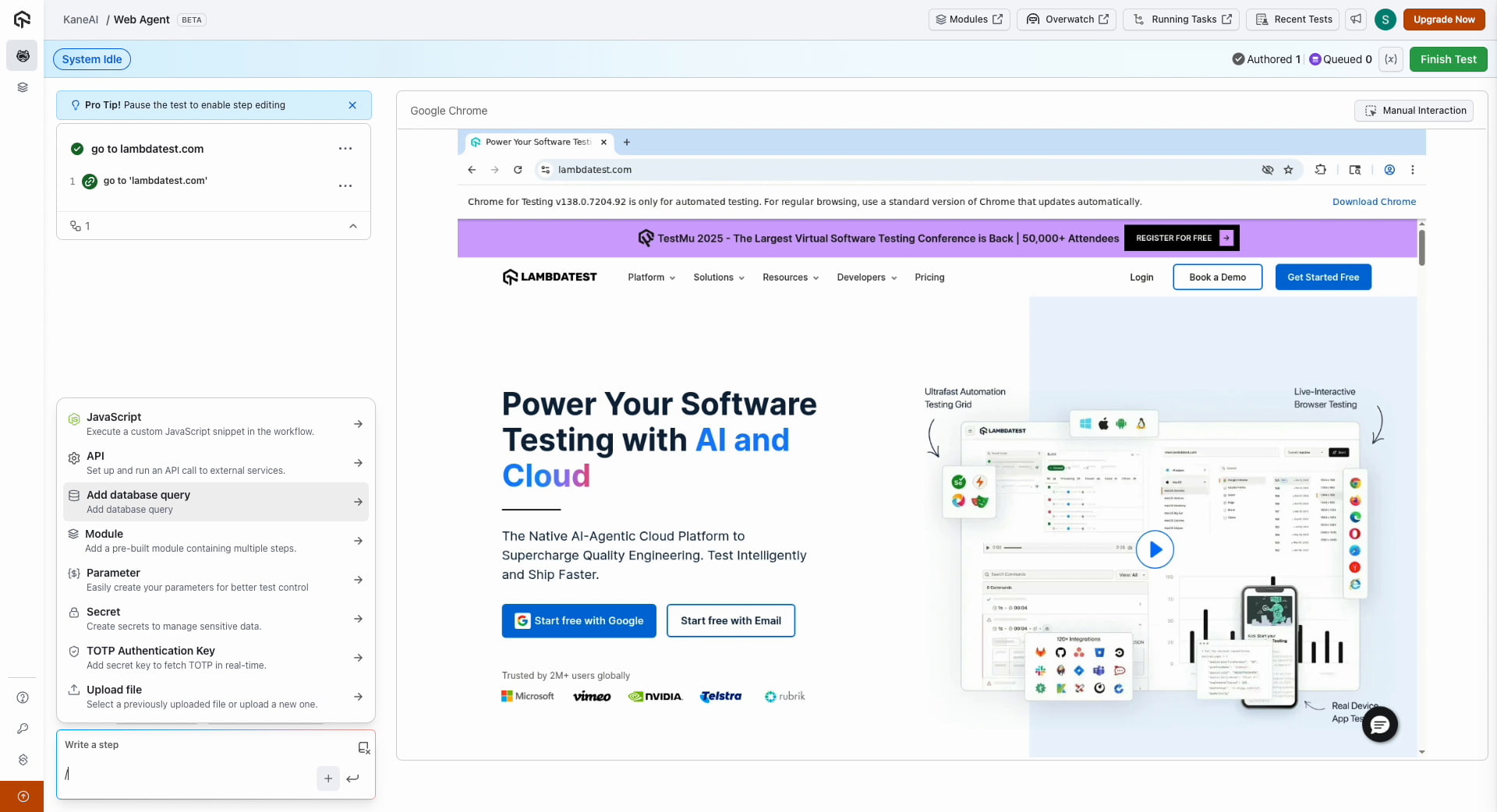
To perform a query, you can select any connected database and input your query to execute. You can leverage variables or parameters as well within the query to make your tests even more robust.
For safety and data integrity, KaneAI only allows SELECT, INSERT, and UPDATE operations. Altering or destructive queries such as ALTER, CREATE, DELETE, or DROP commands are not supported and will return an error.
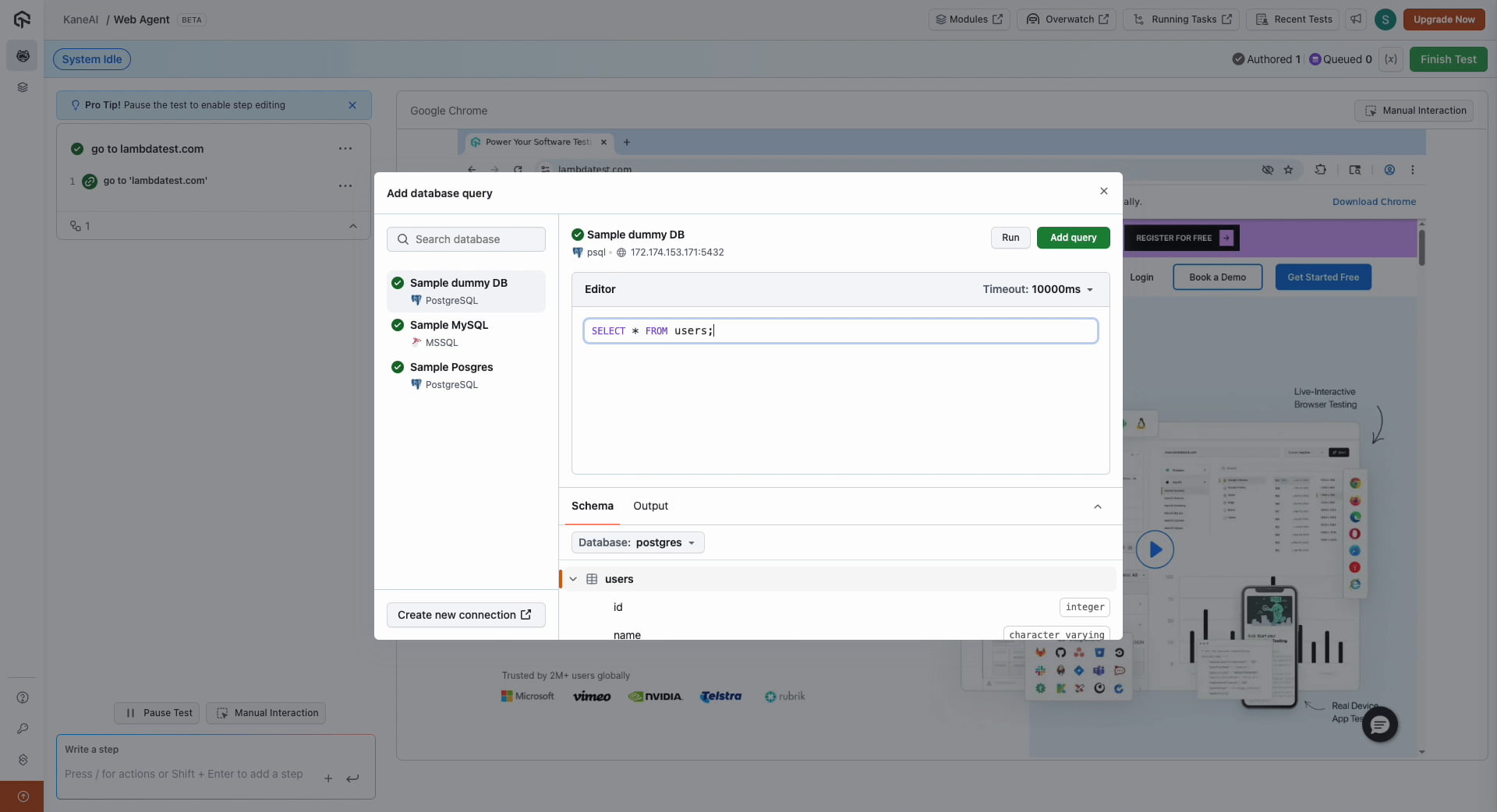
For GCP Spanner queries, a 100-row limit is enforced on all SELECT queries to ensure fast performance and prevent excessive data transfer. It is recommended to use WHERE clauses to filter your data.
Once you Run or Add query, your query will be recorded as a test step within KaneAI, and a JSON variable containing the table response will be generated if the query is successful. This JSON variable can be used to perform various assertions on the data. You can continue adding multiple database queries and validate responses easily.
Video explanation
Have any feedback or request? Reach out to us via [email protected] and we would be happy to hear from you.
